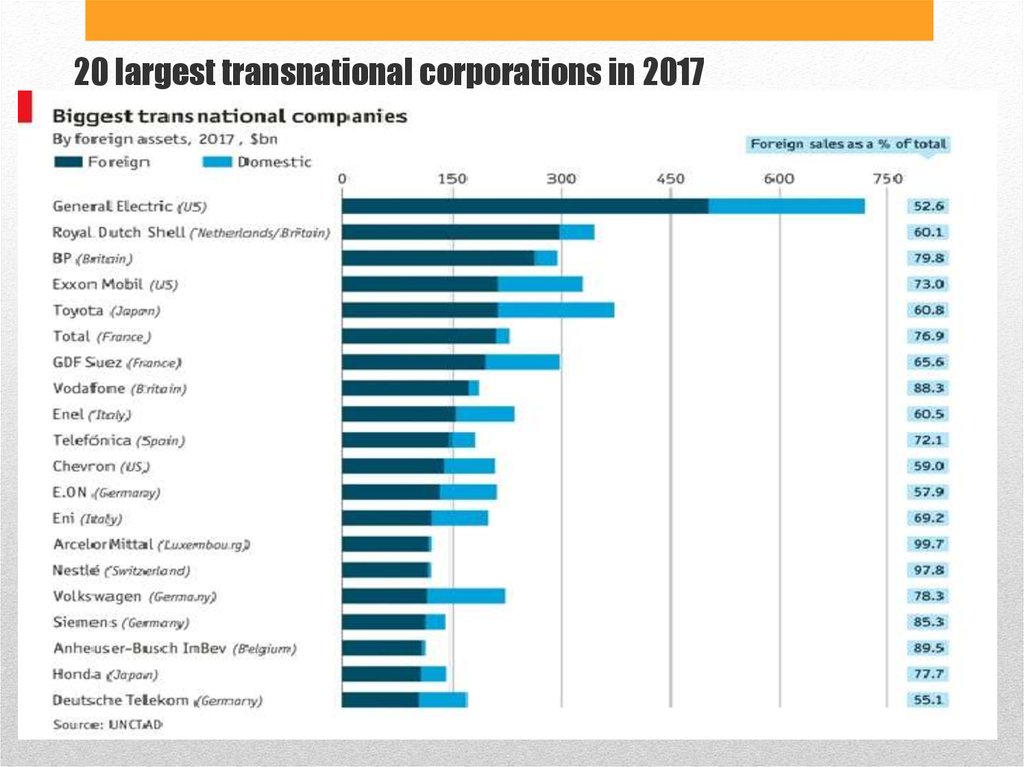
Transnational corporation: definition
- They operate (produce and sell) in more than one country.
- They aim to maximise profits and lower costs.
- They are responsible for 80 percent of global trade. 1
- 69 of the richest 100 entities in the world are TNCs, rather than countries! 2
What are the purposes of transnational corporations?
Transnational corporations and other business enterprises shall ensure equality of opportunity and treatment, for the purpose of eliminating discrimination based on race, colour, sex, religion, political opinion, nationality, social origin, social status, indigenous status, disability, age (except for children who may be given greater ...
What does transnational corporation mean?
So, you may be asking yourself right now, what does it mean to be a transnational corporation. A transnational corporation, also known as a multinational corporation, is a corporation that has a home base, but is registered, operates and has assets or other facilities in at least one other country at one time.
Which company is transnational?
Transnational companies are there all around the world, and they operate truly at the global level. Nestlé S.A is an example of a Transnational company. Difference between Multinational and Transnational Definition. Multinational companies operate in more than one country and have a centralized management system.
What are the characteristics of transnational company?
What are Transnational Corporations?
- Introduction – Definition and Scale of TNCs. ...
- The key characteristics of TNCs are: A substantial part of their workforce is located in the developing world, but often employed indirectly through subsidiaries.
- The Huge Economic Power of TNCs. ...
- SignPosting. ...
- Sources. ...
What do you mean by transnational and multinational corporations?
multinational corporation (MNC), also called transnational corporation, any corporation that is registered and operates in more than one country at a time. Generally the corporation has its headquarters in one country and operates wholly or partially owned subsidiaries in other countries.
What is the role of transnational corporations?
Thus, transnational corporations are the result of the processes occurring in the world economy, leading to the improvement of production relations, the expansion of the geography of production. They contribute to strengthening the economic globalization and global competitive relations.
What are the characteristics of transnational corporations?
The key characteristics of TNCs are: They seek competitive advantaged and maximization of profits by constantly searching for the cheapest and most efficient production locations across the world. They have geographical flexibility – they can shift resources and operations to any location in the world.
What is transnational corporation in social studies?
Transnational Corporations, also known as Multinational Corporations, are large business enterprises involved in foreign investments, the production of goods or services, or asset and income management in a number of different countries.
What are the advantages of transnational corporations?
Multi-national or Trans-national companies are ones which locate their factories throughout the world. This gives them many benefits, such as access to the world market, cheap labour, cheaper production costs, and therefore greater profits.
What is the impact of transnational corporations?
The practices of transnational corporations (TNCs) affect population health through production methods, shaping social determinants of health, or influencing the regulatory structures governing their activities [1–3]. Described as 'the primary movers and shapers of the global economy' ([4] p.
What is an example of a transnational organization?
Some examples of TNCs include Apple, McDonald's, Coca-Cola, Nike, and Amazon. They all operate in multiple countries around the world.
How many transnational corporations are there?
Today, there are an estimated 77,000 TNCs in the world, with more than 770,000 foreign affiliates.
Where are transnational corporations located?
Most TNCs are headquartered in the United States, the European Union or Japan – the so-called Triad, which also accounts for the largest share of foreign direct investment worldwide. The United States is home to the largest number of TNCs (11), followed by France (8), Germany (8), the United Kingdom (7) and Japan (4).
What are 10 examples of the TNCs?
Examples of multinational corporationsShell. Shell petrol station in the UK.McDonald's. Mcdonalds in Kazan, Russia.Vodafone. Vodafone advert in Kumily, India.Coca Cola. Coca Cola advert in Kabul, Afghanistan.Advert for Three in Hong Kong.
Why are TNCs important in Globalisation?
TNCs are a key driver of globalisation because they have been re-locating manufacturing to countries with relatively lower unit labour costs in order to increase profits and returns for shareholders.
What is the effect of transnational companies in global economy?
TNCs strengthen the dependence of less developed countries on the richest countries. By moving production to countries with lower standard of living and wages they can hinder the growth of living standards. By transferring of assets to countries with lower social contribution of payments they minimize their tax burden.
What is the role of TNCs in developing countries?
Some TNCs are able to exert influence over developing countries directly: employing government officials involved in economic policy making. making financial contributions to political parties. bribery.
When did transnational corporations become relevant?
Although TNCs existed before the twentieth century (colonial trading companies such as the East India Company, the Hudson's Bay Company, and the Virginia Company of London were precursors of the modern TNC), only since the 1960s have they become a major force on the world scene (World Bank 1987, p. 45).
What is a transnational corporation quizlet?
A transnational, or multinational, corporation has its headquarters in one country and operates wholly or partially owned subsidiaries in one or more other countries.
Are transnational corporations harmful or not?
They pollute the environment – as with the case of Shell in Nigeria. They take risks with health and safety, which can result in worker injury and death – as with the case of Union Carbide in Bhopal. They profit from human rights abuses – as with Coca Cola in Columbia.
Name some traits of TNCs.
They operate (produce and sell) in more than one country. They aim to maximise profits and lower costs. They are responsible for 75 percent of glob...
What are TNCs? What does TNC stand for? Provide some examples.
TNC stands for Transnational Corporation. TNCs are businesses that have a global reach Examples of TNCs include Apple, Microsoft, Nestle, Shell, N...
Why do Developing countries offer a range of incentives for TNCs to invest in their country? What are some examples of incentives?
Their ability to hire many people and invest more widely in the country as a whole makes many governments regard the presence of TNCs in their coun...
What is meant by ' a race to the bottom' ?
As each country is competing against the other for TNCs to set shop within their borders, nations offer them conditions that work against their own...
Which theories are in favour and are critical of the role of TNCs?
Favour - Modernisation theory and Neoliberalism Critical - Dependency theory
How does Modernisation theory view the role of TNCs for global development?
Modernisation Theory and Neoliberalism view TNCs as a positive force and instrumental in development strategies.
How does Dependency theory view the role of TNCs for global development?
Dependency Theory views TNCs as exploitative, unethical, and immoral.
What are some of the argued benefits of TNCs for development?
Bring in investment More jobs Increased opportunities for women Encourages international trade - opening new markets which should increase economic...
What are some of the criticisms aimed at TNCs?
Poor working conditions that lead to ill-health and even death. Ecological damage. Removal of indigenous people. Examples include Shell in Nigeria...
Why is Nike a transnational corporation?
Nike is a transnational corporation because it has branches in 160 countries. It also employs over 44,000 people collectively in the countries it o...
What are five TNCs?
Some examples of TNCs include Apple, McDonald's, Coca-Cola, Nike, and Amazon. They all operate in multiple countries around the world.
Why is McDonald's a transnational corporation?
McDonald's is a transnational corporation because it operates in over 100 countries worldwide. It also employs over 200,000 people from the differe...
Is Amazon a transnational company?
Yes, Amazon is a transnational e-commerce corporation that operates in thirteen countries. Its employees number over 1.4 million and come from the...
Why is Coca Cola a transnational corporation?
The Coca-Cola beverage company is an example of a transnational corporation because it operates in over 200 countries worldwide and is headquartere...
What is a transnational corporation?
A transnational corporation is an enterprise that is involved with the international production of goods or services, foreign investments, or income and asset management in more than one country. It sets up factories in developing countries as land and labor are cheaper there.
What is the difference between a multinational and a transnational corporation?
Transnational corporations share many qualities with multinational corporations, with the subtle difference being that multinational corporations consist of a centralized management structure, whereas transnational corporations generally are decentralized, with many bases in various countries where the corporation operates.
What are the advantages of transnational companies?
One of the significant advantages of a transnational company is that they are able to maintain a greater degree of responsiveness to the local markets where they maintain facilities. Transnationality also refers to the extent to which a firm engages in value-creating activities across national borders.
What is the United East India Company?
Characteristics. The United East India Company (VOC) was a pioneering early model of the multinational/transnational corporation at the dawn of modern capitalism. 17th-century etching of the Oost-Indisch Huis (Dutch for "East India House"), the global headquarters of the United East India Company (VOC) in Amsterdam.
How many transnational corporations were there in 2007?
According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development there were an estimated 77 000 Transnational Corporations in the world in 2007, that’s the most recent data I could find! That had almost doubled since the late 1990s when there were 37 000.
How many TNCs have 90% of their assets in a different country?
TNC assets are distributed worldwide rather than focused in one or two countries – for example, 17 of the top 100 TNCs have 90% of their assets in a different country from their head office.
What are the characteristics of a TNC?
The key characteristics of TNCs are: 1 They seek competitive advantaged and maximization of profits by constantly searching for the cheapest and most efficient production locations across the world 2 They have geographical flexibility – they can shift resources and operations to any location in the world 3 A substantial part of their workforce is located in the developing world, but often employed indirectly through subsidiaries. 4 TNC assets are distributed worldwide rather than focused in one or two countries – for example, 17 of the top 100 TNCs have 90% of their assets in a different country from their head office.
Why did TNCs invest in the developing world?
Fobel et al (1980) note that from the 1970s TNCs set about investing significantly in the developing world because of high labour costs and high levels of industrial conflict in the West, which reduced profits. The investment was greatly helped by developing countries, which actively sought TNC investment by setting up special areas called Export Processing Zones, or Free-Trade Zones, in which TNCs were encouraged to build factories for export to the West.
How many free trade zones are there in the world?
There are now over 5000 free or export processing zones in the world today which employ over 43 million workers, the majority of which are based in China’s territories.
Do TNCs have more economic power than nation states?
Critics remind us that GDP and annual revenue measure different things, so these figures may not show actual differences in economic power, but this aside, the relative economic power of TNCs has grown in relation to nation states over the last few decades, and today TNCs wield much more economic power than they did in the past.
What is a transnational corporation?
A transnational corporation (TNC) is "any enterprise that undertakes foreign direct investment, owns or controls income-gathering assets in more than one country, produces goods or services outside its country of origin, or engages in international production" (Biersteker 1978, p. xi i). Variously termed multinational corporations (MNCs) ...
How did transnational corporations increase in the 20th century?
The phenomenal increase in transnational corporate activity in the latter part of the twentieth century can be accounted for in large part by technological innovations in transportation, communication, and information processing that have permitted corporations to establish profitable worldwide operations while maintaining effective and timely organizational control. The actual difference in foreign direct investment up to and after 1960 is even greater than the figures in Table 1 indicate. FDI for 1960 and before includes foreign portfolio investment, which is undertaken mainly by individuals, as well as foreign direct investment, which almost always is made by TNCs. These two types of investment were not reported separately for most countries before 1970. Thus, total FDI stocks are inflated. For example, Wilkins (1974, pp. 53–54) reports that in 1929–1930, U.S. foreign portfolio and direct investments were almost equal. American direct investment abroad was only $7.5 billion; the remaining $7.2 billion recorded in Table 1 was foreign portfolio investment.
How do TNCs manipulate borders?
Through the use of these and other innovative strategies, TNCs have manipulated the concept of borders to their advantage. What exactly is the advantage that TNCs achieve through their cross-border flexibility? They gain between-border variability. The fact that different states have different laws and standards regarding all aspects of economic activity contributes to the power of TNCs that strategically play off one country's set of rules against another's. For example, variations in national laws on tariffs, financing, competition, labor, environmental protection, consumer rights, taxation, and transfer of profits are all carefully weighed by TNCs in deciding where and how to conduct business. Together, these considerations form what has come to be known as "the policy environment" (UNCTAD 1993, pp. 173–175). In the internation competition to attract foreign investment by creating a "favorable policy environment," between-border variability encourages a "race to the bottom" (Chamberlain 1982, p. 126), resulting in a continuing erosion of sovereignty. Whereas TNCs operate in a de facto borderless world created by technological ingenuity, de jure political and legal distinctions still mark the boundaries on a world map composed of nation-states. This represents the crux of the inherent conflict between TNCs and nation-states as they are currently structured.
When did TNCs start?
Although TNCs existed before the twentieth century (colonial trading companies such as the East India Company, the Hudson's Bay Company, and the Virginia Company of London were precursors of the modern TNC), only since the 1960s have they become a major force on the world scene ( World Bank 1987, p. 45). Table 1 corroborates this by listing the foreign direct investment (FDI) stock of corporations by country from the beginning of the century to 1997. In 1900, only European corporations were major transnational players, but by 1930, American TNCs had begun to make their presence felt. The year 1960 marks the beginning of a new era in corporate transnationalization. In each of the decades from 1960 to the present, world FDI stock has more than tripled, whereas it only doubled during the first half of the century.
How has technology increased the rate of cross-border mobility?
Developments in transportation, communication, and information technology not only have increased the rate of cross-border mobility among TNCs but also have increased the speed or velocity with which cross-border transactions take place. Concurrently measuring both the location and the velocity of TNC activity often produces "uncertain" results, generating "inderminacy" for a state.
What is the move toward integrated transnational investment?
The move toward integrated transnational investment can be seen as a logical and rational decision by business enterprises to adapt to their environment.
Which countries are TNCs based in?
corporations based in the Triad ( United States, European Union, and Japan) were responsible for nearly four-fifths of world FDI stock (UNCTAD 1998, pp. 379–384). Clearly, TNCs largely operate out of and invest in the developed countries of the global economy.
What is a multinational corporation?
A multinational corporation is an organization that has assets or facilities in multiple countries. While they typically have a main office in their home country, these organizations may have offices, factories and other locations spread out across the globe.
How does a multinational corporation work?
The structure and operations of each multinational corporation may vary depending on the industry they're in, the size of their organization and the goods or services they produce.
Advantages of being a multinational corporation
Organizations that become multinational corporations may experience several benefits, including a faster growth rate. They can also have a positive effect on the international economies they conduct business in by creating more jobs. Becoming a multinational corporation may also benefit your organization by:
Disadvantages of being a multinational corporation
While organizations may benefit from becoming multinational corporations in a variety of ways, there are also some common challenges it's important to be aware of so you can mitigate risks. Here are some potential challenges of operating as a multinational corporation:
Tips for deciding whether to become a multinational corporation
Here are some tips that can help you decide whether becoming a multinational corporation is the right choice for your organization:
Why are transnational companies better than other types of international companies?
Transnational companies often have an advantage over other types of international business strategies, which is that the concentration on local employees and the needs of local customers can make a company more responsive to the needs of the local culture.
What is a transnational strategy in business?
Transnational strategy in business is a type of international business plan that fits two primary criteria. These two criteria are that the business must have high local responsiveness and high global integration. This means that a transnational business is one that usually has branches or offices in all the countries they serve, but that these local branches are integrated into the larger global goals and plans of the business. Transnational businesses consider the cultures in the countries they operate in and how best to appeal to those people specifically rather than assuming every country's population wants the exact same thing.
How does transnational business increase efficiency?
In addition to saving money through local locations, a transnational business may find that those locations also increase efficiency. For instance, rather than new products for that country being designed overseas, manufactured overseas and then shipped to the local area for distribution, a company may have local employees creating the products that will appeal to the local market, they may be manufactured locally and then need to be shipped a shorter distance. This increases the efficiency of the process and likely also reduces costs.
What is the challenge of transnational operations?
The other big challenge with transnational operations is that it can be difficult to centralize all these locations spread across the globe. Since transnational strategies are not just about the local offices but also the global integration of those locations, this is an important aspect of the strategy.
Why do companies use transnational marketing?
A big reason for this is that local employees should know how to interact with others in their culture better than an outsider might. Additionally, if there is a local team deciding on the products or services and the marketing approach, they are likely to be more effective than a team of outsiders. Companies that aren't as involved locally where their products are sold may find less of a positive reception.
What do transnational companies need?
To remedy this, transnational companies usually need an experienced, capable management team that can make sure the brand is managed consistently in all locations. These managers might be at headquarters but travel regularly to local offices, or they might work in local offices and report back to the headquarters. These managers and executives should have a solid grasp of the company's global strategies and how that should be reflected by the local offices.
What are the different types of international business strategies?
Transnational strategy is one of four different types of international business strategies. The other types are multidomestic, which has low global integration and high local responsiveness; global, which has high global integration and low local responsiveness; and international, ...
