What do fungi eat?
There are many different types of fungi that eat different things, but common to them all is that they are important decomposers, playing a vital role in the recycling of nutrients in ecosystems. Fungi have a very broad diet consisting mostly of dead plant and animal matter, simple sugars from fruits, and even radioactivity!
How do fungi help plants grow?
are very effective at extracting nutrients and water from the soil and mulch. One type of fungi, called mycorrhizal fungi, physically attaches to the roots of woody plants and extend the ‘reach’ of the plant’s roots, mining for water and nutrients in the soil that plants have a hard time accessing with their own roots alone.
How do woody plants and fungi feed each other?
The fungi feed the woody plants with the nutrients and water that it has extracted from the soil, and the woody plants feed the fungi food sugars it has produced via photosynthesis, which the fungi cannot produce itself. Fungi do not photosynthesize, this is one of the major characteristics that distinguish fungi from plants.
What are soil bacteria and soil fungi?
Soil bacteria and soil fungi are the start of the soil food web that supports other soil organisms and the functions of a healthy soil. Diverse populations of soil bacteria and fungi can suppress root diseases.

How do fungi feed in soil?
You can encourage fungi in your soil by providing food (organic matter), water and minimal disturbance of the soil. Growing pastures and crops that support mycorrhizal fungi allow fungi to increase in the soil.
What does fungi feed on?
Most fungi are saprophytes, feeding on dead or decaying material. This helps to remove leaf litter and other debris that would otherwise accumulate on the ground. Nutrients absorbed by the fungus then become available for other organisms which may eat fungi.
What do fungi do for soil?
Along with bacteria, fungi are important as decomposers in the soil food web. They convert hard-to-digest organic material into forms that other organisms can use. Fungal hyphae physically bind soil particles together, creating stable aggregates that help increase water infiltration and soil water holding capacity.
What do mycorrhizal fungi eat?
The mycorrhizal fungi want to eat too, and they prefer the sugars and fats that plants exude from their roots. So, in exchange for nutrients, mycorrhizae receive plant root exudates that are loaded with carbon (produced from CO2 pulled from the atmosphere during photosynthesis).
What nutrients do fungi need?
Chemical elements such as phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, magnesium, and small quantities of iron, zinc, manganese, and copper are needed by most fungi for vigorous growth; elements such as calcium, molybdenum, and gallium are required by at least some species.
What do fungi need to survive?
Like us, fungi can only live and grow if they have food, water and oxygen (O2) from the air – but fungi don't chew food, drink water or breathe air. Instead, fungi grow as masses of narrow branched threads called hyphae.
What kills soil fungus?
Baking Soda The most effective treatment calls for four teaspoons per gallon of water, mixed thoroughly. Once mixed, saturate the soil with the solution. You can also sprinkle the baking soda directly on the soil where you see fungal growth but do so sparingly.
How long does fungus live in soil?
Depends on environmental conditions and maintenance. AMF from inocula can survive and persist in plant roots for at least 2 years after introduction. But AMF without host plant can not stay for long time.
What are two fungi food sources?
Mushrooms and yeast, are the different food sources obtained from the fungus.
How do you add mycorrhizae to soil naturally?
How to Use Mycorrhizae in the GardenOne option is to sprinkle granular mycorrhizae directly on the root ball or in the planting hole when transplanting new plants into the garden or into a larger container. ... Another awesome way to add mycorrhizae to soil is to mix up a water-soluble mycorrhizae product and water it in.More items...•
How can I improve mycorrhizal fungi?
The fungi colonize the plant roots, helping with uptake of water and minerals. It is well known that plants in healthy soils with good mycorrhizal colonization are much healthier. You can promote this by appropriate irrigation, minimizing soil disturbance by not tilling, and limiting fertilizer, especially phosphorus.
How long does mycorrhizal fungi last?
Mycorrhizae are hardier than you might think, which has helped them to survive the last 450 million years. There are some conditions to avoid: High temperatures of 140 degrees F and above can reduce the viability of the mycorrhizal propagules.
Does fungi feed on bacteria?
The fungus may actually eat the bacteria, although it's not clear how. “We think digestive enzymes are involved,” she says. “The interaction between fungi and bacteria certainly deserves further study,” says Duur Aanen at Wageningen University and Research Centre in The Netherlands.
Do fungi feed on living things?
They feed on living hosts. As parasites, fungi live in or on other organisms and get their nutrients from their host. Parasitic fungi use enzymes to break down living tissue, which may causes illness in the host. Disease-causing fungi are parasitic.
How do fungi get their energy?
All fungi are heterotrophic, which means that they get the energy they need to live from other organisms. Like animals, fungi extract the energy stored in the bonds of organic compounds such as sugar and protein from living or dead organisms. Many of these compounds can also be recycled for further use.
What are two fungi food sources?
Mushrooms and yeast, are the different food sources obtained from the fungus.
THE LIVING SOIL: FUNGI
Fungi are microscopic cells that usually grow as long threads or strands called hyphae, which push their way between soil particles, roots, and rocks. Hyphae are usually only several thousandths of an inch (a few micrometers) in diameter. A single hyphae can span in length from a few cells to many yards.
Where Are Fungi?
Saprophytic fungi are commonly active around woody plant residue. Fungal hyphae have advantages over bacteria in some soil environments. Under dry conditions, fungi can bridge gaps between pockets of moisture and continue to survive and grow, even when soil moisture is too low for most bacteria to be active.
Mycorrhizal Fungi in Agriculture
Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association between fungi and plant roots and is unlike either fungi or roots alone. Most trees and agricultural crops depend on or benefit substantially from mycorrhizae. The exceptions are many members of the Cruciferae family (e.g., broccoli, mustard), and the Chenopodiaceae family (e.g.
What Do Different Types of Fungi Eat?
Fungi can either be saprotrophic, parasitic, or mutualistic. Each eats a different type of food.
How Does What Fungi Eat Impact Other Species?
While some bacteria are parasitic, others are essential decomposers in their environments.
How do fungi get their nutrition?
Fungi get their nutrition by absorbing organic compounds from the environment. Fungi are heterotrophic: they rely solely on carbon obtained from other organisms for their metabolism and nutrition. Fungi have evolved in a way that allows many of them to use a large variety of organic substrates for growth, including simple compounds such as nitrate, ammonia, acetate, or ethanol. Their mode of nutrition defines the role of fungi in their environment.
What is the role of fungi in the woods?
Shown here are fungi sprouting from dead material in the woods. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling and exchange.
What is the relationship between a fungus and the roots of a plant?
A mycorrhiza (Greek for "fungus roots") is a symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a plant. In a mycorrhizal association, the fungus may colonize the roots of a host plant by either growing directly into the root cells, or by growing around the root cells. This association provides the fungus with relatively constant and direct access to glucose, which the plant produces by photosynthesis. The mycelia of the fungi increase the surface area of the plant’s root system. The larger surface area improves water and mineral nutrient absorption from the soil.
What is the role of saprotrophs in the ecosystem?
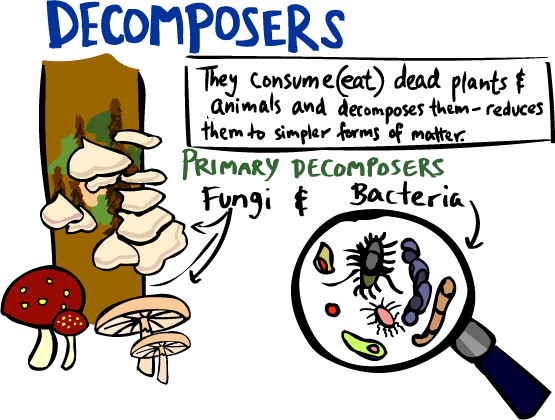
Saprotrophic fungi play very important roles as recyclers in ecosystem energy flow and biogeochemical cycles. Saprophytic fungi, such as shiitake ( Lentinula edodes) and oyster mushrooms ( Pleurotus ostreatus ), decompose dead plant and animal tissue by releasing enzymes from hyphal tips. In this way they recycle organic materials back into the surrounding environment. Because of these abilities, fungi are the primary decomposers in forests (see Figure below ).
What are the primary decomposers of organic matter in terrestrial ecosystems?
Fungi , along with bacteria that are found in soil, are the primary decomposers of organic matter in terrestrial ecosystems.
How do hyphae absorb nutrients?
These adaptations are also complemented by the release of hydrolytic enzymes that break down large organic molecules such as polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids into smaller molecules. These molecules are then absorbed as nutrients into the fungal cells. One enzyme that is secreted by fungi is cellulase, which breaks down the polysaccharide cellulose. Cellulose is a major component of plant cell walls. In some cases, fungi have developed specialized structures for nutrient uptake from living hosts, which penetrate into the host cells for nutrient uptake by the fungus.
Do fungi feed on other organisms?
They feed on living hosts. As parasites, fungi live in or on other organisms and get their nutrients from their host. Parasitic fungi use enzymes to break down living tissue, which may causes illness in the host. Disease-causing fungi are parasitic. Recall that parasitism is a type of symbiotic relationship between organisms of different species in which one, the parasite, benefits from a close association with the other, the host, which is harmed.
How do fungi feed woody plants?
The fungi feed the woody plants with the nutrients and water that it has extracted from the soil , and the woody plants feed the fungi food sugars it has produced via photosynthesis, which the fungi cannot produce itself.
What are beneficial fungi?
Beneficial fungi are certain species of fungi that protect our plants from disease by: 1 Out-competing disease organisms 2 Creating a healthy soil biology 3 Offering direct protection to our plants by producing anti-pathogens 4 Providing nutrients and water directly to the plants for better plant health
What kind of mulch should I use for woody plants?
The ideal soil for woody plants contains beneficial fungi and these ‘fun guys’ thrive with the addition of ramial wood chip mulches. This type of mulch has the optimum balance of carbon to nitrogen and higher nutrient content than other wood chips. This optimum balance is due in large part to the greater ratio of cambium and recently living cells vs. old dead wood cells. It makes sense that using wood chips made with more live tissue or recently-living tissue will have more nutrient value than chips made from older wood, which is mostly carbon.
What kind of wood chips are good for mulch?
Wood chips make a good mulch for woody plants. To go a step further, you want to use ramial wood chips, which are wood chips made from the outer reaches of a deciduous tree. That means the smaller branches, including the leaves if possible, and not so much the trunk and thicker branches (the rule of thumb is nothing more than 2.5 inches thick).
Why do we need a ramial soil?
It’s because we want a fungal dominant soil. We want a soil that’s full of the beneficial fungi that help woody plants grow vibrantly and resiliently. The term ramial is based on a french word, rameal, which means ‘related to the small branch’.
How to kill fungi in mulch?
One way, the crude method, is to dig into your mulch/soil interface and see if it’s populated by white strands. These are the hyphae strands, the mycelium, or ‘body’ of the fungi. Although, I wouldn’t recommend digging stuff up if you don’t have to. It disturbs and kills the fungi to expose it and breaks its hyphae connections. Don’t worry though, if the conditions are right and the soil is well populated, it will undoubtedly recover.
How do fungi connect to plants?
The connection between the fungi and the plant’s roots is intracellular. There is chemical communication going on along with the nutrient exchange. The relationship is symbiotic and has evolved over thousands of years. It has been shown that it goes further than one fungus and one plant; that the fungi connect nearby plants to each other as well. The chemical communication goes on between multiple plants via the fungi.
How can I encourage fungi in my soil?
You can encourage fungi in your soil by providing food (organic matter), water and minimal disturbance of the soil. Growing pastures and crops that support mycorrhizal fungi allow fungi to increase in the soil.
What is soil fungus?
Soil fungi are microscopic plant-like cells that can be single celled (e.g. yeast) or grow in long threadlike structures or hyphae that make a mass called mycelium. They can be symbiotic with plant roots (figure 1). Fungi are generally not as dependent on specific plant species as some bacteria, and populations are slower to develop.
What can suppress root diseases?
Diverse populations of soil bacteria and fungi can suppress root diseases.
How many bacteria are there in the soil?
Bacteria are the most abundant microbes in the soil. They are single celled organisms, and there can be billions of bacteria in a single gram of soil. Populations of bacteria can boom or bust in the space of a few days in response to changes in soil moisture, soil temperature or carbon substrate. Some bacteria species are very fragile and may be killed by slight changes in the soil environment. Others are extremely tough, able to withstand severe heat, cold or drying. Some bacteria are dependent on specific plant species.
Why are bacteria low in soil?
If populations of soil bacteria are low, it is probably because conditions are unfavourable. Effective approaches (that have multiple benefits) to support healthy soil bacteria are to address problems of acidity and compaction, ensure good ground cover and build organic matter.
What is the role of decomposers in soil?
Decomposers: are essential for breaking down woody organic matter, They play an important role in immobilising and retaining nutrients in the soil. The organic acids they produce help create soil organic matter that is resistant to degradation.
Which plant group does not form associations with mycorrhizal fungi?
Plant groups that do not form associations with mycorrhizal fungi are the Cruciferae family (eg mustard, canola, broccoli), Chenopodiaceae (eg spinach, beets, saltbush) and Proteaceae (banksia, macadamia). When these plants are included in a rotation, fungi numbers drop. A bare fallow has the same effect.