Importance of Macroeconomics:
- It helps to understand the functioning of a complicated modern economic system. It describes how the economy as a...
- It helps to achieve the goal of economic growth, higher level of GDP and higher level of employment. It analyses the...
- It helps to bring stability in price level and analyses fluctuations in business activities. It...
What are 5 examples of macroeconomics?
10 Examples of Macroeconomics. We regularly hear terms like GDP, national income, GDP and national consumption expenditure. especially, when comparing the economic states of countries. these concepts are defined as Macroeconomics. In short, Macroeconomics is the economics of economies as a whole at the global, national, regional and city level.
What is the difference between macroeconomics and economics?
Macroeconomics Meaning It is a branch of Economics which studies behaviour of individual economic agents It is branch of economics which studies aggregates of economy as a whole like Domestic Income, National income etc Tools Its main tools are Demand and Supply of a Product
What are the three most important concepts in macroeconomics?
The Top Three Economic Concepts
- People tend to respond to incentives.
- Scarcity, and its important corollary, opportunity cost.
- Markets tend to be low cost allocators of goods and services.
What does the term macroeconomics refer to?
Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that deals with the structure, performance, behavior, and decision-making of the whole, or aggregate, economy. The two main areas of macroeconomic research are long-term economic growth and shorter-term business cycles.

What do you mean by macroeconomics explain?
Definition: Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole. It focuses on the aggregate changes in the economy such as unemployment, growth rate, gross domestic product and inflation.
What do you mean by macroeconomics class 12?
Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that deals with the behaviour and performance of an economy as a whole. It is generally the study of central issues like: Employment. The growth rate of national output.
What is meant by macroeconomics class 11?
Macroeconomics is defined as the branch of economics which studies economic problems (or economic issues) at the aggregate level of economy, i.e, considering the whole economy. It deals with subjects like national income, national output, employment, etc.
What is macroeconomics and why is it important?
Macroeconomics helps to evaluate the resources and capabilities of an economy, churn out ways to increase the national income, boost productivity, and create job opportunities to upscale an economy in terms of monetary development.
What is Introduction to macroeconomics?
Macroeconomics is the study of the behaviour of the whole economy. It is concerned with the determination of the broad aggregates in the economy, in particular the national output, unemployment, inflation and the balance-of-payments position.
Who is the father of macroeconomics?
John Maynard KeynesIf Adam Smith is the father of economics, John Maynard Keynes is the founding father of macroeconomics.
What is microeconomics in simple words?
Definition: Microeconomics is the study of individuals, households and firms' behavior in decision making and allocation of resources. It generally applies to markets of goods and services and deals with individual and economic issues.
What is macro economics Byjus?
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that depicts a substantial picture. It scrutinises itself with the economy at a massive scale and several issues of an economy are considered. The issues confronted by an economy and the headway that it makes are measured and apprehended as a part and parcel of macroeconomics.
What are the types of macroeconomics?
Types of macroeconomic factorsInterest rates. The value of a nation's currency greatly affects the health of its economy. ... Inflation. ... Fiscal policy. ... Gross domestic product (GDP) ... National income. ... Employment. ... Economic growth rate. ... Industrial production.More items...•
What are the 3 main goals of macroeconomics?
In macroeconomics three of these goals receive extra focus: economic growth, price stability and full employment. Economic growth refers to a nation's ability to produce more goods and services over time.
What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics class 12?
Microeconomics is the study of economics at an individual, group, or company level. Whereas, macroeconomics is the study of a national economy as a whole. Microeconomics focuses on issues that affect individuals and companies. Macroeconomics focuses on issues that affect nations and the world economy.
What is the first chapter of class 12th macroeconomics?
Introduction to MacroeconomicsThe first chapter of Class 12 Macroeconomics is - 'Introduction to Macroeconomics. ' This chapter introduces us to the study of economics at the macro level, where a country's economy is studied as a whole.
What are the chapters of macroeconomics class 12?
Chapter wise Revision Notes for Class 12 Macro EconomicsChapter 1 - Introduction to Macro Economics.Chapter 2 - National Income Accounting.Chapter 3 - Money and Banking.Chapter 4 - Determination of Income and Employment.Chapter 5 - Government Budget and the Economy.Chapter 6 - Open Economy Macroeconomics.
What is macroeconomics analysis?
Description: Macroeconomics analyzes all aggregate indicators and the microeconomic factors that influence the economy. Government and corporations use macroeconomic models to help in formulating of economic policies and strategies. Watch the video to learn more about Macroeconomics. PREV DEFINITION.
What is it called when the economy is in a recession?
Generally, when an economy continues to suffer recession for two or more quarters, it is called depression .
What is the study of individuals, households and firms' behavior in decision making and allocation of resources?
Microeconomics is the study of individuals, households and firms' behavior in decision making and allocation of resources. Read More. Definition of 'Macroeconomics'. Definition:Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole.
What is the law of supply?
Law of supply states that other factors remaining constant, price and quantity supplied of a good are directly related to each other.
What is investment expenditure?
In short, the investment expenditure is proficient of creating additional income and fosters employment in a nation. Revenue: Revenue is the total income of an entity through sale of goods and proffering its services to the customers. Revenue can be operating or non-operating.
What is the role of the family circle in macroeconomics?
It plays a decisive role in macroeconomic pursuit for business cycles and economic enhancement in the long run.
What are the characteristics of a capitalist country?
A capitalist country is distinguished by sub-urbanised and voluntary conclusions for economic planning instead of the consolidated political practices. There are a few aspects of a capitalist financial structure (Economy) mentioned that would provide a better intuition into the concept. The attributes of a capitalist nation are as follows: 1 Liberty of customers to pick between goods and services. 2 The privilege of individuals to set up a business to supply goods and services. 3 There is a finite interference of the government. 4 Market forces regulate the distribution of goods.
What is capitalist country?
A capitalist country is distinguished by sub-urbanised and voluntary conclusions for economic planning instead of the consolidated political practices. There are a few aspects of a capitalist financial structure (Economy) mentioned that would provide a better intuition into the concept. The attributes of a capitalist nation are as follows:
What are the issues that an economy confronts?
When one speaks of the issues that an economy confronts, inflation, unemployment, increasing tax burden, etc., are all contemplated.
What are the attributes of a capitalist nation?
The attributes of a capitalist nation are as follows: Liberty of customers to pick between goods and services. The privilege of individuals to set up a business to supply goods and services. There is a finite interference of the government. Market forces regulate the distribution of goods.
What is macroeconomics?
Definition: Macroeconomics is that specialized field of economics which focuses on the overall economy. It works on the aggregate value of the various individual units, to determine its more substantial impact on the whole nation. All the prominent reforms and policies are based on this concept. For instance; the nation’s income is computed as ...
Why is macroeconomics important?
Macroeconomics is a vital field of study for the economists, government, financial bodies and researchers to analyze the general national issues and economic well-being of a country. Macroeconomics widely cover two major fundamentals which are further sub-parted into multiple topics, as explained below:
What is the theory of employment?
Theory of Employment: This stream of macroeconomics helps to figures out the level of unemployment and prevailing employment conditions in the country. Also, to know how it affects the supply, demand, savings, consumption, expenditure behaviour.
What is the basis of various economic reforms and the national decision model in a country?
Macroeconomics is the basis of various economic reforms and the national decision model in a country.
What concept of macroeconomics overlooks the importance of the individual unit or consumer?
Neglects Individual Consumers: The concept of macroeconomics overlooks the importance of the individual unit or consumer since the fundamental is to make use of the aggregates.
What is the theory of money?
Theory of Money: Macroeconomics analyzes the functions of the reserve bank in the economy, the inflow and outflow of money, along with its impact on the employment level.
What are the theories of macroeconomics?
There are six significant theories under macroeconomics: Economic Growth and Development: The status of a country’s economy can be evaluated in terms ...
What is Macroeconomics?
Macroeconomics is the study of economics involving phenomena that affects an entire economy, including inflation, unemployment, price levels, economic growth, economic decline and the relationship between all of these . While microeconomics looks at how households and businesses make decisions and behave in the marketplace, macroeconomics looks at the big picture - it analyzes the entire economy.
Why is macroeconomics important?
The study of macroeconomics is very important to make sound policy decisions that can affect the entire economy and all individuals, organizations, and governments that participate in it. Three major concepts studied in macroeconomics include economic output, unemployment and inflation and deflation. Economic output tells you how much an economy is ...
What is the basic model used in macroeconomics?
The basic model used in macroeconomics to study economic fluctuations is the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply. The model involves two variables: the economy's output, which is measured by real GDP, and the economy's overall price level, measured by a price index (usually the GDP deflator or CPI).
How do economics fluctuate?
Fluctuations in economic output are generally caused by one of two things. First, fluctuations can occur when the aggregate demand shifts. If the aggregate demand curve shifts to the left, output and prices will decline. If the curve shifts to the right, output and prices will rise. Second, economic fluctuations may be caused by a shift in aggregate supply. A right shift in the aggregate supply curve means that the quantity of goods and services supplied will increase at a particular price level. If the short-term aggregate supply curve shifts to the left, output will fall and prices will rise - this is called stagflation.
How do economists measure unemployment?
Economists measure unemployment through calculating the unemployment rate and the labor participation rate. The unemployment rate measures the percentage of people in the labor force that are unemployed. The labor participation rate measures the percentage of people that are eligible to work but are not working.
How does money supply affect inflation?
Money supply is correlated to inflation and deflation. According to the quantity theory of money, the quantity of money available in an economy will determine the general price level, and the growth rate in the quantity of money will determine the rate of inflation.
What happens when the supply curve shifts to the right?
If the curve shifts to the right, output and prices will rise. Second, economic fluctuations may be caused by a shift in aggregate supply. A right shift in the aggregate supply curve means that the quantity of goods and services supplied will increase at a particular price level.
What is macroeconomics?
Macroeconomics is the study of the aggregates and averages of the entire economy. It's the part of economic theory which studies the economy in its totality or as a whole. In microeconomics, we study the individual economic units like a household, a firm, or an industry. However, in macroeconomics we study the whole economic system like national ...
What are the functions of macroeconomics?
The main functions of macroeconomics are the collection, organising, and analysis of data; determining national income; and formulating appropriate economic policies to maintain economic growth and full employment in a developing country. The scope of macroeconomics include the following theories: National income. Money.
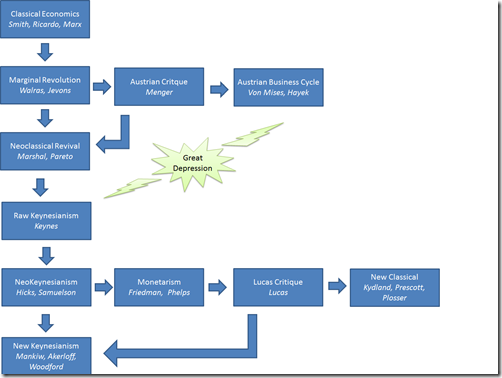
What is macroeconomics before Keynes?
Keynesian economics. Macroeconomics before Keynes is sometimes called “classical” economics. According to classical economics: An economy as a whole always functions at a level of full employment, due to free play of market forces in a free economy. Supply creates its own demand.
Why is macroeconomics important?
Since the study of millions of individual economic units is almost impossible, macroeconomics provided tools for the assessment of economic policy. Macro policies make it possible to control inflation and deflation, and moderate violent booms and recessions.
What is the theory of income and employment?
Macroeconomics is also known as the theory of income and employment, since the subject matter of macroeconomics revolves around determination of the level of employment and income. At the time of the Great Depression, government participation through monetary and fiscal measures in the economy increased considerably.
What are the two major branches of economics?
There are two major branches of economics: Microeconomics. Macroeconomics. In short, microeconomics is the study of individual economic units of the economy, while macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole and its totality. There are two main schools of economic thoughts. These schools are 1. Classical economics or 2.
What was Keynes's theory of economics?
Keynes criticised the Classical assumption of full employment and developed modern macroeconomics: economic theory that attempts to connect money supply, employment, business cycles, and government policy. The incentive for development of modern macroeconomics came from the Great Depression of the early 1930s.
What is macroeconomics?
Macroeconomics is the study of aggregates and averages of the entire economy. Such aggregates are national income, total employment, aggregate savings and investment, aggregate demand, aggregate supply general price level, etc. Here, we study how these aggregates and averages of the economy as a whole are determined and what causes fluctuations in ...
What is macroeconomics in economics?
Macroeconomics is the study of aggregates and averages of the entire economy. ADVERTISEMENTS:
What is the aim of the determinants of the economy?
Having understood the determinants, the aim is how to ensure the maximum level of income and employment in a country.
Why is macroeconomics important?
Importance of Macroeconomics: 1. It helps to understand the functioning of a complicated modern economic system. It describes how the economy as a whole functions and how the level of national income and employment is determined on the basis of aggregate demand and aggregate supply. 2.
What are the effects of macroeconomic policies?
Correct economic policies formulated at macro level have made it possible to control business cycles (inflation and deflation) and as a result violent booms and depressions have become things of the past.
What is the subject matter of macroeconomics?
Since the subject matter of macroeconomics revolves around determination of the level of income and employment, therefore, it is also known as ‘Theory of Income and
What has macroeconomic theory saved us from?
Last but not the least, is that macroeconomic theory has saved us from the dangers of application of microeconomic theory to the problems of the economy as a whole.
What do you mean by Macroeconomics class 12 CBSE Board?
See, the question is, what is macroeconomics in economics in simple words? Define macroeconomics class 12 CBSE Board
Definition of Macroeconomics Class 12 CBSE Board
Macroeconomics is the study of economic aspects of the country as a whole.
What is macroeconomic policy?
Macroeconomic policy is a government plan and action to influence the economy as a whole. The policy is to achieve macroeconomic targets such as: Macroeconomic policy differs from the microeconomic policy. The latter focuses on specific economic agents, for example, raising excise in the tobacco product.
How does macroeconomic policy differ from microeconomic policy?
Macroeconomic policy differs from the microeconomic policy. The latter focuses on specific economic agents, for example, raising excise in the tobacco product. The first two influence the economy through the aggregate demand side. While the last affects aggregate supply. Fiscal policy uses budget instruments.
Why is high inflation bad for the economy?
High inflation is endangering the economy because the purchasing power of money is falling. It requires government intervention. To moderate inflation, the government can take several alternatives, including:
What are the key tools of monetary policy?
The key tools of monetary policy include policy rates, reserve requirements, and open market operations. The supply-side policy seeks to improve the competitiveness and efficiency of the free market. To do this, the government introduces privatization, deregulation, and antitrust policies.
Which policy uses budget instruments to influence the economy?
Monetary policy. Supply-side policy. The first two influence the economy through the aggregate demand side. While the last affects aggregate supply. Fiscal policy uses budget instruments. Governments can change taxes and their spending to influence the economy.
Is monetary policy contractionary or expansionary?
In general, monetary and fiscal policy can be expansionary or contractionary policies. Both policies ensure the economy to operate close to its potential level. By doing so, the economy avoids the adverse effects of the business cycle, such as hyperinflation and recession. Expansionary policies drive up economic growth.
