Is metallic bond stronger than hydrogen bond?
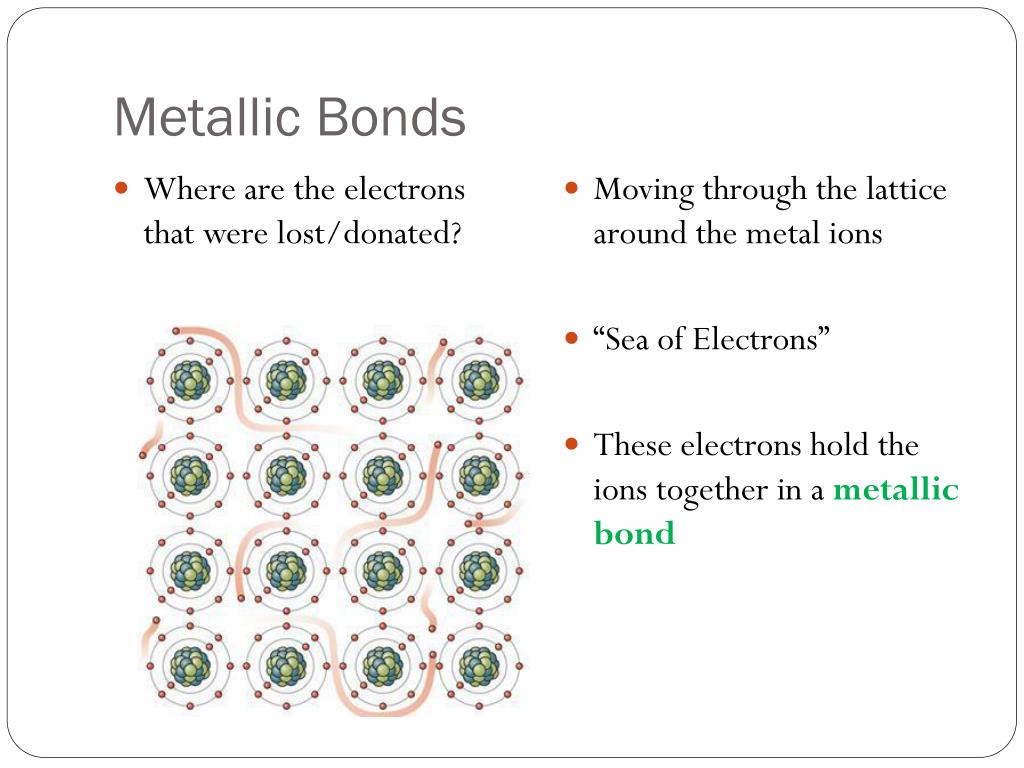
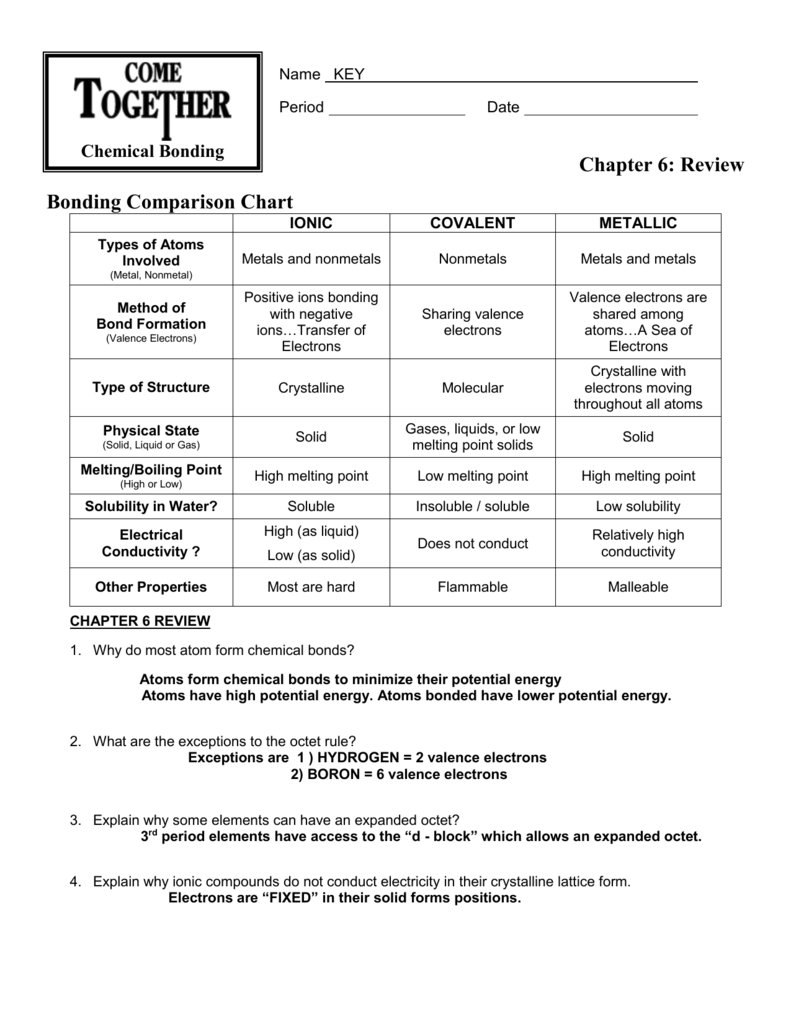
‘Metallic bond’ is a term used to describe the collective sharing of a sea of valence electrons between several positively charged metal ions. Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding and is responsible for several characteristic properties of metals such as their shiny lustre, their malleability, and their conductivities for heat and electricity.
What are facts for metallic bonding?
Nov 10, 2021 · Metallic bonds are formed when the charge is spread over a larger distance as compared to the size of single atoms in solids. They are so close to each other so valence electrons can be moved away from their atoms. A “sea” of free, delocalized electrons is formed surrounding a lattice of positively charged metal ions.
How to name metallic bonds?
What do metallic bonds create? Metallic bond , force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. The atoms that the electrons leave behind become positive ions, and the interaction between such ions and valence electrons gives rise to the cohesive or binding force that holds the metallic crystal together.
What are the characteristics of metallic bonding?
Jan 02, 2022 · Metallic Bonding is a force that binds atoms in a metallic substance together. The atoms that the electrons leave behind become positive ions, and their interaction with valence electrons produces the cohesive or binding force that binds the metallic crystal together.
What does metallic bonding create?
The strong attraction between atoms in metallic bonds makes metals strong and gives them high density, high melting point, high boiling point, and low volatility. There are exceptions. For example, mercury is a liquid under ordinary conditions and has a high vapor pressure.Sep 7, 2019
Do metallic bonds create compounds?
A metallic bond forms from delocalization of the valence electrons of metal atoms. Metallic compounds are usually shiny, malleable and good conductors of heat and electricity.
What happens in a metallic bond give an example?
Examples of Metallic Bond Sodium has a lone electron in its outermost orbital, i.e., the 3s orbital. When sodium atoms arrange together, the outermost electron of one atom shares space with the corresponding electron on a neighboring atom. As a result, a 3s molecular orbital is formed.
What do metallic bonds attract?
In a metallic bond, the valence electrons are delocalised, meaning that an atom's electrons do not stay around that one nucleus. In a metallic bond, the positive atomic nuclei (sometimes called the “atomic kernels”) are surrounded by a sea of delocalised electrons which are attracted to the nuclei (see figure below).
How are metallic bonds formed and what type of structure do they create?
Metallic bonds are formed when the charge is spread over a larger distance as compared to the size of single atoms in solids. Mostly, in the periodic table, left elements form metallic bonds, for example, zinc and copper. Because metals are solid, their atoms are tightly packed in a regular arrangement.
What do metallic compounds do?
It may be described as the sharing of free electrons among a structure of positively charged ions (cations). Metallic bonding accounts for many physical properties of metals, such as strength, ductility, thermal and electrical resistivity and conductivity, opacity, and luster.
How is metallic bond used in everyday life?
Metallic bonds can be used to make metal alloys. Metallic bonds are used via copper wires in a house in order to transfer electricity due to its conductive properties.Oct 20, 2021
How does metallic bonding affect the properties of metals?
Metallic bonds The metallic bond is the force of attraction between these free-moving (delocalised) electrons and positive metal ions . Metallic bonds are strong, so metals can maintain a regular structure and usually have high melting and boiling points. Metals are good conductors of electricity and heat.
What properties do compounds with metallic bonds have?
The properties of metals that are a consequence of metallic bonding include:Malleability.Ductility.High melting and boiling point.High electrical and thermal conductivity.Metallic lustre.
Is metallic bonding an attraction?
Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positive metal ions and a sea of delocalised electrons.
What is the Difference Between Metallic Bonding and Ionic Bonding?
Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between two chemical species. They arise from a difference in the electronegativities of the bonded a...
What are the Factors Affecting the Strength of Metallic Bonds?
The three factors are: The number of electrons delocalized from the metal; the greater the number of delocalized electrons, the stronger the bond C...
Which Properties of Metals can be explained by Metallic Bonding?
The properties of metals that are a consequence of metallic bonding include: Malleability Ductility High melting and boiling point High electrical...
What is a metallic bond and how does it form?
When the charge is dispersed across a wider distance than the size of single atoms in materials, metallic bonds occur. Left elements, like as zinc...
How strong is a metallic bond?
Metals have a high attraction force between their atoms. To overcome it, a lot of energy is required. Metals have high boiling points as a result,...
Q.1. How do metallic bond works?
Ans: In a metal, each kernel is surrounded by several valence electrons and vice versa. The valence electrons being very light, can move in the ele...
Q.2. Why does a metallic bond occur?
Ans: The metallic bond occurs due to the electrostatic force of attraction between delocalized electrons and kernels in the metal.
Q.3. In ionic bond and metallic bond, which is stronger?
Ans: The ionic bond is formed between cation and anion by the electrostatic force of attraction. But in metallic bonds, the electrostatic force of...
Q.4. What are the characteristics of metallic bonding?
Ans: Metallic bonds are non-directional, formed between the delocalized electrons and metal ions. This bond is observed only in solids.
Q.5. Which elements form a metallic bond?
Ans: Metals show the metallic bond. Metalloid and alloys are also shown metallic bonds.
Q.6. How do you identify a metallic bond?
Ans: In a metallic bond, a metal ion is surrounded by delocalized electrons. Hence, they can be identified by passing electricity.
Q.7. Why does metallic bonding decrease down the group?
Ans: As we move down the group, the size of metal increases due to an increase in the number of shells. Hence, the attraction between the Kernel an...
What is the bond between metals?
Therefore, free electrons act as the cohesive force which holds the metal atoms together and forms a metallic bond. The bond produced due to the combination of the electrostatic force ...
What are the factors that affect the strength of a metallic bond?
What are the Factors Affecting Metallic Bond? 1 The number of delocalised valence electron: The strength of the metallic bond increases with an increase in the number of delocalized valence electrons. 2 Size of the kernel: The strength of the metallic bond decreases with an increase in the size of the kernel.
What is the force of attraction between the positively charged kernels and the valence electron?
The force of attraction between the positively charged kernels and the valence electron gives rise to the formation of metallic bonds. Example: Sodium is a metal with the atomic number 11.
What are the electrons in the valence shell?
Electrons present in the valence shell are known as valence electrons which can be easily removed from the metal atom. The rest of the atom is positively charged and is called a kernel. A kernel is the combination of a nucleus and all the shell electrons except the valence shell electrons.
What is the bond between the electrons and the nuclei of a metal called?
The bond produced due to the combination of the electrostatic force of attraction between the electrons and the positive nuclei of metal atoms is called a metallic bond.
Why are meals malleable?
Meals are malleable (i.e., drawn into thin sheets) and ductile (i.e., drawn into thin wires) due to the valence electrons being very light can move in the electron sea from one position to the other in metal. 2. Metals have free electrons, which can transfer energy rapidly.
What is the sea of valence electrons?
A metal is regarded as the sea of valence electrons in which positively charged kernels are supposed to be dipped with the direct linkage between kernels and valence electrons. Each kernel is surrounded by the number of valence electrons and vice versa.
Why do metallic bonds occur?
Metallic bonding may be seen as a consequence of a material having many more delocalized energy states than it has delocalized electrons (electron deficiency), so localized unpaired electrons may become delocalized and mobile. The electrons can change energy states and move throughout a lattice in any direction.
How do metallic bonds work?
How Metallic Bonds Work. The outer energy levels of metal atoms (the s and p orbitals) overlap. At least one of the valence electrons participating in a metallic bond is not shared with a neighbor atom, nor is it lost to form an ion.
What type of bond is formed between positively charged atoms?
Updated September 07, 2019. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond formed between positively charged atoms in which the free electrons are shared among a lattice of cations. In contrast, covalent and ionic bonds form between two discrete atoms. Metallic bonding is the main type of chemical bond that forms between metal atoms.
Why are metals malleable?
Malleability: Metals are often malleable or capable of being molded or pounded into a shape, again because bonds between atoms readily break and reform. The binding force between metals is nondirectional, so drawing or shaping a metal is less likely to fracture it. Electrons in a crystal may be replaced by others.
What type of bond is found between metals?
Metallic bonding is the main type of chemical bond that forms between metal atoms. Metallic bonds are seen in pure metals and alloys and some metalloids. For example, graphene (an allotrope of carbon) exhibits two-dimensional metallic bonding. Metals, even pure ones, can form other types of chemical bonds between their atoms.
Why do electrons in a crystal change?
Further, because the electrons are free to move away from each other, working a metal doesn't force together like-charged ions, which could fracture a crystal through the strong repulsion. Metallic luster: Metals tend to be shiny or display metallic luster.
Why are metals good conductors?
Electrical conductivity: Most metals are excellent electrical conductors because the electrons in the electron sea are free to move and carry charge. Conductive nonmetals (such as graphite), molten ionic compounds, and aqueous ionic compounds conduct electricity for the same reason—electrons are free to move around.
Metallic Bonds
A metallic bond is a chemical bond in which a cloud of free moving valence electrons bonds to positively charged ions in a metal. It is defined as the sharing of free electrons among positively charged metal ions in a lattice.
Functioning of Metallic Bonds
Electrons are liberated from the atoms and delocalized throughout the metal, allowing them to travel freely. Interactions between ions and electrons are still there.These interactions produce a binding force that keeps the metallic crystal together.
Properties of Metallic bonds
Metals have various physical and chemical properties. These properties include the capacity to carry electricity and heat, a low ionisation energy, and a low electronegativity. Their physical characteristics include a glossy look, malleability and ductility. Metals have a crystalline structure but can easily be deformed.
Examples of Metallic Bonds
The metallic bonds are really common in metals. Few examples are mentioned below:
Things to Remember Based on Metallic Bonds
Metallic bond is a type of chemical bond that is formed by the electrostatic attraction of conduction electrons and positively charged metal ions.
Important Questions Based on Metallic Bonds
Ans: Metallic bonds develop when the charge is distributed across a greater distance than the size of individual atoms in solids. Left elements, like zinc and copper, make metallic bonds most of the time on the periodic table. Metal atoms are densely packed in a regular pattern because they are solid.
What is metallic bonding?
Metals can form compounds with non-metals by donating their outer shell electrons (see Ionic Bonding for more information). The metals form positive ions whilst the non-metals, which accept the electrons, form negative ions. However, if a metal is on its own it cannot donate electrons because there is no non-metal atom that can accept them.
Factors affecting the strength of metallic bonding
Some metals are much stronger than others. This is because of the difference in levels of electrostatic attraction within the different metals. There are two factors that affect the strength of the metal bond, and we’ll explore them now.
Properties of metals
Because of their unique arrangement of positive ions within a sea of delocalised electrons, metals have certain properties that differentiate them from ionic and covalent compounds. We use copper, for example, to make wires and pipes. We wouldn’t use ionic compounds like sodium chloride for this.
Alloys
We know that sodium is relatively soft. Pure iron is too. This causes problems when making useful products out of metals. Iron nails wouldn’t be of much use if you could easily bend and distort them. To make pure metals stronger, we turn them into alloys.
Metallic Bonding - Key takeaways
A metallic bond is the electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positive metal ions and a sea of delocalised electrons.
Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between a lattice of positive metal ions and a sea of delocalised electrons.
Metallic Bonds
In simple terms, a metallic bond is the way that metal atoms are kept together within a metal material. A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond similar to a covalent bond. Atoms in metals are held together by forces caused by the valence electrons.
How is a Metallic Bond Formed?
To describe metallic bond formation, the concept of a sea or cloud of electrons has been used to help visualize the delocalization of the electrons. Valence electrons of metals are only loosely bonded to their nuclei because they are shielded by the more inner energy levels of electrons.
Metallic Bond Examples
Some examples of metallic bonds include magnesium, sodium and aluminum. Magnesium has 2 valence electrons which are in the 3s energy level shell. With 2 valence electrons from each atom of magnesium, a medium level of electron density is achieved and also a medium strength of metallic bonding.
Characteristics of Metallic Bonds
The existence of metallic bonds is an important factor that gives metals their special and unique properties. Metals behave in certain ways and have a typical appearance that help us recognize such a material as a metal and help us describe metallic bonding.
Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds are bonds that occur between two metal atoms. Metallic bonds are used in many instances throughout our everyday lives. The questions below will test your knowledge on metallic bonds. Solutions are provided so that you can check your responses.
What is the bond between metals?
Metallic bond, force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance. Such a solid consists of closely packed atoms. In most cases, the outermost electron shell of each of the metal atoms overlaps with a large number of neighbouring atoms. As a consequence, the valence electrons continually move from one atom to another ...
What is the force that holds a metallic crystal together?
The atoms that the electrons leave behind become positive ions, and the interaction between such ions and valence electrons gives rise to the cohesive or binding force that holds the metallic crystal together. chemical bonding of crystals.
Why are valence electrons always free?
The valence electrons are always free to move when an electrical field is applied. The presence of the mobile valence electrons, as well as the nondirectionality of the binding force between metal ions, account for the malleability and ductility of most metals.
What are the characteristics of metals?
Many of the characteristic properties of metals are attributable to the non-localized or free-electron character of the valence electrons. This condition, for example, is responsible for the high electrical conductivity of metals. The valence electrons are always free to move when an electrical field is applied.
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
Do valence electrons move from one atom to another?
As a consequence, the valence electrons continually move from one atom to another and are not associated with any specific pair of atoms. In short, the valence electrons in metals, unlike those in covalently bonded substances, are nonlocalized, capable of wandering relatively freely throughout the entire crystal.
Characteristics of metallic bond
Metals can conduct heat through them. When one end of the metal is heated, mobile electrons absorb heat energy and move rapidly towards another end hence metal shows thermal conductivity.
Sodium (Na)
A sodium atom has one electron in its valence shell. When more than one sodium atom get arranged in a crystal lattice (bcc), Electrons present in the outermost shell share interstitial space with another sodium atom, molecular orbital get formed.
Aluminium (Al)
The aluminium atom has three electrons in its valence shell. When Aluminium atoms get arranged in a crystal lattice (fcc), electrons present in the outermost shell shares interstitial space with other aluminium atoms and molecular orbitals get formed. These electrons are delocalized in space lattice.
Magnesium (Mg)
The magnesium atom has two valence electrons. When magnesium atoms get arranged in a crystal lattice (hcp), electrons present in the valence shell shares space with other Magnesium atoms and molecular orbitals get formed. The electrons which are present in the valence shell are free to move in the crystal.
Copper (Cu)
One electron is present in the outermost shell of the copper atom. When more than one copper atom gets arranged in a crystal lattice (fcc), Electrons present in the outermost shell share interstitial space with another copper atom, molecular orbital get formed.
Iron (Fe)
The iron atom has eight electrons in its electron shell. When Iron atoms get arranged in a crystal lattice (bcc and fcc), electrons present in the outermost shell shares interstitial space with other iron atoms and molecular orbitals get formed. The delocalization of these electrons takes place in interstitial space.
Question 1. What is metallic bonding?
The attractive force is present between negatively charged mobile electrons and positively charged metallic ions. This force of attraction is used to hold the metal atoms together in the metallic crystal.
