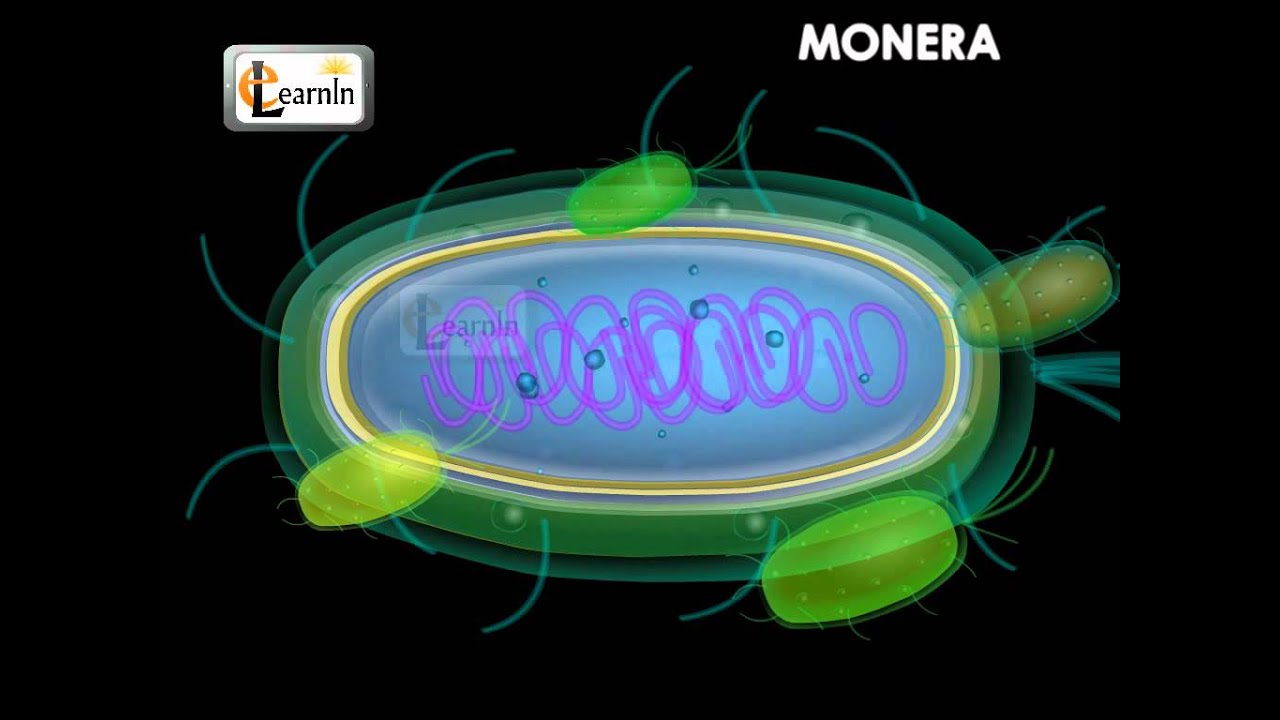
Bacteria also have an organelle that contains DNA and controls the cell. Unlike the nucleus in plant cells, the nucleoid in bacterial cells is not held within a membrane. The nucleoid refers to an area in the cytoplasm where strands of DNA congregate. In bacteria, DNA form a single, circular-shaped chromosome.
What are the three types of bacterial cells?
Bacteria are classified by shape into three basic groups: cocci, bacilli, and spirochetes ( Figure 2–1 ). The cocci are round, the bacilli are rods, and the spirochetes are spiral-shaped. Some bacteria are variable in shape and are said to be pleomorphic (many-shaped). The shape of a bacterium is determined by its rigid cell wall.
What are the three main types of bacteria?
Types of Bacteria According to Shapes
- Coccus
- Bacillus
- Vibrio
- Spirochete or spirilla
- Helicobacter. Bacteria are classified into two main types depending on the results obtained when a sample of bacteria is tested by the Gram Stain Method.
What do bacteria and what do they do?
Bacteria also help out by doing things cells are ill-equipped to do. For instance, bacteria break down carbohydrates (sugars) and toxins, and they help us absorb the fatty acids which cells need to grow. [2] Bacteria help protect the cells in your intestines from invading pathogens and also promote repair of damaged tissue. Most importantly, by ...
Are bacteria made of cells?
The structure of bacteria is known for its simple body design. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles; hence, they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. They are also very versatile organisms, surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions.
What organelles do bacteria cells have?
The organelles that bacteria have include:Capsule.Cell wall.Cell membrane.Cytoplasm.Ribosomes.Genetic material.Cilia.Flagella.
What are 5 characteristics of bacteria?
Five characteristics of bacteria include being unicellular, prokaryotic, microscopic, lacking a nucleus, and having a plasma membrane. These traits are shared by all bacteria.
What types of cells do bacteria have?
Explanation: Bacteria have the presumed most ancient types of cells, known as prokaryotic cells. They are simpler then our cells once they lack a membrane that organize the cell nucleus and any organelles that derive from this membrane.
What features do bacteria have?
There are three notable common traits of bacteria, 1) lack of membrane-bound organelles, 2) unicellular and 3) small (usually microscopic) size. Not all prokaryotes are bacteria, some are archaea, which although they share common physicals features to bacteria, are ancestrally different from bacteria.
What is unique to bacterial cells?
Unique Features Bacteria lack many of the structures that eukaryotic cells contain. For example, they don't have a nucleus. They also lack membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. The DNA of a bacterial cell is also different from a eukaryotic cell.
What are 4 ways to identify bacteria?
Modern Methods for Identifying MicrobesIdentifying Microbes Using PCR. PCR, including Real-Time PCR, is probably the most widely used molecular technique for identifying microbes. ... Microarray-Based Identification. ... Immunological Identification. ... Chemical/Analytical Identification.
Do bacteria have DNA?
Chromosomal DNA Most bacteria have a haploid genome, a single chromosome consisting of a circular, double stranded DNA molecule.
Do bacteria cells have DNA?
In many bacteria the DNA is present as a single circular chromosome, although some bacteria may contain two chromosomes, and in some cases the DNA is linear rather than circular. A variable number of smaller, usually circular (though sometimes linear) DNA molecules, called plasmids, can carry auxiliary information.
Do bacteria have nucleus?
Bacteria, of course, have no nucleus and therefore also nuclear membrane. genetic information- DNA is organized into numerous chromosomes and is packaged in the nucleus. The nucleus is bounded by a membrane mRNA, tRNA and rRNA are made in the nucleus and shipped out into the cytoplasm. locomotion- rigid flagella.
Which one is present only in bacteria?
Thus, the correct answer is 'Diaminopimellic acid.
Do bacteria have cell walls?
In bacteria, the cell wall forms a rigid structure of uniform thickness around the cell and is responsible for the characteristic shape of the cell (rod, coccus, or spiral). Inside the cell wall (or rigid peptidoglycan layer) is the plasma (cytoplasmic) membrane; this is usually closely apposed to the wall layer.
What are 6 structures of a bacterial cell?
A procaryotic cell has five essential structural components: a nucleoid (DNA), ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall, and some sort of surface layer, which may or may not be an inherent part of the wall.
What are 5 examples of bacteria?
Examples include Listeria monocytogenes, Pesudomonas maltophilia, Thiobacillus novellus, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyrogenes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, and Clostridium kluyveri.
What are the 5 types of bacteria?
Bacteria are classified into five groups according to their basic shapes: spherical (cocci), rod (bacilli), spiral (spirilla), comma (vibrios) or corkscrew (spirochaetes). They can exist as single cells, in pairs, chains or clusters. Bacteria are found in every habitat on Earth: soil, rock, oceans and even arctic snow.
What are 5 characteristics of viruses?
These are: 1) attachment; 2) penetration; 3) uncoating; 4) replication; 5) assembly; 6)release. As shown in , the virus must first attach itself to the host cell. This is usually accomplished through special glycoprotiens on the exterior of the capsid, envelope or tail.
What characteristics of life do bacteria have?
Being composed of one or more cells. Being able to carry out metabolism(both catabolism and anabolism). Able to carry out growth. Able to adapt to their environment.
What are the structures of bacteria?
They consists of various cell surface structures, cell wall, plasma membrane, many cytoplasmic inclusions, and the bacterial chromosome (nucleoid). Except some, all structures do not occur in every genus. Furthermore, gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria differ, particularly, with respect to their cell walls.
What does the S layer do to bacteria?
By this act, they help retain proteins near the bacterial cell much like the outer membrane does in gram-negative bacteria. ADVERTISEMENTS: (ii) S-layer may protect bacterial cell against ion and pH fluctuations, osmotic stress, enzymes, or the predaceous bacterium Bdellovibrio.
What are the short hairlike appendages of bacteria?
Bacterial cells possess short, fine, hair like, protein-contributed appendages that extend from the cell surface. These appendages are called fimbriae (ring. fimbria) and pili (sing, pilus), are thinner than flagella, and are not involved in locomotory activities.
How do peritrichous bacteria stop and tumble randomly?
These bacteria stop and tumble randomly by reversing the direction of flagellar rotation. The flagella of peritrichous bacteria rotate counter clockwise, like montrichous and lophotrichous ones, to move forward. The flagella bend at their hooks to form a rotating bundle that propels them forward. Clockwise rotation of the flagella disrupts the bundle and the cell tumbles.
How many spherical molecules are in a chain of bacteria?
Each chain contains approximately 1,000 spherical, smaller flagellin molecules each of 40 Å diameter. In this way, the bacterial flagellum fundamentally differs from the flagellum of an eukaryotic cell, which has 9 + 2 type of arrangement in its filament.
How does slime help bacteria?
Slime layer is more easily deformed, is more difficult to see, and can be very easily removed by washing the bacterial cells. Gliding bacteria often produce slime, which presumably aids in their motility. The slime probably attaches them to the substratum and lubricates the surface for more efficient movement.
What is the role of the S-layer in a cell?
(i) Being interface between the bacterial cell and its environment, the S-layers are thought to act as a selective seive which allows the passage of low molecular weight substances and excludes large molecules and structures (e.g., viruses). By this act, they help retain proteins near the bacterial cell much like the outer membrane does in gram-negative bacteria.
What are the components of a bacterial cell?
Plant and animal cells have some components in common with bacterial cells. These include the cytoplasm and cell membrane. Bacteria have other components that are unique: Structure.
Where is bacterial DNA found?
Chromosomal DNA. The DNA of bacterial cells is found loose in the cytoplasm. It is called chromosomal DNA and is not contained within a nucleus. Plasmid DNA. Bacteria also have small, closed-circles of DNA called plasmids present in their cytoplasm.
What are the cell walls of plants made of?
Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection. Only plant cell walls are made from cellulose. Bacteria are amongst the simplest of organisms. Their cells do not divide by mitosis. Instead they copy themselves by binary fission.
How does plasmid DNA move?
Unlike the chromosomal DNA, plasmid DNA can move from one bacterium to another giving variation. Bacteria can have one or more flagella (singular: flagellum). These can rotate or move in a whip-like motion to move the bacterium. Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection.
Where is DNA found in a nucleus?
DNA in a nucleus. Plasmids are found in a few simple eukaryotic organisms. DNA is a single molecule, found free in the cytoplasm. Additional DNA is found on one or more rings called plasmids.
Do bacteria have nuclei?
Bacteria are all single-celled. The cells are all prokaryotic. This means they do not have a nucleus or any other structures which are surrounded by membranes. Larger bacterial cells may be visible using a light microscope, however an electron microscope would be needed to see the details of the cell organelles.