What are some examples of osmosis in real life?
The real-life examples of osmosis are:
- Feeling thirsty after having salty food.
- Dialysis of kidney in the excretory system.
- Swelling of resins and other seeds when they are soaked in water.
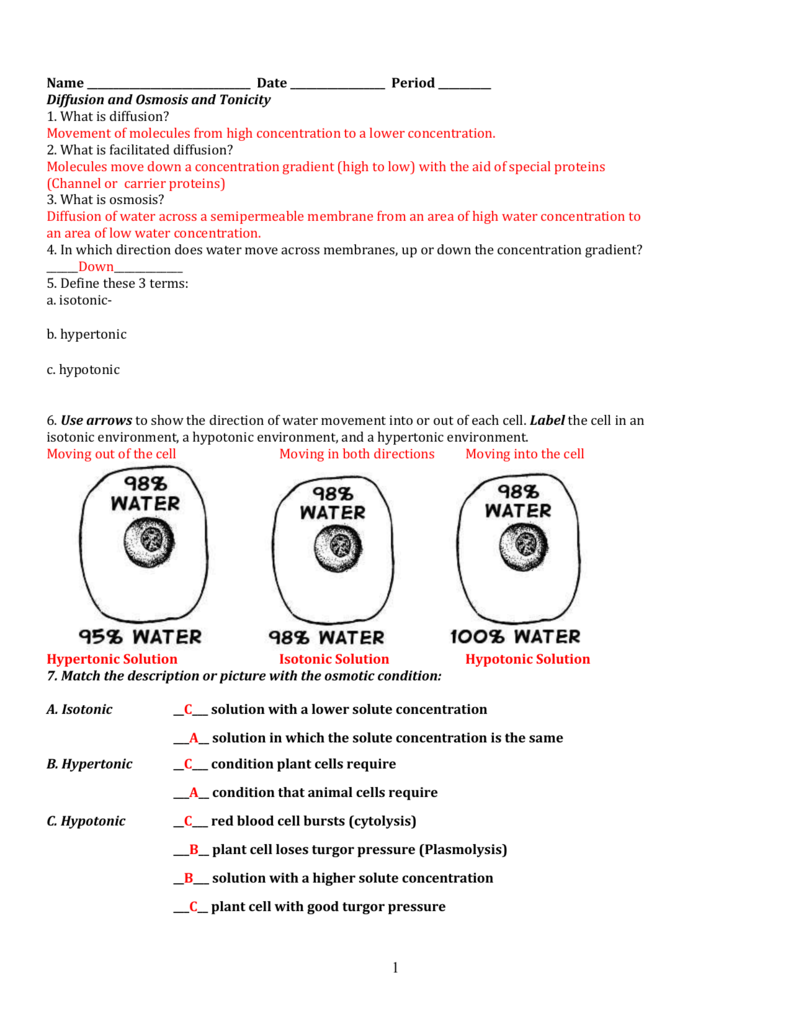
- Movement of salt-water in the animal cell across our cell membrane.
- Movement of water and minerals from root nodules to various parts of plants.
What is the net movement in diffusion and osmosis?
The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from a region where water is highly concentrated to a region where its concentration is lower is known as osmosis. Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion, the diffusion of water. In osmosis water always moves by diffusion across a selectively permeable membrane from a hypotonic
What is an example of osmosis in everyday life?
13 Best Examples of Osmosis In Everyday Life
- Water Purification
- Contact Lens-Induced Dry Eye (CLIDE)
- Pathogenic Bacteria Interfere With Intestinal Cells
- Digested Food Absorbed In Small and Large Intestines
- Food Preservation
- Sugar On Strawberries
- Gargling With Saltwater Provide Relief From Sore Throat
- Fish Absorb Water Through Their Skin and Gills
- Red Blood Cells Placed Into Freshwater
- Salt on Slugs
What happens to cells during osmosis?
Types of Solutions
- Isotonic. An isotonic solution has the same concentration of solutes both inside and outside the cell. ...
- Hypotonic. In a hypotonic solution, there is a higher concentration of solutes inside the cell than outside the cell.
- Hypertonic. A hypertonic solution is the opposite of a hypotonic solution; there is more solute outside the cell than inside it.
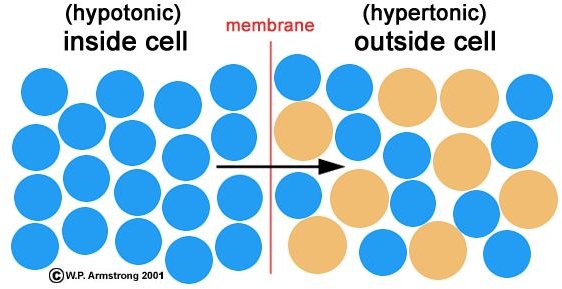
What is the net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to
Formally, osmosis is the net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This may sound odd at first, since we usually talk about the diffusion of solutes that are dissolved in water, not about the movement of water itself.
What happens when more solute water is in a membrane?
Regardless of the exact mechanisms involved, the key point is that the more solute water contains, the less apt it will be to move across a membrane into an adjacent compartment. This results in the net flow of water from regions of lower solute concentration to regions of higher solute concentration.
What is the difference between tonicity and osmolarity?
Tonicity is a bit different from osmolarity because it takes into account both relative solute concentrations and the cell membrane’s permeability to those solutes. Three terms—hyerptonic, hypotonic, and isotonic—are used to describe whether a solution will cause water to move into or out of a cell:
What happens when a cell is placed in a hypotonic environment?
When a cell is placed in a hypotonic environment, water will enter the cell, and the cell will swell. Diagram of red blood cells in hypertonic solution (shriveled), isotonic solution (normal), and hypotonic solution (puffed up and bursting). Image credit: Mariana Ruiz Villareal.
What is the ability of an extracellular solution to make water move into or out of a cell by os
Tonicity. In healthcare settings and biology labs, it’s often helpful to think about how solutions will affect water movement into and out of cells. The ability of an extracellular solution to make water move into or out of a cell by osmosis is known as its tonicity.
Why do molecules move in diffusion?
In diffusion, molecules move from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration—not because they’re aware of their surroundings, but simply as a result of probabilities. When a substance is in gas or liquid form, its molecules will be in constant, random motion, bouncing or sliding around one another.
Can a molecule move from compartment A to compartment B?
If there are lots of mole cules of a substance in compar tment A and no molecules of that substance in compartment B, it’s very unlikely —impossible, actually—that a molecule will randomly move from B to A. On the other hand, it’s extremely likely that a molecule will move from A to B.
How do water molecules travel from A to B?
They are both separated by a cell membrane. Water (solvent) molecules travel from A across the cell membrane / semi permeable membrane to B until the concentrations of A and B become equal. Answer link.
What is the membrane that allows water to pass through?
A membrane with less cholesterol will have a greater permeability for water. Water can also pass through the membrane through channel proteins called aquaporins (AQP). Here is a video which discusses the process of facilitated diffusion. YouTube. Noel Pauller. 4.54K subscribers. Subscribe.
Why can small molecules pass through the membrane?
Small molecules such as water and carbon dioxide can pass directly through the membrane because of they are neutral and so small. The movement of water through the membrane is referred to as osmosis.
What is the process of a solvent moving from a low concentration to a higher concentration?
Osmosis is the process in which a solvent moves from a solution of low concentration to a solution of higher concentration . A gradient is followed for this movement and once the concentration of both the solutions (on either sides of the membrane) becomes equal the solvents stop flowing. They are both separated by a cell membrane.
