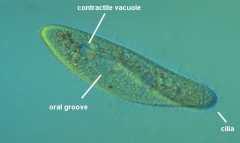
What is the difference between protist and bacteria?
The primary difference between them is their cellular organization. Bacteria are single-celled microbes and are prokaryotes, which means they’re single-celled organisms lacking specialized organelles. In contrast, protists are mostly single-celled eukaryotic organisms that are not plants, fungi, or animals.
What are some of the most interesting protists?
Types
- Archaeplastida. In Archaeplastida, eukaryotic life forms containing chloroplasts are enclosed by two membranes. ...
- Chromalveolata. Chromalveolata are types of eukaryotes and are also single-celled organisms. ...
- Excavata. Excavata are made up of single-celled eukaryotic organisms that might be symbiotic as well as free-living.
- Rhizaria. ...
- Unikont. ...
How are Protista similar to bacteria?
• Protists are classified under Kingdom Protista, while bacteria are classified under Kingdom Monera. • Due to the presence of nuclear envelop, the protists cells are considered as eukaryotic cells, whereas bacteria cells are considered as prokaryotic cells as their cells lack nuclear envelop.
What are facts about protists?
Protists
- Protists. Protists contain one or many cells and they have eukaryotic cells or cells that have a nucleus and contain DNA.
- Evolution of Protists. Some scientists believe that all protists started at as single-celled organisms and that they evolved over time.
- Plant Like Protists. ...
- Animal Like Protists. ...
- Fungi Like Protists. ...
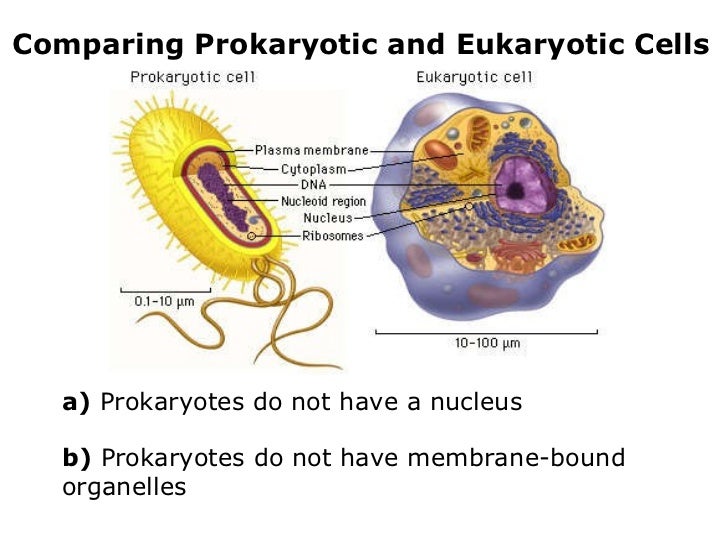
How are bacteria and protists the same?
Bacteria and protists are unicellular organisms....Difference between Bacteria and Protists.BacteriaProtistsBacteria are prokaryotesProtists are eukaryotesNucleus is absentThey possess a well-defined nucleusGenetic material is present in an irregularly shaped region called the nucleoidGenetic material is present inside the nucleus6 more rows
What are two ways bacteria and protists are similar?
Protists are similar to bacteria because both are living organisms made of cells. Bacteria are made of prokaryotic cells, and protists are made of eukaryotic cells. All bacteria are single-celled organisms, and most protists are also single-celled. This means they are microscopic and cannot be seen with the naked eye.
What are the similarities between bacteria and protozoa?
Protozoa (pronounced: pro-toe-ZO-uh) are one-celled organisms, like bacteria. But they are bigger than bacteria and contain a nucleus and other cell structures, making them more similar to plant and animal cells.
Which characteristic do most protists share with bacteria?
What characteristic do many protists share with bacteria and archaea? They are unicellular.
What are the similarities between protists and prokaryotes?
Protists also contain distinct structures that create a cytoskeleton for support within their cells. Both protists and prokaryotes may be unicellular or colonial, but only protists have the ability to be multicellular organisms.
Which structure do both bacteria and protists have in common that allows movement?
flagellum, plural flagella, hairlike structure that acts primarily as an organelle of locomotion in the cells of many living organisms. Flagella, characteristic of the protozoan group Mastigophora, also occur on the gametes of algae, fungi, mosses, slime molds, and animals.
What are the similarities and differences between bacteria and fungi?
Bacteria and fungi are two types of microscopic organisms. The main difference between bacteria and fungi is that bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic organisms whereas fungi are multicellular eukaryotic organisms. Both bacteria and fungi contain DNA as their genetic material.
What are similarities of bacteria and viruses?
Bacteria and viruses are too tiny to be seen by the naked eye, can cause similar symptoms and are often spread in the same way, but that's where the similarities end.
What are the similarities and differences between protists and fungi?
Protists and fungi are both eukaryotes, meaning that they have organelles and nuclei in their single-celled structures and their DNA is in the form of linear chromosomes. The difference between the two is that protists are strictly unicellular whereas fungi have both unicellular and multicellular forms.
Are protists closely related to bacteria?
Both protists and bacteria represent unicellular organisms, with some species able to cause illness or disease in humans. However, in terms of taxonomy, the process by which scientists classify living organisms, protists and bacteria belong to two separate domains.
Are bacteria related to protists?
The relationships between protists and bacteria has been the subject of many evolutionary studies and there is a now a general understanding that protist evolution is highly dependent on the presence of bacteria.
What are the two common characteristics shared by protists?
Characteristics of Protists. Like all other eukaryotes, protists have a nucleus containing their DNA. They also have other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum.
What are some similarities and differences between bacteria and eukarya?
The key difference between bacteria and eukaryotes is that the bacteria lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles while the eukaryotes possess a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The cell is the basic functional and structural unit of all living organisms.
What are the similarities and differences between protists and fungi?
Protists and fungi are both eukaryotes, meaning that they have organelles and nuclei in their single-celled structures and their DNA is in the form of linear chromosomes. The difference between the two is that protists are strictly unicellular whereas fungi have both unicellular and multicellular forms.
What are the similarities of bacteria and viruses?
Bacteria and viruses are too tiny to be seen by the naked eye, can cause similar symptoms and are often spread in the same way, but that's where the similarities end.
What are protists most similar to?
Protists range from single-celled amoebas to multicellular seaweed. Protists may be similar to animals, plants, or fungi.