
What is Hofstede's contribution to the study of Culture?
It has inspired a number of other major cross-cultural studies of values, as well as research on other aspects of culture, such as social beliefs. In 1965 Hofstede founded the personnel research department of IBM Europe (which he managed until 1971).
Where did Hofstede study psychology?
In 1953, Hofstede graduated from Delft Technical University with an M.Sc. in Mechanical Engineering. After working in the industry for ten years, Hofstede entered part-time doctoral study at Groningen University in The Netherlands, and received his PhD in social psychology cum laude in 1967.
What did Hofstede do at IBM?
At IBM International, Hofstede started working as a management trainer and manager of personnel research, and founded and managed the Personnel Research Department. This was his transition from the field of engineering and into psychology.
What is the biography of Geert Hofstede?
about Geert Hofstede. Biography. Geert Hofstede was born in a peaceful country, but his teenage years saw the second World War rage across Europe. He started working as an engineer during turbulent years of rebuilding, and soon became a personnel manager. Fascinated by the human in the system, he did a PhD in organizational behaviour.
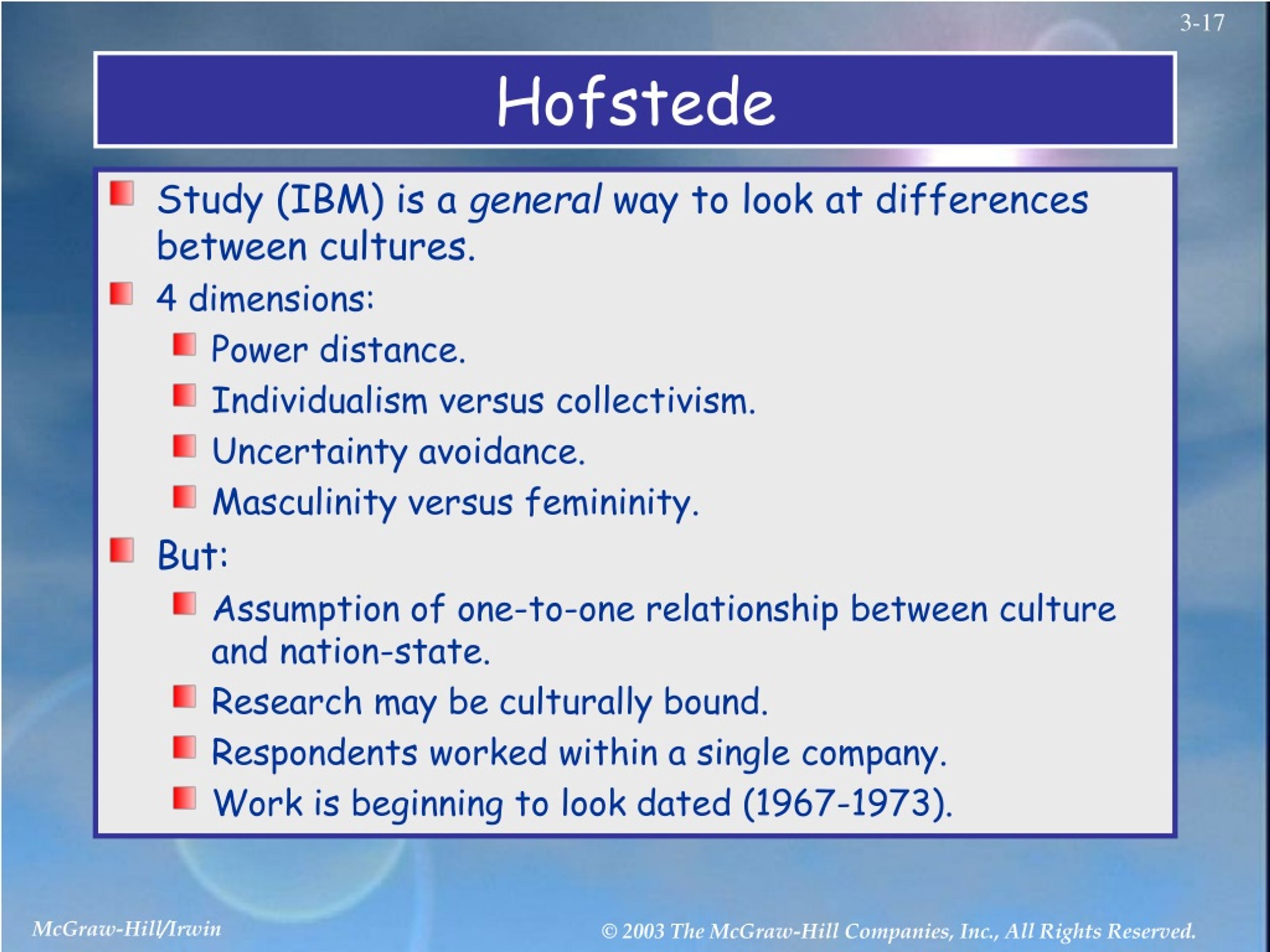
What is Hofstede's study?
Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory is a framework for cross-cultural communication, developed by Geert Hofstede. It shows the effects of a society's culture on the values of its members, and how these values relate to behavior, using a structure derived from factor analysis.
What did Hofstede's five dimensions model mean?
According to Hofstede, the five main dimensions are identity, power, gender, uncertainty, and time. You can think about cultural value dimensions on a scale or a continuum, where one aspect of the value lies on one side of the scale and the other extreme lies at the other end of the scale.
What are Hofstede's six cultural dimensions?
Geert Hofstede's 6 Cultural Dimensions are Power Distance Index (PDI), Individualism Vs Collectivism, Masculinity Vs Femininity, Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI), Long Vs Short Term Orientation, and Indulgence Vs Restraint.
Why is Hofstede Theory important?
Hofstede developed this cultural model primarily on the basis of differences in values and beliefs regarding work goals. Hofstede's framework is especially useful because it provides important information about differences between countries and how to manage such differences.
How did Hofstede create cultural dimensions?
Geert Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory (1980) examined people's values in the workplace and created differentiation along three dimensions: small/large power distance, strong/weak uncertainty avoidance, masculinity/femininity, and individualism/collectivism.
What are three of the dimensions Hofstede identified and studied check all that apply?
Geert Hofstede, in his pioneer study looking at differences in culture across modern nations, identified four dimensions of cultural values: individualism-collectivism, power distance, uncertainty avoidance, and masculinity-femininity.
What is the focus of Hofstede's power distance dimension?
Hofstede's power distance dimension focused on how a society deals with the fact that people are unequal in physical and intellectual capabilities.
What is Hofstede individualism?
Hofstede Individualism Traits. Hofstede: Individualism / Collectivism. This dimension focuses on the relationship between the individual and larger social groups. As mentioned earlier, cultures vary on the amount of emphasis they give on encouraging individuality / uniqueness or on conformity and interdependence.
Who is Geert Hofstede?
Geert Hofstede is perhaps the best known sociologist of culture and anthropologist in the context of applications for understanding international business. Many articles and research papers refer to his publications, with over 26,000 citations to his 2001 book Culture's Consequences: Comparing Values, Behaviors, Institutions and Organizations Across Nations (which is an updated version of his first publication ). The five dimensions model is widely used in many domains of human social life, and particularly in the field of business. Practical applications were developed almost immediately.
When was Hofstede's model developed?
Hofstede developed his original model as a result of using factor analysis to examine the results of a worldwide survey of employee values by IBM between 1967 and 1973. It has been refined since.
What dimension does Hofstede add?
In 2010, Hofstede added a sixth dimension, indulgence versus self-restraint . Hofstede's work established a major research tradition in cross-cultural psychology and has also been drawn upon by researchers and consultants in many fields relating to international business and communication.
When did John Dewey conduct a national values survey?
Between 1967 and 1973, he executed a large survey study regarding national values differences across the worldwide subsidiaries of this multinational corporation: he compared the answers of 117,000 IBM matched employees samples on the same attitude survey in different countries.
Which framework is generally accepted as the most comprehensive framework of national cultures values by those studying business culture?
Even though Hofstede's model is generally accepted as the most comprehensive framework of national cultures values by those studying business culture, its validity and its limitations have been extensively criticized.
What does a high degree in the IQ index mean?
Societies that score a high degree in this index opt for stiff codes of behavior, guidelines, laws, and generally rely on absolute truth, or the belief that one lone truth dictates everything and people know what it is. A lower degree in this index shows more acceptance of differing thoughts or ideas.
Who is Hofstede?
Hofstede was a researcher in the fields of organizational studies and more concretely organizational culture, also cultural economics and management. He was a well-known pioneer in his research of cross-cultural groups and organizations and played a major role in developing a systematic framework for assessing and differentiating national cultures and organizational cultures. His studies demonstrated that there are national and regional cultural groups that influence the behavior of societies and organizations.
What did Hofstede do at IBM?
In this role, he played an active role in the introduction and application of employee opinion surveys in over 70 national subsidiaries of IBM around the world. He traveled across Europe and the Middle East to interview people and conduct surveys regarding people's behavior in large organizations and how they collaborated. He collected large amounts of data, but due to the pressures of his daily job, was unable to conduct a significant amount of research. When he took a two-year sabbatical from IBM in 1971, he delved deeper into the data he had collected from his job, and discovered that there were significant differences between cultures in other organizations, but got the same ranking of answers by country. At the time, the results of the IBM's surveys, with over 100,000 questionnaires, were one of the largest cross-national databases in existence.
What is the Geert Hofstede Lecture?
In 2004, the Hanze University Groningen, the Netherlands established the Geert Hofstede Lecture, a bi-annual conference in the area of intercultural communication. In 2006, Maastricht University, the Netherlands inaugurated a Geert Hofstede Chair in cultural diversity.
Where did Hofstede go to school?
In 1953, Hofstede graduated from Delft Technical University with an MSc in Mechanical Engineering. After working in the industry for ten years, Hofstede entered part-time doctoral study at Groningen University in The Netherlands, and received his PhD in social psychology cum laude in 1967.
How many languages have Hofstede books been published in?
Hofstede's books have appeared in 23 languages. World Wide Web's citation indexes between 1981 and 2011 listed more than 9,000 articles in peer-reviewed journals citing one or more of Geert's publications. This makes him the currently most cited European social scientist.
What is Hofstede's knighthood?
Hofstede received many honorary awards, and in 2011 was made a Knight in the Order of the Netherlands Lion (Orde van de Nederlandse Leeuw).
What was Hofstede's thesis?
His thesis was titled "The Game of Budget Control". Upon his graduation from Delft in 1953, Hofstede joined the Dutch military, working as a technical officer in the Dutch army for two years. After leaving the military he worked in industry from 1955 to 1965, starting as a factory hand in Amsterdam.
Who is Geert Hofstede?
He started working as an engineer during turbulent years of rebuilding, and soon became a personnel manager. Fascinated by the human in the system, he did a PhD in organizational behaviour.
How many dimensions of culture did Geert's theory have?
the book appeared in 1980. The rest is history. The model of societal culture has undergone various major extensions since the first study. It now counts six dimensions instead ...
How many dimensions are there in Hofstede's model of national culture?
The Hofstede model of national culture consists of six dimensions. The cultural dimensions represent independent preferences for one state of affairs over another that distinguish countries (rather than individuals) from each other.
Who conducted the most comprehensive study of how values in the workplace are influenced by culture?
Professor Geert Hofstede conducted one of the most comprehensive studies of how values in the workplace are influenced by culture. He analysed a large database of employee value scores collected within IBM between 1967 and 1973.
What is the high side of individualism?
The high side of this dimension, called Individualism, can be defined as a preference for a loosely-knit social framework in which individuals are expected to take care of only themselves and their immediate families.
Where did Hofstede teach?
Taking a sabbatical from IBM, Hofstede taught at the IMD in Switzerland. It was there that he was allowed the time and academic engagement to analyze the IBM research. He found that nationality could account for the behavioral differences resultant in the survey.
Who is Geert Hofstede?
Posted on 10. May 2019 Leave a comment. If you looked at Geert Hofstede ‘s life, there was nothing particularly remarkable that might make you imagine he’d one day be at the forefront of cross-cultural research. The Dutch researcher called the Netherlands home. He lived and studied there, after which he entered the military.
What did the Dutch researcher do?
He lived and studied there, after which he entered the military. He became a management trainer at IBM, as well as the manager of staff research. It was in the latter role that he became entrenched in systematic research which would later hone in on the field of cross-cultural studies.

Power Distance Index
Individualism vs. Collectivism
- The individualism vs. collectivism dimension considers the degree to which societies are integrated into groups and their perceived obligations and dependence on groups. 1. Individualism indicates that there is a greater importance placed on attaining personal goals. A person’s self-image in this category is defined as “I.” 2. Collectivism indicates that there is a grea…
Uncertainty Avoidance Index
- The uncertainty avoidance index considers the extent to which uncertainty and ambiguity are tolerated. This dimension considers how unknown situations and unexpected events are dealt with. 1. A high uncertainty avoidance index indicates a low tolerance for uncertainty, ambiguity, and risk-taking. The unknown is minimized through strict rules, regulations, etc. 2. A low uncerta…
Masculinity vs. Femininity
- The masculinity vs. femininity dimension is also referred to as “tough vs. tender,” and considers the preference of society for achievement, attitude towards sexuality equality, behavior, etc. 1. Masculinity comes with the following characteristics: distinct gender roles, assertive, and concentrated on material achievements and wealth-building. 2. Femininity comes with the follo…
Long-Term Orientation vs. Short-Term Orientation
- The long-term orientation vs. short-term orientation dimension considers the extent to which society views its time horizon. 1. Long-term orientation shows focus on the future and involves delaying short-term success or gratification in order to achieve long-term success. Long-term orientation emphasizes persistence, perseverance, and long-term growth. 2. Short-term orientati…
Indulgence vs. Restraint
- The indulgence vs. restraint dimension considers the extent and tendency for a society to fulfill its desires. In other words, this dimension revolves around how societies can control their impulses and desires. 1. Indulgence indicates that a society allows relatively free gratification related to enjoying life and having fun. 2. Restraint indicates that a society suppresses gratification of nee…
Related Readings
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions Theory. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful: 1. Demographics 2. Emotional Intelligence 3. Interpersonal Skills 4. Supportive Leadership
Overview
Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory is a framework for cross-cultural communication, developed by Geert Hofstede. It shows the effects of a society's culture on the values of its members, and how these values relate to behavior, using a structure derived from factor analysis.
Hofstede developed his original model as a result of using factor analysis to e…
History
In 1965 Hofstede founded the personnel research department of IBM Europe (which he managed until 1971). Between 1967 and 1973, he executed a large survey study regarding national values differences across the worldwide subsidiaries of this multinational corporation: he compared the answers of 117,000 IBM matched employees samples on the same attitude survey in different countries. He first focused his research on the 40 largest countries, and then extended it to 50 c…
Dimensions of national cultures
• Power distance index (PDI): The power distance index is defined as "the extent to which the less powerful members of organizations and institutions (like the family) accept and expect that power is distributed unequally". In this dimension, inequality and power is perceived from the followers, or the lower strata. A higher degree of the Index indicates that hierarchy is clearly established and executed in society, without doubt or reason. A lower degree of the Index signifies that people q…
Applications of the model
Instead of the convergence phenomena experts expected with information technology proliferation (the "global village culture"), cultural differences are still significant today and diversity has tended to increase. So, in order to be able to have respectful cross-cultural relations, we have to be aware of these cultural differences.
With this model, Geert Hofstede shed light on these differences. The tool can be used to give a g…
Limitations of Hofstede's model
Even though Hofstede's model is generally accepted as the most comprehensive framework of national cultures values by those studying business culture, its validity and its limitations have been extensively criticized.
The most cited critique is McSweeney. Hofstede replied to that critique and McSweeney responded. Also Ailon deconstructed Hofstede's book Culture's Consequences by mirroring it ag…
See also
• Cross-cultural communication
• Cultural relativism
• GLOBE study on Global Leadership and Organizational Behaviour Effectiveness
• Intercultural communication
Further reading
• Culture, leadership, and organizations: the GLOBE study of 62 societies (1st ed.). SAGE Publications. 29 April 2004. ISBN 978-0-7619-2401-2., Read it
• Alvesson, M. & Deetz, S. (2006). Critical Theory and Postmodernism Approaches to Organizational Studies. In S. Clegg, C. Hardy, T. Lawrence, W. Nord (Eds.). The Sage Handbook of Organization Studies (2nd ed). London: Sage, 255–283.
External links
• Geert Hofstede's academic website
• The Hofstede Centre
Overview
Gerard Hendrik (Geert) Hofstede (2 October 1928 – 12 February 2020) was a Dutch social psychologist, IBM employee, and Professor Emeritus of Organizational Anthropology and International Management at Maastricht University in the Netherlands, well known for his pioneering research on cross-cultural groups and organizations.
Biography
Born to Gerrit and Evertine Geessine (Veenhoven) Hofstede, Geert Hofstede attended schools in The Hague and Apeldoorn, and received his high school diploma (Gymnasium Beta) in 1945. In 1953, Hofstede graduated from Delft Technical University with an MSc in Mechanical Engineering. After working in the industry for ten years, Hofstede entered part-time doctoral study at Groningen University in The Netherlands, and received his PhD in social psychology cum laude in 1967. His …
Work
Hofstede was a researcher in the fields of organizational studies and more concretely organizational culture, also cultural economics and management. He was a well-known pioneer in his research of cross-cultural groups and organizations and played a major role in developing a systematic framework for assessing and differentiating national cultures and organizational cultures. His studies demonstrated that there are national and regional cultural groups that influ…
Archives
The Archives of Geert Hofstede at the Library of the University of Groningen are opened to the public as of February 2020.
Publications
Hofstede authored and co-authored numerous publications in the field of social psychology and sociocultural anthropology.
• Hofstede, Geert (July 1978). "The Poverty of Management Control Philosophy". The Academy of Management Review. Academy of Management. 3 (3): 450–461. doi:10.2307/257536. JSTOR 257536.
External links
• Geert Hofstede's academic website
• Geert Hofstede Friends (group of International professionals continuing Geert's work (lead by Prof. Gert Jan Hofstede)[1]