The Rotatores are:
- The deepest muscles in the transversospinalis group and have the shortest fascicles, spanning one (short rotatores) to two segments (long rotatores). ...
- Part of the deep, core muscle groups of the body which assist in powering all limb movement, having a role as dynamic stabilisers [2].
- Proprioceptive role, as they are highly rich in muscle spindles, sensing the positioning of each spinal motion [3].
What is the function of rotatores?
Rotatores muscles are a set of short muscles located laterally along the vertebral column, attaching between the transverse and spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae. As a result, the rotatores function as stabilizers, extensors and rotators of the spine.
Where are The Rotatores muscles located in the body?
The rotatores muscles are a group of 22 small, four-sided muscles found between the thoracic vertebrae on both sides of the spinal column. (I.e. there are 11 pairs of these muscles.) Each rotatores muscle originates from the traverse process of a thoracic vertebra.
How are rotatores supplied by the spinal nerves?
Innervation: Rotatores are supplied by medial branches of dorsal rami of associated spinal nerves [1] Rotatores muscles are identified as thoracic rotators and back extensors in many texts but this action has not been often disputed examples below: The rotatores are more likely stabilizers of the spinal column.
What are rotatores breves and Longi muscles?
Rotatores breves and longi muscles (Musculi rotatores breves et longi) Rotatores muscles are a set of short muscles located laterally along the vertebral column, attaching between the transverse and spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae. As a result, the rotatores function as stabilizers, extensors and rotators of the spine.
What do the Multifidi and rotatores do?
The entire intrinsic layer of the back, including the rotatores (and, as discussed above, the multifidus), produces spinal extension, and assists with lateral flexion (side bending) and rotation (twisting).
Where is the rotatores muscle?
The rotatores are the deepest muscles in the transversospinalis group, the deep layer of the intrinsic back muscles. These muscles lie between the transverse and spinous processes and are grouped by length of the fascicles, as well as region covered. The groups are rotatores, multifidus, and semispinalis.
Where do rotatores insert?
Each of the rotatores muscles inserts or attaches to the spinous process of the thoracic vertebra that is located either one or two vertebra above its originating vertebra.
Which muscle acts as an antagonist to the rotatores?
Movements and anatomy 3 quiz questionsQuestionAnswerWhich muscle acts as an antagonist to the rotatores dduring rotation of the vertebral column to the right side?Internal oblique on the left sideFurther toward the back of the bodyPosteriorA structure of the arm or leg that is further away from the trunkDistal25 more rows
What happens when your erector spinae is weak?
The erector spinae and psoas form a force couple, so if erector spinae becomes weak – psoas may cease to properly function, in turn possibly becoming chronically tight, and further causing low back pain due to increased shear forces.
How do you palpate rotatores?
1:414:37Multifidi and Rotatores Palpation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI'm going to just locate the spinous processes here and then slide over those large erector spinaeMoreI'm going to just locate the spinous processes here and then slide over those large erector spinae muscles. And then just kind of come in through the side door here laterally.
Are rotatores deep to multifidus?
Rotatores. Rotatores muscle lies deep to the multifidus and spans the whole length of the vertebral column, it is most developed in the thoracic region.
Which vertebrae is responsible for nodding?
The atlasThe atlas is the topmost vertebra and, with the axis (the vertebra below it), forms the joint connecting the skull and spine. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head.
How do you palpate rotatores?
1:414:37Multifidi and Rotatores Palpation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI'm going to just locate the spinous processes here and then slide over those large erector spinaeMoreI'm going to just locate the spinous processes here and then slide over those large erector spinae muscles. And then just kind of come in through the side door here laterally.
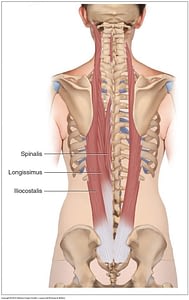
What is the iliocostalis Where is it located and what's its function?
Iliocostalis lumborum is part of the erector spinae muscle group which includes iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis. The muscle bulk formed by this muscle group can be felt running parallel to the spine over the transverse processes of each vertebra. These muscles are vital for allowing free movement of the spine.
Where is sacrospinalis located?
They are also known as the sacrospinalis group of muscles. These muscles lie on either side of the spinous processes of the vertebrae and extend throughout the lumbar, thoracic, and cervical regions.
What are the 3 spinalis muscles?
It is divided into three parts: Spinalis dorsi, spinalis cervicis, and spinalis capitis. Deep muscles of the back (spinalis dorsi visible at center. Other spinalis muscles not visible). Thoracis: Spinous process of upper lumbar and lower thoracic vertebrae.
Which muscle group is responsible for the rotation of the spine?
The rotatores muscle, along with the multifidus and semispinalis muscles, facilitates the unilateral rotation (turning from side to side) and bilateral extension (bending backward and forward) of the spine. The three muscles comprise the transversospinalis muscle group and connect the transverse process (bony projection on the right and left side of each vertebra) to the superior spinous process (bony projections at the back of each vertebra) of the thoracic spine.
How many rotatores are there in the spine?
The rotatores muscle, also referred to as the rotatores spinae, is actually a cluster of 22 small muscles in the thoracic region. There are 11 rotatores muscles on each side of the spine. Each rotatores muscle is small and is classified as being quadrilateral in shape, meaning that each muscle has four sides.
Which muscles help keep the spine straight?
Extensors are muscles that help keep the back straight. It is essential to note that the intrinsic muscles of the spine serve to move the spinal column as well as to provide control of the spine. Intrinsic muscles include superficial and deeper layers. The rotatores muscle belongs to the deeper layer intrinsic back muscles.
Which muscle is the deepest?
The rotatores muscle belongs to the deeper layer intrinsic back muscles. They are, in fact, the deepest layer of muscles that cannot be felt through the skin. Last medically reviewed on January 19, 2018.
Which muscle group connects the transverse process and the superior spinous process?
The three muscles comprise the transversospinalis muscle group and connect the transverse process (bony projection on the right and left side of each vertebra) to the superior spinous process (bony projections at the back of each vertebra) of the thoracic spine.
How many rotatores are there?
The rotatores muscles are a group of 22 small, four-sided muscles found between the thoracic vertebrae on both sides of the spinal column. (I.e. there are 11 pairs of these muscles.)
What muscles move the spine?
Based on the activity from the beginning of the lesson, as well as the location of the rotatores muscles, you probably guessed that these muscles function to move the spine and back. (If this was your guess, then you were right!). Specifically, these muscles cause the following actions of the back/spine: 1 Lateral rotation: twisting toward one side of the body, such as when you turn around to look behind you 2 Flexion: bending forward, such as when you tie your shoes 3 Extension: bending backwards, such as when you are looking straight above your head
Which vertebra does the rotatores muscle attach to?
For example, if a rotatores muscle originates from the left transverse of the 11th thoracic vertebra, it will insert or attach to the spinous process of the 9th or 10th thoracic vertebra.
Where are the rotatores located?
The rotatores muscles are a group of 22 small, four-sided muscles found on the vertebrae of the spine. Specifically, these 22 muscles are found in the thoracic region of the spinal column (middle of the spine). There are 11 rotatores muscles on each side of the thoracic vertebrae (11 x 2 = 22).
Which muscles attach to the spinous process of the thoracic vertebra?
Each of the rotatores muscles inserts or attaches to the spinous process of the thoracic vertebra that is located either one or two vertebra above its originating vertebra. For example, if one of the rotatores muscles originates from the left transverse processes of the 11th thoracic vertebra, it will insert or attach to the spinous process of the 9th or 10th thoracic vertebra. The spinous process is a bony prominence that sticks out the back of the vertebrae.
What muscle is Ch 10.?
Ch 10. Muscles of the Upper Arm
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
What muscles do the multifidus work with?
According to Diane Lee, a physiotherapist based in Canada, the multifidus works in concert with your transverse abdominus (TA), the deepest ab muscle in the body, and pelvic floor muscles (PFM) to stabilize your lumbar area—even before you add movement.
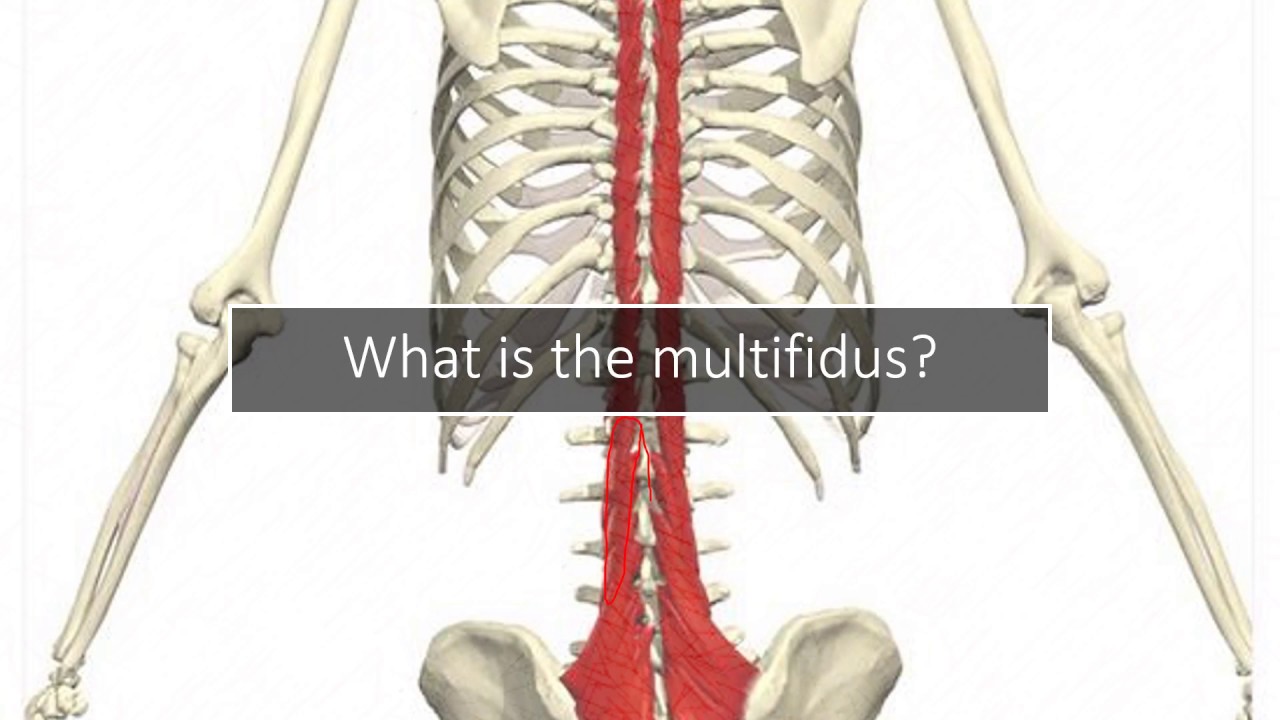
What is the role of the multifidus in the spine?
The multifidus, like the rotatores and other deep back muscles, play a role in upright posture and spinal stability.
What are the four muscles that make up the deep layer of the intrinsic back?
Four muscles comprise the deep layer of the intrinsic back muscles. From superficial to deep: the semispinalis, the multifidus, the rotatores and the interpinalis and intertransversii. The multifidus and rotatores have special functions and jobs as we'll outline below.
What are the two back muscles that belong to the deep layer of the intrinsic back muscles?
Updated on May 15, 2021. The multifidus and rotatores are two back muscles that belong to a group known as the deep layer of the intrinsic back muscles. Jordan Beal / EyeEm / Getty Images.
What are the parts of the multifidus?
These would be cervical (neck), thoracic (mid and upper back), lumbar (lower back), and sacral (sacrum bone). The muscle attaches onto all spinal vertebrae except the atlas, which is the first (and topmost) bone in your neck.
What is the deep intrinsic layer?
The deep intrinsic layer belongs, as the name suggests, to the overall intrinsic layer. (The other intrinsic layers are the superficial and intermediate.) Also as the name suggests, the muscles in the deep intrinsic layer are the ones located most closely to the spine, when you compare them to the other back muscles.
Where are the rotatores located?
Rotatores Muscles. Just below the multifidus lies the rotatores. Like the multifidus, the rotatores are small muscles located on either side of the spine. They are shaped like a quadrilateral and attach on the transverse process of the vertebrae.
What muscles are involved in the rotator cuff?
Four muscles make up the rotator cuff: the subscapularis, teres minor, supraspinatus, and infraspinatus. Together they assist in stabilizing the shoulder joint as well as in performing various arm movements.
What muscles hold your arm in place?
The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles that hold your upper arm in place in your shoulder. It helps you make all the motions of your arm and shoulder.
What causes acromial impingement?
Impingement. This occurs when the top of the shoulder (the acromion) rubs against the tendon and the bursa and irritates the rotator cuff. Between 44 and 64 percent of all shoulder pain is thought to come from subacromial impingement syndrome (SAIS), which is the most common shoulder disorder.
How long does it take for a rotator cuff tear to heal?
Most people regain their range of motion and strength after 4 to 6 months.
What is partial tear of the rotator cuff?
Partial tears of the rotator cuff tendons. The tendon is damaged or frayed but isn’t torn away from the bone.
What muscle is responsible for lateral rotation of the arm?
Infraspinatus is the main muscle responsible for lateral rotation of your arm away from the centerline of your body. It’s a thick triangular muscle. It covers the back of your shoulder blade deep below the skin and close to the bone.
What to do if shoulder pain persists?
If symptoms persist or worsen, your doctor may recommend surgery. Your doctor will also prescribe surgery for severe shoulder injuries.