
Lewis Howard Latimer
Lewis Howard Latimer was an American inventor and patent draftsman for the lightbulb and telephone.
See more
What invention did Lewis Latimer make?
On December 11, 1928, Lewis Howard Latimer died, leaving a remarkable legacy. His name will be forever associated with two of the most revolutionary inventions of all time: the incandescent electric light bulb and the telephone.
Why is Lewis Latimer's invention important?
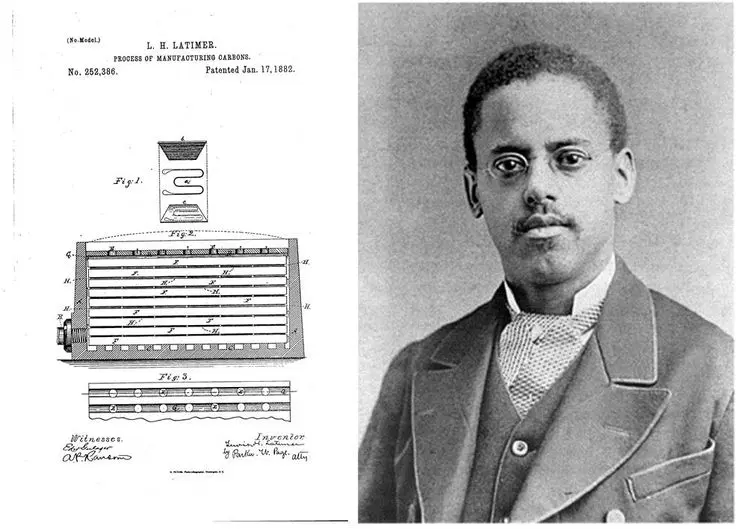
Around this time, Latimer created a way to make the carbon filament more durable by encasing it in cardboard and went on to patent the process for efficiently manufacturing the carbon filament in 1882. His invention made incandescent lighting practical and affordable and was also longer lasting than earlier filaments.
Did Lewis Latimer invent the elevator?
He also invented a safety elevator, a secure rack for hats, coats and umbrellas, a book supporter and an apparatus for cooling and disinfecting hospital rooms. Latimer's contribution of bringing sustainable electric light into homes and businesses cannot be overstated.
What did Lewis Latimer invent for kids?
Lewis Latimer helped develop the electric light bulb.
How did Lewis Latimer change society?
He played a critical role in the development of the telephone, significantly improved the production of carbon filament, and made important contributions to the commercialization of the incandescent light bulb. Outside his professional career, Latimer developed a passion for visual art, creative writing, and music.
What was one of Lewis Latimer's most important discovery?
Lewis Howard Latimer was an inventor and draftsman best known for his contributions to the patenting of the light bulb and the telephone.
Who invented the carbon filament?
Lewis Howard LatimerLewis Howard Latimer (September 4, 1848 – December 11, 1928) was an African-American inventor and patent draftsman. His inventions included an evaporative air conditioner, an improved process for manufacturing carbon filaments for light bulbs, and an improved toilet system for railroad cars.
Who invented the copper filament?
Lewis Latimer invented a method for producing a more durable carbon filament, making incandescent lighting practical and affordable for consumers. Latimer was born in Chelsea, Massachusetts, the son of former slaves.
Who invented the lightbulb before Edison?
Humphry DavyIn 1802, Humphry Davy invented the first electric light. He experimented with electricity and invented an electric battery. When he connected wires to his battery and a piece of carbon, the carbon glowed, producing light. His invention was known as the Electric Arc lamp.
How was the light bulb invented?
By January 1879, at his laboratory in Menlo Park, New Jersey, Edison had built his first high resistance, incandescent electric light. It worked by passing electricity through a thin platinum filament in the glass vacuum bulb, which delayed the filament from melting.
How did Lewis Howard Latimer make a difference?
Lewis Howard Latimer (September 4, 1848 – December 11, 1928) was an African-American inventor and patent draftsman. His inventions included an evaporative air conditioner, an improved process for manufacturing carbon filaments for light bulbs, and an improved toilet system for railroad cars.
What dates are important in Lewis Latimer's life?
Sep 4, 1848. Born. Lewis Latimer was born on September 4, 1848 in Massachusetts.Period: Sep 4, 1848 to Dec 11, 1928. Years of living and Decessed.Advertisements.Jan 1, 1864. Joined the U.S. Navy. ... Sep 20, 1873. Got married. ... Jan 1, 1874. Patents on Train Water. ... Jan 1, 1876. Executes Drawings. ... Jan 1, 1879. Invents Filiment.More items...
What are three interesting facts about Lewis Latimer?
Birthplace: Chelsea, Mass. Born in Chelsea, Mass., Latimer learned mechanical drawing while working for a Boston patent attorney. He later invented an electric lamp and a carbon filament for light bulbs (patented 1881, 1882). Latimer was the only African-American member of Thomas Edison's engineering laboratory.
Who was Lewis Latimer?
Lewis Howard Latimer (September 4, 1848 – December 11, 1928) was a black American inventor and patent draftsman. His inventions included an evaporative air conditioner, an improved process for manufacturing carbon filaments for light bulbs, and an improved toilet system for railroad cars. In 1884, he joined the Edison Electric Light Company ...
What was Lewis Latimer's job?
Lewis Howard Latimer joined the U.S. Navy at the age of 15 on September 16, 1863, and served as a Landsman on the USS Massasoit.
What did Lewis Howard Latimer do?
Lewis Howard Latimer joined the U.S. Navy at the age of 15 on September 16, 1863, and served as a Landsman on the USS Massasoit. After receiving an honorable discharge from the U.S. Navy on July 3, 1865, he gained employment as an office boy with a patent law firm, Crosby Halstead and Gould, with a $3.00 per week salary. He learned how to use a set square, ruler, and other drafting tools. Later, after his boss recognized his talent for sketching patent drawings, Latimer was promoted to the position of head draftsman earning $20.00 a week by 1872.
How much did Latimer make in 1872?
Later, after his boss recognized his talent for sketching patent drawings, Latimer was promoted to the position of head draftsman earning $20.00 a week by 1872 ($438.59 today).
What instruments did Latimer play?
Latimer played the violin and flute, painted portraits and wrote plays.
When did Latimer get his patent?
Latimer received a patent on January 17, 1882 for the "Process of Manufacturing Carbons", an improved method for the production of carbon filaments for lightbulbs. The Edison Electric Light Company in New York City hired Latimer in 1884 as a draftsman and an expert witness in patent litigation on electric lights.
Where is the Latimer Projects house?
His house is located near the Latimer Projects and is a historic house located at 34-41 137th Street in Flushing, Queens, New York City .
What did Latimer do?
Latimer taught himself mechanical drawing and drafting by observing drafters at the firm. Recognizing his talent and promise, the partners promoted him to drafter and, eventually, head drafter.
What was Latimer's job?
Latimer was in charge of setting up an incandescent lamp department for the Maxim-Weston Electric Light Company in London. As part of this role, he supervised the production of his own invention of carbon filaments. Yet it was in London that Latimer suffered some of the greatest discrimination he faced during his career because English businessmen there were not used—or receptive—to being directed by a Black man. Of the experience, Latimer wrote in his diary:
What was Lewis Latimer's most important invention?
11, 1928) is considered one of the most important Black inventors for the number of inventions he produced and patents he secured, but also for the importance of his best-known discovery: a longer-lasting filament for the electric light. He also helped Alexander Graham Bell obtain the patent for the first telephone.
Why did Latimer suffer discrimination?
Yet it was in London that Latimer suffered some of the greatest discrimination he faced during his career because English businessmen there were not used—or receptive—to being directed by a Black man. Of the experience, Latimer wrote in his diary: "In London, I was in hot water from the day I came until I returned.".
Why did Lewis Latimer lie about his age?
Then, In 1864, at age 15, Latimer lied about his age in order to enlist in the U.S. Navy during the Civil War. Latimer was assigned to the gunboat USS Massasoit and received an honorable discharge on July 3, 1865.
Why did George Latimer go underground?
Supreme Court ruled that Scott, an enslaved man, couldn't sue for his freedom. Possibly fearing a return to enslavement, Latimer went underground. It was a great hardship for the rest of the Latimer family.
When did Latimer die?
Latimer died on Dec. 11, 1928, in the Flushing neighborhood of Queens, New York. His wife Mary had died four years earlier.
Who was Lewis Latimer?
Lewis H. Latimer was born in Chelsea, Massachusetts in 1848. Along with Granville T. Woods, Latimer was one of the first major African American inventors. He first worked as an assistant to Alexander Graham Bell.
Why was Latimer important to Thomas Edison?
Latimer made his most important scientific contributions here by improving the light bulb that was invented by Edison.
What filament did Edison use for his light bulb?
Edison's light bulb used a carbonized bamboo filament, which unfortunately burnt out rather quickly. Latimer created a way to make the carbon filament more durable by encasing it in cardboard. Latimer went on to patent the process for efficiently manufacturing the carbon filament in 1882.
What did Latimer do?
Latimer worked to support his family from an early age. In 1864, before he had even turned 16, he enlisted in the Navy (probably having lied about his age to gain admission), and was honorably discharged after two years of service. On his return, he sought and received employment at the Crosby and Gould patent law office for $3 a week. Here he learnt mechanical drawing and drafting, although his official duties were those of an office boy. His employer soon realized his skills in drawing and drafting, and promoted him to head draftsman, where he earned a much better wage. By 1872 his salary had increased to $20 per week. In 1873, he married Mary Wilson Lewis, and the couple had two daughters named Emma Jeanette and Louise Rebecca.
Why was Latimer inducted into the Hall of Fame?
Latimer was inducted into “the National Inventors Hall of Fame” for his work on bulb filaments. He was actively involved in the Unitarian Church and supported Civil War veterans. Apart from his work, he took an active interest in music and could play the flute.
Who was the only African American to work for the Edison Company?
In 1884, he was hired by “The Edison Electric Light Company” in New York City as an expert draftsman. In addition, was also a key witness in patent litigation that Edison was facing. He was also the only African American member of the twenty four engineers in the engineering division of the Edison Company. In 1890, Latimer published a book entitled “Incandescent Electric Lighting” and continued to work with the company even after it became General Electric in 1892. In 1911, he began working as a patent consultant for law firms.
When did Lewis Latimer die?
He also painted portraits and wrote poetry and music for friends and family. Lewis Latimer died on December 11, 1928 and left behind a legacy of achievement and leadership that much of the world owes thanks. Listen to the Great Black Heroes Podcast About Lewis Latimer. Custom Search.
What invention did Latimer make?
Latimer continued to display his creative talents over then next several years. In 1894 he created a safety elevator, a vast improvement on existing elevators. He next received a patent for Locking Racks for Hats, Coats, and Umbrellas. The device was used in restaurants, hotels and office buildings, holding items securely and allowing owners of items to keep the from getting misplaced or accidentally taken by others. He next created a improved version of a Book Supporter, used to keep books neatly arranged on shelves.
What did Lewis do in the Civil War?
Lewis served in the United States Navy for the Union during the Civil War, assigned to the U.S.S. Massasoit gunboat and received an honorable discharge on July 3, 1865. After his discharge he sought employment throughout Boston, Massachusetts and eventually gained a position as an office boy with a patent law firm, Crosby and Gould earning $3.00 each week. After observing Latimer’s ability to sketch patent drawings, he was eventually promoted to the position of head draftsman earning $20.00 a week. In addition to his newfound success, Latimer found additional happiness when he married Mary Wilson in November of 1873.
What did Latimer do to make the bulb last longer?
Latimer set out to make a longer lasting bulb. Latimer devised a way of encasing the filament within an cardboard envelope which prevented the carbon from breaking and thereby provided a much longer life to the bulb and hence made the bulbs less expensive and more efficient.
How much did Latimer make a week?
After observing Latimer’s ability to sketch patent drawings, he was eventually promoted to the position of head draftsman earning $20.00 a week. In addition to his newfound success, Latimer found additional happiness when he married Mary Wilson in November of 1873.
When was the Latimer patent filed?
Working late into the night, Latimer worked hard to finish the patent application, which was submitted on February 14, 1876, just hours before another application was submitted by Elisha Gray for a similar device.
Who was Thomas Edison's chief draftsman?
In 1890, Latimer, having been hired by Thomas Edison, began working in the legal department of Edison Electric Light Company, serving as the chief draftsman and patent expert. In this capacity he drafted drawings and documents related to Edison patents, inspected plants in search of infringers of Edison’s patents, conducted patent searches and testified in court proceeding on Edison’s behalf. Later that year wrote the worlds most thorough book on electric lighting, “Incandescent Electric Lighting: A Practical Description of the Edison System.” Lewis was named one of the charter members of the Edison pioneer, a distinguished group of people deemed responsible for creating the electrical industry. The Edison Electric Lighting would eventually evolve into what is now known as the General Electric Company.
What were Latimer's inventions?
His other patented inventions included the first toilet for railroad cars and a forerunner of the air conditioner ( here ).
Who stole the lightbulb?
The post ( here ) reads: “This is your daily reminder that Thomas Edison did NOT invent the lightbulb, he stole it from a black man named Lewis Latimer.”. U.S. President Joe Biden echoed the message at a community meeting in Kenosha, Wisconsin on the campaign trail on Sept. 3, 2020, when he said: “A Black man invented the lightbulb not ...
Who invented the lightbulb?
Although Edison is commonly credited with inventing the lightbulb, though that is still regularly challenged, as seen here , here , here and here .
Did Latimer invent the lightbulb?
Latimer did not invent the lightbulb but did provide key improvements to the invention. This article was produced by the Reuters Fact Check team. Read more about our work to fact-check social media posts here . Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.
Who was Lewis Latimer's employer?
The early years of the electric industry were fiercely competitive. The chief rival of Latimer's employer was Thomas Alva Edison. In 1884, this genius with electricity invited Latimer to work for him. By then, Lewis Latimer was a highly skilled electrical engineer. He developed a carbon filament that made Edison's bulb commercial viable by improving the quality of light it shed and extending its life from minutes to hours.
What did Lewis Latimer do at the end of the war?
At the close of the war [Lewis Latimer] returned to Boston and was discharged [from the Navy]…To get to work he went from place to place with no results. Finally a colored girl who took care of the office of some lady copyists (there were no typewriters then) was asked to recommend a colored boy as office boy, one "with a taste for drawing." She told [him] and [he] applied and got the place at three dollars a week. He believed then that whatever a man knew he had put in a book, so when he saw the man making drawings he watched to find out what books he used, then he went to a secondhand bookstore and got a book on drawing and soon had a set of drawing instruments. He then looked over the draughtsman's shoulder to see how he used his instruments, and practiced with them at home until he felt thoroughly master of them, then one day he asked the draughtsman to let him do some drawing for him. The man laughed at him but finally consented to look at what he could do on another piece of paper and to his surprise found that Lewis was a real draughtsman, so he let him do some of his work from time to time and one day the boss saw him at work and was so pleased that he let him work every day and gradually raised his wages so that from three dollars when he went to work he rose in eleven years to twenty dollars a week. The regular draughtsman got twenty-five, but he had left and Lewis gave the same work for five dollars a week less.
How did Lewis Latimer respond to prejudice?
All of his life, Lewis Latimer responded to prejudice by redoubling his efforts to improve himself. He was determined to become the kind of learned and cultured man whom whites could not dismiss. He painted, played the flute, wrote poetry and plays. He helped establish a Unitarian church in his predominantly white neighborhood. Largely self-educated himself, he taught technical drawing, mechanical engineering, and English to new immigrants. Having faced — and overcome — so much racial prejudice himself, he was a strong supporter of civil rights.
How did George Latimer get his freedom?
Massachusetts abolitionists immediately began organizing to free him. After a month of meetings, protests, petitions (even a newspaper, the Latimer Journal and North Star, was published on his behalf), they succeeded. George Latimer gained his freedom. All the controversy seems to have persuaded Rebecca Latimer's master not to pursue her. The couple settled into Boston's vibrant abolitionist community.
What did Lewis do at the end of the Civil War?
At the end of the war, he came home to Boston and got a job as an office boy at a firm that handled patent applications.
What did Lewis do to help the draftsman?
He bought a book on drafting, assembled a set of tools, and taught himself mechanical drawing. After learning to use T squares, triangles, and compasses, he was allowed to assist the draftsman. When the man left, Lewis was hired to take his place.
What happened to Young Lewis?
Supreme Court's Dred Scott decision cast a threatening cloud over the family. Because George Latimer had no documents to prove that he had been freed, he was in danger of being returned to slavery. Fearing for his own and his family's safety, he disappeared, leaving his wife and children in desperate financial straits.
What was Latimer's improvement?
Latimer's improvements. Around the same time Edison was experimenting with his bulb -- using carbonized filaments of bay wood, cedar, bamboo and other fibers -- so was Latimer.
Who invented the light bulb?
Latimer created a light bulb with a more durable filament made of carbon. He sold the patent to the US Electric Co. in 1881, and a year later patented a process for efficiently manufacturing the carbon filament. He even wrote a book in 1890 on electric lighting, the first of its kind.
Did Black people invent the light bulb?
No, a Black man didn't invent the light bulb. But Lewis Latimer made it better - CNN

Overview
Lewis Howard Latimer (September 4, 1848 – December 11, 1928) was an inventor and patent draftsman. His inventions included an evaporative air conditioner, an improved process for manufacturing carbon filaments for light bulbs, and an improved toilet system for railroad cars. In 1884, he joined the Edison Electric Light Company where he worked as a draftsman and wrote the …
Early life and family
Lewis Howard Latimer was born in Chelsea, Massachusetts, on September 4, 1848, the youngest of the four children of Rebecca Latimer (1823–1910) and George Latimer (1818–1897). Before Lewis was born, his mother and father escaped from slavery in Virginia and fled to Chelsea, Massachusetts on October 4, 1842. The day they arrived in Boston, George was recognized by a colleague of his former slave owner and was arrested a few days later, on October 20, 1842. Ge…
Career
In 1874, Latimer co-patented (with Charles M. Brown) an improved toilet system for railroad cars called the Water Closet for Railroad Cars (U.S. Patent 147,363).
In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell employed Latimer, then a draftsman at Bell's patent law firm, to draft the necessary drawings required to receive a patent for Bell's telephone.
In 1879, he moved to Bridgeport, Connecticut, and was hired as assistant manager and draftsma…
Death and legacy
For 25 years, from 1903 until his death in 1928, Latimer lived with his family in a home on Holly Avenue in what is known now as East Flushing section of Queens, New York. Latimer died on December 11, 1928, at the age of 80. Approximately sixty years after his death, his home was moved from Holly Avenue to 137th Street in Flushing, Queens, which is about 1.4 miles northwest of its original location.
See also
• The Current War
External links
• Lewis Latimer at the IEEE
• Lewis Howard Latimer: Inventor, Engineer (Mechanical and Electrical)
• Bibliography about Latimer and scans of pages from his book
• Lewis Latimer: Renaissance Man by Luvenia George for the Smithsonian Institution's Lemelson Center for the Study of Invention and Innovation
Early Life
Early Career
- Lewis Latimer worked to help support his mother and siblings. Then, In 1864, at age 15, Latimer lied about his age in order to enlist in the U.S. Navy during the Civil War. Latimer was assigned to the gunboat USS Massasoitand received an honorable discharge on July 3, 1865. He returned to Boston and took a position as an office assistant with the p...
The Telephone
- In 1874, while at the firm, Latimer co-invented an improvement to the bathroom compartment of trains. Two years later, he was sought out as a drafter by an instructor of children who were hard of hearing; the man wanted drawings for a patent application on a device he had created. The instructor was Alexander Graham Bell, and the device was the telephone. Working late into the e…
Latimer and Maxim
- In 1880, after relocating to Bridgeport, Connecticut, Latimer was hired as assistant manager and drafter for the U.S. Electric Lighting Co., which was owned by Hiram Maxim. Maxim was the chief competitor of Edison, who had invented the electric light. Edison’s light consisted of a nearly airless glass bulb surrounding a carbon wire filament, typically made from bamboo, paper, or thr…
Collaboration with Edison
- Latimer started working for Edisonin 1884 and became involved in Edison's infringement lawsuits. He worked in the legal department of the Edison Electric Light Co. as the chief drafter and patent specialist. He drafted sketches and documents related to Edison patents, looked over plants in search of patent infringements, carried out patent searches, and testified in court on Edison’s be…
Later Innovations
- In subsequent years, Latimer continued to innovate. In 1894, he created a safety elevator, a vast improvement on existing elevators. Then he obtained a patent for “Locking Racks for Hats, Coats, and Umbrellas” that was used in restaurants, resorts, and office buildings. He also developed a method for making rooms more hygienic and climate-controlled, named an “Apparatus for Cooli…
Legacy
- Despite racism and discrimination and with unequal access to education and opportunity, Latimer played a major role in the development of two products that greatly impacted the lives of Americans: the light bulb and the telephone. The fact that he was a Black American born in the 19th century made his many successes even more impressive. Upon his death, the Edison Pione…
Sources
- Black Pioneers of Science and Invention. Paw Prints, 2008.
- "Lewis Latimer." Greatblackheroes.com.
- "Lewis Howard Latimer Biography." Biography.com.
- "Lewis Latimer." Famousinventors.org.