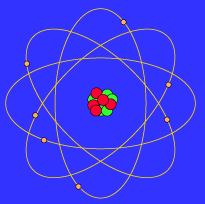
- The Bohr model shows that the electrons in atoms are in orbits of differing energy around the nucleus (think of planets orbiting around the sun).
- Bohr used the term energy levels (or shells) to describe these orbits of differing energy. ...
- The energy level an electron normally occupies is called its ground state. ...
See more
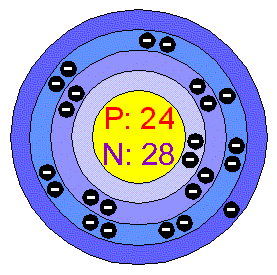
What did Bohr learn about atoms?
The Bohr model shows the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. Bohr was the first to discover that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus and that the number of electrons in the outer orbit determines the properties of an element.
How did Bohr discover his atom model?
It was while Bohr was working in England in 1913 that he developed this atomic model. He developed the model after studying the way glowing, hot hydrogen gives off light. When an incandescent light bulb is lit, it gives off all the different wavelengths of light.
What does the Bohr theory explain?
Summary. The Bohr model postulates that electrons orbit the nucleus at fixed energy levels. Orbits further from the nucleus exist at higher energy levels. When electrons return to a lower energy level, they emit energy in the form of light.
What are the main points of Bohr's model?
Main Points of the Bohr Model Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that have a set size and energy. The energy of the orbit is related to its size. The lowest energy is found in the smallest orbit. Radiation is absorbed or emitted when an electron moves from one orbit to another.
Who discovered atom structure?
This 1922 photo was taken in the dark in the Curie laboratory. Building on the Curies' work, the British physicist Ernest Rutherford (1871–1937) performed decisive experiments that led to the modern view of the structure of the atom.
What was Bohr's model of the atom called?
The Bohr Model is a structural model of an atom. The model was proposed by physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. In this model, the electrons travel around the nucleus of an atom in distinct circular orbits, or shells. The model is also referred to as the planetary model of an atom.
How did Bohr explain the stability of an atom?
Bohr explained the stability of atom by proposing that electrons revolve around the nucleus in the definite circular paths having fixed energy and while moving in the same orbit they do not lose or gain energy.
Why did Bohr create his model?
Bohr Atomic Model : In 1913 Bohr proposed his quantized shell model of the atom to explain how electrons can have stable orbits around the nucleus.
When did Bohr discover the atom?
1913In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed a theory for the hydrogen atom, based on quantum theory that some physical quantities only take discrete values. Electrons move around a nucleus, but only in prescribed orbits, and If electrons jump to a lower-energy orbit, the difference is sent out as radiation.
What experiment did Bohr use?
the “gold foil experiment.” In this experiment, Geiger and Marsden measured the scattering pattern of the alpha particles with a fluorescent screen. If Thomson's model were correct, the alpha particles would pass through the atomic structure of the foil unimpeded.
What experiments led to the Bohr model?
1 Answer. Well there were two experiments back to back one by J.J. Thomson that resulted "Plum Pudding" model of the atom and the 2nd one by Rutherford (a student of J.J. Thomson actually) which blew a big hole in "Plum Pudding Hypothesis" of the atom.
Work
The discovery of the electron and radioactivity in the late 19th century led to different models being proposed for the atom’s structure. In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed a theory for the hydrogen atom, based on quantum theory that some physical quantities only take discrete values.
Nobel Prizes 2021
Thirteen laureates were awarded a Nobel Prize in 2021, for achievements that have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind.
Explore prizes and laureates
Look for popular awards and laureates in different fields, and discover the history of the Nobel Prize.
How did Bohr change the view of the motion of the planetary electrons?
Bohr amended that view of the motion of the planetary electrons to bring the model in line with the regular patterns (spectral series) of light emitted by real hydrogen atoms. By limiting the orbiting electrons to a series of circular orbits having discrete radii, Bohr could account for the series of discrete wavelengths in the emission spectrum ...
What is the Bohr model?
The Bohr model and all of its successors describe the properties of atomic electrons in terms of a set of allowed (possible) values. Atoms absorb or emit radiation only when the electrons abruptly jump between allowed, or stationary, states.
What is the energy lost by an electron in an abrupt transition?
The energy lost by the electron in the abrupt transition is precisely the same as the energy of the quantum of emitted light. In the Bohr model of the atom, electrons travel in defined circular orbits around the nucleus. The orbits are labeled by an integer, the quantum number n.
What is the nucleus of an atom?
Immediately before 1913, an atom was thought of as consisting of a tiny positively charged heavy core, called a nucleus, surrounded by light, planetary negative electrons revolving in circular orbits of arbitrary radii. Britannica Quiz. Matter and More Quiz.
How do electrons jump from one orbit to another?
The orbits are labeled by an integer, the quantum number n. Electrons can jump from one orbit to another by emitting or absorbing energy. The inset shows an electron jumping from orbit n =3 to orbit n =2, emitting a photon of red light with an energy of 1.89 eV. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
What department is the Bohr model?
University of Rochester - Department of Physics and Astronomy - The Bohr Model
Who first proposed quantum theory?
The first attempt to introduce quantum theory to account for the structure of atoms was made by the Danish physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. He asserted that the electron in a hydrogen atom occupies one of an array of discrete (but infinite…
Who was the Nobel Prize winner for the development of the Bohr model?
Bohr was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1922 for the development of the Bohr model. He also played a large role in the development of atomic weapons and nuclear energy, and, in 1957, was awarded the Atoms for Peace Award for his efforts in the responsible use of atomic energy. He was the founder and director of the Institute for Theoretical Physics at the University of Copenhagen and was part of a group of scientists who founded CERN, where much of the world's nuclear and particle physics research goes on today.
Why did Niels Bohr win the Nobel Prize?
In 1922, Niels Bohr was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for his work to advance our understanding of atomic structure. Even though he is best known for the development of the Bohr model of the atom, he also accomplished many other things in his lifetime.
What was Niels Bohr interested in?
Niels Bohr was interested in understanding what was going on inside an atom. Atoms are so tiny that it was impossible to actually see inside them, especially back in the early 1900's. To figure out what was happening inside the atom, he had to study the way atoms behaved and then come up with a model that explained what was happening. In science, a scientific model is an idea about how nature works that can be tested and used to explain many observed phenomena.
What is the name of the location where electrons orbit the nucleus?
According to the Bohr model, electrons orbit the nucleus in defined locations, called shells . Some electron shells require the electrons to have more energy than others, so if an electron absorbs some energy, it can move into a higher energy shell.
Why do some elements form chemical bonds more easily than others?
Bohr said that atoms were most stable when the outer electron orbits were full. In most atoms, this means that they have eight electrons. Elements whose atoms already have a full outer electron shell are very stable and don't readily form bonds with any other atoms. Examples of these types of atoms are the noble gases, like neon and argon. If atoms don't already have eight atoms in their outer electron shell, they tend to bond with other atoms to complete the outer shell and be more stable. These types of atoms rarely exist on their own but are almost always bonded to others in order to maintain a full outer electron shell.
What did Bohr do in 1911?
In 1911, Bohr completed his education at the University of Copenhagen when he was awarded a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in physics for his work on the behavior of electrons in a metal. Just a year later, he married Margrethe Norlund and they went on to have a total of 6 children, including one son, Aage, who would eventually win a Nobel Prize in physics, just like his father!
How many children did Niels Bohr have?
Just a year later, he married Margrethe Norlund and they went on to have a total of 6 children, including one son, Aage, who would eventually win a Nobel Prize in physics, just like his father! Niels Bohr, with his wife, Margrethe.
Where did Bohr study atoms?
Under Rutherford's tutelage, Bohr began studying the properties of atoms. Bohr held a lectureship in physics at Copenhagen University from 1913 to 1914 and went on to hold a similar position at Victoria University in Manchester from 1914 to 1916. He went back to Copenhagen University in 1916 to become a professor of theoretical physics.
What did Bohr discover?
His subsequent work became increasingly theoretical. It was while conducting research for his doctoral thesis on the electron theory of metals that Bohr first came across Max Planck's early quantum theory, which described energy as tiny particles, or quanta.
What did Niels Bohr believe about the atom?
A stylized representation of a lithium atom illustrates Niels Bohr's atomic model, that an atom is a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons.
What did Bohr do in 1920?
In 1920, he was appointed the head of the Institute for Theoretical Physics. Combining Rutherford's description of the nucleus and Planck's theory about quanta, Bohr explained what happens inside an atom and developed a picture of atomic structure. This work earned him a Nobel Prize of his own in 1922.
What is Niels Bohr best known for?
Niels Bohr was one of the foremost scientists of modern physics, best known for his substantial contributions to quantum theory and his Nobel Prize-winning research on the structure of atoms.
Which model shows the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons?
The Bohr model shows the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. Bohr was the first to discover that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus and that the number of electrons in the outer orbit determines the properties of an element.
What did Bohr do to improve the theory of surface tension?
Bohr went above and beyond the current theory of liquid surface tension by taking into account the viscosity of the water as well as incorporating finite amplitudes rather than infinitesimal ones. He submitted his essay at the last minute, winning first place and a gold medal. He improved upon these ideas and sent them to the Royal Society in London, who published them in the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society in 1908, according to Nobelprize.org .
What was Bohr's first contribution to quantum physics?
Bohr’s first contribution to the emerging new idea of quantum physics started in 1912 during what today would be called postdoctoral research in England with Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester. Only the year before, Rutherford and his collaborators had established experimentally that the atom consists of a heavy positively charged nucleus with substantially lighter negatively charged electrons circling around it at considerable distance. According to classical physics, such a system would be unstable, and Bohr felt compelled to postulate, in a substantive trilogy of articles published in The Philosophical Magazine in 1913, that electrons could only occupy particular orbits determined by the quantum of action and that electromagnetic radiation from an atom occurred only when an electron jumped to a lower-energy orbit. Although radical and unacceptable to most physicists at the time, the Bohr atomic model was able to account for an ever-increasing number of experimental data, famously starting with the spectral line series emitted by hydrogen.
What did Bohr do to the periodic table?
He improved upon that aspect of his work into the early 1920s, by which time he had developed an elaborate scheme building up the periodic table by adding electrons one after another to the atom according to his atomic model. When Bohr was awarded the Nobel Prize for his work in 1922, the Hungarian physical chemist Georg Hevesy, together with the physicist Dirk Coster from Holland, were working at Bohr’s institute to establish experimentally that the as-yet-undiscovered atomic element 72 would behave as predicted by Bohr’s theory. They succeeded in 1923, thus proving both the strength of Bohr’s theory and the truth in practice of Bohr’s words at the institute’s inauguration about the important role of experiment. The element was named hafnium (Latin for Copenhagen).
How do electrons travel in the Bohr model?
In the Bohr model of the atom, electrons travel in defined circular orbits around the nucleus. The orbits are labeled by an integer, the quantum number n. Electrons can jump from one orbit to another by emitting or absorbing energy. The inset shows an electron jumping from orbit n =3 to orbit n =2, emitting a photon of red light with an energy of 1.89 eV.
How do electrons jump from one orbit to another?
The orbits are labeled by an integer, the quantum number n. Electrons can jump from one orbit to another by emitting or absorbing energy. The inset shows an electron jumping from orbit n =3 to orbit n =2, emitting a photon of red light with an energy of 1.89 eV. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
Which scientist modeled the atom with electrons that could only have specific stable orbits?
Niels Bohr modeled the atom with electrons that could only have specific stable orbits. This model of the atom was the first to incorporate quantum theory. That electrons could only occur in specific orbits explained why elements such as hydrogen emitted and absorbed light at specific wavelengths.
Which scientist proposed a model of the atom in which the electrons were able to occupy only certain orbit?
Niels Bohr proposed a model of the atom in which the electron was able to occupy only certain orbits around the nucleus. This atomic model was the first to use quantum theory, in that the electrons were limited to specific orbits around the nucleus. Bohr used his model to explain the spectral lines of hydrogen.
Where did Bohr go to school?
Enrolling at the University of Copenhagen in 1903, Bohr was never in doubt that he would study physics. Research and teaching in that field took place in cramped quarters at the Polytechnic Institute, leased to the University for the purpose. Bohr obtained his doctorate in 1911 with a dissertation on the electron theory of metals.
