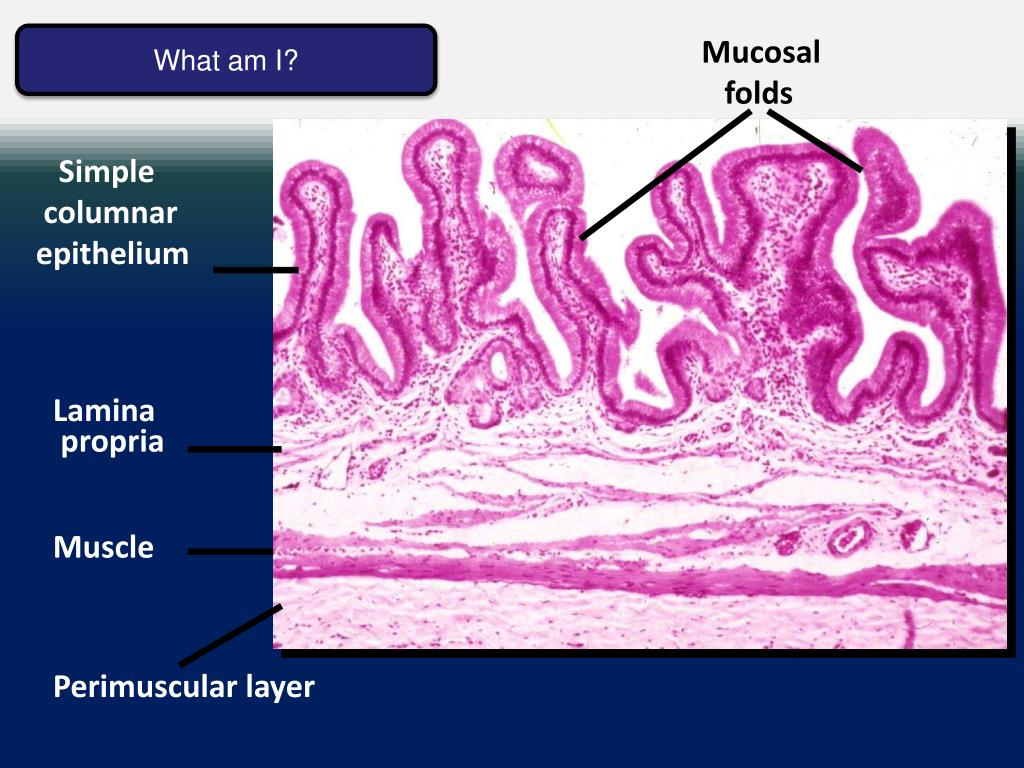
What are submucosal glands?
Submucosal glands are major secretory structures that reside in the interstitium beneath the cartilaginous airways of many mammalian species (Jeffery, 1983) and that have a continuous epithelium with the surface airway.
What is the function of the acini and submucosal glands?
The acini empty into little tubes (tubules) that lead to a reservoir (collecting duct) that has a portal through the skin (mucosa) that can open and close allowing the mucus into the main tube. The submucosal glands are a companion to goblet cells which also produce mucus, and are found lining the same tubes.
What is the function of the mucosa glands?
These glands secrete mucus to facilitate the movement of particles along the body's various tubes, such as the throat and intestines. The mucosa is the lining of the tubes, like a kind of skin.
What is the function of the submucosa?
The submucosa is the tissue that connects the mucosa to the muscle outside the tube. The glands themselves are quite complex. The mucus factory is at the bottom, in the submucosa, it is composed of many little sacs (acini) where the mucus originates. Each sac (acinus) has one end that can open and close (dilate) to allow the mucus out.

Which glands are found in submucosa?
Brunner's glands are located in the submucosa of the duodenum. They secrete an alkaline fluid containing mucin, which protects the mucosa from the acidic stomach contents entering the duodenum.
Which glands secrete mucous?
Cells which are specialized to secrete mucus are called mucous cells. Examples in the GI system include secretory cells of the salivary glands, esophageal glands, stomach surface, pyloric glands, and Brunner's glands of the duodenum. These cells are typically organized into tubular secretory units.
Are submucosal glands in Colon?
In the small intestine villi and intestinal crypts in the mucosa are common to all regions, whereas submucosal glands are found only in the duodenum.
What gland secretes most saliva?
The submandibular gland produces the most saliva (approximately 70%) in the unstimulated state; however, during salivary gland stimulation, the parotid gland produces more than 50% of the saliva [3].
What are the three glands that secrete saliva?
You have three major types of salivary glands, including your parotid glands, submandibular gland and sublingual gland.
What is the function of the submucosa?
The submucosa is a connective tissue layer deep to and supporting the mucosa. Examples: The substance of the submucosa is ordinary loose connective tissue. It allows the mucosa to move flexibly during peristalsis.
What is the function of the submucosa in the small intestine?
It is responsible for gut movement, or peristalsis. It usually has two distinct layers of smooth muscle: circular and longitudinal. The submucosa is the layer of dense, irregular connective tissue or loose connective tissue that supports the mucosa, as well as joins the mucosa to the bulk of underlying smooth muscle.
Where is the submucosal gland located?
Seromucinous submucosal glands are found throughout the larynx, with those on the superior surface of the epiglottis being largely mucous in nature (Lewis, 1991). A large collection of glands occurs in the submucosa of the ventral wall between the epiglottis and the ventral diverticulum or pouch.
Where are mucous secreting glands found?
The submucosal glands are a companion to goblet cells which also produce mucus, and are found lining the same tubes. In the upper respiratory system of mammals there are submucosal glands in the airways, notably in the sinuses, the trachea and the bronchial tubes. In the visual systems of mammals.
Which glands are serous and mucous?
Salivary glands are made up of secretory acini (acini - means a rounded secretory unit) and ducts. There are two types of secretions - serous and mucous. The acini can either be serous, mucous, or a mixture of serous and mucous. A serous acinus secretes proteins in an isotonic watery fluid.
What is the name of the gland that secretes mucus?
Submucosal glands. Submucosal glands can refer to various racemose exocrine glands of the mucous type. These glands secrete mucus to facilitate the movement of particles along the body's various tubes, such as the throat and intestines. The mucosa is the lining of the tubes, like a kind of skin.
Which glands produce mucus?
The submucosal glands are a companion to goblet cells which also produce mucus, and are found lining the same tubes.
Where is the mucosa located?
The mucosa is the lining of the tubes, like a kind of skin. Submucosal means that the actual gland resides in the connecting tissue below the mucosa. The submucosa is the tissue that connects the mucosa to the muscle outside the tube. The glands themselves are quite complex. The mucus factory is at the bottom, in the submucosa, ...
What glands are in the throat?
In the throat there are the esophageal glands, the submucosal glands of the esophagus. For the intestine there are Brunner's glands, the submucosal glands of the duodenum.
What is the function of the esophageal submucosal gland?
A three-tiered defense system exists in the esophagus, which serves a dual purpose of both limiting the degree of gastroesophageal reflux and minimizing the risk of acid-induced mucosal injury.
What are the mechanisms involved in esophageal clearance?
Mechanisms involved in esophageal clearance include gravity and esophageal peristalsis, which remove volume, and secretions from swallowed saliva and esophageal submucosal glands, which neutralize acid.
Which agonist blocks the breakdown of endogenously released acetylcholine?
4) the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor edrophonium, an indirect cholinergic agonist which blocks the breakdown of endogenously released acetylcholine, also stimulated esophageal alkaline secretion.
Does the esophagus secrete bicarbonate?
The human esophagus has been shown to secrete bicarbonate in amounts adequate for the effective buffering of luminal acid [ 1, 2 ]; yet little is known about the regulation of this secretion. Brown et al., however, reported that like the opossum esophagus [ 3 ], the human esophagus can be stimulated to secrete bicarbonate as much as 32 fold by acidification of the esophagus with HCl [ 4 ]. These authors suggested that this could perhaps serve as an autoregulatory mechanism for protection against refluxed gastric acid especially in the nocturnal period when saliva is not delivered into the esophagus. In addition, Brown et al. have suggested a role for the autonomic nervous system in modulating bicarbonate secretion, showing sensitivity to cholinergic and non cholinergic vagal activity. They also showed that cold-induced pain activated sympathetic reflexes and reduced bicarbonate secretion [ 5 ]. Although little else on the regulation of human esophageal bicarbonate secretion is known, insights into this secretion have been obtained from studies in the opossum esophagus. First, the importance of submucosal glands as a likely source in this secretion was suggested by Hamilton and Orlando from their work with the opossum and rabbit esophagus [ 3 ]. They showed that like the human as shown in Figure 1, the opossum esophagus with its extensive submucosal glands could secrete bicarbonate [ 3 ]. In contrast, the rabbit esophagus, lacking submucosal glands, could not secrete bicarbonate. Because of the importance of the glands in secretion, the opossum has continued to be used as an experimental model for studies of regulation of secretion. The technique used is recirculation through the cannulated esophagus of an opossum anesthetized with diazepam: pentobarbital of a CO2-free N2-bubbled unbuffered saline solution maintained by automatic pH stat at pH 7.4 [ 3 ]. The addition of HCl to the perfusate to maintain pH at 7.4 permits calculation of the amount of alkaline secretion.
Does epinephrine affect basal alkaline secretion?
The administration of drugs with adrenergic agonist or antagonist properties had no significant effect on basal esophageal alkaline secretion in the opossum and the effect was the same whether selective a or b receptor agonists or antagonists were used [ 6 ]. Neither epinephrine with a and b receptor stimulating properties, nor methoxamine with a alone, nor isoproterenol with b alone were able to alter secretion. A similar lack of effect was seen with the a-adrenergic receptor antagonist, phentolamine and the b-adrenergic receptor antagonist, propanalol.
Is the opossum esophagus under autonomic control?
Basal alkaline secretion in the opossum esophagus is not thought to be under autonomic nervous system control because it is unaffected by pharmacologic agents that inhibit adrenergic or cholinergic activity [ 6 ]. However, endogenous release of acetylcholine (presumably from parasympathetic nervous fibers) can stimulate alkaline secretion through activation of cholinergic M1 receptors [ 6 ]. This was concluded from the following observations:
Does vagal stimulation affect esophageal secretion?
These experiments showed that electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve increased esophageal secretion which is in part mediated by activation of nicotinic receptors without involvement of cholinergic muscarinic receptors or receptors for bombesin [ 7 ]. These conclusions were reached based on the following observations by this group: