Symptoms
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a category of conditions that includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It is a progressive condition that gets steadily worse. Over time, the body becomes less able to take in enough oxygen. This can ultimately result in death.
Causes
Even though there is no cure for COPD, there are treatments to improve symptoms. If you take steps to quit smoking, to exercise, and to improve your diet, you can increase your life expectancy and...
Prevention
The main symptoms of COPD are:
- increasing breathlessness, particularly when you're active
- a persistent chesty cough with phlegm – some people may dismiss this as just a "smoker's cough"
- frequent chest infections
- persistent wheezing
Complications
What’s the Prognosis for COPD?
- Talk to Your Doctor About What to Expect. Your first step is to make sure you understand which stage of COPD you have. ...
- Follow Your Treatment Plan. It’s important to start treatment as soon as you’re diagnosed and stick with it. ...
- Eat Well and Exercise. ...
- Don’t Go It Alone. ...
- Consider Palliative Care. ...
Is COPD a deadly disease?
Can a person with COPD get better?
What are the 4 conditions of COPD?
How to treat mild COPD in the early stages?
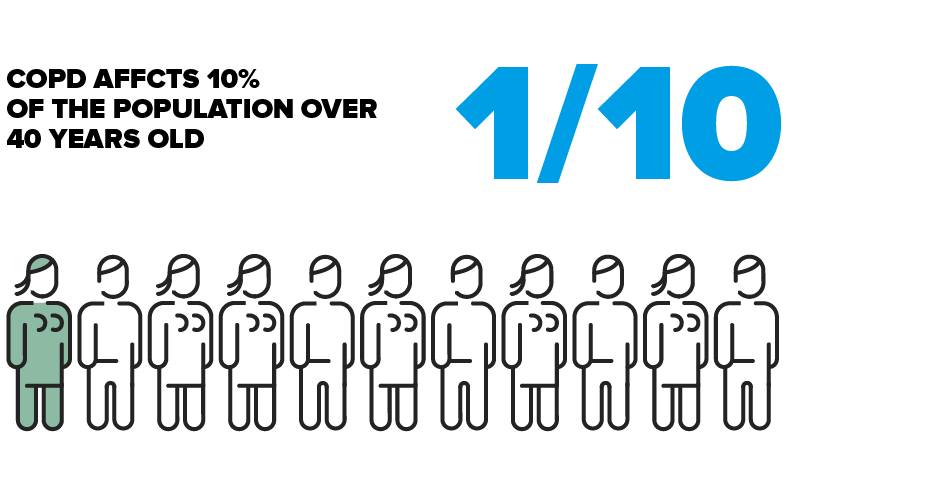
What illnesses are classified COPD?
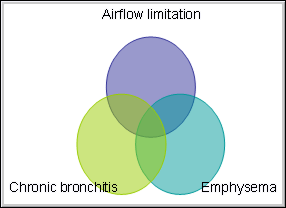
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an umbrella term given to a group of chronic lung diseases that make it harder to breathe air out of the lungs. These diseases include emphysema, chronic bronchitis, and sometimes asthma.
How many COPD diseases are there?
There are two main forms of COPD: Chronic bronchitis, which involves a long-term cough with mucus. Emphysema, which involves damage to the lungs over time.
What are the three most common diseases that produce a COPD?
Pipe smokers, cigar smokers and marijuana smokers also may be at risk, as well as people exposed to large amounts of secondhand smoke. People with asthma. Asthma, a chronic inflammatory airway disease, may be a risk factor for developing COPD . The combination of asthma and smoking increases the risk of COPD even more.
What are the 4 main categories of lung diseases?
Lung disease is a general term for several disorders that include airway diseases, lung tissue diseases, and lung circulation diseases, some of which may lead to respiratory failure.
What are the two most common COPD conditions?
What Are the Different Types of COPD? The two most common conditions of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Some physicians agree that asthma should be classified as a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, while others do not.
What is chronic bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term inflammation of the bronchi (breathing passages in the lungs), which results in increased production of mucus, as well as other changes. These changes may result in breathing problems, frequent infections, cough, and disability. 1.
What are the characteristics of asthma?
The characteristics of asthma include the following: The lining of the airways become swollen and inflamed. The muscles that surround the airways tighten. The production of mucus is increased, leading to mucus plugs. Click to See Chart.
What is COPD in a lung?
Overview. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, mucus (sputum) production and wheezing. It's typically caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter, most often from cigarette smoke.
What is the main cause of COPD in developed countries?
The main cause of COPD in developed countries is tobacco smoking. In the developing world, COPD often occurs in people exposed to fumes from burning fuel for cooking and heating in poorly ventilated homes.
How does air travel through the lungs?
Air travels down your windpipe (trachea) and into your lungs through two large tubes (bronchi). Inside your lungs, these tubes divide many times — like the branches of a tree — into many smaller tubes (bronchioles) that end in clusters of tiny air sacs (alveoli).
What is the term for a person who loses weight in later stages of COPD?
Unintended weight loss (in later stages) Swelling in ankles, feet or legs. People with COPD are also likely to experience episodes called exacerbations, during which their symptoms become worse than the usual day-to-day variation and persist for at least several days.
What causes COPD?
People with COPD are at increased risk of developing heart disease, lung cancer and a variety of other conditions.
Where is AAt made?
AAt is made in the liver and secreted into the bloodstream to help protect the lungs. Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency can cause liver disease, lung disease or both. For adults with COPD related to AAt deficiency, treatment options include those used for people with more-common types of COPD.
What is the gas that is exhaled in the air sac?
The oxygen in the air you inhale passes into these blood vessels and enters your bloodstream. At the same time, carbon dioxide — a gas that is a waste product of metabolism — is exhaled.
What are the two most common COPD conditions?
What are the different types of COPD? The two most common conditions of COPD are chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Some doctors agree that asthma should be classified as a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, while others do not.
How to improve COPD?
In order to reach these goals, COPD rehabilitation programs may include the following: 1 Medication management 2 Exercises to decrease respiratory symptoms and improve muscle strength and endurance 3 Respiratory treatments to improve breathing ability 4 Assistance with obtaining respiratory equipment and portable oxygen 5 Methods to increase independence with activities of daily living (ADLs) 6 Exercises for physical conditioning and improved endurance 7 Stress management, relaxation exercises, and emotional support 8 Smoking cessation programs 9 Nutritional counseling 10 Patient and family education and counseling 11 Vocational counseling
What causes COPD?
The causes of COPD are not fully understood. It is generally agreed that the most important cause of chronic bronchitis and emphysema is cigarette smoking. Other causes such as air pollution and occupational exposures may play a role, especially when combined with cigarette smoking. Heredity may also be a factor.
What are the goals of COPD rehabilitation?
In order to reach these goals, COPD rehabilitation programs may include the following: Medication management. Exercises to decrease respiratory symptoms and improve muscle strength and endurance. Respiratory treatments to improve breathing ability. Assistance with obtaining respiratory equipment and portable oxygen.
What is the condition where the alveoli are damaged?
Emphysema is a chronic lung condition in which alveoli (the air sacs in the lungs) may become: Destroyed. Narrowed. Collapsed. Stretched. Overinflated. This can cause a decrease in respiratory function and breathlessness. Damage to the air sacs is irreversible and results in permanent "holes" in the lung tissue.
What are the characteristics of asthma?
The characteristics of asthma include the following: The lining of the airways becomes swollen and inflamed. The muscles that surround the airways tighten. The production of mucus is increased, leading to mucus plugs.
Is a COPD patient part of a rehabilitation team?
Most COPD health professionals consider the patient and his or her family part of the rehabilitation team. In fact, in order to develop the most appropriate care possible, many teams refer to the need for equal "partnerships" between patients and medical teams.
How to treat COPD?
Treating your COPD can greatly improve your quality of life. Treatment options that your doctor may consider include: 1 Quitting smoking. For people who smoke, the most important aspect of treatment is to stop smoking. 2 Avoiding tobacco smoke and other air pollutants at home and at work. 3 Medication. Symptoms such as coughing or wheezing can be treated with medication. 4 Pulmonary rehabilitation, a personalized treatment program that teaches you how to manage your COPD symptoms to improve quality of life. Plans may include learning to breathe better, how to conserve your energy, and advice on food and exercise. 5 Avoiding lung infections. Lung infections can cause serious problems in people with COPD. Certain vaccines, such as flu and pneumonia vaccines, are especially important for people with COPD. Learn more about vaccination recommendations. Respiratory infections should be treated with antibiotics, if appropriate. 6 Supplemental oxygen from a portable oxygen tank may be needed if blood oxygen levels are low.
What is the treatment for COPD?
Medication. Symptoms such as coughing or wheezing can be treated with medication. Pulmonary rehabilitation, a personalized treatment program that teaches you how to manage your COPD symptoms to improve quality of life.
How many people have COPD?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis, makes breathing difficult for the 16 million Americans who have been diagnosed with COPD. Millions more suffer from COPD, but have not been diagnosed and are not being treated.
Can you get COPD from smoking?
Could you have COPD? The main cause of COPD is tobacco smoke, so if you smoke or used to smoke, you are at a higher risk of having COPD. Exposure to air pollution in the home or at work, family history, and respiratory infections like pneumonia also increase your risk.
Can COPD cause lung infections?
Lung infections can cause serious problems in people with COPD. Certain vaccines, such as flu and pneumonia vaccines, are especially important for people with COPD. Learn more about vaccination recommendations. Respiratory infections should be treated with antibiotics, if appropriate.
What are the causes of COPD?
There are two causes of COPD: chronic bronchitis and emphysema. While asthma is not typically considered one of the conditions classified as COPD, some people may have both. You may have COPD if you notice persistent, prolonged changes to your breathing. Symptoms include: tightness in your chest.
What are the two conditions that cause COPD?
Types. Two conditions cause COPD: chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Both affect your lungs in different ways. Asthma is not typically considered a type of COPD, but it is a chronic respiratory condition. You can have asthma along with COPD.
How to diagnose COPD?
Your doctor will diagnose COPD using a breathing test called a spirometry test. This measures how much air you exhale. You take deep breaths into a tube that a computer monitors to determine if you have COPD or another condition like asthma.
What causes a swollen bronchial artery?
Two conditions cause it: emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Your doctor will diagnose the condition with a breathing test. You will likely need to make lifestyle changes, in addition to medication, to prevent the condition from worsening.
What causes a cough and mucus?
You will also have mucus in your cough. This condition makes it difficult for your lungs to bring air in and let it out. Chronic bronchitis is the condition that causes COPD. It means that you have had bronchitis for at least three months in two different years.
How does emphysema affect the alveoli?
Emphysema causes damage to the alveoli. These are your lungs’ air sacs. The damage destroys the walls of the alveoli. There are 300 million alveoli in your lungs. This causes them to increase in size. The larger size makes it harder for your lungs to move oxygen into your bloodstream.
What happens if you don't get COPD?
These symptoms will get worse over time if you don’t seek treatment. You can also develop conditions like irregular heartbeats, heart failure, and high blood pressure if you don’t get COPD diagnosed and treated.
Why do I cough and have shortness of breath?
Damage to the bronchial (brawn-key-el) tubes causes chronic bronchitis. Bronchitis (brawn -ki-tus) occurs when the bronchial tubes are irritated and swollen. This causes coughing and shortness of breath. If mucus comes up with the cough and the cough lasts at least three months for two years in a row, the bronchitis is called chronic bronchitis.
What are the hairs in the lungs called?
There are hair-like fibers lining the bronchial tubes of the lungs. These tiny hairs are called cilia (seal lee ah). The cilia help move mucus up the bronchial tubes so it can be coughed out. In chronic bronchitis, the tubes lose their cilia.
Why do I feel shortness of breath when I breathe?
These larger sacs do not transfer oxygen from the air to the blood as well. Also, when the alveoli are damaged , the lungs become stretched out and lose their springiness. The airways become flabby, and air is trapped in the lungs. This creates a feeling of shortness of breath.
What is COPD in medical terms?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a term used to describe chronic lung diseases including emphysema, and chronic bronchitis. This disease is characterized by breathlessness. Some people with COPD also experience tiredness and chronic cough with or without mucus.
What is the term for the ability to move air in and out of your lungs?
Obstructive -. The ability to move air in and out of your lungs is blocked or obstructed. This is caused by swelling and extra mucus in the tubes of the lungs (airways) which carry air in and out.
What is COPD360social?
The COPD Foundation offers resources such as COPD360social, an online community where you can connect with patients, caregivers and health care providers and ask questions, share your experiences and receive and provide support.
What are the health conditions that can affect COPD?
If you have another health condition in addition to COPD (comorbidity), such as high blood pressure, heart disease, heartburn, depression, or diabetes, this can also affect your COPD and how it is managed. Here are some things that can help determine your particular type of COPD.
What is the cause of emphysema?
, the leading cause of emphysema and chronic bronchitis involves long-term exposure to substances that irritate the airways and lungs. The NHLBI note that the primary sources of irritants include tobacco smoke from: cigarettes.
What is the difference between COPD stage 2 and 2?
Someone in this stage may not be aware that their lung function is abnormal. Stage 2: Moderate COPD: In Stage 2, airflow limitation worsens, and people tend to experience shortness of breath during exercise.
What are the different types of COPD?
The main types of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are emphysema and chronic bronchitis. They differ in the kind of damage they do to the airways and lungs. However, the causes, symptoms, and treatment of the two conditions are almost completely identical. There are four stages of COPD that range from mild to very severe.
What happens to the alveoli in emphysema?
In emphysema, the alveoli, which are the walls of the air sacs, and the small airways suffer damage. As a result of this damage, the sacs lose their shape and ability to recoil during the expiratory phase of the breathing cycle, resulting in trapped air in the lung.
Why do airways become thick?
The airways and sacs become too compliant, especially in emphysema, and lose their elastic recoil, leading to alveolar destruction. The airway walls become thick and inflamed in a manner similar to chronic bronchitis. The airways produce more mucus, which clogs airflow, as seen in people with asthma.
Why is it so hard to breathe?
In chronic bronchitis, the lining of the airways stays inflamed. This leads to swelling and the formation of large amounts of mucus. These effects make it hard to breathe. Learn more about the differences between emphysema and chronic bronchitis here.
How many stages of COPD are there?
There are four stages of COPD that range from mild to very severe. A person with mild COPD may not know that they have the condition, while someone with very severe COPD will experience life threatening symptoms. Keep reading to learn about the types and stages of COPD, including causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
Prevention
- COPDsymptoms often don't appear until significant lung damage has occurred, and they usually worsen over time, particularly if smoking exposure continues. Signs and symptoms of COPDmay include: 1. Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities 2. Wheezing 3. Chest tightness 4. A chronic cough that may produce mucus (sputum) that may be clear, white, yellow …