Bone Remodeling Occurs at periosteum and endosteum when bone is injured or need more strength Calcium homeostasis control calcium levels in the blood Hormonal control - negative feedback mechanisms Parathyroid hormone Calcitonin Bone deposition + Bone resorption
Why does bone remodeling occur in the human skeleton?
Regional areas of mechanical stress Blood calcitonin levels Blood parathyroid hormone levels Regional areas of mechanical stress Why does bone remodeling occur in an adult skeleton? To heal a broken bone To increase the size of bones To maintain adequate blood calcium levels To increase the overall density and weight of bones
What is the difference between resorption and deposition in bone remodeling?
Resorption in remodeling involves removal of minerals and collagen fibers by osteoclasts. Deposition in remodeling involves Addition of minerals and collagen fibers by osteoblasts. 1. Benefit of Remodeling Provides bone with continued strength 2. Benefit of Remodeling Regenerates Ca and P levels in blood. 3. Benefit of Remodeling
What is the second factor that controls bone growth and remodeling?
Second factor which controls bone growth and remodeling Gravity (mechanical stress) stress on skeleton causes bone growth Muscular stress stimulates osteoblasts If you increase muscle mass you must also increase bonemass. bone become thicker Ecersise increases calcitonin which inhibits osteoclasts and bone resorption No stress weakens bones through
How are osteoporosis and bone formation related?
Bone formation occurs by osteoblasts secreting an organic matrix (osteoid) and then mineralizing the matrix. When the remodeling process is skewed such that, over time, there is more eating than replenishing, you get osteoporosis. When the remodeling process is aborted, say in avascular necrosis,

What is bone remodeling?
What is bone remodeling? The bone remodeling process, also called bone metabolism, is unique and occurs when exhausted bone tissue is removed from the skeleton through bone resorption. Then, new bone is formed by ossification.
Does a one year old have a skeleton replaced?
This process occurs throughout an individual’s life. A one-year-old child has had nearly all of their skeleton replaced by this process, although it does tend to slow with age. The bone remodeling definition applies to all bones within the body, however, this process is of particular importance in implant dentistry.
What factors regulate bone remodeling?
Bone remodeling is regulated by two factors; osteoprotegerin and the surface ligand Rank to which it binds, both of which are activated by Tgfβ-1. Inhibiting Tgfβ-receptor signaling in osteoblasts leads to decreased bone remodeling and increased trabecular bone mass ( Box 15.1).
How is bone remodelling controlled?
Bone remodelling process is controlled by mechanical usage and biological factors. Osteocytes act as sensors of mechanoreceptors and regulators of bone mass by mediating osteoblasts for bone formation and osteoclasts for bone resorption ( Cowin et al., 1991; Lanyon, 1993 ). The computational model of bone remodelling we developed was shown here as an example ( Gong et al., 2010 ). The total mechanical stimulus at location x on the trabecular surface ( P ( x, t )) is the contribution of all the osteocytes in the forms of strain energy density (SED), relative to their distance from x ( Mullender and Huiskes, 1995; Gong et al., 2010 ):
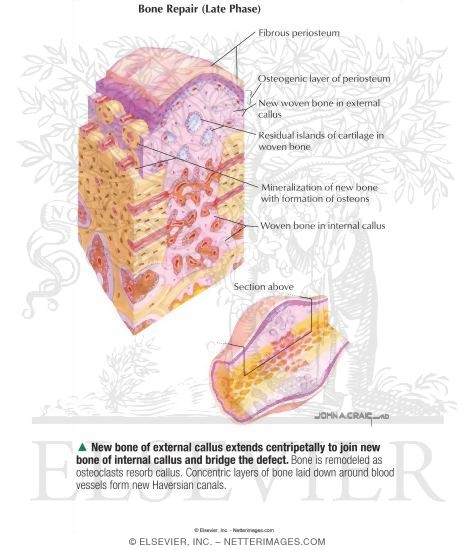
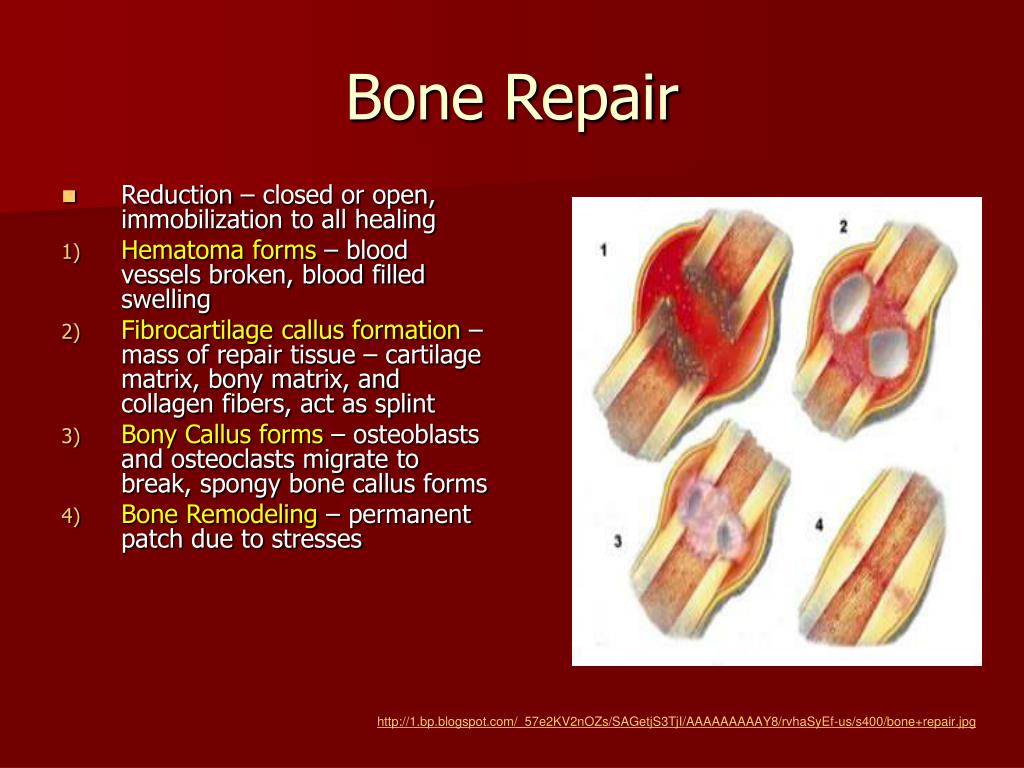
What is bone repair?
Bone repair and fracture healing are complex processes that follow an ordered sequence of distinct steps including an initial inflammatory reaction, mimicking the processes of endochondral or membranous bone formation as seen during organogenesis .
What are the three principles of bone tissue engineering?
The three principles, in addition to traditional criteria, are also the major considerations of materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Polymers, ceramics, glass, metals and their composites have all been intensively investigated as candidate for bone-repair materials and substitutes.
What biomaterials are used for bone regeneration?
Today, ideal biomaterials used for bone repair and regeneration should be osteoinductive (induce bone formation and differentiation), osteoconductive (allow bone tissue to attach and pass through) and have a good osteointegration (adequately strong bonding to bone tissue).
What is the role of miRNA in bone repair?
miRNAs play an integral role in lineage commitment and differentiation, as well as function, of osteoblasts, chondrocytes, osteoclasts, and vascular cells. The effects of individual miRNAs are cell context–dependent, and as yet no miRNA has been identified that can be targeted for the purpose of facilitating repair. However, increased understanding of the bone repair process, coupled with advances in the understanding of miRNA–target interactions in cells present at the fracture site and in other tissues, will facilitate the translation of miRNA-based therapeutics to the clinic. Bone remodeling, fracture repair, and some key miRNA–target interactions active in these functions are outlined in this chapter.
Where are stem cells found in bone?
Two major sources for these stem cells are found in the periosteum and the bone marrow and differentially contribute to bone repair.
Why do bone skeletons increase in size?
They proportionally increase the size of the medullary cavity as the bone grows to prevent the weight of the growing skeleton from becoming too heavy. They proportionally increase the size of the medullary cavity as the bone grows to prevent the weight of the growing skeleton from becoming too heavy.
What is the effect of hormones on bone growth?
It results from the effects of hormones that target parts of a bone for growth. Fetal bones begin with most of these features, but the features increase in size as the bones grow. The periosteum contains an abundance of osteoblasts where projections form, and an abundance of osteoclasts where depressions or holes form.
Which cells differentiate and form cartilage?
Fibroblasts give rise to chondrocytes that differentiate and form cartilage. Unspecialized cells from mesenchyme develop into chondrocytes, which divide and form cartilage. Growth occurs in the lining of the long bones. Chondrocytes in the lacunae divide and secrete matrix, allowing the cartilage to grow from within.
What is endochondral ossification?
Endochondral ossification occurs within fibrous connective tissue membranes. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone. Endochondral ossification leads to the formation of the clavicles and cranial bones. During endochondral ossification, hyaline cartilage is broken down and replaced with bone.