Why is it important to know about cellular respiration?
All living things would eventually die, no matter the quality and amount of food. Cellular respiration is used to create usable energy from the foods that living things eat. It's important to know that the reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic, meaning they break down molecules into smaller ones.
What do u know about cellular respiration?
cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water.
What are three things that are important to remember about cellular respiration?
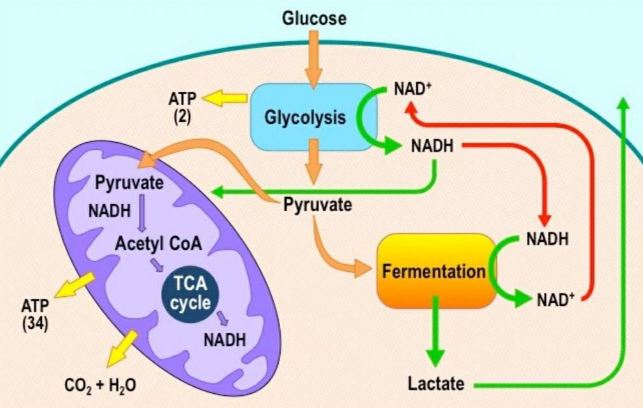
Cellular respiration has three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport. In glycolysis, glucose is split into two molecules. This process occurs in the cell's cytoplasm.
What are 3 details about cellular respiration?
The reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle), and electron transport.
What are the 4 steps of cellular respiration?
The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What would happen without cellular respiration?
Without the process of cellular respiration, there is no gaseous exchange and the cells, tissue and other organs die due to the lack of oxygen and by the accumulation of carbon dioxide within the cells and tissues. Also Explore: Where is oxygen used in cellular respiration?
What is the main product of cellular respiration?
The main product of cellular respiration is ATP; waste products include carbon dioxide and water.
What is cellular respiration examples?
An example of cellular respiration in plants is the use of photoautotrophic processes to obtain the glucose needed for cellular respiration. This means that plants can use the light energy they acquire from the sun to yield glucose and oxygen.
What is cellular respiration kid definition?
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to break down food molecules to get chemical energy for cell functions. Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of animals, plants, and fungi, and also in algae and other protists.
What is cellular respiration quizlet?
cellular respiration definition. The process of converting glucose into a form of energy (ATP) that is useable by cells.
What is a sentence for cellular respiration?
The complete process of ATP generation is called cellular respiration, and consists of three main stages. Paul knew that Uncle Edward was a biochemist, and a specialist in natural processes, such as photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for ene...
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for...
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where o...
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide deriv...
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H2O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH,...
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest rea...
What diseases can affect cellular respiration?
Several diseases can affect cellular respiration. Since cellular respiration is so vital to bodily functions, many of these diseases severely affec...
What are the most important facts to know about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions...
What is the process of breaking down glucose?
Glucose, derived from food, is broken down during cellular respiration to provide energy in the form of ATP and heat. Cellular respiration has three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport. In glycolysis, glucose is split into two molecules. This process occurs in the cell's cytoplasm.
How does NADH 2 produce ATP?
NADH and FADH 2 carry electrons on to the electron transport system. In the electron transport stage, ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation. In oxidative phosphorylation, enzymes oxidize nutrients resulting in the release of energy. This energy is use to convert ADP to ATP.
Where does glycolysis occur?
In glycolysis, glucose is split into two molecules. This process occurs in the cell's cytoplasm. The next stage of cellular respiration, the citric acid cycle, occurs in the matrix of eukaryotic cell mitochondria. In this stage, two ATP molecules along with high energy molecules (NADH and FADH 2) are produced.
How do plants get energy?
Plants capture this energy and convert it to organic molecules. Animals in turn, can gain this energy by eating plants or other animals. The energy that powers our cells is obtained from the foods we eat. The most efficient way for cells to harvest energy stored in food is through cellular respiration.
Which organelle is responsible for aerobic respiration?
Mitochondria are the cell organelles in which the aerobic phases of cellular respiration occur. 2. Glucose and _______ are consumed during cellular respiration. Glucose and oxygen are consumed during cellular respiration in order to obtain the stored energy (ATP) within the foods we eat.
Is glucose a product of cellular respiration?
Glucose is not a product of cellular respiration. During cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to yield the products water, carbon dioxide, and ATP. 4. In the presence of oxygen, the first stage of cellular respiration is ______ . glycolysis. citric acid cycle.
Is it okay to cheer up on cellular respiration?
Cheer up, it's okay. You didn't do as well as you hoped, but you can take this opportunity to delve deeper into cellular respiration. To increase your knowledge of this subject, study up on glycolysis, the Citric Acid Cycle, and mitochondria. Don't stop there.
What is the last step of acetyl CoA?
The acetyl CoA made in the last step combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. ATP, , and are produced, and carbon dioxide is released. Oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the cycle of carbon dioxide and NADH?
Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. ATP (or, in some cases, GTP), NADH, and FADH_2 are made, and carbon dioxide is released.
How do protons flow back into the matrix?
The protons flow back into the matrix through an enzyme called ATP synthase, making ATP. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water.
How is ATP produced?
Oxidative phosphorylation is powered by the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain , a series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
What is the process of converting glucose into pyruvate?
Glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. In the end, it gets converted into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon organic molecule. In these reactions, ATP is made, and is converted to . Pyruvate oxidation.
Which three stages of cellular respiration require oxygen?
The other three stages of cellular respiration—pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation— require oxygen in order to occur. Only oxidative phosphorylation uses oxygen directly, but the other two stages can't run without oxidative phosphorylation. Each stage of cellular respiration is covered in more detail in other ...
How does cellular respiration work?
Discover how cellular respiration transforms your food into energy usable by your cells. Cellular respiration releases stored energy in glucose molecules and converts it into a form of energy that can be used by cells. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen ...
How many NAD molecules are in the TCA cycle?
The products of a single turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NAD + molecules, which are reduced (through the process of adding hydrogen, H +) to the same number of NADH molecules, and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to a single FADH 2 molecule. These molecules go on to fuel the third stage of cellular respiration, ...
What is the process of cellular respiration in which glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water?
(For longer treatments of various aspects of cellular respiration, see tricarboxylic acid cycle and metabolism .) During the process of glycolysis in cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water.
What is the process of glycolysis?
Glycolysis (which is also known as the glycolytic pathway or the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway) is a sequence of 10 chemical reactions taking place in most cells that breaks down a glucose molecule into two pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules. Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during glycolysis is captured and stored in ATP. In addition, the compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is converted to NADH during this step ( see below ). Pyruvate molecules produced during glycolysis then enter the mitochondria, where they are each converted into a compound known as acetyl coenzyme A, which then enters the TCA cycle. (Some sources consider the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl coenzyme A as a distinct step, called pyruvate oxidation or the transition reaction, in the process of cellular respiration.)
What is the process by which food molecules are metabolized to obtain chemical?
algae: Cellular respiration. Cellular respiration in algae, as in all organisms, is the process by which food molecules are metabolized to obtain chemical...
What are the three main metabolic processes?
The overall process, however, can be distilled into three main metabolic stages or steps: glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation ...
What is the energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during
Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during glycolysis is captured and stored in ATP. In addition, the compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is converted to NADH during this step ( see below ).
What are the metabolic pathways of cellular respiration?
Other metabolic pathways of cellular respiration include oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate (which is when pyruvates are oxidized to acetyl-CoA and CO2) , Citric Acid Cycle (also known as the Kreb Cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation, with the latter producing water as a was te product.
What are the two types of respiration?
There are 2 kinds of reactions in Cellular Respiration: Aerobic Respiration. Anaerobic respiration. Aerobic Respiration is when the biological fuels (i.e., nutrients) are oxidized. In this case, it happens in the presence of an inorganic electron receptor (i.e. oxygen).
Why is cellular respiration important?
Cellular respiration is essential in creating biochemical energy by converting different kinds of nutrients into adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, ...
What happens during cellular respiration?
During cellular respiration, catabolic reactions occur, which is the process wherein large molecules are broken down. As nutrients like fatty acids, aminos, and sugars are broken down into ATP, their molecules release a large amount of biochemical energy.
What is the process of ATP?
Instead, it ferments. Fermentation is another biochemical process wherein energy is extracted from carbohydrates. Fermentation is the primary way for microorganisms like eukaryotes and bacteria to produce ATP. In higher organisms like mammals, fermentation usually occurs during strenuous activities like exercise.
Is cellular respiration a combustion reaction?
Although cellular respiration can be classified as a combustion reaction (thanks to its release of energy in the form of heat), because it occurs inside of cells, the energy is released in slow bursts, and only after a series of reactions and processes. As cellular respiration occurs, it produces CO2, carbon dioxide, as a waste product.
Who is Jerry from Daily Science Journal?
As our Editor-in-Chief, Jerry is one of the founding members of Daily Science Journal and has about a decade of experience working in the field of quantum physics. He graduated with a degree in Physics from Harvard (something he likes to remind people of on a daily basis) and got his Ph.D in Theoretical Physics, Astronomy, and Astrophysics from Charles University in Prague. When he’s not writing for Daily Science Journal, he lectures on Quantum Theory in both Charles University in Prague and in Cambridge University in England. When he’s not busy being a scientist, he helps his wife restore Chateaus in the French countryside.
What happens to lactic acid after exercise?
This process occurs in animal and bacterial cells. After strenuous exercise, this fermentation will occur in muscle cells causing fatigue and lactic acid build up.
How many ATP molecules does aerobic respiration produce?
ATP synthase will then allow a proton to move from the high to low concentration, and it will use the energy that it releases to create ATP. The electron transport chain produces 34 ATPs using this process of oxidative phosphorylation. Overall, aerobic cellular respiration will produce: 6CO2, 6H2O and 38 ATP molecules.
What is the molecule that forms in the Krebs cycle?
The acetyl coA molecule made in step two of cellular respiration will then enter into the Krebs Cycle. Acetyl-CoA will first be bonded to a four carbon molecule called oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate is made in the final step of the Krebs Cycle. When the two join together, they form citric acid, a six carbon molecule.
What happens after glycolysis?
In alcoholic fermentation, after glycolysis pyruvate is converted to carbon dioxide and ethanol. In this process, the NADH is recycled to NAD+ which allows for glycolysis to keep occurring. This fermentation occurs in yeast and certain bacteria which are used to create bread and wine.
Why are electron carriers important?
The electron carriers are important because they must carry the electrons to step four of the process, the electron transport chain. The Krebs Cycle produces 6 NADH, 2 FADH 2, 2 ATP, and 4CO 2 molecules. Most of the energy produced in this step is contained in the electron carriers.
How is ATP generated?
ATP is generated by the step wise release of energy using the folds of the cristae in the mitochondria. The first step of the electron chain is when one of the electron carriers that were created in the Krebs Cycle will release an electron.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process that cells use to release energy from chemical bonds in food. The cell can then use this energy for the essential processes of life that require energy. It is possible for cellular respiration to be aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic respiration is more favorable and produces more energy.
What is the process of converting one type of energy into another?
Photosynthesis uses water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to create glucose molecules, and releases oxygen as a by-product. Cellular respiration uses glucose molecules and oxygen to produce ATP molecules and carbon dioxide as the by-product. Photosynthesis involves conversion of one type of energy into another: light energy ...
How does cellular respiration work?
Living cells obtain the products of photosynthesis (sugar molecules) and undergo cellular respiration to produce ATP molecules. Some cells respire aerobically, using oxygen, while others undergo anaerobic respiration, without using oxygen. The process involves a set of chemical reactions to convert chemical energy from the glucose molecules into ATP molecules.
How do plants produce ATP?
Plant cells, after creating sugar molecules through photosynthesis, undergo cellular respiration to create ATP molecules. Animals obtain food molecules from plants and other organisms, and then undergo cellular respiration to obtain ATP molecules. All living organisms utilize these stored ATP molecules to carry out their metabolic processes.
What is the process of plant cells turning light energy into chemical energy?
Well, we're looking for good writers who want to spread the word. Get in touch with us and we'll talk... Let's Work Together! Photosynthesis is the process by which plant cells convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy, so as to create energy-rich carbohydrate molecules like glucose. Cellular respiration is the process ...
What is the process of obtaining energy from the environment?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are the life processes performed by most living organisms to obtain usable energy from nature. While photosynthesis is performed by most plants which can prepare their own food, most animals fulfill their energy requirements through cellular respiration.
What is the Calvin cycle?
Light-independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle) In this stage of photosynthesis, energy-containing sugar molecules are synthesized. The ATP and NADPH produced are used to fuel the reactions in this stage. Here, CO2 molecules are broken down and converted into sugars and other compounds.
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the cell. Photosynthesis utilizes sunlight to produce food molecules. Cellular respiration utilizes glucose molecules to obtain energy-storing ATP molecules. Photosynthesis uses water, sunlight, and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to create glucose molecules, ...