- They provide specific information about particular locations.
- They provide general information about spatial patterns.
- They can be used to compare patterns on two or more maps.
What types of information can a thematic map show?
What are the 5 thematic maps?
- Choropleth Map. The choropleth map is one of the most frequently used maps in Geospatial data. …
- Dot Distribution Map. …
- Graduated Symbol Map. …
- Heat Maps. …
- Cartogram. …
- Bivariate Choropleth Map. …
- Value by Alpha Map.
What are some examples of thematic maps?
What Are The 3 Types Of Thematic Maps?
- Choropleth maps
- Dot distribution maps
- Graduated symbol maps
What are some interesting thematic maps?
These tasks tend to fall into three types: : 2
- Provide specific information about particular locations. For example, "what is the Hispanic proportion of Chicago?"
- Provide general information about spatial patterns. For example, "where is maize grown?"
- Compare patterns on two or more maps. For example, "how did the vote change between the 2008 and 2012 U.S. presidential elections?"
What can thematic maps be used for?
Thematic maps have attributes that make spatial patterns more clear, shedding new light on the theme in questions and allowing for further insights. Why Use a Thematic Map? These maps are very useful when you want to analyze the spatial distribution of your information, or look for any geographic patterns and trends contained within your data sets.

What do thematic maps mainly show?
A thematic map shows the spatial distribution of one or more specific data themes for selected geographic areas. The map may be qualitative in nature ( e.g. , predominant farm types) or quantitative ( e.g. , percentage population change).
What do thematic maps show answer?
A thematic map is a type of map that portrays the geographic pattern of a particular subject matter (theme) in a geographic area. This usually involves the use of map symbols to visualize selected properties of geographic features that are not naturally visible, such as temperature, language, or population.
What is an example of thematic map?
Weather, population density and geology maps are examples of thematic maps.
Why are thematic maps useful short answer?
Thematic maps serve three primary purposes. They provide specific information about particular locations. They provide general information about spatial patterns. They can be used to compare patterns on two or more maps.
What are thematic maps for kids?
A thematic map is a kind of map. Different from normal maps, a thematic map is designed to show the distribution of human or natural features or data. The information may or may not be related to geography. For example, a map which shows population is a thematic map.
Why is it called a thematic map?
It is called a thematic map because the map has a specific theme. The theme corresponds to the data selected, and the data is connected to a particular geographic location.
Which map gives more information?
Large scale maps provide detailed information on which we can represent any part of earth like village ,town, country , state etc. Answer: Large scale maps. Explanation: The maps are one of the most important physical components which we use in the field of geography.
What map shows hills and mountains?
Explain that a landform map shows the locations of landforms in a place. These maps often use color to show mountains, hills, plateaus, plains, and more. They also show major bodies of water.
What is thematic map?
Thematic maps are maps that emphasize a specific subject area or theme connected to a specific geographical area. Unlike general reference maps that show a variety of features, thematic maps focus on a specific feature. Thematic maps use base data only as points of reference and do not show natural features such as boundaries, rivers, cities, ...
What are the techniques used to create thematic maps?
There are five techniques used by cartographers to create thematic maps. The most commonly used technique is choropleth mapping, which shows statistical data that has been aggregated over a predefined region by shading or coloring these regions. It portrays data as color and can show features such as population density. The proportional symbol technique uses symbols to represent data associated with locations such as cities. Another technique is the isarithmic or contour maps which use isolines to depict smooth continuous values such as precipitation level. A dot distribution map can be used to show the presence of a theme and display a spatial pattern. The final technique is dasymetric mapping which is related to choropleth mapping and uses statistics and other information to link areas with the same values instead of administrative boundaries used in choropleth mapping .
Why were thematic maps not developed?
Thematic maps were not developed as maps until the 17th century because there were no accurate maps before then. The development of accurate maps was gradual and even in the 17th century, maps were still of poor quality. Once the maps became accurate enough to display features such as boundaries, cities, and coastlines, the first thematic map was produced by Jodocus Hondius in 1607 that showed the dispersion of major religions. In 1686, a star chart was developed by Edmond Halley, an English astronomer. Later that year he published his first meteorological chart and in 1701 he published the first chart showing lines of magnetic variations. Edmond’s maps were mainly used for navigation. In 1854, John Snow created the first thematic map used for problem analysis. He first mapped London’s neighborhood, then mapped the exact location for the cholera incident. Snow was able to find death cluster around a particular pump and was able to conclude that water from that pump was the cause of cholera.
Why do thematic maps use only base data?
Thematic maps use base data only as points of reference and do not show natural features such as boundaries, rivers, cities, or even highways. Instead, if the show these features, they are only used as reference points to make it easy for the users to understand the map.
What is the most important factor in designing a thematic map?
When cartographers are designing a thematic map, there are several factors that they put into consideration. The most important factor is the audience. The map users determine what items to be included on the thematic map in addition to the map’s theme. For instance, a thematic map for political use will have political ...
Who created the first thematic map?
Once the maps became accurate enough to display features such as boundaries, cities, and coastlines, the first thematic map was produced by Jodocus Hondius in 1607 that showed the dispersion of major religions. In 1686, a star chart was developed by Edmond Halley, an English astronomer.
Can a map be univariate?
The data can be used in various ways and each must be considered in line with the map’s theme. The mapping can be univariate (one type of data), bivariate (two data sets) or multivariate (more than two data sets).
Thematic Map Definition
What does thematic map mean? A thematic map can be defined as a specifically themed map for a particular geographic area. Thematic maps are maps that tend to be about specific topics. The subject matter and the location are determined in the mapmaking process and are required for making all thematic maps. Cartography is the act of mapmaking.
What Is a Thematic Map Used for?
The purpose of a thematic map is to explain something. Unlike traditional reference maps of a specific place that provide directions or a simple location, thematic maps are explanatory. They do so by depicting data with a location to identify spatial patterns and trends.
Isoline Map Definition
What is an isoline map? Isoline maps use continuous lines that delineate data of the same value. Examples of isoline maps are elevation maps and weather maps. The continual lines depict elevation changes in a map, a specific elevation on one side and another on the other. These elevations will be labeled.
Cartogram Map Definition
A cartogram is a particularly unique type of thematic map. It takes the represented data and stretches or shrinks the data's location on the map. In other words, a cartogram does not represent real physical space.
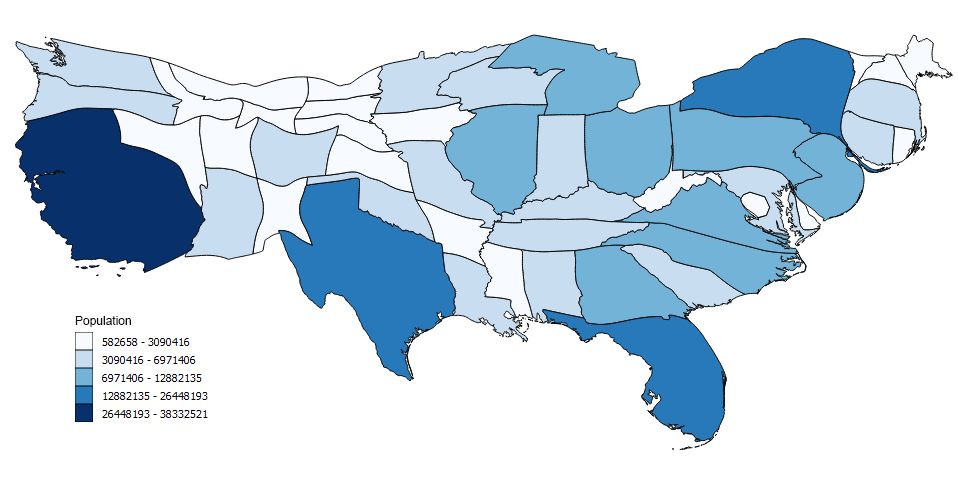
Choropleth Map Definition
Choropleth maps are one of the most common types of thematic maps. A choropleth map is known for shading colors within the geographic extent of the data to highlight patterns. Often values such as percent, density, or quantity are displayed.
Graduated Symbol Map Definition
A graduated symbol map uses the size and shape to indicate the amount of the data. This symbol is placed over the location it represents on the map. The larger or smaller the symbol is, the greater or lesser the concentration of data. The symbol is often selected in a shape, form, or color that increases the readability of the map and its data.
What is thematic map?
A thematic map is a type of map that portrays the geographic pattern of a particular subject matter (theme) in a geographic area. This usually involves the use of map symbols to visualize selected properties of geographic features that are not naturally visible, such as temperature, language, or population. In this, they contrast ...
What is the purpose of a thematic map?
The most common purpose of a thematic map is to portray the geographic distribution of one or more phenomena. Sometimes this distribution is already familiar to the cartographer, who wants to communicate it to an audience, while at other times the map is created to discover previously unknown patterns (as a form of Geovisualization ). Thematic maps accomplish these two goals by leveraging the natural ability of the human visual perception system to recognize patterns in a complex visual field, which is necessary for common tasks such as object recognition. A thematic map usually focuses on visualizing the distribution of values of a single property or type of feature (a univariate map), occasionally including two ( bivariate) or more ( multivariate) properties or feature types that are hypothesized to be statistically correlated or otherwise closely related.
What is a chorochromatic map?
A chorochromatic or area-class map represents a categorical or nominal variable distributed over space (also known as a discrete field ), by using different area symbols (usually color hue) to represent regions of homogeneous value.
How does a cartogram work?
A cartogram is a map that intentionally distorts geographic space based on a given variable, usually by scaling features so their size is proportional to their value of the variable. For example, the countries of the world could be scaled proportional to their population.
What is the purpose of reference information in a map?
The primary purpose of reference information is to establish the location of the thematic information in a context understood by the map readers (i.e., to answer questions such as "where is this red region in the real world?"). Common reference layers include government administrative boundaries, roads, cities, a latitude/longitude graticule, or even terrain. These layers play a secondary role in the use of the map, so they are usually included sparingly, and symbolized to be low in the visual hierarchy, but not so faded that they cannot be used.
What is isoline map?
Isarithmic maps, also known as contour maps or isoline maps, depict continuous quantitative fields ( sometimes conceptualized as "statistical surfaces" by cartographers), such as precipitation or elevation by partitioning space into regions, each containing a consistent range of values of the field. The boundary of each region, an isoline, thus represents the set of locations of constant value. For example, on a topographic map, each contour line indicates an area at the listed elevation.
What was the most important development in cartography?
Prior to this, the most important cartographic development was the production of accurate general base maps. Their accuracy improved slowly, and even in the mid-17th century, they were usually of poor quality; but they were good enough to display basic information, allowing the production of the first thematic maps.
Why are thematic maps important?
Cartographers must find accurate, recent, reliable sources of information on a wide range of subjects, from environmental features to demographic data, to make the best possible maps.
Why are thematic maps different from general reference maps?
They're different from general reference maps because they don't just show natural and manmade features such as rivers, cities, political subdivisions, and highways. If these items appear on a thematic map, they're reference points to enhance one's understanding of the map's theme and purpose. Normally, thematic maps use coastlines, city locations, ...
How high should the isoline be on an isarithmic map?
Isarithmic maps also follow the basic rule that there are high and low sides in relation to the isoline. For example, in elevation, if the isoline is 500 feet, then one side must be higher than 500 feet and one side must be lower.
What is the most common method of mapping?
Although cartographers can use data sets in different ways to create thematic maps, five thematic mapping techniques are used most often: The most common is the choropleth map , which portrays quantitative data as a color and can show density, percent, average value, or quantity of an event within a geographic area.
What is the most important factor to consider when designing thematic maps?
The most significant factor to consider when designing thematic maps is the map's audience, which helps determine what items should be included on the map as reference points in addition to the theme. A map being made for a political scientist, for example, would need to show political boundaries, whereas one for a biologist might need contours showing elevation.
When were thematic maps invented?
Thematic maps didn't develop until the mid-17th century, because accurate base maps didn't exist before then. Once maps became accurate enough to correctly display coastlines, cities, and other boundaries, the first thematic maps were created. In 1686, for example, English astronomer Edmond Halley developed a star chart and published ...
When was the first map of magnetic variation created?
In 1701, Halley published the first chart to show lines of magnetic variation, a thematic map that later became useful in navigation. Halley's maps were largely used for navigation and study of the physical environment.
Choropleth Map ( example)
Description: These maps contain areas that are shaded or patterned in proportion to the statistical variable being displayed on the map. Data are aggregated over predefined areal units (politically-defined area or administrative—census or zip).
Graduated Symbol Map ( example)
Description: These maps contain symbols varying in size to show their relative quantitative values; used with point/location data.
Dot Map ( example)
Description: Uses dots to show the presence of a feature or occurrence; displays a spatial pattern and relative density. Individual dots can represent single or multiple occurrences.
Isopleth Map ( example)
Description: A contour map that depicts smooth continuous information (such as weather or pollution data); data are depicted using lines that connect points of equal numerical value.
What is the purpose of a thematic map?
Thematic maps are designed to highlight and reveal the subject's information. This means the geographic features on a thematic map are tailored to reflect or best support the map's theme. Where you might see 12 lakes on a regional map, a thematic map of the same area may simply show the 3 largest. In this way more space is available to show information directly relating to the subject of the map. It improves the overall clarity without losing the important backdrop the topography provides.
Why are thematic maps so beautiful?
Because they delve into a focused idea, the artistry of the cartography and additional map elements are usually much more exciting and appealing.
Who created the Planisphere?
Planisphere by Rumold Mercator 1587. In fundamental ways maps began as a means of understanding the lands and waterbodies that comprised the world, charting exploration and discoveries of previously unknown places, and defining a nation's imperialistic extents.
Why are thematic maps important?
Thematic maps are of immense importance. These maps are designed to illustrate a specific theme in relation to a geographic area. Whether it’s trading patterns, the spread of a disease, or even the definitive ranking of people’s favorite beverage by state, thematic maps always have something fascinating to share.
What is a theme map?
A particular theme is set for areas that are high and low on the intensity. All thematic maps are composed of two important elements: a base map and statistical data. Normally, the two are available as digital files, such as a cartographic boundary file and census data.
What are the techniques used to make maps?
Of all the procedures used, the primal techniques for designing maps were choropleth, proportional symbol, Isopleth, Dot, and Cartograms.
Who created the first thematic map?
One of the earliest thematic maps was a map entitled ‘Designatio Orbis Christiani’ (1607) by Jodocus Hondius showing the dispersion of major religions, using map symbols in the French edition of his Atlas Minor (1607).
Can you make your own maps on MapTrove?
MapTrove not only offers you a huge collection of world maps at one place but also allows you to make your own maps. You can easily create custom maps with the places that matter to you. Plus, you can draw, add points or add shapes anywhere.
What is a thematic map?
Thematic maps can portray physical, social, political, cultural, economic, sociological, or any other aspects of a city, state, region, nation, continent, or the entire globe. A thematic map is designed to serve a special purpose or to illustrate a particular subject, in contrast to a general map, on which a variety of phenomena appear together, ...
What are the features of a thematic map?
Thematic maps also portray basic features such as coastlines, boundaries and places , but they are only used as a point of locational reference for the phenomenon being mapped. Thematic maps also emphasize spatial variation of one or a number of geographic distributions.
What is the difference between a thematic and a general reference map?
While general reference maps show where something is in space, thematic maps tell a story about that place based on spatial patterns.
What is the best known example of using thematic maps for analysis?
Though disease had been mapped thematically, Snow’s cholera map in 1854 is the best-known example of using thematic maps for analysis. Essentially, his technique and methodology anticipate principles of a geographic information system ( GIS ).
What is the primary theme of a thematic map?
A thematic map will typically consist of three types of information: Primary theme: the geographic phenomena that represent the topic being discussed. In a map of population density of a city, this would be population density. Most thematic maps have a single primary theme.
What is a reference layer?
Reference theme: a layer of geographic features that usually have little to do with the theme of the map, but help map readers locate the thematic information in a context of recognizable geography. Roads, administrative boundaries, terrain, and latitude/longitude graticules are common reference layers.
What is a dot density map?
A dot density map is a popular way to use dots in creating a thematic map. When one dot represents one phenomena or one object, it is referred to as one-to-one; if that one dot represents many phenomena or objects, it is referred to as one-to-many.
Choropleth Maps
Dot Density Maps
- These maps represent each data point with a dot and are a great way to measure density. Regions with a large number of dots packed close to together are easily identified as high-density areas, whereas regions with few or no dots are clearly areas where your data is lacking. Dot maps have been around for a long time but are still extremely popular ...
Isopleth Maps
- Isopleth maps use colors and shades to represent data, similar to choropleth maps. However, they differ in that data isn’t grouped within predefined boundaries such as census tracts, counties, or states. Instead, contoured lines divide the map into different areas and show where data levels change.
Heat Maps
- Heat mapsmeasure density across a map. Like many other map types, they represent data using color. Darker shades indicate higher density areas while lighter shades show lower density areas. This type of map doesn’t use geographic boundaries. Instead, it works similarly to a dot density map. Plot individual data points on the map with colors assigned based on the distribution and n…
Graduated Symbol Maps
- These maps show data using varying sizes of symbols. Larger symbols represent higher concentrations of data while smaller symbols represent lower concentrations of data. Similar to choropleth maps, data is placed into different categories. However, instead of color or shades representing data, different symbol sizes stand in for data categories. The number of symbol siz…
What About Cartograms?
- Cartograms visualize the concentration of data in a boundary by distorting its shape and size relative to other geographic areas on a map. While good for presenting the variance in density of data, cartograms tend to be hard to read and aesthetically displeasing. Cartograms provide a great value. However, the types of thematic maps listed above also measure the density of your …
Overview
History
Purpose
- There are five techniques used by cartographers to create thematic maps. The most commonly used technique is choropleth mapping, which shows statistical data that has been aggregated over a predefined region by shading or coloring these regions. It portrays data as color and can show features such as population density. The proportional symbol tech...
Mapping methods
A thematic map is a type of map that portrays the geographic pattern of a particular subject matter (theme) in a geographic area. This usually involves the use of map symbols to visualize selected properties of geographic features that are not naturally visible, such as temperature, language, or population. In this, they contrast with general reference maps, which focus on the location (more …
Reference layers
According to Arthur Robinson, thematic maps were largely an Industrial Age innovation, with some Enlightenment-era roots; almost all of the modern graphical techniques were invented between 1700 and 1850. Prior to this, the most important cartographic development was the production of accurate general base maps. Their accuracy improved slowly, and even in the mid-17th …
See also
The most common purpose of a thematic map is to portray the geographic distribution of one or more phenomena. Sometimes this distribution is already familiar to the cartographer, who wants to communicate it to an audience, while at other times the map is created to discover previously unknown patterns (as a form of Geovisualization). Thematic maps accomplish these two goals by leveraging the natural ability of the human visual perception system to recognize patterns in a co…
Further reading
Cartographers use many methods to create thematic maps. These are often referred to as different types of thematic maps, but it is more proper to call them types of thematic map layers or thematic mapping techniques, as they can be combined with each other (forming a bivariate or multivariate map) and with one or more reference map layers in a single map. For example, a cartogram t…