In 1944, two Canadians, Oswald Avery
Oswald Avery
Oswald Theodore Avery Jr. was a Canadian-American physician and medical researcher. The major part of his career was spent at the Rockefeller University Hospital in New York City. Avery was one of the first molecular biologists and a pioneer in immunochemistry, but he is best kno…
Colin Munro MacLeod
Colin Munro MacLeod was a Canadian-American geneticist. He was one of a trio of scientists who discovered that deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA is responsible for the transformation of the physical characteristics of bacteria, which subsequently led to its identification as the molecule responsible f…
Maclyn McCarty
Maclyn McCarty was an American geneticist. Maclyn McCarty, who devoted his life as a physician-scientist to studying infectious disease organisms, was best known for his part in the monumental discovery that DNA, rather than protein, constituted the chemical nature of a gene. Uncovering the molecular secret of the gene in question — that for the capsular polysaccharide of pneumococcal bacteria — led the …
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule composed of two chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. DNA and ribonucleic acid are nucleic aci…
What did Avery MacLeod and McCarty discover?
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty discovered that DNA was responsible for the genetic exchange of information. Their studies identified that DNA caused the transforming principle to transfer heredity.
What did Oswald Avery discover about DNA?
Oswald Avery: the professor, DNA, and the Nobel Prize that eluded him In 1944, two Canadians, Oswald Avery and Colin MacLeod, and an American, MacLyn McCarty, published a paper in The Journal of Experimental Medicine that demonstrated genes to be the chemical, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
What did Avery and his collaborators do?
Avery and his collaborators Colin MacLeod and Maclyn McCarty at Rockefeller University (then Rockefeller Institute) in New York wanted to elucidate the chemical nature of the transforming substance.
What is the Avery-MacLeod-McCarty experiment?
Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment. The Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment was an experimental demonstration, reported in 1944 by Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty, that DNA is the substance that causes bacterial transformation, in an era when it had been widely believed that it was proteins that served the function ...
See more

What did Maclyn McCarty discover?
Maclyn McCarty, (born June 9, 1911, South Bend, Indiana, U.S.—died January 2, 2005, New York, New York), American biologist who, with Oswald Avery and Colin M. MacLeod, provided the first experimental evidence that the genetic material of living cells is composed of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
What did Avery and his team discover?
Seventy years ago, Oswald Avery and his colleagues from the Rockefeller Institute published the first evidence that genes are made of DNA. Their discovery was received with a mixture of enthusiasm, suspicion and perplexity.
What did Oswald Avery's experiment show?
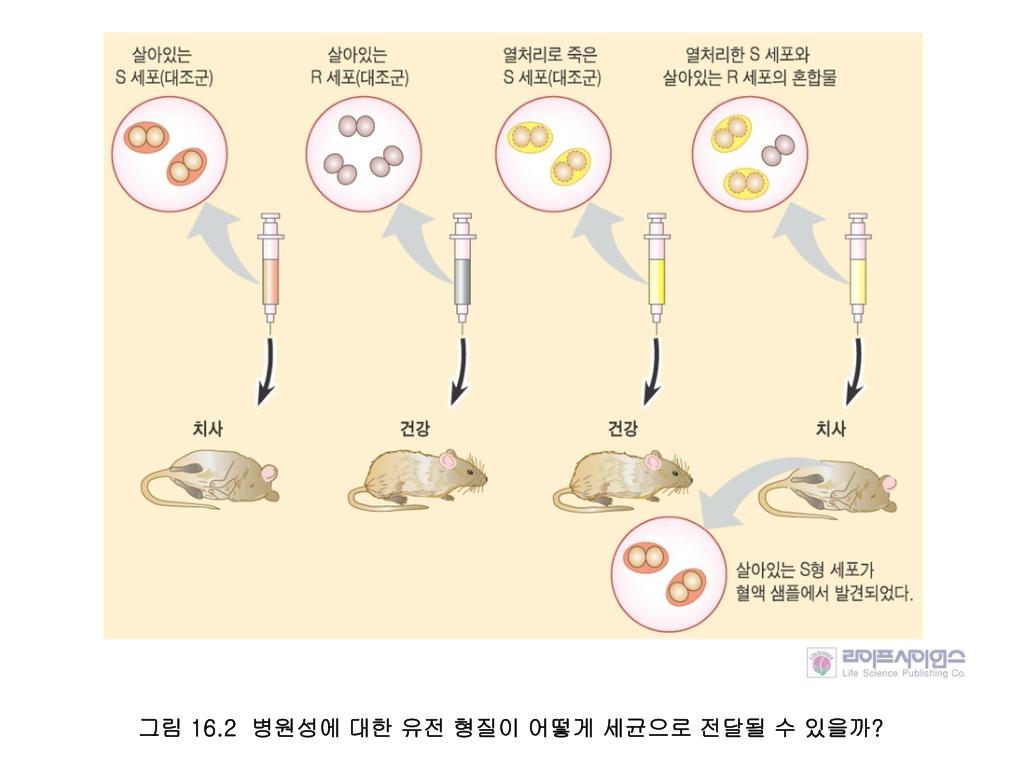
In a very simple experiment, Oswald Avery's group showed that DNA was the "transforming principle." When isolated from one strain of bacteria, DNA was able to transform another strain and confer characteristics onto that second strain.
What did these people discover about DNA Avery and MacLeod?
In 1944, Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty published their discovery that the transforming principle was DNA in "Studies on the Chemical Nature of the Substance Inducing Transformation of Pneumococcal Types," in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Who discovered that DNA was genetic material?
Friedrich MiescherWho first identified DNA? Although James Watson and Francis Crick determined the double-helical structure of DNA, DNA itself was identified nearly 90 years earlier by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher.
Who discovered DNA?
Friedrich MiescherMany people believe that American biologist James Watson and English physicist Francis Crick discovered DNA in the 1950s. In reality, this is not the case. Rather, DNA was first identified in the late 1860s by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher.
What did the Avery MacLeod and McCarty experiment prove?
Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty showed that DNA (not proteins) can transform the properties of cells, clarifying the chemical nature of genes. Avery, MacLeod and McCarty identified DNA as the "transforming principle" while studying Streptococcus pneumoniae, bacteria that can cause pneumonia.
What did Oswald Avery discover about DNA?
His research career culminated in 1944, when, with McCarty and MacLeod, Avery published his seminal paper proving that the "transforming principle," or hereditary material, was DNA and not protein as most scientists had assumed.
What was the purpose of the experiments of Avery MacLeod and McCarty quizlet?
What discovery did Avery, Macleod & McCarty's experiment lead to? They discovered that DNA was a much more likely carrier of genetic information than proteins, which was what was previously believed.
How was DNA first discovered?
How Was DNA Discovered? DNA was discovered in 1869 by Swiss researcher Friedrich Miescher, who was originally trying to study the composition of lymphoid cells (white blood cells). Instead, he isolated a new molecule he called nuclein (DNA with associated proteins) from a cell nucleus.
How did Avery Macleod prove that DNA was the genetic material?
Avery and McCarty observed that proteases - enzymes that degrade proteins - did not destroy the transforming principle. Neither did lipases - enzymes that digest lipids. They found that the transforming substance was rich in nucleic acids, but Ribonuclease, which digests RNA, did not inactivate the substance.
Who discovered the base pairing rule?
Erwin ChargaffErwin Chargaff found that in DNA, the ratios of adenine (A) to thymine (T) and guanine (G) to cytosine (C) are equal.
What did Frederick Griffith and Oswald Avery discover?
Frederick Griffith and Oswald Avery were key researchers in the discovery of DNA. Griffith was a British medical officer and geneticist. In 1928, in what is today known as Griffith's experiment, he discovered what he called a "transforming principle" that caused inheritance.
What happened after Avery and his team discovered the transforming factor?
Avery and his team concluded that DNA was the transforming factor. These conclusions contributed to DNA by discovering that the nucleic acid DNA stores and transmits genetic information from one generation of bacteria to the next.
Why is Avery's discovery important?
The work which began with Avery's identification of DNA as the "transforming principle" thus led to research that overturned the old conception of DNA as a repetitive and simple molecule, confirmed DNA's role in genetic transmission, and, with James Watson and Francis Crick's 1953 paper, elucidated its structure with ...
Where did Oswald Avery make his discovery?
Rockefeller InstituteRockefeller Institute At the institute, Cole, Avery and Alphonse Dochez developed the first effective immune serum against a strain of pneumococcus, a bacterium causing pneumonia. The serum was produced from the blood of infected horses.
What did the Avery experiment involve?
Oswald Avery's studies identified DNA as the transforming principle to transfer genetic information. Using Griffith's studies on Streptococcus pneu...
Who was Oswald Avery?
Oswald Avery was an American bacteriologist responsible for identifying DNA as the substance that carries genetic information. His studies on Strep...
What did Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty discover?
Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty discovered that DNA was responsible for the genetic exchange of information. Their studies identified that DNA caused t...
What is the transforming principle?
In 1944, Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty published their discovery that the transforming principle was DNA in "Studies on the Chemical Nature of the Substance Inducing Transformation of Pneumococcal Types, " in the Journal of Experimental Medicine. Although their findings were clearly revolutionary, their conclusions in this paper were cautious, and they presented several interpretations of their results. The phenomenon of transformation, Avery wrote, "has been interpreted from a genetic point of view. The inducing substance has been likened to a gene, and the capsular antigen which is produced in response to it has been regarded as a gene product." Yet they also gave another interpretation, that there might be an "analogy between the activity of the transforming agent and that of a virus." However, they concluded that, "the transformation described represents a change that is chemically induced and specifically directed by a known chemical compound. If the results of the present study on the chemical nature of the transforming principle are confirmed, then nucleic acids must be regarded as possessing biological specificity." Their findings were accepted almost immediately by some, but for several years they would be the source of considerable debate among genetic researchers.
What did Avery and McCarty do in 1940?
Avery and McCarty focused first on purifying the transforming substance. Using refined versions of Colin M. MacLeod's preparation techniques, Avery and McCarty isolated biologically active "transforming principle" from samples of pneumococci. After jump-starting the research, Avery was increasingly preoccupied with the step-by-step purification of the transforming agent and its identification. Initially, transformation had been a tentative and delicate phenomenon that was difficult to consistently recreate. Avery later told Rollin Hotchkiss, "Many are the times we were ready to throw the whole thing out the window!" Eventually, Avery and McCarty were able to take a culture of pneumococci of an R form that had been attenuated from an S of Type II over the course of thirty generations, and add to it to the highly purified deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extracted from an S of Type III. This process resulted, by the next generation, in large and fully developed colonies of S Type III, which remained stable through several generations. After achieving reliable and long-lasting transformation, Avery turned to prove that it was caused by DNA alone, despite the prevailing conviction of most geneticists, and even his own earlier belief, that DNA was a simple molecule and that genes must be composed of protein, a seemingly more complex substance.
When was the Avery study published?
Although the paper describing their extraordinary findings was not submitted until December of 1943, and published in the spring of 1944, Avery, McCarty, and MacLeod had accumulated all the basic experimental information and presented it to the Rockefeller Institute's Board of Scientific Directors by early April 1943. Avery anticipated significant skepticism of their claim of genetic specificity for DNA, and was weary of a repeat of the turmoil caused by his work with Alphonse Dochez on antiblastic immunity several decades earlier. Therefore he submitted the manuscript to several months of review and scrutiny by associates at the Hospital. What is more, despite Avery's confidence in their purification technique, he included in the final paper several cautionary statements that acknowledged the possibility that "the biological activity of the substance described is not an inherent property of the nucleic acid, but is due to minute amounts of some other substance absorbed to it or so intimately associated with it as to escape detection."

Overview
The Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment was an experimental demonstration, reported in 1944 by Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty, that DNA is the substance that causes bacterial transformation, in an era when it had been widely believed that it was proteins that served the function of carrying genetic information (with the very word protein itself coined to indicate a belief that it…
Background
With the development of serological typing, medical researchers were able to sort bacteria into different strains, or types. When a person or test animal (e.g., a mouse) is inoculated with a particular type, an immune response ensues, generating antibodies that react specifically with antigens on the bacteria. Blood serum containing the antibodies can then be extracted and applied to cultured bacteria. The antibodies will react with other bacteria of the same type as the origina…
Experimental work
Pneumococcus is characterized by smooth colonies which have a polysaccharide capsule that induces antibody formation; the different types are classified according to their immunological specificity.
The purification procedure Avery undertook consisted of first killing the bacteria with heat and extracting the saline-soluble components. Next, the protein was pr…
Reception and legacy
The experimental findings of the Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment were quickly confirmed, and extended to other hereditary characteristics besides polysaccharide capsules. However, there was considerable reluctance to accept the conclusion that DNA was the genetic material. According to Phoebus Levene's influential "tetranucleotide hypothesis", DNA consisted of repeating units of the four nucleotide bases and had little biological specificity. DNA was therefo…
Notes
1. ^ Avery, Oswald T.; Colin M. MacLeod; Maclyn McCarty (1944-02-01). "Studies on the Chemical Nature of the Substance Inducing Transformation of Pneumococcal Types: Induction of Transformation by a Deoxyribonucleic Acid Fraction Isolated from Pneumococcus Type III". Journal of Experimental Medicine. 79 (2): 137–158. doi:10.1084/jem.79.2.137. PMC 2135445. PMID 19871359.
Further reading
• Lederberg J (February 1994). "The transformation of genetics by DNA: an anniversary celebration of Avery, MacLeod and McCarty (1944)". Genetics. 136 (2): 423–6. doi:10.1093/genetics/136.2.423. PMC 1205797. PMID 8150273.
• McCarty, Maclyn (1986). The transforming principle: discovering that genes are made of DNA. New York: Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-30450-3.
External links
• Profiles in Science: The Oswald T. Avery Collection