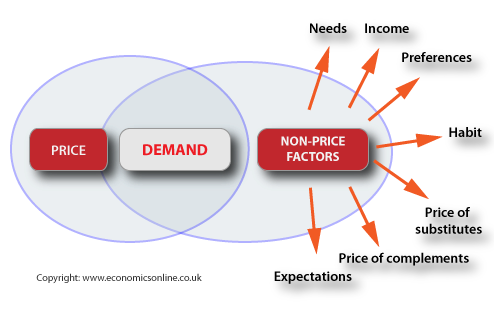
The five determinants of demand are:
- The price of the good or service
- The income of buyers
- The prices of related goods or services—either complementary and purchased along with a particular item, or substitutes bought instead of a product
- The tastes or preferences of consumers will drive demand
- Consumer expectations about whether prices for the product will rise or fall in the future
What does factors determine demand?
What 3 Factors Determine The Price Elasticity Of Demand?
- Relative need for the product. The need of every individual is not the same for the same product. …
- Availability of substitute goods. As discussed in the previous chapters, the availability of substitutes has major impact on the demand for a product.
- Impact of income. …
- Time under consideration. …
- Perishability of the product. …
- Addiction. …
What are the six determinants of market demand?
What Are The Six Determinants Of Market Demand? Buyers’ real incomes or wealth change. The preferences and tastes of buyers. Prices of related products or services. Expectations of the product’s future price from buyers. Expectations of future income and wealth for buyers. A number of buyers (population) is expressed.
What are the factors determinants of individual demand?
The five determinants of demand are:
- The price of the good or service
- The income of buyers
- The prices of related goods or services—either complementary and purchased along with a particular item, or substitutes bought instead of a product
- The tastes or preferences of consumers will drive demand
- Consumer expectations about whether prices for the product will rise or fall in the future
What are the determinants of demand in economics?
Top 10 Determinants of Demand for an Economy
- The Prices of Goods or Services. When the price of goods & services rises, the quantity demand falls & when the price of goods & services falls, the ...
- Price of Substitute/Complementary Goods & Services. Substitute goods are goods that satisfy the same needs. ...
- Buyers’ Tastes and Preferences. ...
- Buyers’ Expectations of the Goods’ Future Price. ...

What are determinants of demand?
The 5 Determinants of Demand The price of the good or service. The income of buyers. The prices of related goods or services—either complementary and purchased along with a particular item, or substitutes bought instead of a product. The tastes or preferences of consumers will drive demand.
What are the 7 determinants of demand?
7 Factors which Determine the Demand for GoodsTastes and Preferences of the Consumers: ... Incomes of the People: ... Changes in the Prices of the Related Goods: ... The Number of Consumers in the Market: ... Changes in Propensity to Consume: ... Consumers' Expectations with regard to Future Prices: ... Income Distribution:
What are the 12 determinants of demand?
Determinants of demand and consumptionLevels of income. A key determinant of demand is the level of income evident in the appropriate country or region under analysis. ... Population. Population is of course a key determinant of demand. ... End market indicators. ... Availability and price of substitute goods. ... Tastes and preferences.
What are the 4 types of demand?
The different types of demand are as follows:i. Individual and Market Demand: ... ii. Organization and Industry Demand: ... iii. Autonomous and Derived Demand: ... iv. Demand for Perishable and Durable Goods: ... v. Short-term and Long-term Demand:
What are the 6 determinants of demand?
What are the 6 factors that affect demand?Price of product.Consumer's Income.Price of Related Goods.Tastes and Preferences of Consumers.Consumer's Expectations.Number of Consumers in the Market.
What are the 6 factors that can cause a change in demand?
6 Important Factors That Influence the Demand of GoodsTastes and Preferences of the Consumers: ADVERTISEMENTS: ... Income of the People: ... Changes in Prices of the Related Goods: ... Advertisement Expenditure: ... The Number of Consumers in the Market: ... Consumers' Expectations with Regard to Future Prices:
What are the 10 factors affecting demand?
These factors include:Price of the Product. ... The Consumer's Income. ... The Price of Related Goods. ... The Tastes and Preferences of Consumers. ... The Consumer's Expectations. ... The Number of Consumers in the Market.
What are the 5 determinants of supply?
Supply Determinants. Aside from prices, other determinants of supply are resource prices, technology, taxes and subsidies, prices of other goods, price expectations, and the number of sellers in the market. Supply determinants other than price can cause shifts in the supply curve.
What Does Determinants of Demand Mean?
1. Consumer preferences: personality characteristics, occupation, age, advertising, and product quality, all are key factors affecting consumer behavior and, therefore, demand.
What is the difference between an increase in the price of one product and an increase in the quantity demanded of a?
In contrast, an increase in the price of one product will cause an increase in the demand for a substitute product.
What is consumer expectation?
Consumer expectations: expectations for a higher income or higher prices increase the quantity demanded. Expectations for a lower income or lower prices decrease the quantity demanded. 5. The number of buyers: the higher the number of buyers, the higher the quantity demanded, and vice versa. 6.
When demand is increased, what does it mean?
When demand is increased that means the demand curve will shift to upward/right shift,
When the price of goods and services rises, the quantity demand falls?
When the price of goods & services rises, the quantity demand falls & when the price of goods & services falls, the quantity demand will rise . It is also called the Law of demand.
What is the relationship between the price and consumer behavior?
Demand is an economic principle, which explains the relationship between the prices and the consumer behaviors due to change in the price for goods & services; There are many factors in the economy which affects the demand for goods & services, those factors are called determinants of demand.
What does QD mean in math?
Quantity Demand (qD) = f ( Prices of goods or services, Price of substitute/complementary goods & services, Buyers’ tastes and preferences, Buyers’ expectations of the goods’ future price, change in buyers’ real incomes or wealth, Buyers’ expectations of their future income and wealth, The number of buyers, Government policies & Climate changes, Income distribution)
What does QD mean in economics?
Quantity Demand (qD) = f ( Prices of goods or services, Price of substitute/complementary goods & services, Buyers’ tastes and preferences, Buyers’ expectations of the goods’ future price, change in buyers’ real incomes or wealth, Buyers’ expectations of their future income and wealth, The number of buyers, Government policies & Climate changes, Income distribution)
How does brand advertising affect the consumer?
The demand for any products can change based on buyer’s tastes & preferences, brand advertising plays a vital role in changing the buyer’s tastes & preferences. For example, earlier people used to think chocolates are mainly for kids but the advertising industry has changed this concept by showing that chocolates are for everyone from kids to very elderly person.
Why does a decrease in the interest rate lead to higher housing demand?
For example, Decrease in the borrowing interest rate leads to raising in the housing loan demands because people will start buying houses since the loan interest rate is reduced.
What are the determinants of demand?
Determinants of Demand are: Price of a commodity. Price of related goods. Income of consumers. Tastes and preferences of consumers. Consumers expectations. Credit policy. Size and composition of the population.
Why is it important to understand the relationship between the demand and its each determinant?
It is essential for organisations to understand the relationship between the demand and its each determinant to analyse and estimate the individual and market demand for a commodity or service.
What is Demand in Economics?
Demand is an economic principle can be defined as the quantity of a product that a consumer desires to purchase goods and services at a specific price and time.
What causes a rise in demand for a product?
Consumers expectations. Demand for commodities also depends on the consumers’ expectations regarding the future price of a commodity, availability of the commodity, changes in income, etc. Such expectations usually cause rise in demand for a product.
What is the difference between normal goods and inferior goods?
Normal goods: These are goods whose demand rises with an increase in the level of income of consumers. For example, the demand for clothes, furniture, cars, mobiles, etc. rises with an increase in individuals’ income. Inferior goods: These are goods whose demand falls with an increase in consumers’ income.
How does demand for a good or service depend on its own price?
The demand for a good or service not only depends on its own price but also on the price of related goods. Two items are said to be related to each other if the change in price of one item affects the demand for the other item. Related goods can be categorised as follow.
What are the factors that determine the purchase of a product?
When an individual intends to purchase a particular product, he/she may take into consideration various factors, such as the price of the product, the price of substitutes, level of income, tastes and preferences, and the features of the product.
How many determinants of demand are there?
The factors that impact individual consumer demand in the real world are complex, but economic theory simplifies this to five determinants of demand. This article explores those five things and how they can affect your business’s bottom line.
What is demand in economics?
In economics, demand can be explained as consumers’ willingness and ability to purchase or consume a given item/good. Therefore, the determinants of this demand are crucial for explaining the consumer’s behavior towards any particular good. The market is made up of buyers and sellers. Buyers are represented by demand, which describes all quantities of a good or service they would be willing to purchase at each price point within the market.
What are the other factors that affect the demand?
Branding. By using advertising, product differentiation, and high-quality products. Sellers can create such strong brand images that buyers prefer the seller’s goods over others similar to them.
What is the key feature of substitutes and complements?
A key feature of substitutes and complements is that a change in price for one good impacts the demand for the other good.
Why is demand curve important?
The graphical representation of demand is often called the “demand curve” because it shows how many units consumers would be willing and able to purchase at a given price. Thus, the determinants for economic demands cause fluctuations in consumer purchasing behavior, impacting market prices.
What happens when the price of a good increases?
For example, if the price of a good increase, then buyers will most likely buy less. Similarly, when the selling or cost price decreases, people would probably want to buy more from that company.
What is demand curve?
The demand curve shows the relationship between price and quantity. If one of these variables changes, this entire relationship shifts: if a lot happens when prices change regarding how much is demanded, then we have elastic demand; however, if regardless of price, there’s not much response – that would be considered inelastic demand.
What is demand in economics?
Income brings about a purchasing power that they practise in the market through effective demand. Economic demand is something that runs the commerce. With no economic demand, companies would no longer be willing to supply products as they wouldn't be making any profit by entering the market.
What is market demand?
Market demand is also known as aggregate demand. It refers to the total economic demand in view of all the individual demand in any particular market. Individual demand is a demand for a product by an individual at a certain price. Customer tastes, distinguished quality and brand commitment or loyalty affect individual demand.
How does price affect demand?
In the case of a complementary product, if one product determines the sale of the other product, the products are said to be complimenting each other. Hence, if the price of any one of the products increases or decreases, it will surely affect the demand of the other product as well.
What is short term demand?
As the name implies, short-term demand is limited for a brief duration of time; it reflects trends, necessity and modifications in the price more dramatically than the long-term demand. For example, winter wear is worn only during winter, making the demand much shorter when compared to clothing worn all over the year. On the other hand, long-term demands pertain for a longer period of time and this demand doesn't change with respect to time and price.
Why do people have jobs?
Ans: The reason why individuals have a job is because of economic demand. In case someone works in finance, economics or accounting, individuals can excel better in business by understanding economic demands. It also assists in forecasting how much of a good or service to produce or when it’s fortunate to scale back production. This could help individuals save money in long-term and short-term, increasing money flows. Moreover, to determine economic demand is one of the primary expenditures of companies and businesses. Also, depending on the demand for skills, companies hire people who possess the skill. If the skills are not in demand in the market, then jobs which require that skill also decreases.
Why is price used as a parameter?
Price is used as a parameter by the people to decide if all the other factors remain constant or equal. According to the law of demand, the decrease in the demand follows an increase in the price and an increase in the demand follows a reduction in price.
What is the determinant of demand?
determinants of demand. changes in conditions that cause the demand curve to shift; the mnemonic TONIE can help you remember the changes that can shift demand (T-tastes, O-other goods, N-number of buyers, I-income, E-expectations) normal good. a good for which demand will increase when buyers’ incomes increase.
What is change in demand?
change in demand. when buyers are willing to buy a different quantity at all possible prices, which is represented graphically by a shift of the entire demand curve; this occurs due to a change in one of the determinants of demand. determinants of demand.
How does price change affect quantity demanded for a good?
A change in the price of a good will cause the quantity demanded for that good to change, but a change in the demand for related goods (complements and substitutes) causes the demand curve to shift.
How does price change affect demand?
How a price change affects quantity demanded for a good and demand for related goods 1 A change in the price of a good will cause the quantity demanded for that good to change, but a change in the demand for related goods (complements and substitutes) causes the demand curve to shift. 2 For example, when the price of hot dogs falls three things happen: Quantity demanded for hot dogs increases, demand for hot dog buns (a complement) increases, and demand for hamburgers (a substitute) decreases
Why is the demand curve downward sloping?
all other factors being equal, there is an inverse relationship between a good’s price and the quantity consumers demand; in other words, the law of demand is why the demand curve is downward sloping; when price goes down, people respond by buying a larger quantity. quantity demanded.
What influences demand besides price?
What influences demand besides price? Factors like changes in consumer income also cause the market demand to increase or decrease. For example, if the number of buyers in a market decreases, there will be less quantity demanded at every price, which means demand has decreased.
What is demand represented graphically as?
all of the quantities of a good or service that buyers would be willing and able to buy at all possible prices; demand is represented graphically as the entire demand curve.
What are the determinants of demand?
The first and the most important determinant of demand is the product itself. You can expect high demand if the quality of your goods and services is not good. If a company wants to attract customers, then it must make sure that your goods and services meet the expectations of customers.
What is the ultimate determinant of demand?
The ultimate determinant of demand is very volatile. The expectation of consumers changes with the change in income and economic condition. For example, when the health of the economy is weak, they tend to spend less.
How does demand affect supply and demand?
Therefore, businesses must decide the price of goods and services correctly so that both suppliers and consumers can take advantage of it because the demand for the products and services is directly proportional to the price of the goods and services.
Why do businesses have to decide the price of goods and services correctly?
Therefore, businesses must decide the price of goods and services correctly so that both suppliers and consumers can take advantage of it because the demand for the products and services is directly proportional to the price of the goods and services.
How to determine if demand is elastic?
The elasticity of demand can be of three types: 1 Unit elasticity: The demand elasticity is called unit elasticity when the percentage of changed demand is equal to the percentage of price changed. 2 Elastic: The demand is elastic when the demand of the goods changes tremendously with the little change in the cost of the goods. 3 Inelastic: The demand is inelastic when the demand of the goods changes by a smaller percentage than the amount of price changed.
Why is the demand curve flat?
This is because people purchase fewer products when the price of the goods is high and a lesser number of products at a high cost. If the demand curve of a product is flat, that means people will buy a lot even if the price of goods changes a little.
How to find elasticity of demand?
The elasticity of demand can be obtained by dividing the percentage change in the quantity with the percentage change in the price of the goods.
The Prices of Goods Or Services
Price of Substitute/Complementary Goods & Services
- Substitute goods are goods that satisfy the same needs. For example, groundnut oil-sunflower oil and tea-coffee are substitutes. Hence, a rise in groundnut oil price can increase the demand for sunflower oil and vice-versa. Complementary goods[/wsm-tooltip are those goods consumed together. For example, car and diesel or tea and sugar, so the vehicle price decreases the deman…
A Change in Buyers’ Real Incomes Or Wealth
- Buyers’ purchasing power is dependent on their incomes and wealthWealthWealth refers to the overall value of assets, including tangible, intangible, and financial, accumulated by an individual, business, organization, or nation.read more. Suppose we see it in the non-developed areas where jobs are not easily available, and people do not have much income. Hence, the demand for good…
Buyers’ Expectations of Their Future Income and Wealth
- The higher expectation of future income & wealth increases consumption, and a lower expectation of future revenue will reduce consumption. For example, students who will complete higher studies and are about to join the job will start spending more than the salaries of people who will retire in the coming years.
The Number of Buyers
- If there is an increase in the number of buyers willing to buy goods or services affects the overall demand. The population has a large influence on the market. Population increase can create a makeshift in the demand curve. The new buyers help raise the quantity demand, so demand changes even if the price does not change.
Government Policies
- For many products, demand is dependent on government policies. For example, a decrease in the borrowing interest rate leads to raising housing loanLoanA loan is a vehicle for credit in which a lender will give a sum of money to a borrower or borrowing entity in exchange for future repayment.read moredemands because people will start buying houses since the loan interest r…
Climate Changes
- There are many products for which demand is seasonal or dependent on the climate. For example, demand for winter clothes is high in the winter season, and demand for ice creams is higher in the summer season. So, when winter is going to end, and there is no need for winter clothes, companies sell winter clothes at discounted prices. There are discount sales in the sho…
Income Distribution
- Luxurious goods are high in the area where very rich people are staying. On the other hand, in non-developed places where middle-income groups people visit, the demand for luxury goods is less. You are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkHow to Provide Attribution?Article Link to be Hyperlinked For eg: Source: Determi…