What conditions can affect lung compliance? Compliance also increases with increasing age. Both peak inspiratory and plateau pressure increase when elastic resistance increases or when pulmonary compliance decreases (e.g. during abdominal insufflation, ascites, intrinsic lung disease, obesity, pulmonary edema A condition where ankles and/or feet are swollen due to accumulation of the interstitial fluid.Pedal Edema
What decreases lung compliance?
- Lung surfactant
- Lung volume: compliance is at its highest at FRC
- Posture (supine, upright)
- Loss of lung connective tissue associated with age
- Emphysema
How to calculate lung compliance?
- in mechanically ventilated, normal patients: compliance = 50-100mL/cmH20, resistance = 1-8cmH20/L/s
- ARDS or cardiogenic pulmonary oedema: low compliance (around 40mL/cmH2O), and elevated resistance (15cmmH2O/L/s).
- COPD or asthma: high compliance (66mL/cmH2O) and higher resistance (25cmH2O/L/s).
What is normal value of lung compliance?
NORMAL AND PATHOLOGICAL STATES. in mechanically ventilated, normal patients: compliance = 50-100mL/cmH20, resistance = 1-8cmH20/L/s. ARDS or cardiogenic pulmonary oedema: low compliance (around 40mL/cmH2O), and elevated resistance (15cmmH2O/L/s). COPD or asthma: high compliance (66mL/cmH2O) and higher resistance (25cmH2O/L/s).
What is a normal lung compliance?
What is normal lung compliance? Normal adult lung compliance ranges from 0.1 to 0.4 L/cm H20. Compliance is measured under static conditions; that is, under conditions of no flow, in order to eliminate the factors of resistance from the equation.
What is compliance measured under?
Does pulmonary compliance increase with age?

Lung Compliance Static vs Dynamic - MAK95
Hysteresis • The phenomenon whereby the transmural pressure required to distend an elastic body, such as the lungs, is greater during expansion compared to during contraction, for a given volume • It is caused by time dependent behaviours of the lung Time dependent behaviours of the lung
Lung compliance, airway resistance, and work of breathing in children ...
Pathophysiologic changes associated with inhalation injury make mechanical ventilation in children a challenge. Decreased lung compliance and increased airway resistance after inhalation injury may lead to elevated airway pressures and barotrauma. Previous studies have shown significant decreases in …
Physiology, Lung Compliance - PubMed
Pulmonary compliance, a measure of the expansion of the lung, is critical to the proper function of the respiratory system. Lung compliance can be calculated by dividing volume by pressure. Factors affecting lung compliance include elasticity from the elastin in connective tissue and surface tension …
What are the factors that contribute to lung compliance?
Two important factors of lung compliance are elastic fibers and surface tension. More elastic fibers in the tissue lead to ease in expandability and, therefore, compliance. Surface tension within the alveoli is decreased by the production of surfactant to prevent collapse. Compliance is more easily achieved by decreasing surface tension.
What does it mean when your lung compliance changes?
Pathophysiology. Lung compliance changes can indicate when there are issues with the lungs. A decreased compliance might show restrictive lung diseases. Restrictive lung disease can result from mechanical issues with peripheral hypoventilation, including poor muscular effort or structural dysfunction.
Why is the recoiling force of alveolar surface tension so powerful?
The recoiling force of alveolar surface tension is so powerful that special surfactant chemicals must be synthesized and secreted into the inner lining fluid to reduce the surface tension.
How do lungs expand?
Similar to a balloon, the lungs expand by generating positive transmural pressures. However, unlike a balloon, these positive transmural pressures are generated by creating negative surrounding pressure within the intrapleural space.
What is the force of surface tension in the lung?
The combined force of surface tension throughout the lung's alveoli serves as a powerful contributor to the elastic recoil of the lung. Increased lung volumes would require expansion of individual alveoli which is highly resisted by the surface tension of the alveolar fluid inner lining.
What does increased compliance mean?
Increased compliance can indicate a state of disease where there is degeneration of tissue that causes the lungs to have to work harder to expand, such as emphysema. With emphysema, the tissue damage means that it is easier to inhale, as there is less resistance, but it is harder to exhale.
Does scoliosis increase lung compliance?
Scoliosis decreases the che st wall and lung compliance that results in increased respiratory workload. Aging is accompanied by a decrease in muscular strength and elastic recoil. Therefore, lung compliance increases and chest wall compliance decreases as age increases. Loss of surfactant (eg.
Respiratory System Mechanics and Energetics
V. Courtney Broaddus MD, in Murray & Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 2022
Hemodynamics of the Right Heart in Health and Disease
D.M. Gopal, A. Alsamarah, in Encyclopedia of Cardiovascular Research and Medicine, 2018
Respiratory Physiology
The pressure-volume relationship in an isolated lung is illustrated in Figure 5.7. For this demonstration, a lung is excised and placed in a jar. The space outside the lung is analogous to intrapleural pressure. The pressure outside the lung is varied with a vacuum pump to simulate changes in intrapleural pressures.
Smoke Inhalation
Shailen Jasani MA, VetMB, MRCVS, DACVECC, in Small Animal Critical Care Medicine (Second Edition), 2015
Pulmonary Ventilation
John E. Hall PhD, in Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 2021
Respiratory Failure
Robert L. Dekerlegand, ... Christiane Perme, in Physical Rehabilitation, 2007
Smoke Inhalation
Shailen Jasani MA, VetMB, MRCVS, Dez Hughes BVSc, MRCVS, DACVECC, in Small Animal Critical Care Medicine, 2009
What are the main pathophysiological aspects of respiratory disease?
The main pathophysiological aspects of the disease are airflow obstruction and hyperinflation. The mechanical properties of the respiratory system and its component parts are studied by determining the corresponding volume-pressure ( P-V) relationships.
What is the most common risk factor for COPD?
The most common risk factor for COPD globally is cigarette smoke. Cigarette smokers show a higher prevalence of respiratory symptoms and lung function abnormalities than nonsmokers. As a consequence, the annual rate of decline in FEV 1 is higher than the expected FEV 1 decline with decreasing age.
What causes airflow during exhalation?
Airflow during exhalation is the result of the balance between the elastic recoil of the lungs promoting flow and resistance of the airways that limits flow. The factors that lead to the obstruction of the lumen and the increased resistance, with the consequence of flow limitation, are the presence of secretions, the increased tone of bronchial smooth muscle, the hypertrophy of submucosal glands, and the protrusion towards the internal part of the lumen of the dorsal part of trachea during expiration. These factors are involved in airflow obstruction due to the great difference between intraluminal pressure and the pressure in the surroundings. The loss of elastic recoil concerning the wall of the small airways, due to the reduction of elastic tissue in the pulmonary parenchyma, is an evident mainly in emphysema. The absence of cartilage in the wall of the small peripheral airways contributes further more to the loss of the elastic recoil [ 8#N#P. T. Macklem, “The pathophysiology of chronic bronchitis and emphysema,” Medical Clinics of North America, vol. 57, pp. 669–679, 1973. View at: Google Scholar#N#See in References#N#]. Patients with COPD are said to be flow limited when the expiratory flow that they generate during tidal respiration represents the maximal possible flow that they can generate at that volume. In flow-limited patients, the time available for lung emptying (expiratory time) during spontaneous breathing is often insufficient to allow end expiratory lung volume (EELV) to decline to its natural relaxation volume. This leads to lung hyperinflation [ 9#N#D. E. O'Donnell and K. A. Webb, “Exercise,” in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, P. M. A. Calverley, W. MacNee, N. B. Pride, and S. I. Rennard, Eds., pp. 243–269, Arnold, London, UK, 2nd edition, 2003. View at: Google Scholar#N#See in References#N#].
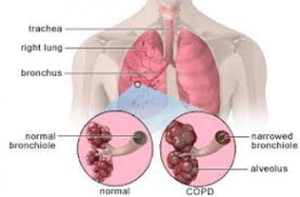
What is COPD pulmonary disease?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a common preventable and treatable disease, is characterized by persistent airflow limitation that is usually progressive and associated with an enhanced chronic inflammatory response in the airways and the lung to noxious particles or gases [ 1#N#“Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (GOLD),” 2011, http://www.gold.copd.org/. View at: Google Scholar#N#See in References#N#]. Airway limitation is attributed to three different mechanisms: (1) partial block of the lumen (e.g., due to excessive mucous production forming semisolid plugs), (2) thickening of the airway wall, which occurs because of edema or muscle hypertrophy, and (3) abnormality of the tissue surrounding the airways (destruction of the parenchyma and narrowing of the airway due to loss of radial traction). Both entities of COPD, namely, chronic bronchitis and emphysema, are characterized by the former mechanisms. Chronic bronchitis is characterized by partial block of the lumen and airway wall thickening, while emphysema by radial traction loss [ 2#N#J. B. West, Pulmonary Pathophyiology: The Essentials, vol. 52, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, MD, USA, 6th edition, 2007.#N#See in References#N#].
What is the difference between static and dynamic studies of the lung in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease?
The static and dynamic studies of the lung in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease differ according to the pathological aspects of the disease . The loss of elastic recoil of the lung affects the pressure difference between the interior of the alveoli and the pleural surface of the lungs, that is, the transpulmonary pressure.
What is a chronic inflammatory response of the airways to noxious particles or gases?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , namely, pulmonary emphysema and chronic bronchitis, is a chronic inflammatory response of the airways to noxious particles or gases, with resulting pathological and pathophysiological changes in the lung. The main pathophysiological aspects of the disease are airflow obstruction and hyperinflation. The mechanical properties of the respiratory system and its component parts are studied by determining the corresponding volume-pressure ( P-V) relationships. The consequences of the inflammatory response on the lung structure and function are depicted on the volume-pressure relationships.
What are the two entities of COPD?
Both entities of COPD, namely, chronic bronchitis and emphysema, are characterized by the former mechanisms. Chronic bronchitis is characterized by partial block of the lumen and airway wall thickening, while emphysema by radial traction loss [ 2.
What is the disease that affects the joints but can affect the organs such as the lungs?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease that primarily affects the joints but can affect the organs such as the lungs. Connective tissue diseases are diseases that affect connective tissues throughout the body. Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease that primarily affects the joints but can affect the organs such as the lungs.
What causes interstitial lung disease?
Drugs and Inhaled Substances 1 Exposure to certain inhaled substances, such as at work, can lead to interstitial lung disease. 2 In addition, some drugs cause interstitial lung disease in certain people.
What is pulmonary fibrosis?
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a disease of the connective tissue of the lungs in which, for unknown reasons, the elastic tissues are replaced by scar tissue.
What is connective tissue disease?
Connective tissue diseases are diseases that affect connective tissues throughout the body. These diseases can also affect the lungs, though not in every case. Lupus is a chronic disease in which the immune system attacks the organs and tissues such as the heart, lungs, joints, skin and kidneys.
Volume vs. pressure ventilation control
Firefighters in the crowd could also relate this to volume versus pressure pump settings. Generally, they measure the amount of water pumped using GPM, or PSI. Similarly, in the ventilator world, volume control essentially involves setting the tidal volume to be delivered, while the pressure is determined afterward.
Understanding acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a condition where fluid collects in the lungs and is often associated with severely ill patients. Because of this excess fluid, the surface area available for gas exchange to occur is decreased, and supplemental oxygenation or ventilation is often required.
Applying positive-end expiratory pressure
When the lungs need a little help to handle the higher repeated pressure being supplied, applying PEEP can aid your patient’s work of breathing.
Poor saturation may be responsible for problems with oxygenation
If there are no suspected obstructions hindering the patient’s oxygenation, then increased pressure may not be the solution. The patient may just need more – or better controlled – volume.
Ventilation protection
It’s only fitting that we discuss PPE or BSI in the wake of a global pandemic: COVID-19.
About the author
Tim is the founder and CEO of Emergency Medical Solutions, LLC, an EMS training and consulting company that he developed in 2010.
What does a nurse note about a patient's sputum?
The patient has developed a fever and cough, so a sputum specimen has been obtained. The nurse notes that the sputum is greenish and that there is a large quantity of it.
What is PFT in pulmonary perfusion?
A) A PFT measures how much air moves in and out of your lungs when you breathe. A patient is being treated for a pulmonary embolism and the medical nurse is aware that the patient suffered an acute disturbance in pulmonary perfusion.
What is compliance measured under?
Compliance is measured under static conditions; that is, under conditions of no flow, in order to eliminate the factors of resistance from the equation. The chest wall has elastic properties just as the lung does, based on the.
Does pulmonary compliance increase with age?
Compliance also increases with increasing age . Both peak inspiratory and plateau pressure increase when elastic resistance increases or when pulmonary compliance decreases (e.g. during abdominal insufflation, ascites, intrinsic lung disease, obesity, pulmonary edema, tension pneumothorax). Click to see full answer.

Introduction
- Pulmonary compliance, a measure of the lung expandability, is important in ideal respiratorysystem function. It refers to the ability of the lungs to stretch and expand. Lung compliance can be calculated by dividing volume by pressure (C = V/P). 1. Two factors affecting lung compliance are elasticity from the elastin in connective tissue,and surface tension which is …
Transmural Pressures
- The compliance of the lung describes the relationship between the transmural pressure (ie. pressure passing through a wall/hollow structure) across the lung, compared to the organ's volume. Transmural pressure indicates the relative pressure between the alveoliand the intrapleural space. Positive transmural pressures indicate greater alveolar pressures than intrapl…
Function
- Compliance of the respiratory system describes the expandability of the lungs and chest wall. There are two types of compliance: dynamic and static. 1. Dynamic compliance describes the compliance measured during breathing, which involves a combination of lung compliance and airway resistance. This is defined as the change in lung volume by the change in pressure, in th…
Important Factors
- As mentioned above, two important factors of lung compliance are elastic fibers and surface tension.More elastic fibers in the tissue lead to ease in expandability and, therefore, compliance. Surface tension within the alveoli is decreased by the production of surfactant, to prevent collapse. Compliance is more easily achieved by decreasing surface...
Pathophysiology
- Changes in lung compliance can indicate issues within the lungs. These generally cause, or are caused by, injuries, illnesses, or impairments. 1. A decreased compliance might show restrictive lung diseases. Restrictive lung disease can result from mechanical issues with peripheral hypoventilation, including poor muscular effort or structural dysfunction. Conditions like muscul…