
What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
Main Difference between Homologous and Analogous Structures
- Homologous structures have similar anatomy while analogous structures have dissimilar anatomy.
- Homologous structures have dissimilar functions while analogous structures have similar functions.
- Homologous structures are inherited from a common ancestor whereas analogous structures are not inherited from a common ancestor
What are homologus structures?
Homologous Structures: Evidence for Evolution A homologous structure is a similar structure that can be found in very different animals, often pointing towards a common ancestor. When animals look very different on the outside yet have certain structures that appear similar in form or function, they have homologous structures.
What are examples of analogous structures?
These Examples of Analogous Structures Will Surely Surprise You
- Insane Similarity! Though differing in their evolutionary pathways, the eyes of humans and octopuses are almost the same regarding structure and appearance.
- Wings. Analogous structures are easily identifiable when wings of different organisms are studied. ...
- Limbs. ...
- Fins. ...
- Storage of Food. ...
- Behavioral Characteristics. ...
- Other Examples. ...
Which are analogous structures?
The term analogous structures comes from the root word Analogy, which means where two different things are the basis of their similarities. Analogous structures are structures that perform the same function but are found in creatures with different ancestral origins and represent different evolutionary lines. Furthermore, they do not share a place.
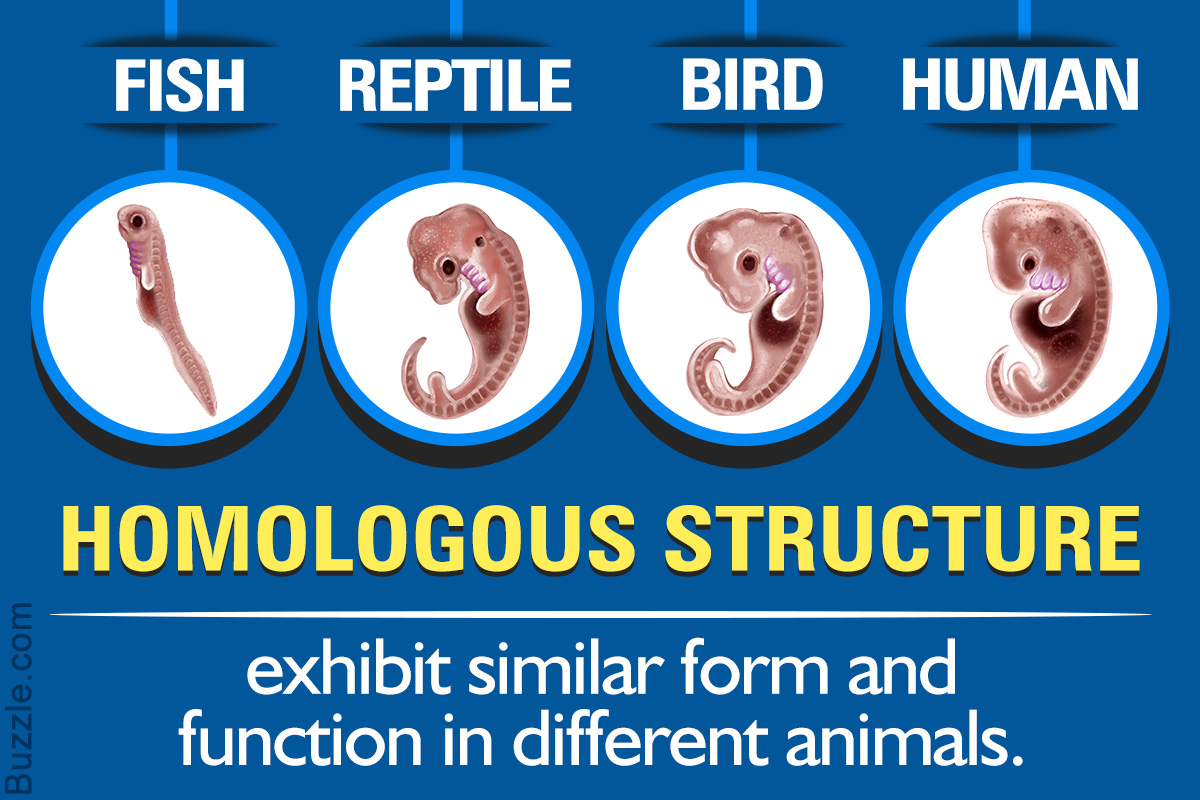
Do homologous have similar structures?
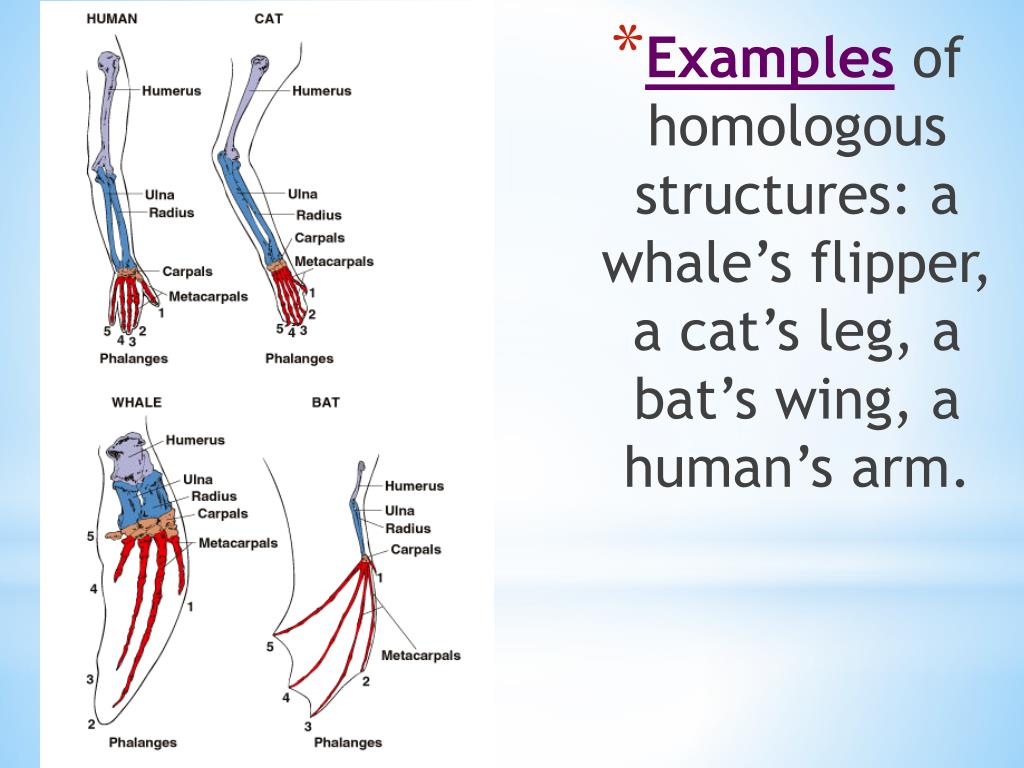
Homologous structures are similar physical features in organisms that share a common ancestor, but the features serve completely different functions. An example of homologous structures are the limbs of humans, cats, whales, and bats.
What are homologous similarities?
Homologies are traits present in two or more organisms that were inherited from the common ancestor of those organisms. The human five-fingered hand and the five-toed foot of a lizard, for example, were both inherited from our common ancestor that lived more than 300 Mya (Fig. 1).
What is common in the homologous structures of the five organisms?
The homologous structures all have the same bones, humerus, raidus, ulna, carpals, meta carpals and phalanges. This suggests that all of the organisms had a common ancestor, even though a bat's wing and human's arm have different functions.
How does the existence of homologous structures support the theory of evolution?
Multiple types of evidence support the theory of evolution: Homologous structures provide evidence for common ancestry, while analogous structures show that similar selective pressures can produce similar adaptations (beneficial features).
What do the similarities of the structures suggest?
structures are similar because they come from a common ancestor, such as the bones in the forelimbs of mammals. Homologous structures are similarities throughout a group of closely related species.
Why are homologous characters similar?
0:121:53So homologous structures have a similar structure meaning they're anatomy or the bone structure isMoreSo homologous structures have a similar structure meaning they're anatomy or the bone structure is similar. They have a differing function so a wing versus an arm versus a fin for example.
Which best describe homologous structures?
So, the correct answer is 'organs with anatomical similarities but, performing different functions'.
What best defines homologous structure?
Homologous structures are body parts of organisms that have the same anatomical features, thus, indicating a common ancestor or developmental origin. They may share the same trait but they do not necessarily have the same function. For example, the forelimbs of the bats and of humans are homologous structures.
How do you identify a homologous structure?
0:121:53So homologous structures have a similar structure meaning they're anatomy or the bone structure isMoreSo homologous structures have a similar structure meaning they're anatomy or the bone structure is similar. They have a differing function so a wing versus an arm versus a fin for example.
How do homologous structures provide evidence for evolution quizlet?
How do homologous structures provide evidence for evolution? Homologous structures show that a certain species of animals is related to other species through common ancestors by having similar structures in their bodies.
What is the similarities in homologous chromosomes?
The two chromosomes in a homologous pair are very similar to one another and have the same size and shape. Most importantly, they carry the same type of genetic information: that is, they have the same genes in the same locations. However, they don't necessarily have the same versions of genes.
What are 3 examples of homologous structures?
The arm of a human, the wing of a bird or a bat, the leg of a dog and the flipper of a dolphin or whale are homologous structures. They are different and have a different purpose, but they are similar and share common traits.
What are the three similarities between homologous chromosomes?
They essentially have the same gene sequence, loci (gene position), centromere location, and chromosomal length. Although they may have the same genetic sequence and loci, they may differ in alleles.
What is the example of homology and similarity?
In the glossary, "homologous structure" is [mis]defined as "a body part that is similar in structure and position in two or more species but has a different function in each; for example, the forelimbs of bats, porpoises and humans" ( EE , p. 146).
What is an example of a homologous structure?
An example of a homologous structure would be the human arm and the wing of a bat. Although these two forelimb have different functions, all the s...
Where are homologous structures?
Homologous structures refer to the same structures that are observed in different species. Homologous structures, while either the same or extremel...
What do homologous structures prove?
Homologous structures provide evidence that two organisms share a recent common ancestor. This, in turn, provides evidence of evolutionary forces a...
What is homologous structure?
Homologous Structures Definition. Homologous structures are organs or skeletal elements of animals and organisms that , by virtue of their similarity, suggest their connection to a common ancestor. These structures do not have to look exactly the same, or have the same function. The most important part, as hinted by their name, ...
Why do humans see in light?
However, despite our ability to see full images and the chimera being restricted to only shadow, the fact that both eyes and light receptors “see” by taking in light confirms there possible connection to a common ancestor and, therefore, structurally homologous .
How many vertebrae are there in the Sahara?
Although they measure up to eight feet in length and weigh over 600 pounds, they contain only seven cervical vertebrae , or neck bones.
What do rod-shaped photoreceptors do?
More specifically, rod-shaped photoreceptors allow us to see black-and-white and shadow, and cone-shaped photoreceptors allow us to see color and saturation. The image shows a blind chimera that “sees” with light receptors. The image shows a human eye uses rods and cones to convert light into images.
How many bones are in a giraffe's neck?
Nonetheless, both human and giraffe necks contain seven bones. This number, when combined with the similar structure of the human and giraffe spine, allows the scientific community to posit that humans and giraffes, as different as they may be, share a common ancestor. As such, their cervical vertebrae are structurally homologous.
What animals have tails?
Monkeys, cats, rats and other mammals have tails. In mammals, the tail is an extension of the torso, made of flexible vertebrae. Tails primarily function to ward off insects, but they can also serve as sources of balance for more aloof species, like cats. Humans possess a similar feature known as the coxxyx, or tailbone.
Which vertebrae provide support for the upper spine?
Cervical vertebrae – The bones that provide support for the upper spine.
What are the two types of evolution?
When biologists study evolution, they often distinguish between two different forms of evolution: convergent evolution and divergent evolution. Divergent evolution is where an evolutionary lineage splits apart over the course of time, giving rise to many diverse species from a few closely related species. Divergent evolution often occurs when a species migrates to a new environment or environmental changes occur in the area a species lives in.
How many vertebrae are in a giraffe's neck?
The long necks of giraffes are also examples of homologous structures. Giraffes necks have seven cervical vertebrae, and together they are approximately eight feet in length and weigh over 600 pounds. Humans have cervical vertebrae as well, though they are obviously much smaller and shorter than the cervical vertebrae found in giraffes. Yet the bones in the human neck and giraffe neck are still seven cervical vertebrae. Once more this is evidence that giraffes and humans share a common ancestor.
What are some examples of homologous structures?
Examples Of Homologous Structures. Many mammals have tails , which are one of the best examples of homologous structures. The tails of rats, cats, monkeys and many other mammals are extensions of the torso, being made out of vertebrae capable of flexing. Tails are used for balance in many animals, and to ward off insects.
Why did the jaws and teeth of the Characidae evolve?
The jaws and teeth of the Characidae evolved to adapt to food supplies within the new environment of the fish. Divergent evolution is also sometimes referred to as adaptive radiation, as the evolutionary trajectory seems to radiate outwards into different species.
How does DNA sequencing help identify homologous structures?
Two particular segments of DNA may have shared an ancestry if their DNA points to either a speciation event or a duplication event. If DNA sequencing shows that two species are closely related to one another and they have similar skeletal structures as well, it provides more evidence for the claims that the structures are homologous in nature.
What is primary homology?
Primary homology refers to the initial hypothesis a researcher makes based upon anatomical connections – homologous structures. Secondary homology is used in parsimony analysis, where an organism’s character state is considered to be homologous if it arises only once on a specific tree.
What is the cladistic approach to biology?
Cladistics is a specific approach to the biological classification of organisms, involving the grouping of organisms into clades based on their most recent common ancestor. Within cladistics, there are various types of homology. Primary homology refers to the initial hypothesis a researcher makes based upon anatomical connections – homologous structures. Secondary homology is used in parsimony analysis, where an organism’s character state is considered to be homologous if it arises only once on a specific tree.
How to tell if a muscle is homologous?
We determine whether a muscle is homologous by looking at which bones it attaches to and what function it performs. For example, the muscles in your arm, the biceps and triceps, help to flex and extend your arm. What about in cats? Or horses? Or other animals? Do they perform the same function? Do they attach to the same bones?
Why are bat bones different from whale bones?
The shape of a bat's bones are longer, skinnier and lighter, aiding in flight. The whale's phalanges are long and spread out , and when covered in skin and muscle, aid in swimming.
What does "similar and not identical" mean?
What this means, for example, is that all vertebrates share the commonality of having, say, upper and lower limbs. Those limbs are made up of similar bones and muscles between species.
What are homologous structures?
When these traits share a common evolutionary origin - meaning they develop from the same embryonic tissue in the fetus - and when they share a common ancestor, they are called homologous structures. In the case of the donkey and the horse, it's easy to see these two share a common ancestor; however, it's a little more difficult when looking at a whale versus a bat, isn't it? Well, in this case, way, way, way back in time, these two shared a common, four-legged ancestor, but over time, their pathways have diverged greatly, each adapting to totally different environments.
What are some examples of similar parts?
In some cases, those parts are similar in structure, function or both. For example, the bones in the legs of a horse and donkey are similar in both structure and function. Both animals use them primarily for walking and running.
Why do monkeys have longer arms than legs?
Many species of monkeys, in particular, have longer arms than legs, or some, like dogs and cats, have four limbs all of similar length. This is because the specific function of those limbs differs from humans. Monkeys do a lot more climbing than walking, while dogs and cats use all four limbs to walk and run.
What is the function of the arms and legs?
The general function is the same, even if the specific functions vary slightly. Think about it this way: all animals use their arms and legs to move; however, in some animals, they are used primarily for walking and running, while in others, they are used for swimming, climbing or even flying.
Homologous Structures Definition
Examples of Homologous Structures
- A Tale of Tails
Monkeys, cats, rats and other mammals have tails. In mammals, the tail is an extension of the torso, made of flexible vertebrae. Tails primarily function to ward off insects, but they can also serve as sources of balance for more aloof species, like cats. Humans possess a similar feature … - Eye Have a Light Bulb
Not all animals can see the way humans do. Deep sea creatures, like the chimera, live in an environment so dark, their eyes have not developed the sophisticated discriminatory skills that have, human eyes. Their visual cues come from light receptors near the front of their skull, and t…
Related Biology Terms
- Coccyx– The “tail bone” at the end of a mammal’s spinal column. The coccyx may be composed of fused vertebrae, or it may extend into a tail.
- Photoreceptor– A structure, usually a cell or small organ, which detects any light that falls on it.
- Cervical vertebrae– The bones that provide support for the upper spine.
Quiz
- 1. Homologous structures do not have to have the same function. Instead, they must: A. Link both species to a common ancestor. B. Look exactly the same. C. Move in the same direction. D.Follow similar growth patterns. 2. Only mammals can share homologous structures. A. True B.False 3. Human photoreceptors are different from chimera photoreceptors because: A. They a…
Different Forms of Evolution
Further Explanation of Homologous Structures
- In the study of evolutionary biology, homology refers to the existence of shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in a different classification unit or taxa. The term “homologous structures” refers specifically to similar structures found in different species that have a common ancestry or developmental origin. Note that homologous structuresdon’t have to perform the sa…
Examples of Homologous Structures
- Many mammals have tails, which are one of the best examples of homologous structures. The tails of rats, cats, monkeys and many other mammals are extensions of the torso, being made out of vertebrae capable of flexing. Tails are used for balance in many animals, and to ward off insects. While humans don’t have tails, we do have a tailbone. The tail...