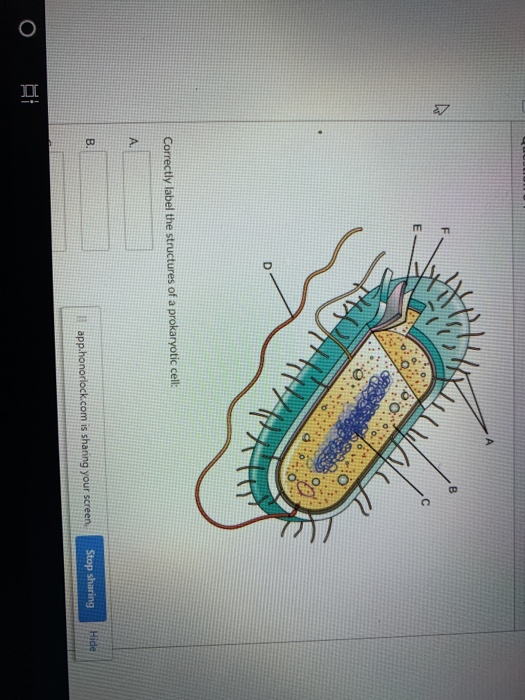
What kind of cell does not possess a true nucleus?
Monerans do not have a true nucleus, while protists have nuclei bound in their own nuclear membranes. Scientists classify organisms with true nuclei as eukaryotes and organisms without them as prokaryotes.
What structure would not be in prokaryotic cells?
The DNA of prokaryotic cells within one chromosome is composed of a single DNA strand. A vital protein, the histone protein, found in the chromosomes eukaryotes is not present in prokaryotic cells.
Does a prokaryotic contain a lack of nucleus?
Though they do not have a nucleus, prokaryotic cells still store their genes on chromosomes and still regulate their DNA. These cells carry out many of these DNA functions in a special spot called the nucleoid region. The nucleoid region contains proteins and typically just one circular chromosome.
Which type of cell does not contain a nucleus?
Red blood cells, while not considered to be prokaryotes, also do not have a nucleus. This helps them to maximize space inside the cell for haemoglobin, which is essential in the transport of oxygen. By comparison, white blood cells do contain a nucleus.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
How do Prokaryotic Cells Divide?
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Why are prokaryotic cells smaller than eukaryotic cells?
What is the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell?
What are the elements that make a prokaryotic cell a living organism?
See 4 more
About this website
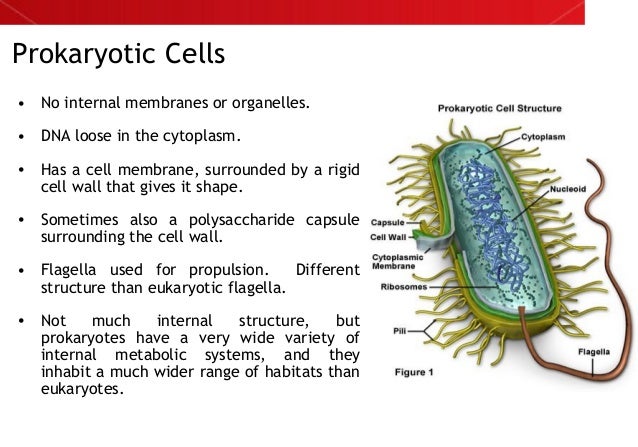
Does prokaryotic cells have a nucleus?
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups: the bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages. Most prokaryotes are small, single-celled organisms that have a relatively simple structure.
Does a prokaryotic cell have a nucleoid?
Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, have a free-floating chromosome that is usually circular and is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane. Instead, the DNA simply exists in a region of the cell called the nucleoid. Prokaryotic cells only have a small range of organelles, generally only a plasma membrane and ribosomes.
Does a prokaryotic cell have a nucleolus?
Prokaryotes, which do not have a nucleus, don't have nucleoli and build their ribosomes in the cytosol.
What do prokaryotic cells have instead of organelles?
Prokaryotic Cells They do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. In prokaryotic cells, the DNA, or genetic material, forms a single large circle that coils up on itself. The DNA is located in the main part of the cell. Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus.
What is only found in prokaryotic cells?
By definition, prokaryotes lack a membrane-bound nucleus to hold their chromosomes. Instead, the chromosome of a prokaryote is found in a part of the cytoplasm called a nucleoid. Prokaryotes generally have a single circular chromosome that occupies a region of the cytoplasm called a nucleoid.
What do prokaryotic cells contain?
All prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid region, DNA and RNA as their genetic material, ribosomes that make proteins, and cytosol that contains a cytoskeleton that organizes cellular materials.
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes are always unicellular, while eukaryotes are often multi-celled organisms. Additionally, eukaryotic cells are more than 100 to 10,000 times larger than prokaryotic cells and are much more complex. The DNA in eukaryotes is stored within the nucleus, while DNA is stored in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes.
What is difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic?
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information.
Do all prokaryotic cells have mitochondria?
Mitochondria, for example, are organelles that provide eukaryotes with most of their energy by producing energy-rich molecules called ATP. Prokaryotes lack mitochondria and instead produce their ATP on their cell surface membrane.
What organelles are found only in prokaryotic cells?
The only cell organelle seen in a prokaryotic cell is the ribosome. Ribosomes in prokaryotes are of the 70s type.
What is found in prokaryotic cells but not eukaryotic?
Which structure could be found in a prokaryotic cell? Explanation: Prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells in that they lack any membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus. Instead, prokaryotic cells simply have an outer plasma membrane, DNA nucleoid structure, and ribosomes.
What organelles do prokaryotic cells have?
Prokaryotic Cells do not have any membrane bound organelles, so no nucleus, mitochondria, nor chloroplasts. They have a cell wall, cell membrane, nucleoid, ribosomes, and cytoplasm.
Is nucleoid prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
prokaryoteThe nucleoid (meaning nucleus-like) is an irregularly-shaped region within the cell of a prokaryote that contains all or most of the genetic material. In contrast to the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, it is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
How many nucleoid are in a prokaryotic cell?
Instead, their genetic material can be found in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. A prokaryotic cell typically has only a single, coiled, circular chromosome. However, there are a few prokaryotes that have more than one—Vibrio cholerae, the bacterium that causes cholera, has two circular chromosomes.
Does a eukaryotic cell have a nucleoid region?
They have genetic material (DNA) but it is in a nucleoid region. The eukaryotes have their DNA in a nucleus that is enclosed by a membranous nuclear envelope. The nucleus of the eukaryotes is surrounded in the cell by the cytoplasm. The organelles are located in the cytoplasm.
Where are Nucleoids found?
The nucleoid is a chromatin-dense area within the cytoplasm and contains the bacterial DNA, associated proteins and RNA that are responsible for controlling the bacteria's activity and reproduction (Fig.
What are the 3 main features of a prokaryotic cell?
Three features of a prokaryotic cell are: 1. the lack of a nucleus, 2. the presence of a cell wall, 3. a single, circular chromosome.
Does a prokaryotic cell lack DNA?
Prokaryotic cells do not lack DNA. They usually have a single, circular chromosome composed of DNA and special proteins. This chromosome is contai...
What are 5 differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
1. Prokaryotic cells do not contain internal membranes. 2. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. 3. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound or...
Why do prokaryotes not have a nucleus?
Scientists believe that prokaryotes do not have a nucleus because they evolved prior to the development of more complex cells with internal membran...
Is the nucleus prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
The nucleus is a feature of eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes are defined by their lack of a nucleus. However, recent observations have found that a fe...
Prokaryotic cell | definition of prokaryotic cell by Medical dictionary
prokaryotic cell: The form of cell composing many primitive unicellular organisms, such as bacteria. Prokaryotic cells do not have nuclei, which are partitioned by an intracellular membrane; instead the DNA forms one main coil in the cell cytoplasm. See also: cell
What does pro mean in eukaryotes?
By contrast, the word eukaryote stems from eu (true) and karyon (kernel), indicating that these cells have true nuclei.
Which chromosomes are not associated with proteins?
Prokaryotic chromosomes are not associated with proteins, while eukaryotic chromosomes are associated with proteins.
What is the nucleoid region?
The nucleoid region contains proteins and typically just one circular chromosome. Unlike the nucleus in eukaryotic cells, there is no distinct boundary (called a nuclear envelope) around the nucleoid region of a prokaryotic cell.
What is the process of making DNA compact?
Prokaryotic cells face a very similar problem: they have a lot of DNA to fit into a small space. The process of making DNA compact is called supercoiling. In eukaryotic cells, supercoiling takes place when the linear DNA is wrapped or twirled on protein structures called histones.
Where are ribosomes found?
Ribosomes, where the cell's proteins are built, are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, though they may be different in size and other features. The nucleus of a eukaryotic cell contains a specialized region called the nucleolus, and that's where ribosomes are assembled and then shipped out to the cytoplasm.
Which region of the cell stores genes?
Nucleoid Region. Though they do not have a nucleus, prokaryotic cells still store their genes on chromosomes and still regulate their DNA. These cells carry out many of these DNA functions in a special spot called the nucleoid region. The nucleoid region contains proteins and typically just one circular chromosome.
Where is DNA carried out?
Rather, many of the DNA functions necessary for these units of life are carried out in the nucleoid region. Additionally, ribosomes are built directly in cytoplasm, and supercoiling DNA into chromosomes is done slightly differently to meet the needs of the circular chromosome.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Definition. A prokaryotic cell is a type of cell that does not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Organisms within the domains Bacteria and Archaea are based on the prokaryotic cell, while all other forms of life are eukaryotic. However, organisms with prokaryotic cells are very abundant and make up much of Earth’s biomass.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
The difference between the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell is simple. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane and other membrane-bound organelles that perform specific functions in the cell. These membranes form the endomembrane system, which creates a series of specialized chambers within eukaryotic organisms that can complete a diverse range of tasks. By contrast, a prokaryotic cell only has a cellular membrane with no membranes extending on the inside of the cell.
How do Prokaryotic Cells Divide?
Prokaryotic cells divide through the process of binary fission. Unlike mitosis, this process does not involve the condensation of DNA or the duplication of organelles. Prokaryotic cells have only a small amount of DNA, which is not stored in complex chromosomes. Further, there are no organelles so there is nothing to divide.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
While this makes the cells slightly less efficient, prokaryotic cells still have a remarkable reproductive capacity. A prokaryote reproduces through binary fission, a process that simply splits duplicated DNA into separate cells. Without any organelles or complex chromosomes to reproduce, most prokaryotic cells can divide every 24 hours, or even faster with an adequate supply of food.
Why are prokaryotic cells smaller than eukaryotic cells?
In general, a prokaryotic cell is smaller because it has less DNA to create the proteins needed to make an ultra-efficient membrane. So, the cells reach a size where they can no longer import the number of nutrients they need for the volume of cytosol they contain. This is known as a surface-area-to-volume ratio limit. However, bacteria are much larger than viruses because they are actively carrying out the biochemical reactions of life within their cells.
What is the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell?
Like eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm, a gel-like substance that makes up the “filling” of the cell, and a cytoskeleton that holds components of the cell in place. Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes, which are organelles that produce proteins, and vacuoles, small spaces in cells that store nutrients and help eliminate waste.
What are the elements that make a prokaryotic cell a living organism?
This membrane allows them to create a specific environment within the cytosol that allows biochemical reactions to take place. Second, these cells house both loose DNA and ribosomes.
