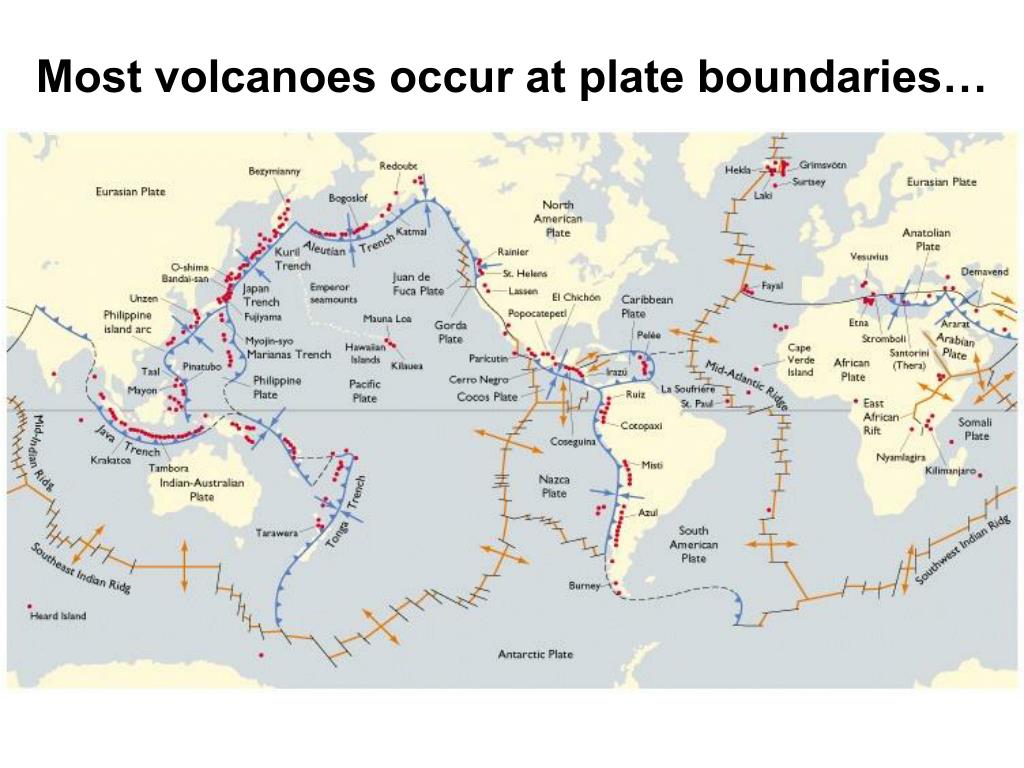
Why are there so many volcanoes in Hawaii?
That’s because the Hawaiian Islands were born from volcanic activity. In fact, that volcanism can still be observed today in Hawai'i. The six largest Hawaiian Islands—the Big Island, Maui, Lanai, Molokai, Oahu, and Kauai—form a chain of islands running to the northwest.
How do volcanoes form?
The magma rises to the surface, underplating the oceanic crust of the overriding plate and generating a line of volcanoes (the island arc). Island arcs form when one oceanic plate subducts beneath another. When the ocean basin is closed, or subduction ceases, the volcanoes in the island arc become extinct.
What is a chain of active volcanoes called?
Chains of active volcanoes, such as those occurring at island arcs, are commonly marked by individual high mountains separated by large expanses of low and gentle topography. In some chains, namely those associated with “hot spots” ( see below ), only the volcanoes at one end of….
Where are the majority of volcanic arcs located?
The majority of volcanic arcs are located within the Ring of Fire, including: Not all Island chains are volcanic island arcs. For example, the Hawai'ian Islands are formed by a hot spot in the mantle. At these types of Island chains, the volcanoes have different formation ages, with the oldest becoming extinct as the youngest is still forming.
What is the name of the rock that pushes through the crust to form volcanoes?
Which island has the oldest volcanic rock?
What is the name of the volcano that erupts in Yellowstone National Park?
How does a hot spot form?
How big are seamounts?
What are the hot spots in the North Atlantic?
Which type of volcano is less explosive?
See 4 more
About this website
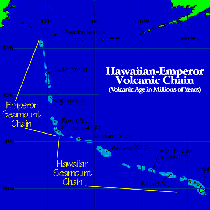
How are high volcanic islands formed?
HOW ARE VOLCANIC ISLANDS FORMED? Volcanic islands are formed by volcanic activity on the seabed, often near the boundaries of the tectonic plates that form Earth's crust. Where two plates pull apart, lava erupts to form an undersea ridge. Layers of lava build up until a ridge breaks the sea's surface to form an island.
What causes volcanic island chains?
As a crustal tectonic plates move over hot spots mantle material upwells and erupts on the surface of the plate to form a volcano, seamount or volcanic island. The islands and seamounts of the Hawaiian Archipelago were created by a hot spot under the Pacific Plate that has been active for the past 41 million years.
How is volcanic chain formed?
Geological experts differ on how volcanic chains such as the Hawaiian or Canary Islands are formed in the ocean. It is understood that some volcanic chains are formed by mantle plumes, hot matter rising from the Earth's inner core, while other oceanic volcanoes emerge from tectonic-plate activity.
What type of landform causes a chain of islands?
When tectonic plates are pushed and pulled apart, they form volcanoes, causing eruptions when the plates are pulled apart. As hot magma rises from the crevasses created, it eventually builds up to form islands.
What is island volcanic chain?
A volcanic arc is a chain of volcanoes, hundreds to thousands of miles long, that forms above a subduction zone. An island volcanic arc forms in an ocean basin via ocean-ocean subduction. The Aleutian Islands off the coast of Alaska and the Lesser Antilles south of Puerto Rico are examples.
What are volcanic chains?
A linear sequence of volcanoes that occurs within a tectonic plate. As the plate moves over a stationary hot spot, new volcanoes are created.
How hotspot island chains are developed?
The Hawaiian Islands were formed by such a hot spot occurring in the middle of the Pacific Plate. While the hot spot itself is fixed, the plate is moving. So, as the plate moved over the hot spot, the string of islands that make up the Hawaiian Island chain were formed.
How would I get an island chain created at a convergent boundary?
As the sinking plate moves deeper into the mantle, fluids are released from the rock causing the overlying mantle to partially melt. The new magma (molten rock) rises and may erupt violently to form volcanoes, often building arcs of islands along the convergent boundary.
What are Volcanic Hotspots? - WorldAtlas
Geography and Geology of the Arago Hotspot . The Arago seamount lies 81 miles to the southeast of Rurutu. The South Pacific Superswell in the Southern Pacific Ocean is very shallow, approximately 2,300 feet spread over an area of 1,900 miles by 1,900 miles.
What is a hotspot and how do you know it's there? - USGS
Most volcanic eruptions occur near the boundaries of tectonic plates, but there are some exceptions. In the interior of some tectonic plates, magma has been erupting from a relatively fixed spot below the plate for millions of years. As the plate continuously moves across that spot, a trail of progressively older volcanic deposits is left at the surface.
Hot Spot Volcanism | Volcano World | Oregon State University
Hot Spot Volcanism Hot Spot volcanoes are recognized by an age progression from one end of the chain to the other. An active volcano commonly serves as an "anchor" at one end of the chain. The most studied and best well-known hot spot volcanoes and seamounts define the Hawaii-Emperor volcanic chain. The origin and evolution of Hawiian volcanoes, seamounts, and guyots are
Learn about this topic in these articles
Chains of active volcanoes, such as those occurring at island arcs, are commonly marked by individual high mountains separated by large expanses of low and gentle topography. In some chains, namely those associated with “hot spots” ( see below ), only the volcanoes at one end of…
geomorphic characteristics
Chains of active volcanoes, such as those occurring at island arcs, are commonly marked by individual high mountains separated by large expanses of low and gentle topography. In some chains, namely those associated with “hot spots” ( see below ), only the volcanoes at one end of…
What is the name of the rock that pushes through the crust to form volcanoes?
The melted rock , known as magma, often pushes through cracks in the crust to form volcano es. Hot spot volcanism is unique because it does not occur at the boundaries of Earth’s tectonic plate s, where all other volcanism occurs. Instead it occurs at abnormal ly hot centers known as mantle plume s. Scientific models depict these plumes ...
Which island has the oldest volcanic rock?
Of all the inhabit ed Hawaiian Islands, Kauai is located farthest from the presume d hot spot and has the most eroded and oldest volcanic rocks, dated to be around 5.5 million years old. Meanwhile, on the “Big Island” of Hawaii, the oldest rocks are less than 0.7 million years old and volcanic activity continues to create new land.
What is the name of the volcano that erupts in Yellowstone National Park?
These eruptions are called geyser s. A famous geyser is Old Faithful in Yellowstone National Park. When it erupts, the water is 95.6 degrees Celsius (204 degrees Fahrenheit) and can reach more than 55 meters (180 feet) high. Kilauea, above, is one of five volcanoes on the "Big Island" of Hawaii—three of them active.
How does a hot spot form?
A hot spot is fed by a region deep within the Earth’s mantle from which heat rises through the process of convection. This heat facilitate s the melting of rock at the base of the lithosphere, where the brittle, upper portion of the mantle meets the Earth’s crust. The melted rock, known as magma, often pushes through cracks in the crust to form volcano es.
How big are seamounts?
Some scientists estimate that seamounts make up 28.8 million square kilometers (17.9 million square miles) of the Earth’s surface, an area larger than any other habitat. Depending on the amount of volcanic activity, seamounts can rise hundreds or thousands of meters from the seafloor.
What are the hot spots in the North Atlantic?
Major hot spots include the Iceland hot spot, under the island of Iceland in the North Atlantic; the Réunion hot spot, under the island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean; and the Afar hot spot, located under northeastern Ethiopia. Volcanic activity at hot spots can create submarine mountains known as seamount s.
Which type of volcano is less explosive?
Island volcanoes that form over hot spots are generally less explosive than volcanic arcs that form over subduction zones.
What is the name of the rock that pushes through the crust to form volcanoes?
The melted rock , known as magma, often pushes through cracks in the crust to form volcano es. Hot spot volcanism is unique because it does not occur at the boundaries of Earth’s tectonic plate s, where all other volcanism occurs. Instead it occurs at abnormal ly hot centers known as mantle plume s. Scientific models depict these plumes ...
Which island has the oldest volcanic rock?
Of all the inhabit ed Hawaiian Islands, Kauai is located farthest from the presume d hot spot and has the most eroded and oldest volcanic rocks, dated to be around 5.5 million years old. Meanwhile, on the “Big Island” of Hawaii, the oldest rocks are less than 0.7 million years old and volcanic activity continues to create new land.
What is the name of the volcano that erupts in Yellowstone National Park?
These eruptions are called geyser s. A famous geyser is Old Faithful in Yellowstone National Park. When it erupts, the water is 95.6 degrees Celsius (204 degrees Fahrenheit) and can reach more than 55 meters (180 feet) high. Kilauea, above, is one of five volcanoes on the "Big Island" of Hawaii—three of them active.
How does a hot spot form?
A hot spot is fed by a region deep within the Earth’s mantle from which heat rises through the process of convection. This heat facilitate s the melting of rock at the base of the lithosphere, where the brittle, upper portion of the mantle meets the Earth’s crust. The melted rock, known as magma, often pushes through cracks in the crust to form volcano es.
How big are seamounts?
Some scientists estimate that seamounts make up 28.8 million square kilometers (17.9 million square miles) of the Earth’s surface, an area larger than any other habitat. Depending on the amount of volcanic activity, seamounts can rise hundreds or thousands of meters from the seafloor.
What are the hot spots in the North Atlantic?
Major hot spots include the Iceland hot spot, under the island of Iceland in the North Atlantic; the Réunion hot spot, under the island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean; and the Afar hot spot, located under northeastern Ethiopia. Volcanic activity at hot spots can create submarine mountains known as seamount s.
Which type of volcano is less explosive?
Island volcanoes that form over hot spots are generally less explosive than volcanic arcs that form over subduction zones.