Divergent Plate Boundaries
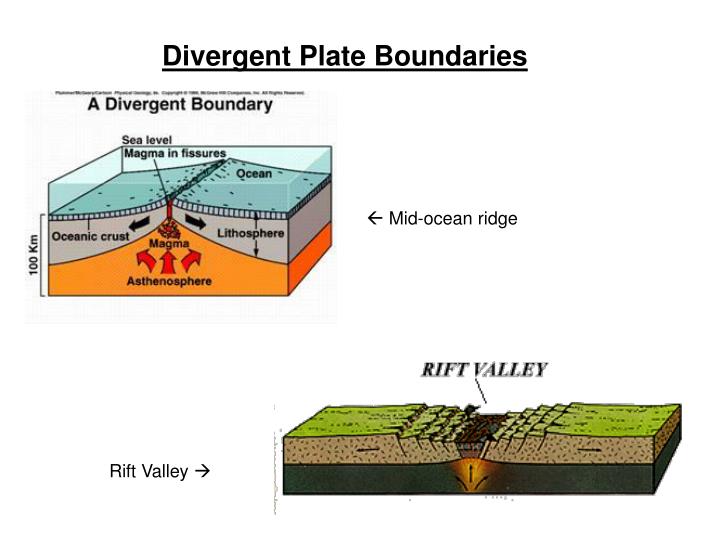
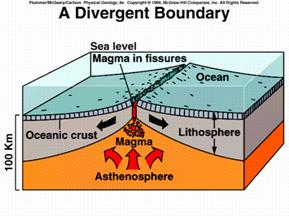
- Mid-Ocean Ridges. At oceanic divergent boundaries, new lithosphere is born hot and cools over millions of years. ...
- Iceland. At over 10,000 miles, the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is the longest mountain chain in the world, stretching from the Arctic to just above Antarctica.
- Continental Spreading. ...
- String Cheese and Moving Rifts. ...
What does it mean if a plate boundary is divergent?
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rifts which produce rift valleys.
What are two plates that are probably a divergent boundary?
Visit the Interactive Plate Boundary Map to explore satellite images of divergent boundaries between oceanic plates. Two locations are marked: 1) the Mid-Atlantic Ridge exposed above sea level on the island of Iceland, and 2) the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Africa.
What is likely to happen at a divergent boundary?
Where two plates separate, or diverge, the boundary is termed a divergent plate boundary. The plates at these spots are moving apart and magma rises to fill in the separation resulting in lava flows and volcanoes. This divergence is also referred to as sea floor spreading.
What are facts about divergent plate boundaries?
Plate Tectonics
- Convergent Boundaries. Where plates serving landmasses collide, the crust crumples and buckles into mountain ranges. ...
- Divergent Boundaries. At divergent boundaries in the oceans, magma from deep in the Earth's mantle rises toward the surface and pushes apart two or more plates.
- Transform Boundaries. ...
Where are divergent boundaries found?
The vast majority of divergent boundaries are found in the ocean, where they were not mapped or understood until the mid-to-late 20th century.
Where does divergence occur?
Divergence happens in the continental setting too—that's how new oceans form. The exact reasons as to why it happens where it does, and how it happens, are still being studied. The best example on Earth today is the narrow Red Sea, where the Arabian plate has pulled away from the Nubian plate.
Why do divergent zones take the form of long, wide swells running along the ocean floor?
As it cools it shrinks, thus the fresh seafloor stands higher than the older lithosphere on either side. This is why divergent zones take the form of long, wide swells running along the ocean floor: mid-ocean ridges. The ridges are only a few kilometers high but hundreds wide.
Why do ridges have steeper sides?
Slow-spreading ridges like the Mid-Atlantic Ridge have steeper-sloping sides because it takes less distance for their new lithosphere to cool. They have relatively little magma production so that the ridge crest can develop a deep dropped-down block, a rift valley, at its center.
What are the magnetic stripes on the seafloor?
These stripes mirrored each other on both sides of divergent boundaries, giving geologists irrefutable evidence of seafloor spreading.
What is the main force driving plate motion?
In divergent zones, the plates are pulled, and not pushed, apart. The main force driving this plate motion (although there are other lesser forces) is the "slab pull" that arises when plates sink into the mantle under their own weight at subduction zones.
What are some examples of continental divergence?
A much better example of how continental divergence creates oceans is easy to see in the South Atlantic Ocean. There, the precise fit between South America and Africa testifies to the fact that they were once integrated with a larger continent. Early in the 1900s, that ancient continent was given the name Gondwanaland.
What forces pull apart the continental crust?
As a plate capped by thick continental crust pulls apart, the crust thins and elevates a broad region. These forces result in long mountain ranges, intervening valleys (basins) and volcanic activity characteristic of the Basin and Range Province and Rio Grande Rift.
What is the rift in the continental crust?
Continental Rift—Plate Rip s Apart. As the plate stretches and thins, the underlying asthenosphere flows upward and expands like a hot-air balloon, lifting the region to higher elevations. The continental crust breaks along faults, forming long mountain ranges separated by rift valleys.
Why does the ocean basin sink below sea level?
The ocean basin sinks below sea level because the crust is thinner and more dense, and therefore less buoyant.
What happens when tectonic plates move away from one another?
The underlying asthenosphere rises and expands like a hot-air balloon, elevating a broad region . If the plate is capped by thick continental crust, the resulting continental rift zone rises high above sea level.
What happens to the asthenosphere as the plate stretches and thins?
As the plate stretches and thins, the underlying asthenosphere flows upward and expands like a hot-air balloon, lifting the region to higher elevations. The continental crust breaks along faults, forming long mountain ranges separated by rift valleys.
Why does magma become rich in silica?
The magma becomes enriched in silica because high-silica minerals tend to melt first. Some of the lava that initially pours out at continental rift zones is thus thick and pasty, cooling to light-colored rocks (rhyolite and dacite), and steep-sided lava domes and composite volcanoes.
What causes valley floors to drop down along fault lines in the Basin and Range Province?
Continental rifting causes valleys floors to drop down along fault lines in the Basin and Range Province. Snake Valley, Tucson Basin and Death Valley are the basins, while the Snake Range, Rincon Mountains, Tucson Mountains and Panamint Mountains are the adjacent ranges.
What is the topography of the Basin and Range Province and Rio Grande Rift?
The topography of the Basin and Range Province and Rio Grande Rift reveals the full range of characteristics of a continental rift zone. First, much of the region—particularly the northern portion—is well above sea level.
What is the Rio Grande Rift?
The Rio Grande Rift is an arm of the Basin and Range Province extending across westernmost Texas, New Mexico, and southern Colorado. Earthquakes, fault-block mountains, and volcanism at Guadalupe Mountains National Park and Bandelier and White Sands national monuments are consequences of the ongoing continental rifting.
How did the lava flow form?
The dark-colored lava flows formed over a billion years ago in the Keweenawan Rift, as the ancient North American continent tried to rip apart and low-silica (basaltic) magma poured out on the surface.
What is divergent plate boundary?
Divergent plate boundaries are those tectonic borders where tectonic plates pull away from each other and form a new crust. ScienceStruck takes you through some interesting facts about these divergent boundary zones on this Earth.
What are the three types of plate boundaries?
According to the Plate Tectonics theory, there are three basic types of plate boundaries: 1. Convergent: Where two plates move towards each other and get pushed one below the other. 2. Divergent: Where the plates move apart. 3. Transform: Where plates slide past each other.
What is the zone where two tectonic plates move away from each other?
Definition and Meaning of Divergent Plate Boundary. The zone where two tectonic plates move away from each other is called the divergent plate boundary. Divergence or separation of two plates occurs due to convection currents in the Earth’s upper mantle or asthenosphere.
What causes the lithosphere to melt?
The heat within the mantle makes the lithosphere (layer below the Earth’s crust) melt. The molten magma that is under pressure, forces the plates to move apart. A rift is thus created between the two plates. The upwelling magma comes to the ocean surface, cools down, and forms the new oceanic crust of basalt.
What plate is Gakkel Ridge on?
Gakkel Ridge is a divergent plate between the Eurasian and the North American Plate. Chile Rise: Between the Nazca and the Antarctic plate lies the Chile rise, which is being subducted (or pushed under at a convergent boundary) on its eastern end.
How do tectonic plates move?
Tectonic plates move slowly and steadily. The ridge spreads or widens by a few centimeters every year. The sea floor spreading results in the formation of parallel sea mounts or even bigger mountains on the ocean floor.
Where is the East African Rift Zone?
East African Rift zone: It includes the rift valleys present on the east and west side of Lake Victoria; also the larger Great Rift Valley refers to this region. There are many rift valley lake formations in this area, like Koka, Awasa, Abaya, etc.
What happens when plates move apart?
As the plates move apart, an opening is created which allows the asthenosphere to rise toward the surface to fill that space. As the plates pull apart, the load on the asthenosphere decreases which decreases the pressure in the asthenosphere and leads to decompression melting.
What is the difference between a divergent and a mid-ocean ridge?
When a divergent boundary occurs between two oceanic plates a mid-ocean ridge. This is where new oceanic lithosphere forms. Mid-ocean ridges are also called spreading centers because of the way the plates spread apart.
What happens to the continents when rifting continues?
If rifting continues, the continent splits into two pieces and a narrow ocean basin forms as seafloor spreading takes place. As the edges of the continents move away from the heat associated with active spreading , the thinned continental crust cools and drops in elevation, eventually dropping below sea level.
Why are mid ocean ridges elevated above the seafloor?
Mid-ocean ridges are elevated above the surrounding seafloor because they consist of hotter, less dense materials and the underlying asthenosphere is thinner and bulging right beneath the ridges. The elevation of the seafloor decreases away from the ridge because the rock cools and contracts.
What happens to the seafloor during continental rifting?
If continental rifting progresses it can lead to seafloor spreading and the formation of a new ocean basin. The initial stage of continental rifting commonly includes broad uplift of the surface as mantle-derived magma ascends into crust. That magma can melt parts of the continental crust which produces additional magma.
What are the three types of plate boundaries?
Plate Boundaries: Divergent, Convergent, and Transform. YouTube. 0. Movement in narrow zones along plate boundaries causes most earthquakes. Most seismic activity occurs at three types of plate boundaries—divergent, convergent, and transform. As the plates move past each other, they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up.
What happens when the plates move past each other?
As the plates move past each other, they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is released as seismic waves, causing the ground to shake. This is an earthquake. Some of the plates have ocean water above them.
What is the term for the movement of plates towards each other?
Convergent (Colliding): This occurs when plates move towards each other and collide. When a continental plate meets an oceanic plate, the thinner, denser, and more flexible oceanic plate sinks beneath the thicker, more rigid continental plate. This is called subduction.
What are spreading centers?
The earthquakes that occur along these zones , called spreading centers, are relatively small. The Great Rift Valley in Africa, the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden all formed as a result of divergent plate motion. Convergent (Colliding): This occurs when plates move towards each other and collide.
What happens when two tectonic plates slide past each other?
When two tectonic plates slide past each other, the place where they meet is a transform or lateral fault.
What is subduction in science?
This is called subduction. Subduction causes deep ocean trenches to form, such as the one along the west coast of South America. The rocks pulled down under the continent begin to melt. Sometimes the molten rock rises to the surface, through the continent, forming a line of volcanoes.
Divergent Plate Boundaries
Divergent plate boundaries cause similar effects in oceans as they do on land. New seafloor erupts through rift valleys when plates diverge at mid-ocean ridges. The flow of magma at mid-ocean ridges form convection cells, and this movement is very likely to cause earthquakes.
Transform Faults
A transform fault is when one plate slides past another, causing earthquakes on land and divide mid-ocean ridges into segments.
Continental Rifting
Divergent plate boundaries on land rip apart continents and create new ocean basins; this is called continental rifting. Magma rises and splits, and new ocean crust erupts through the space left behind. The Atlantic Ocean is a final stage example of continental rifting where a whole ocean now separates the Americas from Europe.