What are aminoglycosides used to treat?
Print Share. Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics used mainly in the treatment of aerobic gram-negative bacilli infections, although they are also effective against other bacteria including Staphylococci and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. They are often used in combination with other antibiotics.
How do Aminoglycosides work in bacteria?
These amino acids are used to compile proteins, which in turn are the workhorses of cell processes. So, aminoglycosides, by inhibiting the subunits of bacterial ribosomes, prevent bacteria from producing proteins that keep them alive. Sneaky sneaky aminoglycosides…
What are the side effects of aminoglycosides?
Aminoglycosides are extremely powerful antibiotics with serious side effects, particularly when taken orally or intravenously. The FDA has given black-box warnings for aminoglycosides taken orally or intravenously, citing the following potential side effects: Hearing loss is caused by damage to the ear's hearing structures.
What is an example of an aminoglycoside?
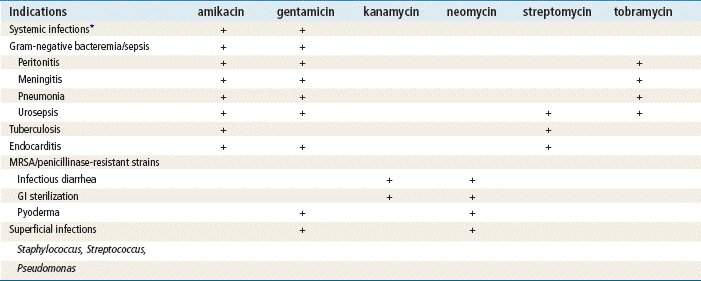
Examples of aminoglycosides include: Gentamicin (generic version is IV only) Amikacin (IV only) Tobramycin Gentak and Genoptic (eye drops) Kanamycin Streptomycin Neo-Fradin (oral) Neomycin (generic version is IV only)
How do aminoglycosides work?
Aminoglycosides act through inhibition of protein synthesis. Once inside the bacterial cell, they bind to the A-site in ribosomal RNA of the 30S subunit and cause a misreading of transfer RNA codons.
What do aminoglycosides target?
Aminoglycosides are a class of clinically important antibiotics used in the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms. They are bactericidal, targeting the bacterial ribosome, where they bind to the A-site and disrupt protein synthesis.
What do aminoglycosides inhibit?
Aminoglycosides inhibit protein synthesis by binding, with high affinity, to the A-site on the 16S ribosomal RNA of the 30S ribosome (Kotra et al. 2000). Although aminoglycoside class members have a different specificity for different regions on the A-site, all alter its conformation.
How do aminoglycosides inhibit bacteria?
Aminoglycosides are highly potent, broad-spectrum antibiotics that kill bacteria by binding to the ribosomal decoding site and reducing the fidelity of protein synthesis.
What bacteria do aminoglycosides treat?
The most common clinical application (either alone or as part of combination therapy) of the aminoglycosides is for the treatment of serious infections caused by aerobic gram-negative bacilli [1,2].
What are the main indications of aminoglycosides?
Since this drug class has demonstrated effectiveness in multi-drug resistant Gram-negative pathogens, aminoglycosides are indicated for empiric therapy in patients with severe illness; this includes empiric treatment for patients with infective endocarditis, sepsis, complicated intraabdominal infections, and ...
Why do aminoglycosides cause ototoxicity?
Aminoglycosides appear to generate free radicals within the inner ear, with subsequent permanent damage to sensory cells and neurons, resulting in permanent hearing loss. Two mutations in the mitochondrial 12S ribosomal RNA gene have been previously reported to predispose carriers to aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity.
What are two major side effects of aminoglycosides?
The major side effects of aminoglycosides are kidney injury, hearing impairment and vestibular toxicity.
How do aminoglycosides affect protein synthesis?
Aminoglycoside drugs bind the bacterial ribosome, and decades of results from in vitro biochemical and structural approaches suggest that these drugs disrupt protein synthesis by inhibiting the ribosome's translocation on the messenger RNA, as well as by inducing miscoding errors.
Why are aminoglycosides given with other antibiotics?
This combination enhances bactericidal activity, whereas aminoglycoside monotherapy may allow resistant staphylococci to persist during therapy and cause a clinical relapse once the antibiotic is discontinued.
Why are aminoglycosides bactericidal?
Aminoglycosides are called bactericidal antibiotics because they kill bacteria directly. They accomplish this by stopping bacteria from producing proteins needed for their survival.
What's the purpose for adding aminoglycosides to some vaccines?
These substances may be added as stabilizers. They help protect the vaccine from adverse conditions such as the freeze-drying process, for those vaccines that are freeze dried.
What organs can be affected by aminoglycosides?
The major side effects of aminoglycosides are kidney injury, hearing impairment and vestibular toxicity.
Why do aminoglycosides cause ototoxicity?
Aminoglycosides appear to generate free radicals within the inner ear, with subsequent permanent damage to sensory cells and neurons, resulting in permanent hearing loss. Two mutations in the mitochondrial 12S ribosomal RNA gene have been previously reported to predispose carriers to aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity.
What's the purpose for adding aminoglycosides to some vaccines?
These substances may be added as stabilizers. They help protect the vaccine from adverse conditions such as the freeze-drying process, for those vaccines that are freeze dried.
Do all aminoglycosides cover Pseudomonas?
The aminoglycosides tobramycin, gentamicin, and amikacin are commonly used to treat hospital-acquired infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These infections generally require treatment with a combination of antimicrobials in order to achieve a greater bactericidal effect and reduce the levels of resistance1.
Why is it important to monitor aminoglycosides?
Therapeutic drug monitoring is necessary with aminoglycosides to optimize patient outcomes and limit toxicity. However, there is no universal agreement on the method of monitoring. Therapeutic drug monitoring has been shown to reduce hospital stay duration and toxicities. Studies also suggest that therapeutic drug monitoring reduces mortality. It is important to note that monitoring clearance should be considered in critically ill, burn, and obese patients due to their abnormal distribution volume. [15]
What are the adverse effects of aminoglycosides?
The main noted adverse effects of aminoglycosides are ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and neuromuscular blockade. Therefore, patients should be educated to look out for warning signs of these adverse effects before the initiation of aminoglycoside therapy. [1]
How long can you use aminoglycosides?
For directed treatment, aminoglycoside use for longer than 48 hours is acceptable. They are part of directed combination treatment for brucellosis, listeriosis, CNS nocardiosis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosainfection. Aminoglycosides monotherapy is for tularemia, resistant mycobacteria, bacteremia caused by Campylobacterspp.and Yersinia spp., and drug-resistant gram-negative pathogens. The Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines should be referenced to see if an aminoglycoside is the correct agent to use for a particular patient. [1][2]
What subunit does aminoglycoside bind to?
Aminoglycosides have bactericidal activity in which they bind to the bacteria ribosomal 30S subunit. Specifically, they are believed to bind to the A-site (aminoacyl) on the 16S rRNA, a component of the ribosomal 30S subunit. Through this binding, the genetic code gets misread, and the translation is disrupted, leading to the bacteria being unable to carry out protein synthesis. [3][4]
Is amikacin an aminoglycoside?
Aminoglycosides have a broad spectrum of activity covering aerobic organisms, including gram-negative bacteria and mycobacteria. There are several drugs within the aminoglycoside class, including gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, neomycin, plazomicin, and streptomycin, and FDA-approved indications vary between the for these individual aminoglycosides. This activity reviews the indications, contraindications, mechanism of action, adverse event profile, and other key factors (e.g., off-label uses, dosing, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, monitoring, relevant interactions) pertinent to members of the interprofessional team who wish to prescribe aminoglycosides.
Can aminoglycosides be used for genitourinary infections?
Typically, in these settings, aminoglycosides should not be used for more than two days, due to toxic ity to the patient .
Is aminoglycoside a new class of antimicrobials?
Although not a new class of antimicrobials, aminoglycosides have continued to prove their clinical value in fighting infections. Aminoglycosides have a broad spectrum of activity covering aerobic organisms, including gram-negative bacteria and mycobacteria. Because there are several drugs within the aminoglycoside class, including gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, neomycin, plazomicin, paromomycin, and streptomycin, FDA approved indications vary between the different individual aminoglycosides.
What is aminoglycoside used for?
Aminoglycosides are mainly used in the treatment of aerobic gram-negative bacilli infections. They are also effective in treating other bacterial infections, including: Complicated urinary tract infections. Pneumonia and upper respiratory tract infections. Endocarditis ( inflammation of the heart valves)
How do aminoglycosides affect the cell membrane?
Aminoglycosides act through inhibition of protein synthesis. Once inside the bacterial cell, they bind to the A- site in ribosomal RNA of the 30S subunit and cause a misreading of transfer RNA codons. This subsequently leads to the interruption of normal bacterial protein synthesis and results in the formation of an incorrect protein, which may damage the cell membrane. The damaged cell membrane allows an increased amount of drug to enter the bacteria, eventually leading to its death.
Why are aminoglycosides used in antibiotics?
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics used to treat serious infections caused by bacteria that either multiply very quickly or are difficult to treat. Aminoglycosides are called bactericidal antibiotics because they kill bacteria directly. They accomplish this by stopping bacteria from producing proteins needed for their survival.
Where are aminoglycosides administered?
Because aminoglycosides are normally used to treat serious infections, they are typically administered into the veins of the body (intravenously, or IV). However, some aminoglycosides can be taken orally, or as ear or eye drops. Examples of aminoglycosides include:
What is the drug that prevents patients from moving during surgery called?
Certain drugs called neuromuscular blocking agents, often used to prevent patients from moving during surgery, enhance some of the side effects of aminoglycosides.
Can aminoglycoside cause paralysis?
Although side effects and their severity may vary from person to person, the higher the dose of an aminoglycoside you receive, or the longer the duration of use, the greater your risk of side effects.
Can aminoglycosides be taken by mouth?
Aminoglycosides are very powerful antibiotics, and their side effects can be severe — especially when taken by mouth or IV.
Sar of Aminoglycosides
Streptomycin, neomycin, gentamicin, paromomycin, sisomicin, ribostamycin, tobramycin, nebramycin, dibekacin, amikacin, and kanamycin are all aminocyclitol-containing antibiotics. Streptomyces and Micromonospora species produce them.
Mechanism of Action
They only need a brief contact period and are most successful against rapidly multiplying susceptible bacterial populations.
Types of Aminoglycosides
There are several different antibiotics in the aminoglycoside class. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, plazomicin, streptomycin, neomycin, and paromomycin for clinical use in the United States.
Clinical Use
The recent appearance of infections caused by Gram-negative bacterial strains with advanced antimicrobial resistance trends has led doctors to reconsider their use of these antibiotics.
Common Side Effects
Aminoglycosides are extremely powerful antibiotics with serious side effects, particularly when taken orally or intravenously.
Warnings and Precautions
If you're allergic to aminoglycosides or any of the inactive ingredients in these products, stay away from them.
What are Aminoglycosides?
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics used mainly in the treatment of aerobic gram-negative bacilli infections , although they are also effective against other bacteria including Staphylococci and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. They are often used in combination with other antibiotics.
What are the side effects of aminoglycosides?
Impairment of kidney function and hearing loss are the most common side effects of aminoglycosides. Aminoglycosides tend to be used when other less toxic antibiotics are contraindicated or ineffective. Aminoglycosides are not well absorbed when given by mouth, so need to be given by injection by healthcare personnel.
Does aminoglycoside increase the kill rate?
Kill rates of bacteria are increased when higher concentrations of amino glycosides are present; however, the margin between a safe and a toxic dose is narrow and monitoring is often needed, although once daily dosing increases the safety window. Impairment of kidney function and hearing loss are the most common side effects of aminoglycosides.
Can aminoglycosides be absorbed by mouth?
Aminoglycosides are not well absorbed when given by mouth, so need to be given by injection by healthcare personnel.
Pharmacology
Traditionally, the antibacterial properties of aminoglycosides were believed to result from inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis through irreversible binding to the 30S bacterial ribosome.
Clinical Uses
Aminoglycosides display bactericidal, concentration-dependent killing action and are active against a wide range of aerobic gram-negative bacilli. They are also active against staphylococci and certain mycobacteria.
Drug Resistance
Most resistance to aminoglycosides is caused by bacterial inactivation by intracellular enzymes. Because of structural differences, amikacin is not inactivated by the common enzymes that inactivate gentamicin and tobramycin.
Drug Interactions and Adverse Effects
Because the body does not metabolize aminoglycosides, aminoglycoside activity is unchanged by induction or inhibition of metabolic enzymes, such as those in the cytochrome P450 system. Certain medications may increase the risk of renal toxicity with aminoglycoside use ( Table 3 ).
Single vs. Multiple Daily Doses
Aminoglycoside antibiotics exhibit rapid concentration-dependent killing action. 5, 11 Increasing concentrations with higher dosages increases both the rate and the extent of bacterial cell death.
Cost
A comparison of the costs of single daily dosing and traditional multiple dosing should include not only the cost of the antibiotic but also the costs of labor, laboratory monitoring and drug toxicity.
What are Aminoglycosides?from drugs.com
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics used mainly in the treatment of aerobic gram-negative bacilli infections , although they are also effective against other bacteria including Staphylococci and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. They are often used in combination with other antibiotics.
What is aminoglycoside antibiotic?from sciencedirect.com
Aminoglycoside antibiotics are a large group of aminocyclitols that are used clinically to treat serious infections. They are among the earliest antibiotics to be used in clinical practice.
What is the most active aminoglycoside against NTM?from sciencedirect.com
Amikacin is the most active aminoglycoside against the NTM. 148,170-172 However, marked variability exists between mycobacterial species in susceptibility. All strains of M. marinum, M. kansasii, and M. fortuitum are susceptible to 4 µg/mL or less, 166,171,172 whereas isolates of M. chelonae, M. abscessus, and M. avium-intracellulare are more resistant but are usually inhibited by 8 to 32 µg/mL of amikacin. 171,172 Doses for streptomycin and amikacin are generally the same as those for treatment of tuberculosis. Tobramycin is the most active aminoglycoside and is the recommended aminoglycoside for treatment of M. chelonae.171,172 Other aminoglycosides, such as gentamicin, are less active and are generally not clinically useful.
What antibiotics are used for NTM?from sciencedirect.com
Aminoglycoside antibiotics have been used extensively for the treatment of rapidly growing and some slow-growing NTM infections. Among M. kansasii strains, 86% demonstrated streptomycin susceptibility. Forty-four percent of strains of M. avium-intracellulare have been susceptible to streptomycin.
What is AGA research?from sciencedirect.com
Research on aminoglycoside antibiotics (AGAs) is still ongoing and the main interests are (1) the mechanisms of action on the bacterial ribosome; (2) biosynthesis and physiology of AGAs in their producers, (3) biochemistry and genetics of resistance determinants in both producers and clinically relevant bacteria, and (4) the recent molecular biological analysis of the biosynthetic potential of AGA producers. Our main focus will be on the aminocyclitol-containing AGAs (ACAGAs) and a summary of the genetics and biosynthetic pathways for the major classes thereof as well as a look at the future possibilities for understanding the biochemical and genetic evolution of ACAGAs and on using this knowledge for pathway engineering leading to new end products with improved therapeutic properties. We will concentrate on the ACAGAs binding to the 16S rRNA component of the small subunit (30S) of the bacterial ribosome. Also, a short account of the current situation resulting from resistance development against the major groups of therapeutically used ACAGAs will be given.
Can antibiotics enter the channel conduction pathway?from sciencedirect.com
In this model, an aminoglycoside antibiotic can enter the channel conduction pathway; however, it only partially blocks the channel. (Bottom, right) Records showing the block of single MS channels with increasing concentrations of neomycin.
Is it rare to have allergic reactions to aminoglycosides?from sciencedirect.com
Allergic reactions are rare . The cost of many aminoglycosides is low compared to other agents. Despite the decline in aminoglycoside use over the past 10–20 years, recent reviews have reported that use is again increasing due to the emergence of gram-negative resistance to other available drugs. 3.
What is aminoglycoside used for?
Aminoglycosides can be used for a wide range of infections. From double covering for Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospital-acquired pneumonias, to treating urinary tract infections, to synergistic coverage for endocarditis. But their use can come with a price…. Part II: Aminoglycosides and Concentrations.
Why do we need to reach a certain concentration of aminoglycosides?
Remember, they're concentration-dependent drugs, so we need to reach a certain concentration in the serum in order to stop those nasty bacteria.
Why do we combine aminoglycosides with beta lactam?
We sometimes combine aminoglycosides with a cell wall-active agent (like a beta lactam) in order to add synergistic action against Gram positive bacteria. Think of this strategy as the beta lactam opening the cell wall door for the aminoglycoside to go in and fulfill its death mission from within the bacteria itself.
What is the peak concentration of aminoglycoside?
For example, when using gentamicin or tobramycin, target peaks for serious or life threatening infections can range from 6-10 mcg/mL. A UTI may only require peaks of 4-6 mcg/mL. And we only shoot for 3 - 5 mcg/mL with Gram positive syner gy.
What does PAE mean in antibiotics?
In a nutshell, PAE means that the antibiotic's inhibitory action extends beyond the period of exposure. So even AFTER the aminoglycoside concentration falls below the MIC, the bacteria are not able to grow. Many antibiotics show some degree of PAE.
Which aminoglycosides are the most popular?
For the remainder of this post, let’s focus on gentamicin and tobramycin since those are the most popular aminoglycosides.
What drugs fall under aminoglycosides?
That way we’re all on the same page. When we talk about aminoglycosides, we’re referring to gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin .