During the rest of this particular voyage, Columbus and his crew went on to find and explore various places:
- The northeast coast of Cuba (28th October onwards)
- Babeque (possibly Baneque, 22nd November)
- The northern coast of Hispaniola (5th December onwards)
- The Bay of Rincon, Northeast Hispaniola (13th January onwards)
See more

Where did Christopher Columbus first sail?
The first voyage of Christopher Columbus. The ships for the first voyage—the Niña, Pinta, and Santa María —were fitted out at Palos, on the Tinto River in Spain. Consortia put together by a royal treasury official and composed mainly of Genoese and Florentine bankers in Sevilla (Seville) provided at least 1,140,000 maravedis to outfit ...
What island did Columbus sail to?
Adverse winds carried the fleet to an island called Ayti ( Haiti) by its Taino inhabitants; on December 6 Columbus renamed it La Isla Española, or Hispaniola. He seems to have thought that Hispaniola might be Cipango or, if not Cipango, then perhaps one of the legendarily rich isles from which King Solomon ’s triennial fleet brought back gold, gems, and spices to Jerusalem (1 Kings 10:11, 22); alternatively, he reasoned that the island could be related to the biblical kingdom of Sheba ( Sabaʾ ). There Columbus found at least enough gold and prosperity to save him from ridicule on his return to Spain. With the help of a Taino cacique, or Indian chief, named Guacanagarí, he set up a stockade on the northern coast of the island, named it La Navidad, and posted 39 men to guard it until his return. The accidental running aground of the Santa María on December 25, 1492, provided additional planks and provisions for the garrison.
What happened to Columbus after he was freed?
After securing their freedom Columbus sailed on, stormbound, and the damaged ship limped to port in Lisbon. There he was obliged to interview with King John II. These events left Columbus under the suspicion of collaborating with Spain’s enemies and cast a shadow on his return to Palos on March 15. On this first voyage many tensions built up ...
What was Columbus determined to do?
Moreover, Columbus was determined to take back both material and human cargo to his sovereigns and for himself, and this could be accomplished only if his sailors carried on looting, kidnapping, and other violent acts, especially on Hispaniola.
What did Columbus find on his return to Spain?
There Columbus found at least enough gold and prosperity to save him from ridicule on his return to Spain. With the help of a Taino cacique, or Indian chief, named Guacanagarí, he set up a stockade on the northern coast of the island, named it La Navidad, and posted 39 men to guard it until his return.
Where did Columbus land?
The place of the first Caribbean landfall, called Guanahani, is hotly disputed, but San Salvador (Watlings) Island in the Bahamas is generally preferred to other Bahamian ...
When did Columbus leave Spain?
On January 16, 1493, Columbus left with his remaining two ships for Spain. The journey back was a nightmare. The westerlies did indeed direct them homeward, but in mid-February a terrible storm engulfed the fleet.
What was the first voyage of Christopher Columbus?
The First Voyage. Niña, Pinta and Santa Maria. Christopher Columbus's Later Voyages. Legacy of Christopher Columbus. The explorer Christopher Columbus made four trips across the Atlantic Ocean from Spain: in 1492, 1493, 1498 and 1502. He was determined to find a direct water route west from Europe to Asia, but he never did.
Where did Columbus go in 1493?
In January 1493, leaving several dozen men behind in a makeshift settlement on Hispaniola (present-day Haiti and the Dominican Republic), he left for Spain.
What happened to the native Taino people after Columbus landed?
Meanwhile, the native Taino population, forced to search for gold and to work on plantations, was decimated (within 60 years after Columbus landed, only a few hundred of what may have been 250,000 Taino were left on their island).
What did the Portuguese ship carry?
Starting in about 1420, small Portuguese ships known as caravels zipped along the African coast, carrying spices, gold and other goods as well as enslaved people from Asia and Africa to Europe.
What did Columbus want from Isabella?
Columbus wanted fame and fortune. Ferdinand and Isabella wanted the same, along with the opportunity to export Catholicism to lands across the globe. (Columbus, a devout Catholic, was equally enthusiastic about this possibility.)
Why not sail west across the Atlantic instead of around the massive African continent?
He argued (incorrectly) that the circumference of the Earth was much smaller than his contemporaries believed it was; accordingly, he believed that the journey by boat from Europe to Asia should be not only possible, but comparatively easy via an as-yet undiscovered Northwest Passage .
What was Columbus' contract with the Spanish rulers?
Columbus’ contract with the Spanish rulers promised that he could keep 10 percent of whatever riches he found, along with a noble title and the governorship of any lands he should encounter.
What did Columbus describe the Natives he first encountered as?
Columbus described the Natives he first encountered as “timid and full of fear.” Why did he then capture some Natives and bring them aboard his ships?
What was the name of the island that Columbus landed on?
On October 12, more than two months later, Columbus landed on an island in the Bahamas that he called San Salvador; the natives called it Guanahani. Christopher Columbus’s letter to Ferdinand and Isabella, 1493.
What did Columbus say about the natives?
Writing that the natives are "fearful and timid . . . guileless and honest," Columbus declares that the land could easily be conquered by Spain, and the natives "might become Christians and inclined to love our King and Queen and Princes and all the people of Spain.".
How many Native Americans did Columbus kidnap?
He also kidnapped several Native Americans (between ten and twenty-five) to take back to Spain—only eight survived. Columbus brought back small amounts of gold as well as native birds and plants to show the richness of the continent he believed to be Asia.
Where did Christopher Columbus settle?
He left thirty-nine men to build a settlement called La Navidad in present-day Haiti.
When did Columbus arrive in Spain?
When Columbus arrived back in Spain on March 15, 1493, he immediately wrote a letter announcing his discoveries to King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, who had helped finance his trip. The letter was written in Spanish and sent to Rome, where it was printed in Latin by Stephan Plannck.
Who wrote the letter to King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella?
When Columbus arrived back in Spain on March 15, 1493, he immediately wrote a letter announcing his discoveries to King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella, who had helped finance his trip. The letter was written in Spanish and sent to Rome, where it was printed in Latin by Stephan Plannck. Plannck mistakenly left Queen Isabella’s name out of the pamphlet’s introduction but quickly realized his error and reprinted the pamphlet a few days later. The copy shown here is the second, corrected edition of the pamphlet.
Background
Many Europeans of Columbus's day assumed that a single, uninterrupted ocean surrounded Europe and Asia, although Norse explorers had colonized areas of North America beginning with Greenland c. 986. The Norse maintained a presence in North America for hundreds of years, during which some degree of contact with Europe was maintained.
First voyage (1492–1493)
For his westward voyage to find a shorter route to the Orient, Columbus and his crew took three medium-sized ships, the largest of which was a carrack (Spanish: nao ), the Santa María, which was owned and captained by Juan de la Cosa, and under Columbus's direct command.
Second voyage (1493–1496)
The stated purpose of the second voyage was to convert the indigenous Americans to Christianity. Before Columbus left Spain, he was directed by Ferdinand and Isabella to maintain friendly, even loving, relations with the natives. He set sail from Cádiz, Spain, on 25 September 1493.
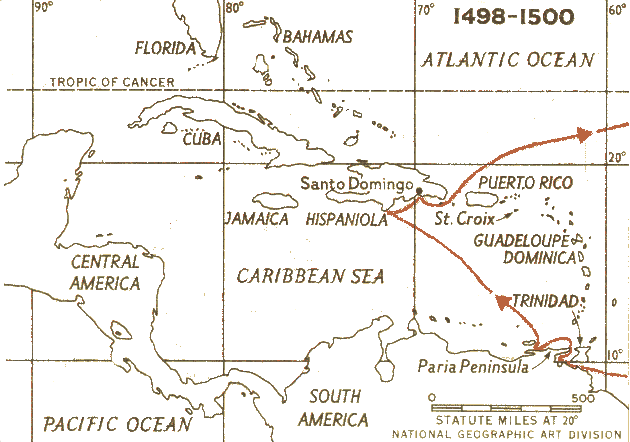
Third voyage (1498–1500)
According to the abstract of Columbus's journal made by Bartolomé de Las Casas, the objective of the third voyage was to verify the existence of a continent that King John II of Portugal suggested was located to the southwest of the Cape Verde Islands.
Fourth voyage (1502–1504)
After much persuasion, the sovereigns agreed to fund Columbus's fourth voyage. It would be his final chance to prove himself and become the first man ever to circumnavigate the world. Columbus's goal was to find the Strait of Malacca to the Indian Ocean.
Legacy
The news of Columbus's first voyage set off many other westward explorations by European states, which aimed to profit from trade and colonization. This would instigate a related biological exchange, and trans-Atlantic trade.
Further reading
Landstrom, Bjorn, 1966. Columbus: The story of Don Cristobal Colon Admiral of the Ocean. Macmillan.
Where did Christopher Columbus sail?
Christopher Columbus, a Genoese captain in the service of the Crown of Castile, set out on his first voyage in August 1492 with the objective of reaching the East Indies by sailing west across the Atlantic Ocean. As is well known, instead of reaching Asia, Columbus stumbled upon the Caribbean islands of the Americas. Convinced nonetheless he had discovered the edges of Asia, Columbus set sail back to Spain on January 15, 1493, aboard the caravel Niña. According to the journal of his voyage, on February 14, Columbus was caught in a storm off the Azores islands. The resulting poor condition of his ship forced him to put in at Lisbon ( Portugal) on March 4, 1493. Columbus finally arrived at Palos de la Frontera in Spain eleven days later, on March 15, 1493.
How long did it take Christopher Columbus to get to the islands?
In the letter, Christopher Columbus does not describe the journey itself, saying only that he traveled thirty-three days and arrived at the islands of "the Indies" ( las Indias ), "all of which I took possession for our Highnesses, with proclaiming heralds and flying royal standards, and no one objecting".
Where is the letter of Columbus?
The published Latin versions of the letter are almost all titled "Letter of Columbus, on the islands of India beyond the Ganges recently discovered". The term "India beyond the Ganges" ( India extra Gangem) was the archaic term frequently used by earlier geographers (e.g., Ptolemy) to refer vaguely to Southeast Asia (roughly from Burma down to the Malay peninsula); the Indian subcontinent proper was referred to as "India within the Ganges" ( India intra Gangem ). Thus the islands of "India beyond the Ganges" claimed to have been reached would roughly correspond to modern Indonesia or thereabouts. The earlier printed Spanish edition bears no title, nor does the manuscript copy of the letter to the Catholic monarchs ( Libro Copiador ).
What was the rapid dissemination of Columbus's letter?
The rapid dissemination of Columbus's letter was enabled by the printing press, a new invention that had established itself only recently. Columbus's letter (particularly the Latin edition) forged the initial public perception of the newly discovered lands.
What was the purpose of the letter Columbus sent to the Spanish court?
The letter was instrumental in spreading the news throughout Europe about Columbus's voyage.
How many copies of the Columbus letter were published?
It is estimated that, on the whole, between 1493 and 1500, some 3,000 copies of the Col umbus letter were published, half of them in Italy, ...
What was the first letter written by Christopher Columbus?
Columbus's letter on the first voyage is the first known document announcing the results of the first voyage of Christopher Columbus that set out in 1492 and reached the Americas. The letter was ostensibly written by Columbus himself, on February 15, 1493, aboard the caravel Niña, while still at sea, on the return leg of his voyage. A post-script was added upon his arrival in Lisbon on March 4, 1493, and it was probably from there that Columbus dispatched two copies of his letter to the Spanish court.
What did Columbus find on his first voyage?
There had originally been promise of a reward for the first person to discover new land on the voyage, but Columbus claimed to have spotted it himself the night before without alerting anybody. Rodrigo de Triana is honoured with a statue in Seville now.
When was Christopher Columbus’ first voyage?
Christopher Columbus’ first voyage departed on August 3rd 1492. It was evening, and the three ships left Palos de la Frontera in modern day Andalusia. He returned to the same port seven months later, on March 15th 1493, with stories to tell and a wealth of experience under his belt.
Why did Christopher Columbus want to travel to Asia?
The long and short of it is, Christopher Columbus wanted to be the one to find a seaward route to Asia in order to allow for the continuation of trade, political and cultural negotiations and religious interactions between these two parts of the world.
What is the name of the island that Columbus named?
Columbus named this land San Salvador. This literally means ‘holy saviour’, and the land is located in what is now the Bahamas. The natives of the island called it Guanahani. During the rest of this particular voyage, Columbus and his crew went on to find and explore various places:
Where did Christopher Columbus travel?
Columbus kept trying. He travelled to Genoa, Venice and England but all to no avail. He eventually got an audience with King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella in Spain – they also weren’t sure about Christopher Columbus’ plans but in order to keep their options open they gave him an annual allowance. On top of this, they gave him a letter which ordered all towns and cities under their ruling domain to provide Columbus with food and lodging at no cost.
Who was the first explorer to discover America?
Christopher Columbus, the Italian explorer best known for discovering America, is an interesting character. This post looks at Christopher Columbus’ first voyage – why did he go, who went with him, where was he heading and what did he find? Read on if you want to know…
What triggered this brave first voyage?
Back in the 1400s and before, there was a physical connection between The West and The East. This was known as the Silk Road. It allowed for the safe land passage between Europe and Asia – China as well as south and east Asia, then known as the Indies.
