Eventually, seven countries came together to form the Warsaw Pact:
- Albania (until 1968)
- Bulgaria
- Czechoslovakia
- East Germany (until 1990)
- Hungary
- Poland
- Romania
- The Soviet Union
Which countries were members of the Warsaw Pact?
What nations were in the Warsaw Pact?
- Albania.
- Bulgaria.
- Czechoslovakia.
- East Germany.
- Hungary.
- Poland.
- Romania.
- Soviet Union.
What was true about the Warsaw Pact?
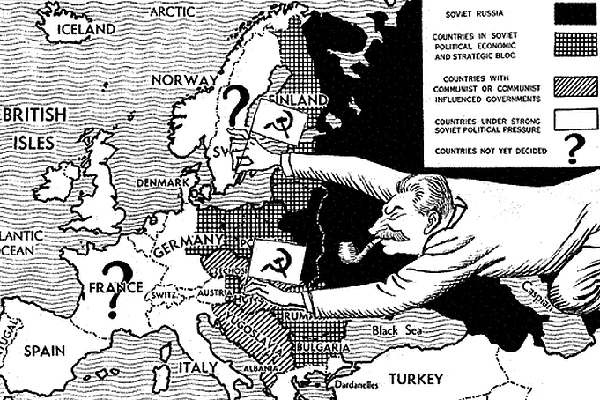
With the help of the Russian rulers, the Warsaw Pact was established to defend Eastern European countries against a NATO attack. The establishment agreement of this pact stipulated the establishment of a unified military command among the members and the establishment of Soviet Army units in the territories of Eastern European countries.
What is NATO and Warsaw Pact?
This agreement was signed as a reaction to the integration of West Germany into NATO in 1955. Amidst the tensions of the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union post World War II, the Warsaw Pact was created as a counterweight to NATO and to improve the cooperation between the two major superpowers of the world.
What does Warsaw Pact mean?
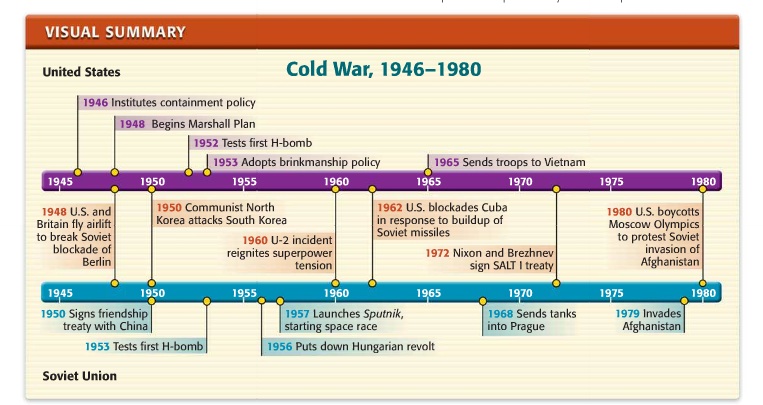
The Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance, more commonly referred to as the Warsaw Pact, was a mutual defense treaty between eight communist states of Central and Eastern Europe in existence during the Cold War. The founding treaty was established under the initiative of the Soviet Union and signed on 14 May 1955, in Warsaw.
See more
Was Poland part of NATO during the Cold War?
On 12 March 1999, the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Poland joined NATO; Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, and Slovakia joined in March 2004; Albania joined on 1 April 2009.
How does the Warsaw Pact relate to the Cold War?
The Soviet Union dominated Central and Eastern Europe during the Cold War. After World War II, it formed the Warsaw Pact, a military alliance of European communist states meant to counter NATO.
Did the Warsaw Pact end the Cold War?
After 36 years in existence, the Warsaw Pact—the military alliance between the Soviet Union and its eastern European satellites—comes to an end. The action was yet another sign that the Soviet Union was losing control over its former allies and that the Cold War was falling apart.
What were the communist countries during the Cold War?
In May 1955, Khruschev set up a military group of communist countries called the Warsaw Pact, in response to the formation of Nato. It included the USSR, Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Bulgaria, Romania, East Germany and Albania. Western countries were not part of it.
What countries are in the Warsaw Pact today?
Tphe original members of the alliance included Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and the Soviet Union. Albania was the first nation to withdraw, an event that occurred in 1968....Warsaw Pact Countries 2022.Country2022 PopulationBrazil215,313,498Russia144,713,314Mexico127,504,125Ethiopia123,379,92445 more rows
How did NATO and Warsaw Pact contribute to the Cold War?
Ideologically opposed, NATO and the Warsaw Pact developed their own defense systems over time, stimulating an arms race that lasted for the whole duration of the Cold War. However, these two organizations had never waged direct war, particularly in Europe.
What came first NATO or the Warsaw Pact?
In 1949 the United States and Canada joined with Britain and other western European countries to form the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), and in 1955 the Soviet Union and its central and eastern European satellites formed the Warsaw Pact following West Germany's accession to NATO.
Was Ukraine part of the Warsaw Pact?
The Treaty of Warsaw (also the Polish-Ukrainian or Petliura-Piłsudski Alliance or Agreement) of April 1920 was a military-economical alliance between the Second Polish Republic, represented by Józef Piłsudski, and the Ukrainian People's Republic, represented by Symon Petliura, against Bolshevik Russia.
How were NATO and the Warsaw Pact similar?
Like NATO, the Warsaw Pact focused on the objective of creating a coordinated defense among its member nations in order to deter an enemy attack. There was also an internal security component to the agreement that proved useful to the USSR.
Which country sided with American bloc in Cold War?
Though not parties to the Warsaw Pact, Vietnam, North Korea, Cuba and Laos, maintained Cold War alliances with the Eastern Bloc.
What are the five communist countries?
Today, the existing communist states in the world are in China, Cuba, Laos, North Korea, and Vietnam. These communist states often do not claim to have achieved socialism or communism in their countries but to be building and working toward the establishment of socialism in their countries.
Who were the United States allies in the Cold War?
Initial member-states of the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) included the United States and all five Brussels treaty nations, Canada, Denmark, Iceland, Italy, Norway and Portugal. Several countries were invited to join NATO but refused, including Finland, Ireland, Sweden and the ever-neutral Switzerland.
What were the two primary causes of the Cold War?
Historians have identified several causes that led to the outbreak of the Cold War, including: tensions between the two nations at the end of World War II, the ideological conflict between both the United States and the Soviet Union, the emergence of nuclear weapons, and the fear of communism in the United States.
Why was the Warsaw Pact important?
The Warsaw Pact provided for a unified military command and the systematic ability to strengthen the Soviet hold over the other participating countries.
How did NATO affect the Cold War?
During the Cold War, NATO focused on collective defence and the protection of its members from potential threats emanating from the Soviet Union. With the collapse of the Soviet Union and the rise of non-state actors affecting international security, many new security threats have emerged, such as terrorism.
What did both the Warsaw Pact and NATO have in common?
Like NATO, the Warsaw Pact focused on the objective of creating a coordinated defense among its member nations in order to deter an enemy attack. There was also an internal security component to the agreement that proved useful to the USSR.
What was Warsaw Pact formally called?
The Warsaw Pact formally was called the Warsaw Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance. It was established on May 14, 1955.
What event prompted the creation of the Warsaw Pact?
In May 1955 West Germany joined NATO, which prompted the Soviet Union to form the Warsaw Pact alliance in central and eastern Europe the same year.
Which countries were part of the Warsaw Pact?
Warsaw Pact was a treaty that established a mutual-defense organization. It was composed originally of the Soviet Union and Albania, Bulgaria, Czec...
What did the Warsaw Pact do?
The Warsaw Pact provided for a unified military command and the systematic ability to strengthen the Soviet hold over the other participating count...
When did the Warsaw Pact end?
After the democratic revolutions of 1989 in eastern Europe, the Warsaw Pact became moribund and was formally declared “nonexistent” on July 1, 1991...
Why was the Warsaw Pact created?
The Warsaw Pact was created in reaction to the integration of West Germany into NATO in 1955 per the London and Paris Conferences of 1954. The Warsaw Pact was established as a balance of power or counterweight to NATO.
What was the Warsaw Treaty?
The Warsaw Treaty's organization was two-fold: the Political Consultative Committee handled political matters, and the Combined Command of Pact Armed Forces controlled the assigned multi-national forces, with headquarters in Warsaw, Poland.
What countries were part of the communists?
The founding signatories to the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance consisted of the following communist governments: 1 Albania (withheld support in 1961 because of the Soviet–Albanian split, but formally withdrew on 13 September 1968) 2 Bulgaria 3 Czechoslovakia 4 East Germany (officially withdrew on 24 September 1990 in preparation for German reunification, with Soviet consent and a "remarkable yet hardly noticed" ceremony, ceasing to exist altogether at midnight on 3 October) 5 Hungary (temporarily withdrew from 1–4 November 1956 during the Hungarian Revolution) 6 Poland 7 Romania (the only permanent Pact member to undergo de-satellization.) 8 Soviet Union
Why did the Soviet Union create the Warsaw Pact?
The strategy behind the formation of the Warsaw Pact was driven by the desire of the Soviet Union to prevent Central and Eastern Europe being used as a base for its enemies. Its policy was also driven by ideological and geostrategic reasons. Ideologically, the Soviet Union arrogated the right to define socialism and communism and act as the leader of the global socialist movement. A corollary to this was the necessity of intervention if a country appeared to be violating core socialist ideas, explicitly stated in the Brezhnev Doctrine.
How many countries were in the Warsaw Pact?
The eight-member countries of the Warsaw Pact pledged the mutual defense of any member who would be attacked. Relations among the treaty signatories were based upon mutual non-intervention in the internal affairs of the member countries, respect for national sovereignty, and political independence.
What does the black dot represent?
The black dot represents West Berlin, an exclave of West Germany. Albania withheld its support to the Warsaw Pact in 1961 due to the Soviet–Albanian split and formally withdrew in 1968. The Warsaw Treaty Organization ( WTO ), officially the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, commonly known as the Warsaw Pact ( WP ), ...
What is the Soviet Big Seven poster?
A "Soviet Big Seven" threats poster, displaying the equipment of the militaries of the Warsaw Pact. Again all proposals, including the request to join NATO, were rejected by the UK, US, and French governments shortly after.
What was the Warsaw Pact?
The Warsaw Pact, made up of Central and Eastern European countries, was meant to counter the threat from the NATO countries. Each country in the Warsaw Pact pledged to defend the others against any outside military threat. While the organization stated that each nation would respect the sovereignty and political independence of the others, ...
Why did Albania leave the Warsaw Pact?
Albania eventually left the Warsaw Pact because of the invasion. The military action was an attempt by the Soviet Union to oust Czechoslovakia's Communist Party leader Alexander Dubcek whose plans to reform his country did not align with the Soviet Union's wishes.
How long did the Warsaw Pact last?
The Soviet Union. The Warsaw Pact lasted for 36 years. In all of that time, there was never a direct conflict between the organization and NATO. However, there were many proxy wars, especially between the Soviet Union and the United States in places such as Korea and Vietnam.
What was the name of the war that took place in 1968?
Invasion Of Czechoslovakia. On Aug. 20, 1968, 250,000 Warsaw Pact troops invaded Czechoslovakia in what was known as Operation Danube. During the operation, 108 civilians were killed and another 500 were wounded by the invading troops. Only Albania and Romania refused to participate in the invasion.
When was the Warsaw Pact established?
Matt Rosenberg. Updated September 30, 2018. The Warsaw Pact was established in 1955 after West Germany became a part of NATO. It was formally known as the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance. The Warsaw Pact, made up of Central and Eastern European countries, was meant to counter the threat from the NATO countries.
When did the Soviet Union dissolve the Cold War?
The pact dissolved at the end of the Cold War in 1991.
What did the Soviet Union hope the Warsaw Pact would help?
The Soviet Union hoped the Warsaw Pact would help it contain West Germany and allow it to negotiate with NATO on a level playing field of power. In addition, Soviet leaders hoped a unified, multilateral political and military alliance would help them reign in the growing civil unrest in Eastern European countries by strengthening the ties between the Eastern European capitals and Moscow.
What was the Soviet Union's role in World War II?
In January 1949, the Soviet Union had formed “Comecon,” the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, an organization for the post-World War II recovery and advancement of the economies of the eight communist nations of Central and Eastern Europe. When West Germany joined NATO on May 6, 1955, the Soviet Union viewed the growing strength of NATO and a freshly rearmed West Germany as a threat to communist control. Just one week later, on May 14, 1955, the Warsaw Pact was established as a mutual military defense complement of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance.
Why did the Warsaw Pact have eight nations?
Seeing the NATO Western Bloc as a security threat, the eight Warsaw Pact nations all pledged to defend any other member nation or nations that came under attack. The member nations also agreed to respect each other’s national sovereignty and political independence by not intervening in each other’s internal affairs. In practice, however, the Soviet Union, due to its political and military dominance in the region, indirectly controlled most of the governments of the seven satellite nations.
What was the closest war between the Warsaw Pact and NATO?
Fortunately, the closest the Warsaw Pact and NATO ever came to actual war against each other during the Cold War years from 1995 to 1991 was the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis . Instead, Warsaw Pact troops were more commonly used for maintaining communist rule within the Eastern Bloc itself.
What was the Warsaw Pact?
Updated February 02, 2020. The Warsaw Pact was a mutual defense treaty between the Soviet Union (USSR) and seven Soviet satellite nations of Eastern Europe signed in Warsaw, Poland, on May 14, 1955, and disbanded in 1991. Officially known as the “Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance,” ...
How many weapons systems were there in the Warsaw Pact?
The Seven Primary Weapons Systems of the Warsaw Pact Nations. Wikimedia Commons
How many people died in the Prague Spring?
Dubček’s so-called “ Prague Spring ” of freedom ended after Warsaw Pact troops occupied the country, killing over 100 Czechoslovakian civilians and wounding another 500.

Overview
History
Before the creation of the Warsaw Pact, the Czechoslovak leadership, fearful of a rearmed Germany, sought to create a security pact with East Germany and Poland. These states protested strongly against the re-militarization of West Germany. The Warsaw Pact was put in place as a consequence of the rearming of West Germany inside NATO. Soviet leaders, like many European leaders on …
Structure
The Warsaw Treaty's organization was two-fold: the Political Consultative Committee handled political matters, and the Combined Command of Pact Armed Forces controlled the assigned multi-national forces, with headquarters in Warsaw, Poland.
Although an apparently similar collective security alliance, the Warsaw Pact differed substantially from NATO. De jure, the eight-member countries of the Warsaw Pact pledged the mutual defens…
Strategy
The strategy behind the formation of the Warsaw Pact was driven by the desire of the Soviet Union to prevent Central and Eastern Europe being used as a base for its enemies. Its policy was also driven by ideological and geostrategic reasons. Ideologically, the Soviet Union arrogated the right to define socialism and communism and act as the leader of the global socialist movement. A corollary to this was the necessity of intervention if a country appeared to be violating core soci…
Post-Warsaw Pact
On 12 March 1999, the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Poland joined NATO; Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, and Slovakia joined in March 2004; Albania joined on 1 April 2009.
Russia and some other post-USSR states joined the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) in 1992, or the Shanghai Five in 1996, which was renamed …
See also
• Finno-Soviet Treaty of 1948 – treaty that defined Finland's level of neutrality towards Soviet Union
• Treaty of friendship – any treaty establishing close ties between countries
• Russosphere
• Eastern Bloc
Further reading
• Faringdon, Hugh. Confrontation: the strategic geography of NATO and the Warsaw Pact. (London: Routledge & Kegan Paul, 1986.)
• Heuser, Beatrice (1998). "Victory in a Nuclear War? A Comparison of NATO and WTO War Aims and Strategies". Contemporary European History. 7 (3): 311–327. doi:10.1017/S0960777300004264. S2CID 159502812.
External links
• "What was the Warsaw Pact?". North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
• The Woodrow Wilson Center Cold War International History Project's Warsaw Pact Document Collection
• Parallel History Project on Cooperative Security
Warsaw Pact Countries
Warsaw Pact History
- In January 1949, the Soviet Union had formed “Comecon,” the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, an organization for the post-World War II recovery and advancement of the economies of the eight communist nations of Central and Eastern Europe. When West Germany joined NATO on May 6, 1955, the Soviet Union viewed the growing strength of NATO and a freshl…
The Warsaw Pact During The Cold War
- Fortunately, the closest the Warsaw Pact and NATO ever came to actual war against each other during the Cold War years from 1995 to 1991 was the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis. Instead, Warsaw Pact troops were more commonly used for maintaining communist rule within the Eastern Bloc itself. When Hungary tried to withdraw from the Warsaw Pact in 1956, Soviet troops entered the …
End of The Cold War and The Warsaw Pact
- Between 1968 and 1989, Soviet control over the Warsaw Pact satellite nations slowly eroded. Public discontent had forced many of their communist governments from power. During the 1970s, a period of détentewith the United States lowered tensions between the Cold War superpowers. In November 1989, the Berlin Wall came down and communist governments in Pol…