Common Causes
Your hypoglossal nerve is the 12th cranial nerve which is responsible for the movement of most of the muscles in your tongue. It starts in the medulla oblongata and moves down into the jaw, where it reaches the tongue. Explore this interactive 3-D diagram below to learn more about the 12 cranial nerves.
Related Conditions
the last of the 12 cranial nerves/ carries impulses controlling the tongue muscles. Thalamus sorts and redirects sensory input. Hypothalamus maintains homeostasis, controls autonomic nervous system and pituitary gland. Connects Cerebrum and Diencephalon with spinal cord. Has reflex centers concerned with vision and hearing.
What are cranial nerves involved in the tongue?
Cranial nerves; CN 0 – Terminal; CN I – Olfactory; CN II – Optic; CN III – Oculomotor; CN IV – ...
What nerve controls the impulses to the tongue?
What cranial nerves are involved with swallowing?
- Trigeminal ( cranial nerve V)
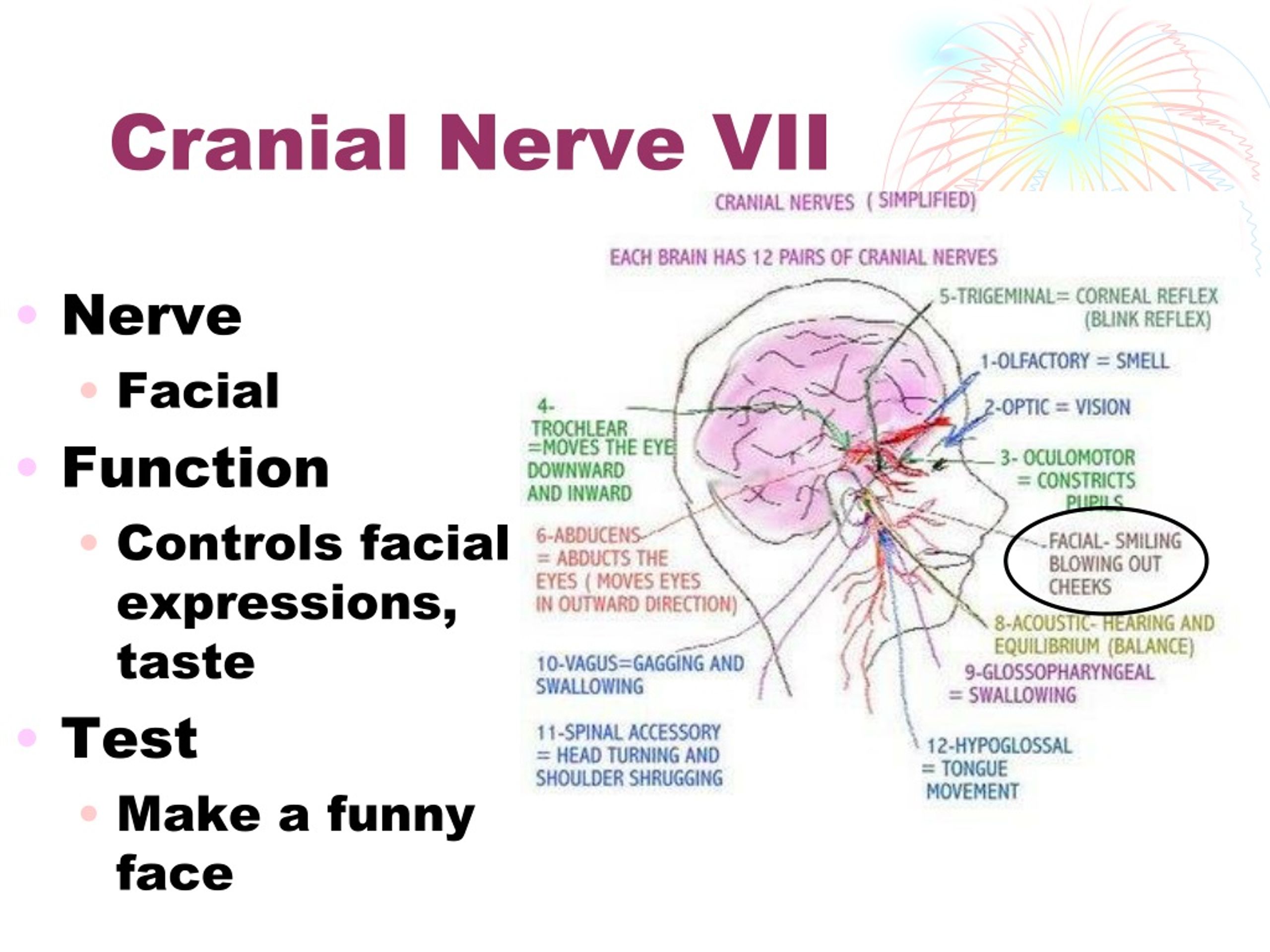
- Facial ( cranial nerve VII)
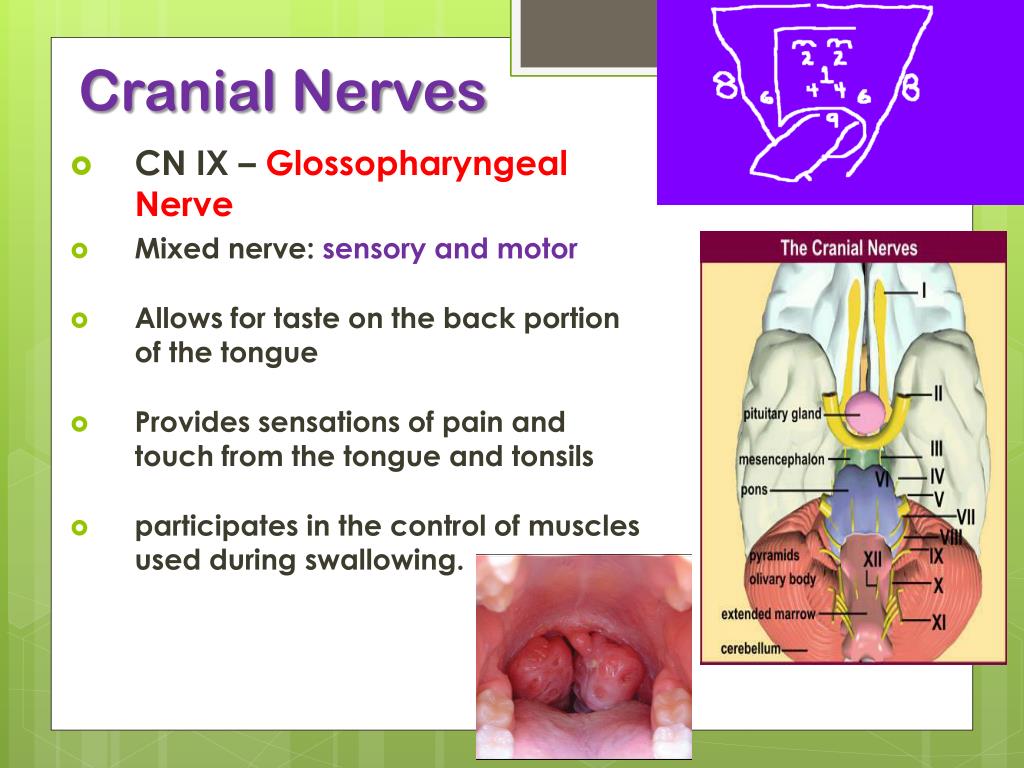
- Glossopharyngeal ( cranial nerve IX)
- Vagus (cranial nerve X)
- Hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII)
What are the ten cranial nerves?
What cranial nerves are responsible for swallowing?
What nerve controls sensation of tongue?
General sensation to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is by innervation from the lingual nerve, a branch of the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3). The lingual nerve is located deep and medial to the hyoglossus muscle and is associated with the submandibular ganglion.
What three cranial nerves innervate the tongue?
Sensory supplyAnterior two-thirds: Lingual nerve (a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve – V3)Posterior one-third: Glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve IX), plus a small branch of the internal laryngeal nerve (branch of the vagus nerve, cranial nerve X).More items...•
Does cranial nerve 7 innervate the tongue?
The facial nerve provides motor innervation of facial muscles that are responsible for facial expression, parasympathetic innervation of the glands of the oral cavity and the lacrimal gland, and sensory innervation of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
What cranial nerve mediates tongue movement?
hypoglossal nerveCN XII, is the hypoglossal nerve, Another motor nerve that originates in the medulla. It controls tongue movement, innervating both the intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles.
What happens if cranial nerve 12 is damaged?
Disorders of the 12th cranial nerve (hypoglossal nerve) cause weakness or wasting (atrophy) of the tongue on the affected side. This nerve moves the tongue. Hypoglossal nerve disorders may be caused by tumors, strokes, infections, injuries, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
What causes loss of tongue control?
Tongue movement problems are most often caused by nerve damage. Rarely, problems moving the tongue may also be caused by a disorder where the band of tissue that attaches the tongue to the floor of the mouth is too short. This is called ankyloglossia.
What happens if cranial nerve 7 is damaged?
Paralysis can occur if any part of the facial nerve, called the seventh cranial nerve, becomes inflamed or damaged. The facial nerve has branches throughout both sides of the face and controls many muscle groups, including those in the brow, eyelid, cheek, and lips.
What does cranial nerve 7 affect?
What is the function of Cranial Nerve VII? The main function of each of the two 7th cranial nerves is facial movement on the same side (ipsilateral). Left sided forehead wrinkle, left eyelid closure, and movement of the left half of the face is stimulated by the left 7th cranial nerve.
What does the 7th cranial nerve do?
The seventh cranial nerve sends information between the brain and the muscles used in facial expression (such as smiling and frowning), some muscles in the jaw, and the muscles of a small bone in the middle ear.
What happens if cranial nerve 10 is damaged?
The voice is hoarse and nasal. The vocal cord on the affected side is immobile. The result is dysphagia and dysphonia (trouble swallowing and trouble speaking).
What controls the tongue?
The hypoglossal nerve is a motor nerve, and it controls the muscles of the tongue that allow for speech and swallowing. The tongue's extrinsic muscles help it move in different directions, while the intrinsic muscles help it make movements such as curling.
What do the 12 cranial nerves control?
The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your brain. Cranial nerves send electrical signals between your brain, face, neck and torso. Your cranial nerves help you taste, smell, hear and feel sensations. They also help you make facial expressions, blink your eyes and move your tongue.
Which cranial nerves innervate the muscles of the tongue quizlet?
Cranial nerve 12. This supplies motor fibers to the muscles of the tongue.
How many cranial nerves move the tongue?
12 cranial nervesThe hypoglossal nerve is one of 12 cranial nerves. It's also known as the 12th cranial nerve, cranial nerve 12 or CNXII. This nerve starts at the base of your brain. It travels down your neck and branches out, ending at the base and underside of your tongue.
Which cranial nerve does not innervate the tongue?
The Hypoglossal nerve is the 12th cranial nerves that originate from the medulla obligate of the brain stem. It innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue, except for the palatoglossus which is innervated by the vagus nerve. It is a nerve with a solely motor function.
Which cranial nerve is responsible for taste to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
Answer. CN VII, or the facial nerve, is responsible for taste in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
How do I remember the 12 cranial nerves?
There are many mnemonics a person can use to remember the 12 cranial nerves. One example is: "Oh Oh Oh To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet — Ah, Hea...
Which cranial nerve is largest?
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve as it starts in the medulla — the bottom part of the brain — and extends to the abdomen.
Which is the shortest nerve?
The shortest cranial nerve is the trochlear nerve, as it has the lowest number of axons.
How many cranial nerves are there?
The twelve cranial nerves are a group of nerves that start in the brain and provide motor and sensory functions to the head and neck. Each cranial nerve has its unique anatomical characteristics and functions. Doctors can identify neurological or psychiatric disorders by testing cranial nerve functions. Last medically reviewed on October 10, 2019.
What nerve helps the body sense changes in the position of the head with regard to gravity?
The vestibular nerve helps the body sense changes in the position of the head with regard to gravity. The body uses this information to maintain balance.
Which nerve provides movement to most of the muscles that move the eyeball and upper eyelid, known as extraocular?
The oculomotor nerve provides movement to most of the muscles that move the eyeball and upper eyelid, known as extraocular muscles.
What are the functions of the cranial nerves?
Each has a different function for sense or movement. The functions of the cranial nerves are sensory, motor, or both: Sensory cranial nerves help a person to see, smell, and hear. Motor cranial nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck.
Which nerve is involved in eye movement?
The trochlear nerve is also involved in eye movement.
Which nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck?
Motor cranial nerves help control muscle movements in the head and neck.
Where do olfactory receptors travel?
When a person inhales fragrant molecules, olfactory receptors within the nasal passage send the impulses to the cranial cavity, which then travel to the olfactory bulb. Specialized olfactory neurons and nerve fibers meet with other nerves, which pass into the olfactory tract. The olfactory tract then travels to the frontal lobe and other areas ...
What nerve innervates the muscles of the tongue?
Hence, the nerve that innervates the muscles of the tongue is called the hypoglossal nerve or cranial nerve XII.
What nerve is responsible for a person's facial sensation?
This is all thanks to the fact that the most important nerve involved in facial sensation is called the trigeminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve V.
Why do cats lick doughnuts?
Now I know exactly why he's so fat. Since the twelve doughnuts are a little bit too big for the cat to swallow, he decides to lick the frosting off of the top of the twelve doughnuts with his tongue. The twelfth cranial nerve innervates the tongue used to lick the twelve doughnuts. It's called the hypoglossal nerve - again, 'glossal' referring to the tongue.
How many nerves are involved in chewing steak?
When chewing on a juicy steak, there's a lot more to what goes on than meets the eye. Besides the obvious preparation of the food, there are four major nerves involved in helping you taste, chew, and swallow the delicious meat. In addition, the way you relay your satisfaction with the food to others through facial expressions and words has to do with these four nerves as well.
Why do I smile when I'm not vegetarian?
Assuming you're not a vegetarian, the smell of a nice steak is going to bring a smile to your face. You use your smile to nonverbally communicate your pleasure. The most important nerve controlling muscles of facial expression, including those involved in a smile, is unsurprisingly called the facial nerve, also known as cranial nerve VII.
Which nerve is responsible for taste sensation?
Well, it's the glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as cranial nerve IX, that is the nerve responsible for the sensation of taste in the posterior one-third of the tongue. Cranial nerve IX is important for swallowing.
Which nerve innervates the muscles of facial expression?
Hence, while CN VII provides motor movement for the muscles of facial expression, CN V is the most important nerve in facial sensation. In addition, CN V is the nerve that innervates the muscles that help move your jaw up and down in order to chew that savory steak. Hence, CN V innervates the muscles of mastication.
What are the parts of the innervation of the tongue?
Nerve Supply of Tongue. Tongue’s innervation is divided into three parts: anterior 2/3, posterior 1/3 and root of tongue. Foramen cecum marks the boundary of anterior 2/3 and posterior 1/3.
What part of the tongue is the posterior part?
Posterior part of the root of tongue, upper larynx, upper esophagus. vagus ( CN X) For more information on Nerve Supply of the Tongue visit Medicalopedia Reference Encyclopedia.
How to treat cranial nerve problems?
Some treatments for cranial nerve problems involve surgery. Of course, this is risky and should be used as a last resort. Some cranial nerve problems, like tumors, may be successfully treated with radiation. The focused beam of radiation can help to shrink or eliminate a tumor that is affecting the cranial nerve.
Why are cranial nerves important?
The cranial nerves have several functions critical for day-to-day life , so they are an important focus for physicians as well as patients affected by disorders of cranial nerve function.
What nerve does not enter the olfactory bulb?
Originally thought to support the function of smell, it is now known that the terminal nerve does not enter the olfactory bulb and does not function in smelling things.
What is the function of cranial nerves?
Cranial nerves function to relay various types of information to and from the body. Some of the nerves are motor nerves, and they move muscles. Others are sensory nerves; they carry information from the body to the brain. Some cranial nerves are a combination of motor and sensory nerves.
Which nerves are responsible for causing the iris to constrict?
First, the oculomotor nerve transmits signals that allow the eyes to move in every direction not controlled by other cranial nerves. Second, the oculomotor nerve carries parasympathetic fibers to the iris, causing the iris to constrict when you're in bright light.
Where are the cranial nerves located?
The cranial nerves are all located on the underside of your brain inside your skull. They come in pairs, one on each side of the brain, and are numbered in Roman numerals I through XII. These are often labeled as CN I, CN II, and so on. The first two cranial nerves, the olfactory nerve, and the optic nerve arise from the cerebrum, and the remaining ten nerves originate in the brain stem. The nerves then travel from their origin to various body parts in your head, face, mouth, and — in some cases — in the periphery of the body.
What is the CN II?
The Optic Nerve (CN II) The optic nerve transmits electrical signals from the retina of your eye to the brain, which transforms these signals into an image of what we see in the world around us. Disorders of the optic nerve, such as optic neuritis, can lead to visual disturbances, double vision, and blindness. 1 .
What nerve is responsible for hearing and balance?
Vestibulocochlear nerve (auditory vestibular nerve): Vestibulocochlear (auditory vestibular nerve) is responsible for hearing and balance. This helps eyes to keep track of moving objects while your head is stable. The sensation of spinning and dizziness are the symptoms of damage to this nerve.
What nerves help with double vision?
Damage to this nerve leads to distortion in vision or double vision and even problem in the coordination of eyes. Trochlear and Abducens nerves: These nerves also help in eye movement. Damage to the Trochlear nerve might cause inability to move eyeball downwards and damage to abducens nerve might result in diplopia.
What are the functions of cranial nerves?
Functions of Cranial Nerves. Following is the cranial nerves list along with the important functions they perform: Olfactory nerve: This nerve helps to feel the sense of smell. This is the primary nerve that is responsible for the smell. Damage to this nerve may result in distortion of smell and taste.
Why are cranial nerves mixed?
Others are mixed nerves because they include both sensory and motor fibres. Only cranial nerves I and II are purely sensory and are responsible for the sense of smell and vision (optic nerve II). The rest of the cranial nerves contain both afferent and efferent fibres and are therefore referred to as the mixed cranial nerves.
How many pairs of spinal nerves are there in the human body?
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve that transmits sensory, motor or autonomic signals between the spinal cord to the body. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves in the human body.
What nerve is responsible for the sensation of spinning?
The sensation of spinning and dizziness are the symptoms of damage to this nerve. This nerve branches into the vestibular nerve and cochlear nerve. Glossopharyngeal: Oral sensation and sense of taste are stimulated by this nerve. Damage to this nerve disables the sense of taste.
What happens if the vestibulocochlear nerve gets damaged?
If the vestibulocochlear nerve gets damaged it results in dizziness and spinning.
What nerve helps you move your tongue?
The hypoglossal nerve helps you move your tongue. It enables you to speak, swallow and push substances around in your mouth. Conditions affecting hypoglossal nerve function include stroke, cancer and ALS. You can protect cranial nerve 12 from some of these conditions by living a healthy lifestyle.
What is the name of the 12th cranial nerve?
The hypoglossal nerve is one of 12 cranial nerves. It’s also known as the 12th cranial nerve, cranial nerve 12 or CNXII.
What nerve controls the back of the throat?
Sleep apnea: The hypoglossal nerve controls muscles in the back of your throat. If they relax too much during sleep, your tongue can slide out of place, blocking the airway.
Which nerve controls the tongue?
The hypoglossal nerve enables tongue movement. It controls the hyoglossus, intrinsic, genioglossus and styloglossus muscles. These muscles help you speak, swallow and move substances around in your mouth.
Where does the hypoglossal nerve start?
The hypoglossal nerve starts in the base of the brain near the top of the spinal cord (brain stem).
What is the function of branches off?
Branches off to connect with muscles that control different types of tongue movement.
How to prevent sleep apnea?
Maintaining a healthy weight to avoid sleep apnea or prevent it from worsening.
What Might Damage the Twelfth Cranial Nerve?
It's rare to see damage to the twelfth cranial nerve on its own. However, several reasons could cause you to experience hypoglossal nerve damage. As noted in the Merck Manual, these reasons include strokes, tumors, specific injuries or infections, injuries, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Why does my tongue feel twitchy?
If your hypoglossal nerve has been damaged, it may affect how you move your tongue. This can, in turn, affect your speech, chewing, and swallowing, making the tongue feel like it's twitching. Sometimes, a person could even experience slurred speech or feel as though they're choking when eating or drinking.
How many cranial nerves are there in the human body?
Our bodies contain twelve cranial nerves, and one of these nerves, the hypoglossal nerve, is intimately related to the oral cavity. Also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, it controls the muscles of the tongue. Let's go over this nerve's anatomy and function, how it can potentially be damaged, and symptoms of damage to be aware of.
What nerves are in the tongue?
If you're concerned about a weakness or paralysis you've recently noticed in your tongue, or if you're just curious about the nerves that make up this unique muscular organ, you may come across the term "hypoglossal nerve.". Our bodies contain twelve cranial nerves, and one of these nerves, the hypoglossal nerve, ...
Which muscle moves the tongue out of the mouth?
The genioglossus muscle helps move the tongue out of the mouth. The hyoglossus muscle moves the tongue down to flatten it. The styloglossus muscle retracts the tongue back into the mouth and elevates it. Clinical Oral Anatomy notes that there is another extrinsic muscle, but the hypoglossal nerve does not control it.
Which nerve controls the muscles of the tongue that allow for speech and swallowing?
The hypoglossal nerve is a motor nerve, and it controls the muscles of the tongue that allow for speech and swallowing. The tongue's extrinsic muscles help it move in different directions, while the intrinsic muscles help it make movements such as curling. The extrinsic muscles controlled by the hypoglossal nerve are as follows:
Where does the 12th cranial nerve come from?
The twelfth cranial nerve comes from the medulla oblongata, a part of the brain stem. From there, it passes through the space underneath the tongue to reach the tongue muscles. Did you know that the hypoglossal nerve's name comes from the path it takes below the tongue?
What is the most common disorder of the trigeminal nerve?
Trigeminal neuralgia. The most frequent disorder of the trigeminal nerve is trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux), and the severity of the pain sometimes generates a referral for a psychiatric consultation.6Trigeminal neuralgia can be idiopathic, but it often is caused by compression, demyelination,7or other injury of the trigeminal nerve root entry zone at the level of the pons or by pressure from an adjacent artery or vein.8–10Trigeminal neuralgia primarily affects the elderly, with a 3:2 preponderance in women. The pain is unilateral, tends to involve the second and third divisions of the sensory part of the nerve (maxillary and mandibular), and is intense enough to cause the patient to grimace (tic). There are initiating or trigger points. There is no sensory or motor “loss” per se. If trigeminal neuralgia is preceded or accompanied by hemifacial spasm, this may indicate that there is a tumor, aneurysm, or arteriovenous malformation compressing both the trigeminal (V) and facial (VII) nerves. Trigeminal neuralgia can also be associated with glossopharyngeal neuralgia (in the tonsillar region, cranial nerve IX).11
How many nuclei are in the trigeminal nerve ganglion?
In the brainstem, the sensory part of the trigeminal nerve ganglion has three nuclei. The fibers of one of them (spinal sensory) carry pain and temperature sensation from the face. The spinal sensory trigeminal tract extends into the cervical cord.
What nerves are involved in taste?
Connoisseurs and wine experts intuit that there are interactions between somato-sensation (cranial nerve V) on the tongue and “taste” itself (cranial nerve VII). Recently, the interaction between the sensory parts of cranial verves V and VII has been illuminated.1For example, electrophysiological studies reveal that the trigeminal nerve (V), which innervates somato-sensation on the tongue, modulates the gustatory (taste) neurons arising from cranial nerve VII at the level of the solitary nucleus (medulla and lower pons) of cranial nerve VII.1,2Within the motor system, although the muscles of mastication are innervated by the trigeminal nerve (V), the muscles of facial expression are innervated mainly by the facial nerve (VII). The close functional and anatomical relationships between cranial nerves V and VII in both their sensory and motor divisions have induced us to discuss them together in this article.
How to perform jaw jerk reflex?
To perform the jaw jerk reflex, which tests both motor and sensory divisions of cranial nerve V, place your finger on the tip of patient’s jaw and tap your finger lightly with a reflex hammer. Increased symmetrical closure rate reflects an upper motor neuron lesion in the same way that hyperactivity of other muscle stretch reflexes suggests an upper motor neuron lesion.
Why do tears spill over my cheek?
If there is hyperacusis (increased auditory volume in an affected ear), this is due the stapedius muscle in the middle ear being affected.
Which cranial nerve has a motor division?
The trigeminal nerve (V) is the largest cranial nerve, and it has both a sensory and a motor division. The motor division of the trigeminal nerve, which has its own nucleus located in the pons, innervates the “muscles of mastication” and also the tensor muscle of the tympanic membranes of the ear.
What is the name of the neurocutaneous disorder that is characterized by port-wine stains in the trige?
Sturge-Weber syndrome. Sturge-Weber syndrome (also called encephalofacial or encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis) is a neurocutaneous syndrome that is characterized by facial port-wine stains in the trigeminal nerve distribution, plus open angle glaucoma, and vascular lesions in the ipsilateral brain and meninges.
What nerves do not branch off?
The hypoglossal nerve doesn't branch off until it reaches the muscles of the tongue, at which time it sends off numerous small branches to innervate those muscles.
What nerve is responsible for chewing and swallowing?
The hypoglossal nerve supplies all of the motor function to your tongue. It's the 12th cranial nerve. 1 Damage to this nerve can affect speech, chewing, and swallowing. The prefix hypo is of Greek origin and means "under.". Glossal, also from the Greek, mean "tongue.".
Which nerve controls the tongue?
The hypoglossal nerve controls two sets of muscles. One set is extrinsic (on the exterior of the tongue) while the other set is intrinsic (fully contained within the tongue). The extrinsic muscles include: Genioglossus: Makes up the bulk of the tongue and allows you to stick your tongue out and move it side to side.
Which nerve is purely a motor nerve?
The hypoglossal nerve is purely a motor nerve; it doesn't send any sensory information to and from the brain.
Which nerves do not join together?
A branch of the cervical plexus runs inside the sheath of the hypoglossal nerve, but the fibers of these two nerves don't join together in any way. The hypoglossal nerve doesn't branch off until it reaches the muscles of the tongue, at which time it sends off numerous small branches to innervate those muscles.
Where does the hypoglossal nerve run?
That's where it meets up with the cervical plexus. The hypoglossal nerve then runs between the carotid artery and the jugular vein, down into the neck, where it crosses the sternocleidomastoid muscle and runs along the mylohyoid muscle.
What are the intrinsic muscles?
The intrinsic muscles include: 1 . Superior longitudinal: A thin muscle right underneath the mucous membranes in the back of the tongue; works with the inferior longitudinal to retract the tongue and make it short and thick. Inferior longitud inal: A narrow band under the surface of the tongue between the genioglossus and the hyoglossus muscles;