
What GMO crops are in the United States?
- Corn: Corn is the most commonly grown crop in the United States, and most of it is GMO. ...
- Soybean: Most soy grown in the United States is GMO soy. ...
- Cotton: GMO cotton was created to be resistant to bollworms and helped revive the Alabama cotton industry. ...
- Potato: Some GMO potatoes were developed to resist insect pests and disease. ...
- Papaya: ...
- Summer Squash: ...
- Canola: ...
- Alfalfa: ...
- Corn: Corn is the most commonly grown crop in the United States, and most of it is GMO. ...
- Soybean: Most soy grown in the United States is GMO soy. ...
- Cotton: ...
- Potato: ...
- Papaya: ...
- Summer Squash: ...
- Canola: ...
- Alfalfa:
What do crops have a GMO trait?
Which crops are GMOs?
- Alfalfa
- Apple
- Canola
- Corn (Maize)
- Cotton
- Eggplant
- Papaya
- Pineapple
- Potato
- Soybeans
What foods have GMO ingredients?
- Yogurt. Though dairy cows are not genetically engineered, their soy- or corn-based feed could be. ...
- Salad Dressing. If you’re committed to organic greens, don’t pour GMOs over them. ...
- Granola bars. ...
- Veggie burgers. ...
- Yellow Squash & Zucchini. ...
- Low-sugar foods that use the sweetener aspartame. ...
- Protein shakes. ...
- Margarine. ...
- Whole wheat breads. ...
Why we are against GMOs?
Read our position paper on GMOs
- Biodiversity. Where they are grown, GM crops occupy large surface areas and are linked to intensive monoculture systems that wipe out other crop and ecosystems.
- Toxic Crops, Toxic Land. ...
- Corporate Control. ...
- Threat to Small-Scale Farmers. ...
- Food Culture. ...
- Health and Safety. ...
Why do we need GMO crops in agriculture?
Why do we need GMO crops in agriculture? Most of the GMO crops grown today were developed to help farmers prevent crop and food loss and control weeds. The three most common traits found in GMO crops are: Resistance to certain damaging insects. Tolerance of certain herbicides used to control weeds.

What are the top 10 genetically modified foods?
Here are the top ten most common GMO products:Soy. Of all crops, soy is the most heavily modified. ... Corn. Corn is one of the most heavily modified crops. ... Rice. ... Potato. ... Tomato. ... Canola Oil. ... Papaya. ... Beets.More items...•
What crops are not genetically modified?
Shop at farmer's markets and remember that most produce is safe non GMO, even conventional varieties, with the exception of corn, radicchio, beets, Hawaiian papaya, zucchini and yellow summer squash. Organic whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds are safe.
What are 4 examples of GMOS?
The Most Common GMO ExamplesAlfalfa. Most of the alfalfa that is commercially available today consists of a genetically modified gene that allows the produce to be resistant to the herbicide roundup. ... Papaya. ... Soy. ... Canola. ... Cotton. ... Potato. ... Sugar Beet. ... Yellow Summer Squash and Zucchini.More items...•
How many genetically modified crops are there?
In the United States there are 11 commercially available genetically modified crops in the United States: soybeans, corn (field and sweet), canola, cotton, alfalfa, sugar beets, summer squash, papaya, apples and potatoes.
Is any popcorn GMO?
The good news, if you are concerned about GMO? Popcorn is a distinct type of corn from field and sweet corn and has not been genetically modified. Any kind of popcorn you buy that was grown in the US – organic or not – is non-GMO.
Is broccoli a GMO?
Broccoli IS NOT, I repeat, IS NOT considered a genetically modified organism (GMO). If you want to sound even smarter than you already are, refer to broccoli as the product of selective breeding. In short, by controlling the environment, and taking buds from the wild cabbage, broccoli can be forced to reproduce.
What are 5 common foods that are genetically modified?
What GMO crops are in the United States?Corn: Corn is the most commonly grown crop in the United States, and most of it is GMO. ... Soybean: Most soy grown in the United States is GMO soy. ... Cotton: ... Potato: ... Papaya: ... Summer Squash: ... Canola: ... Alfalfa:More items...•
Which fruits and vegetables are GMO?
Genetically modified organisms, often shortened to GMOs, have been used in the American food supply system for more than 20 years....Examples of the crops, including GMO vegetables, that are produced in the U.S. are:Corn.Soybeans.Cotton.Potatoes.Papaya.Squash.Canola.Alfalfa.More items...•
What are the top 3 genetically modified foods?
The top three GMO crops grown in the U.S. are soy, corn and cotton, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA).
Are bananas GMO?
Are bananas GMOs? The short answer is no. The banana available in U.S. grocery stores is a cultivar called the Cavendish banana. This type of banana is a non-GMO banana that is not currently available as a GM variety, or GMO, in the United States.
Can apples be genetically modified?
Last year, genetically modified apples, particularly the Arctic apple (engineered to prevent browning), entered the consumer market in a big way.
What are the 8 GMO crops?
Corn (field & sweet) The GM version of field corn protects the crop against corn rootworms and the Asian corn borer. ... Soybeans. The GM soybean plant is resistant to pests and disease as well as being tolerant of herbicides.Cotton. GM cotton protects against the cotton bollworm.Canola. ... Alfalfa. ... Sugar Beets. ... Papaya. ... Squash.
Which of the following is not a GMO?
So, the correct answer is 'Dolly'
Which of the following is not a genetically modified organism?
So the correct answer is 'Dogie'.
Is corn genetically modified?
Corn is the most commonly grown crop in the United States, and most of it is GMO. Most GMO corn is created to resist insect pests or tolerate herbicides.
Is wheat a GMO crop?
There is no genetically modified wheat currently commercialized anywhere in the world, and GMOs are not related to gluten.
Why are some crops genetically modified?
Genetic modifications to some crops also exist, which make it easier to process the crop, i.e. by growing in a more compact form. Also, some crops (such as tomatoes) have been genetic modified to contain no seed at all.
How can genetically modified plants be modified?
Genetically modified plants can also be developed using gene knockdown or gene knockout to alter the genetic makeup of a plant without incorporating genes from other plants. In 2014, Chinese researcher Gao Caixia filed patents on the creation of a strain of wheat that is resistant to powdery mildew. The strain lacks genes that encode proteins that repress defenses against the mildew. The researchers deleted all three copies of the genes from wheat's hexaploid genome. Gao used the TALENs and CRISPR gene editing tools without adding or changing any other genes. No field trials were immediately planned. The CRISPR technique has also been used by Penn State researcher Yinong Yang to modify white button mushrooms ( Agaricus bisporus) to be non-browning, and by DuPont Pioneer to make a new variety of corn.
Why is glyphosate used in agriculture?
Thus, developing crops that could withstand spraying with glyphosate would both reduce environmental and health risks, and give an agricultural edge to the farmer.
What are transgenic plants?
Transgenic plants have genes inserted into them that are derived from another species. The inserted genes can come from species within the same kingdom (plant to plant), or between kingdoms (for example, bacteria to plant). In many cases the inserted DNA has to be modified slightly in order to be correctly and efficiently expressed in the host organism. Transgenic plants are used to express proteins, like the cry toxins from B. thuringiensis, herbicide -resistant genes, antibodies, and antigens for vaccinations. A study led by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) also found viral genes in transgenic plants.
What is GM in agriculture?
Genetically modified crops ( GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of Agrobacterium for the delivery of sequences hosted in T-DNA binary vectors. In most cases, the aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. Examples in food crops include resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental conditions, reduction of spoilage, resistance to chemical treatments (e.g. resistance to a herbicide ), or improving the nutrient profile of the crop. Examples in non-food crops include production of pharmaceutical agents, biofuels, and other industrially useful goods, as well as for bioremediation.
What are some examples of non-food crops?
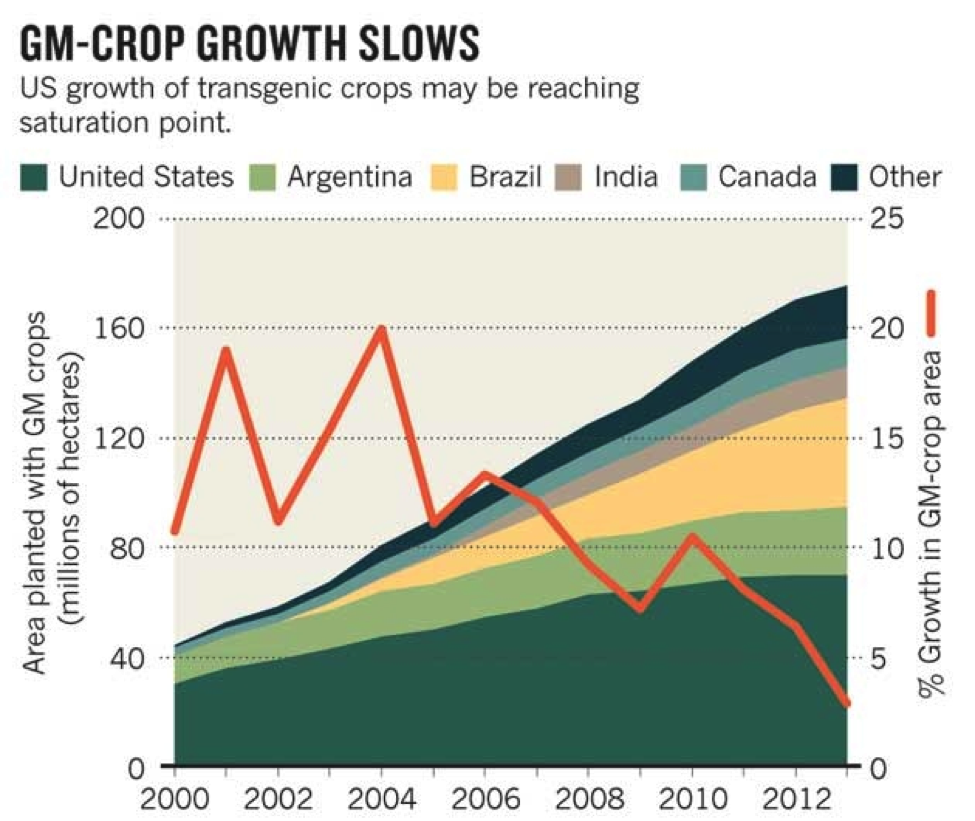
Examples in non-food crops include production of pharmaceutical agents, biofuels, and other industrially useful goods, as well as for bioremediation. Farmers have widely adopted GM technology. Acreage increased from 1.7 million hectares in 1996 to 185.1 million hectares in 2016, some 12% of global cropland.
How have humans influenced the genetic makeup of plants?
Humans have directly influenced the genetic makeup of plants to increase their value as a crop through domestication. The first evidence of plant domestication comes from emmer and einkorn wheat found in pre-Pottery Neolithic A villages in Southwest Asia dated about 10,500 to 10,100 BC. The Fertile Crescent of Western Asia, Egypt, and India were sites of the earliest planned sowing and harvesting of plants that had previously been gathered in the wild. Independent development of agriculture occurred in northern and southern China, Africa's Sahel, New Guinea and several regions of the Americas. The eight Neolithic founder crops ( emmer wheat, einkorn wheat, barley, peas, lentils, bitter vetch, chick peas and flax) had all appeared by about 7,000 BC. Traditional crop breeders have long introduced foreign germplasm into crops by creating novel crosses. A hybrid cereal grain was created in 1875, by crossing wheat and rye. Since then traits including dwarfing genes and rust resistance have been introduced in that manner. Plant tissue culture and deliberate mutations have enabled humans to alter the makeup of plant genomes.
What are some foods that are made with GMOs?
Many GMO crops are used to make ingredients that Americans eat such as cornstarch, corn syrup, corn oil, soybean oil, canola oil, or granulated sugar. A few fresh fruits and vegetables are available in GMO varieties, including potatoes, summer squash, apples, and papayas. Although GMOs are in a lot of the foods we eat, most of the GMO crops grown in the United States are used for animal food.
What GMO crops are grown and sold in the United States?
Only a few types of GMO crops are grown in the United States, but some of these GMOs make up a large percentage of the crop grown (e.g., soybeans, corn, sugar beets, canola, and cotton).
What about animals that eat food made from GMO crops?
More than 95% of animals used for meat and dairy in the United States eat GMO crops. Independent studies show that there is no difference in how GMO and non-GMO foods affect the health and safety of animals. The DNA in the GMO food does not transfer to the animal that eats it. This means that animals that eat GMO food do not turn into GMOs. If it did, an animal would have the DNA of any food it ate, GMO or not. In other words, cows do not become the grass they eat and chickens don’t become the corn they eat.
Are GMOs used to make anything besides food?
When you hear the term “GMO” you probably think of food. However, techniques used to create GMOs are important in creating some medicines as well. In fact, genetic engineering, which is the process used to create GMOs, was first used to make human insulin, a medicine used to treat diabetes. Medicines developed through genetic engineering go through an in-depth FDA approval process. All medicines must be proven to be safe and effective before they are approved for human use. GMOs are also used in the textile industry. Some GMO cotton plants are used to create cotton fiber that is then used to make fabric for clothing and other materials.
What is the name of the GMO that wiped out the papaya crop?
Papaya: By the 1990s, ringspot virus disease had nearly wiped out Hawaii’s papaya crop, and in the process almost destroyed the papaya industry in Hawaii. A GMO papaya, named the Rainbow papaya, was created to resist ringspot virus. This GMO saved papaya farming on the Hawaiian Islands.
Why are sugar beets used in grocery stores?
More than half the granulated sugar packaged for grocery store shelves is made from GMO sugar beets. Because GMO sugar beets are resistant to herbicides, growing GMO sugar beets helps farmers control weeds in their fields.
What is Bt corn used for?
While a lot of GMO corn goes into processed foods and drinks, most of it is used to feed livestock, like cows, and poultry, like chickens.
What is genetically modified?
The term genetically modified (GM), as it is commonly used, refers to the transfer of genes between organisms using a series of laboratory techniques for cloning genes, splicing DNA segments together, and inserting genes into cells. Collectively, these techniques are known as recombinant DNA technology. Other terms used for GM plants or foods derived from them are genetically modified organism (GMO), genetically engineered (GE), bioengineered, and transgenic. ‘Genetically modified’ is an imprecise term and a potentially confusing one, in that virtually everything we eat has been modified genetically through domestication from wild species and many generations of selection by humans for desirable traits. The term is used here because it is the one most widely used to indicate the use of recombinant DNA technology. According to USDA standards for organic agriculture, seeds or other substances derived through GM technology are not allowed in organic production.
Why are GM crops so large?
Because several of them are major crops, the area planted to GM varieties is very large. Most current GM crops have been engineered for resistance to insects, tolerance to herbicides (weed control products) or both. Figure 1. Currently grown GM crops in the U.S., traits for which they are modified, and percent of total acreage ...
What is GM technology?
Genetic modification (GM) technology allows the transfer of genes for specific traits between species using laboratory techniques. GM crops were first introduced in the U.S. in the mid-1990s. Most current GM crops grown in the U.S. are engineered for insect resistance or herbicide tolerance. Corn, soybeans, and cotton are ...
What is a GM plant?
Other terms used for GM plants or foods derived from them are genetically modified organism ( GMO), genetically engineered (GE), bioengineered, and transgenic. ‘Genetically modified’ is an imprecise term and a potentially confusing one, in that virtually everything we eat has been modified genetically through domestication from wild species ...
How do plant breeding programs work?
Most plant breeding programs rely on manual cross-pollination between genetically distinct plants to create new combinations of genes. The progeny plants are intensively evaluated over several generations and the best ones are selected for potential release as new varieties.
How do organisms store genetic information?
Most organisms store their genetic information in the form of DNA molecules in chromosomes. The sequence of chemical bases in a DNA strand encodes a specific order of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins . Proteins carry out many functions in cells and tissues, which together are responsible for an organism’s characteristics. Because most life forms share this same language of heredity—and due to scientific advances in molecular biology—it is now possible to transfer a gene from one species to another, for example from a bacterium to a plant, and have it function in its new host.
What are the benefits of GM crops?
Some potential applications of GM crop technology are: 1 Nutritional enhancement: Higher vitamin content; more healthful fatty acid profiles; 2 Stress tolerance: Tolerance to high and low temperatures, salinity, and drought; 3 Disease resistance: For example, orange trees resistant to citrus greening disease or American chestnut trees resistant to fungal blight; 4 Biofuels: Plants with altered cell wall composition for more efficient conversion to ethanol; 5 Phytoremediation: Plants that extract and concentrate contaminants like heavy metals from polluted sites.
What are the top 7 genetically modified crops?
Here are the Top 7 Genetically Modified Crops: 1. Corn: Corn is the No. 1 crop grown in the U.S. and nearly all of it — 88 percent — is genetically modified. In addition to being added to innumerable processed foods, genetically modified corn is a staple of animal feed. 2.
What are the top 3 GMO crops?
The top three GMO crops grown in the U.S. are soy, corn and cotton, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). During the past 12 years, the percentage of acreage planted with GMO crops soared to over 80 percent for each of the top three. (See this graph at Mother Jones .)
What percentage of cotton is genetically modified?
Cottonseed: According to the USDA, 94 percent of cotton grown in the U.S. is genetically modified. Cottonseeds are culled from cotton, and then used for vegetable oil, margarine or shortening production, or frying foods, such as potato chips. 4.
What is the fourth largest crop grown in the U.S.?
Alfalfa: Farmers feed alfalfa to dairy cows, the source of milk, butter, yogurt, meat and so much more. Alfalfa is the fourth largest crop grown in the U.S., behind corn, soybeans, and wheat (though there is no genetically engineered wheat on the market). 5. Papaya: 75 percent of the Hawaiian papaya crop is genetically modified to withstand ...
Where are transgenic soy plants?
Transgenic soy plants are seen in a field near Santa Fe city, some 500 Km northwest of Buenos Aires, Argentina, on April 10, 2012. Transgenic soy, corn and wheat plants, resistant to the drought and salinity were created by a team led by Dr. Raquel Chan at the vegetable biotechnology lab of the Universidad del Litoral.
Do you have to test for GMOs?
Research links GMOs to allergies, organ toxicity, and other health issues, though the U.S. Food and Drug Administration does not require safety testing for GMOs. Market watchers estimate that upwards of 70 percent of processed foods in your local supermarket contain genetically modified ingredients.
Is True Food testing for genetic modification?
The organization True Food Now has a list of foods currently being tested for genetic modification, as well as those foods that are approved but not yet sold in the U.S. For a full snapshot of the future GMO landscape, visit this link.
What is genetic engineering?
Genetic engineering is a method that, among other things, enables scientists to copy a gene with a desired trait in one organism and put it into another. Genetic engineering has been used since the 1970s and builds on the scientific advances we have made in the study of DNA. A gene in a soil bacterium (Bt) ...
What is the gene that is inserted into the DNA of corn?
A gene in a soil bacterium (Bt) is inserted into the DNA of the corn to create an insect-resistant corn.
What is genome editing?
Genome editing is a new method that gives scientists more precise and targeted ways to develop new crop varieties. Genome editing tools can make it easier and quicker to make changes that were previously done through traditional breeding. One example of genome editing is removing an unwanted gene.
When were genetically engineered crops first introduced?
The first genetically engineered plants to be produced for human consumption were introduced in the mid-1990s. Today, approximately 90 percent of the corn, soybeans, and sugar beets on the market are GMOs. Genetically engineered crops produce higher yields, have a longer shelf life, are resistant to diseases and pests, and even taste better.
What are GMOs used for?
Most animals that are GMOs are produced for use in laboratory research. These animals are used as “models” to study the function of specific genes and, typically, how the genes relate to health and disease. Some GMO animals, however, are produced for human consumption.
Why are GMOs important?
In the future, GMOs are likely to continue playing an important role in biomedical research. GMO foods may provide better nutrition and perhaps even be engineered to contain medicinal compounds to enhance human health. If GMOs can be shown to be both safe and healthful, consumer resistance to these products will most likely diminish.
How can we modify plants and animals?
Conventional methods of modifying plants and animals— selective breeding and crossbreeding —can take a long time. Moreover, selective breeding and crossbreeding often produce mixed results, with unwanted traits appearing alongside desired characteristics. The specific targeted modification of DNA using biotechnology has allowed scientists to avoid this problem and improve the genetic makeup of an organism without unwanted characteristics tagging along.
What is a GMO?
Encyclopedic Entry. Vocabulary. A genetically modified organism (GMO) is an animal, plant, or microbe whose DNA has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. For thousands of years, humans have used breeding methods to modify organisms. Corn, cattle, and even dogs have been selectively bred over generations to have certain desired traits.
What is the term for a natural substance that kills organisms that threaten agriculture or are undesirable?
natural or manufactured substance used to kill organisms that threaten agriculture or are undesirable. Pesticides can be fungicides (which kill harmful fungi), insecticides (which kill harmful insects), herbicides (which kill harmful plants), or rodenticides (which kill harmful rodents.)
What is the basic unit of heredity?
part of DNA that is the basic unit of heredity. living thing whose genes (DNA) have been altered for a specific purpose. process of altering and cloning genes to produce a new trait in an organism or to make a biological substance, such as a protein or hormone. tiny organism, usually a bacterium.
What are the most commonly distributed genetically modified crops in the United States?
These commodities include corn, potato, canola, squash, soy, rice, tomato, sugar beet, chicory and papaya. The soy, transgenic corn and papaya are the most often distributed genetically modified crops in the United States.
Why are genetically modified crops valuable?
The genetically modified crops can be valuable to humans since it is more nutritious and it has the potential to boost the nourishment of public & increase the earnings of farmers. One example of genetically modified crops is the golden rice which is the kind of transgenic cultivar rice that contains beta carotene which is very useful ...
How Do You Feel about Genetically Modified Crops?
The debates about the Genetically Modified Crops are still ongoing. Some are saying that the genetically modified crops are harmful to human health while others conclude that it plays a vital role in the human health. What do you think?
What are the effects of genetically modified crops on humans?
2. Occurrence of Allergic Issues. The pesticides that the genetically modified crops generate can disrupt the natural conservation relationships. It will also influence the survival pace of the predators and it can cause allergic issues to humans.
How do genetically modified crops affect the environment?
Most of the genetically modified crops have the ability to distribute the foreign genes in the environment in a form of interbreeding the non-genetically modified plants. The genetically modified crops can generate pesticides that will lead to tougher pests. The pesticides that these crops generate will destroy the susceptible pests.
What is genetically modified?
The genetically modified crops are known as the transgenic crops that are associated with practical and important ethical issues. Before delving the advantages and disadvantages of genetically modified crops, it is very important that you have a clear and better understanding when it comes to the factors that might affect a certain individual ...
Which crops are tolerant to glyphosate?
The efficient and effective herbicide has the ability to destroy crops. However, the crops like corn and soy cotton can be tolerant to herbicide glyphosate.
Overview
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of Agrobacterium for the delivery of sequences hosted in T-DNA binary vectors. In most cases, the aim is to introduce a new trait to the plant which does not occur naturally in the species. Examples in food crops include resistance to certain pests, diseases, environmental co…
History
Humans have directly influenced the genetic makeup of plants to increase their value as a crop through domestication. The first evidence of plant domestication comes from emmer and einkorn wheat found in pre-Pottery Neolithic A villages in Southwest Asia dated about 10,500 to 10,100 BC. The Fertile Crescent of Western Asia, Egypt, and India were sites of the earliest planned sowing and harvesting of plants that had previously been gathered in the wild. Independent development of …
Methods
Genetically engineered crops have genes added or removed using genetic engineering techniques, originally including gene guns, electroporation, microinjection and agrobacterium. More recently, CRISPR and TALEN offered much more precise and convenient editing techniques.
Gene guns (also known as biolistics) "shoot" (direct high energy particles or radiations against ) target genes into plant cells. It is the most common method. DNA is bound to tiny particles of gol…
Types of modifications
Transgenic plants have genes inserted into them that are derived from another species. The inserted genes can come from species within the same kingdom (plant to plant), or between kingdoms (for example, bacteria to plant). In many cases the inserted DNA has to be modified slightly in order to be correctly and efficiently expressed in the host organism. Transgenic plants are used to express proteins, like the cry toxins from B. thuringiensis, herbicide-resistant genes, an…
Economics
GM food's economic value to farmers is one of its major benefits, including in developing nations. A 2010 study found that Bt corn provided economic benefits of $6.9 billion over the previous 14 years in five Midwestern states. The majority ($4.3 billion) accrued to farmers producing non-Bt corn. This was attributed to European corn borer populations reduced by exposure to Bt corn, leaving fewer to attack conventional corn nearby. Agriculture economists calculated that "world …
Yield
In 2014, the largest review yet concluded that GM crops' effects on farming were positive. The meta-analysis considered all published English-language examinations of the agronomic and economic impacts between 1995 and March 2014 for three major GM crops: soybean, maize, and cotton. The study found that herbicide-tolerant crops have lower production costs, while for insect-resistant crops the reduced pesticide use was offset by higher seed prices, leaving overa…
Traits
GM crops grown today, or under development, have been modified with various traits. These traits include improved shelf life, disease resistance, stress resistance, herbicide resistance, pest resistance, production of useful goods such as biofuel or drugs, and ability to absorb toxins and for use in bioremediation of pollution.
Recently, research and development has been targeted to enhancement of crops that are locally i…
Crops
Several modifications of Camelina sativa have been done, see §Edible oils and §Non-pesticide pest management products above.
The number of USDA-approved field releases for testing grew from 4 in 1985 to 1,194 in 2002 and averaged around 800 per year thereafter. The number of sites per release and the number of gene constructs (ways that the gene of interest is packaged together with other elements) – have rapi…