What connects the two layers of the nuclear envelope?
nuclear poresThe nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayers: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The gap between the two membranes is called the perinuclear space. The two membranes are connected by nuclear pores that control the movement of materials into and out of the nucleus.
What organelles connect to the nuclear envelope?
Solution : Endoplasmic reticulum connect nuclear envelope with cells membrane.
What is connected to the nuclear pore?
Nuclear pore complexes are multiprotein channels that span the nuclear envelope, which connects the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
What is the nuclear envelope how many layers is it?
two layersThe nuclear envelope is a double membrane composed of an outer and an inner phospholipid bilayer. The thin space between the two layers connects with the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and the outer layer is an extension of the outer…
Is the nuclear envelope connected to the Golgi apparatus?
The nuclear envelope serves as an intermediary between the ER and Golgi complex in the intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii. J Cell Sci.
What cell part is directly connected to the nuclear membrane envelope and holds ribosomes?
Like the cell membrane, the nuclear membrane is a lipid bilayer, meaning that it consists of two layers of lipid molecules. The outer layer of lipids has ribosomes, structures that make proteins, on its surface. It is connected to the endoplasmic reticulum, a cell structure that packages and transports proteins.
What are the pores in the nuclear envelope called?
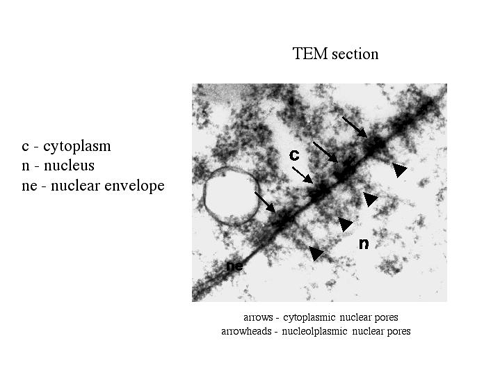
The nuclear envelope is perforated with tiny holes known as nuclear pores, which were first discovered in the mid-twentieth century. These pores regulate the passage of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm, permitting some to pass through the membrane, but not others.
What is the structure of nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope is composed of two concentric lipid bilayer membranes separated by an intermembrane space of about 20-40 nm. The outer membrane is continuous in many places with the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Like the rough ER the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope is dotted with ribosomes.
What is attached to the rough ER?
The ribosome that is synthesizing the protein is directly attached to the ER membrane. These membrane-bound ribosomes coat the surface of the ER, creating regions termed rough endoplasmic reticulum, or rough ER (Figure 12-36A).
What are the 3 layers of the cell envelope?
There are three principal layers in the envelope; the outer membrane (OM), the peptidoglycan cell wall, and the cytoplasmic or inner membrane (IM).
What is directly connected to the outer nuclear membrane?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) consists of an interconnected system of membrane bound channels in the cytoplasm. There is continuity between the outer nuclear membrane and ER. Was this answer helpful?
Why does the nuclear envelope have two membranes?
The nuclear membrane is a double layer that encloses the cell's nucleus, where the chromosomes reside. The nuclear membrane serves to separate the chromosomes from the cell's cytoplasm and other contents.
What organelles interact with the nucleus?
The main organelles that work directly with the nucleus are the ribosomes (although some scientist does not consider the ribosomes as an organelle, because it does not have an encapsulating membrane).
What does nuclear envelope have in common with mitochondria?
Answer and Explanation: The nucleus and mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) both contain DNA.
Which among the following organelle is connected to nucleus?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a membranous organelle that shares part of its membrane with that of the nucleus.
Does mitochondria have nuclear envelope?
The aim of the present study was to show that close contacts of mitochondria with nuclear envelope need not be just an accidental situation in the cell, but that such contacts could serve for flow of energy from a place of origin directly to a place of consumption.
How is the nuclear envelope formed?
The nuclear envelope is formed by two lipid bilayer membranes. These are connected to each other by nuclear pores that control the movement of mole...
What is the main function of the nuclear envelope?
The main function of the nuclear envelope is to keep the contents of the nucleus separate from the rest of the cell. The nucleus contains the genet...
What is the nuclear envelope connected to?
The outer membrane of the nuclear envelope is connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum is the major transportation system...
What does the nuclear envelope do in the nucleus?
The nuclear envelope separates the nucleus of a cell from the other cell organelles. It also controls the movement of molecules into and out of the...
What is the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surrounds the nucleus, which encases the genetic material .
How are nuclear membranes connected?
These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets of intermediate filaments provide support for the nuclear envelope. An internal network forms the nuclear lamina on the inner nuclear membrane. A looser network forms outside to give external support. The actual shape of the nuclear envelope is irregular.
How does the nuclear membrane break down?
In mammals, the nuclear membrane can break down within minutes, following a set of steps during the early stages of mitosis. First, M-Cdk's phosphorylate nucleoporin polypeptides and they are selectively removed from the nuclear pore complexes. After that, the rest of the nuclear pore complexes break apart simultaneously. Biochemical evidence suggests that the nuclear pore complexes disassemble into stable pieces rather than disintegrating into small polypeptide fragments. M-Cdk's also phosphorylate elements of the nuclear lamina (the framework that supports the envelope) leading to the disassembly of the lamina and hence the envelope membranes into small vesicles. Electron and fluorescence microscopy has given strong evidence that the nuclear membrane is absorbed by the endoplasmic reticulum—nuclear proteins not normally found in the endoplasmic reticulum show up during mitosis.
What are the proteins that connect the nucleoskeleton to the nuclear membrane?
All four nesprin proteins (nuclear envelope spectrin repeat proteins) present in mammals are expressed in the outer nuclear membrane. Nesprin proteins connect cytoskeletal filaments to the nucleoskeleton. Nesprin-mediated connections to the cytoskeleton contribute to nuclear positioning and to the cell’s mechanosensory function. KASH domain proteins of Nesprin-1 and -2 are part of a LINC complex (linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton) and can bind directly to cystoskeletal components, such as actin filaments, or can bind to proteins in the perinuclear space. Nesprin-3 and-4 may play a role in unloading enormous cargo; Nesprin-3 proteins bind plectin and link the nuclear envelope to cytoplasmic intermediate filaments. Nesprin-4 proteins bind the plus end directed motor kinesin-1. The outer nuclear membrane is also involved in development, as it fuses with the inner nuclear membrane to form nuclear pores.
Which membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane?
The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane ...
What is the origin of the nucleus?
A study of the comparative genomics, evolution and origins of the nuclear membrane led to the proposal that the nucleus emerged in the primitive eukaryotic ancestor (the “prekaryote”), and was triggered by the archaeo -bacterial symbiosis.
What stage of mitosis does the nuclear membrane break down?
In other eukaryotes (animals as well as plants), the nuclear membrane must break down during the prometaphase stage of mitosis to allow the mitotic spindle fibers to access the chromosomes inside. The breakdown and reformation processes are not well understood.
What is the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayers: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The gap between the two membranes is called the perinuclear space. The two membranes are connected by nuclear pores that control the movement of materials into and out of the nucleus. The inner nuclear membrane has a meshwork of protein filaments that provide support and regulate cellular processes. These are known as the nuclear lamina.
How are nuclear envelopes formed?
The nuclear envelope is formed by two lipid bilayer membranes. These are connected to each other by nuclear pores that control the movement of molecules into the nucleus.
What happens to the nucleus during cell division?
During cell division the nucleus disassembles itself and reforms. But what does the nuclear envelope do? Mitosis describes cell division in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two nuclei. In mammals, the nuclear envelope is broken down during the early stages of mitosis. The nuclear lamina are phosphorylated, which is the addition of a phosphoryl group to a molecule. This causes the nuclear enveloped to begin to disintegrate into small membrane structures or vesicles. At the same time, microtubules move into the nuclear space. This is known as open mitosis, and this occurs in animal cells. Some organisms, such as fungi, undergo closed mitosis where the microtubules penetrate the intact nuclear envelope.
What is the inner nuclear membrane?
The inner nuclear membrane is also made of a lipid bilayer that separates the perinuclear space from the nucleoplasm. As mentioned previously, it is connected to the outer membrane by nuclear pores. It is covered in nuclear lamina which stabilize the nuclear envelope, giving the nucleus its structure and shape.
What is the outer membrane?
The outer membrane is a lipid bilayer membrane. This means that it is made up of two layers of lipids that separate the cytoplasm from the perinuclear space, the space between the inner and outer membranes. The outer membrane is contiguous with the endoplasmic reticulum, which is involved in lipid and protein synthesis. It contains high concentrations of proteins, including nesprin proteins. Nesprin proteins, or nuclear envelope spectrin repeat proteins, connect the structure of cytoskeleton to the nuclear envelope, as well as connecting the nuclear envelope to the nuclear lamina.
What is the role of the nuclear envelope in eukaryotic cells?
In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus contains all the genetic information. It is responsible for maintaining the integrity of DNA and for regulating gene expression, which controls cellular activities such as metabolism, growth and reproduction. As a result, it is very important to keep the nucleus protected and separate from the rest of the cell.
What is the role of the nuclear envelope in chromatin?
The nuclear envelope plays an important role in chromatin organization by attaching and securing it to the nuclear lamina. Chromatin is involved in regulating gene expression and DNA replication. It also facilitates proper segregation of chromosomes during cellular reproduction.
What is the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope is a double membrane composed of an outer and an inner phospholipid bilayer. The thin space between the two layers connects with the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and the outer layer is an extension of the outer…. …a double membrane, called the nuclear envelope, that fuses at intervals to form pores allowing ...
What is the nucleus?
In nervous system: Nucleus. …a double membrane, called the nuclear envelope, that fuses at intervals to form pores allowing molecular communication with the cytoplasm. Within the nucleus are the chromosomes, the genetic material of the cell, through which the nucleus controls the synthesis of proteins and the growth and differentiation ...
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells?
Endoplasmic reticulum, a continuous membrane system in eukaryotic cells that plays an important role in the biosynthesis, processing, and transport of proteins and lipids. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The process of cell division by mitosis. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
Do fungi have nuclear membranes?
Whereas nuclear division in other eukaryotes, such as animals, plants, and protists, involves the dissolution and re-formation of the nuclear membrane, in fungi the nuclear membrane remains intact throughout the process, although gaps in its integrity are found in some species. The nucleus of the fungus…
What is the nuclear envelope?
Nuclear envelope: double membrane enclosing the nucleus; perforated by pores; continuous with ER
What is the name of the membrane that fuses with the outer membrane of a vesicle?
A damaged organelle or small amount of cytosol becomes surrounded by a double membrane, which is of unknown origin, and a lysosome fuses with the outer membrane of this vesicle
What is NL in biology?
NL (like cytoskeleton): a netlike array of protein filaments that maintains the shape of the nucleus by mechanically supporting nuclear envelope

Overview
Structure
The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets of intermediate filaments provide support for the nuclear envelope. An internal network forms the nuclear lamina on the inner nuclear membrane. A looser network forms outside to giv…
Cell division
During the G2 phase of interphase, the nuclear membrane increases its surface area and doubles its number of nuclear pore complexes. In eukaryotes such as yeast which undergo closed mitosis, the nuclear membrane stays intact during cell division. The spindle fibers either form within the membrane, or penetrate it without tearing it apart. In other eukaryotes (animals as well as plants), the nu…
Origin of the nuclear membrane
A study of the comparative genomics, evolution and origins of the nuclear membrane led to the proposal that the nucleus emerged in the primitive eukaryotic ancestor (the “prekaryote”), and was triggered by the archaeo-bacterial symbiosis. Several ideas have been proposed for the evolutionary origin of the nuclear membrane. These ideas include the invagination of the plasma membrane in a prokaryote ancestor, or the formation of a genuine new membrane system follo…
External links
• Histology image: 20102loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
• Animations of nuclear pores and transport through the nuclear envelope Archived 2009-02-07 at the Wayback Machine
• Illustrations of nuclear pores and transport through the nuclear membrane Archived 2009-02-07 at the Wayback Machine