
What does a flat tympanogram indicate?
Type B shows a flat line. It indicates a constant middle ear pathology which is a build-up of fluid or ear infection behind the eardrum. A flat tympanogram (type B) also indicates a stiff tympanic membrane. Some of the cases of type B shows – presence of hole inside the eardrum, the dissimilarity lies in the ear canal volume,
When does a tympanogram look too “flat”?
If the tympanogram is abnormal, it may peak before or after the 0 daPa mark, or a flat line will be plotted if the eardrum doesn't move (due to perforation) or can't move (due to fluid or another cause). Note that daPa stands for decapascals, a unit of air pressure. Why is tympanometry used?
What is a normal tympanogram?
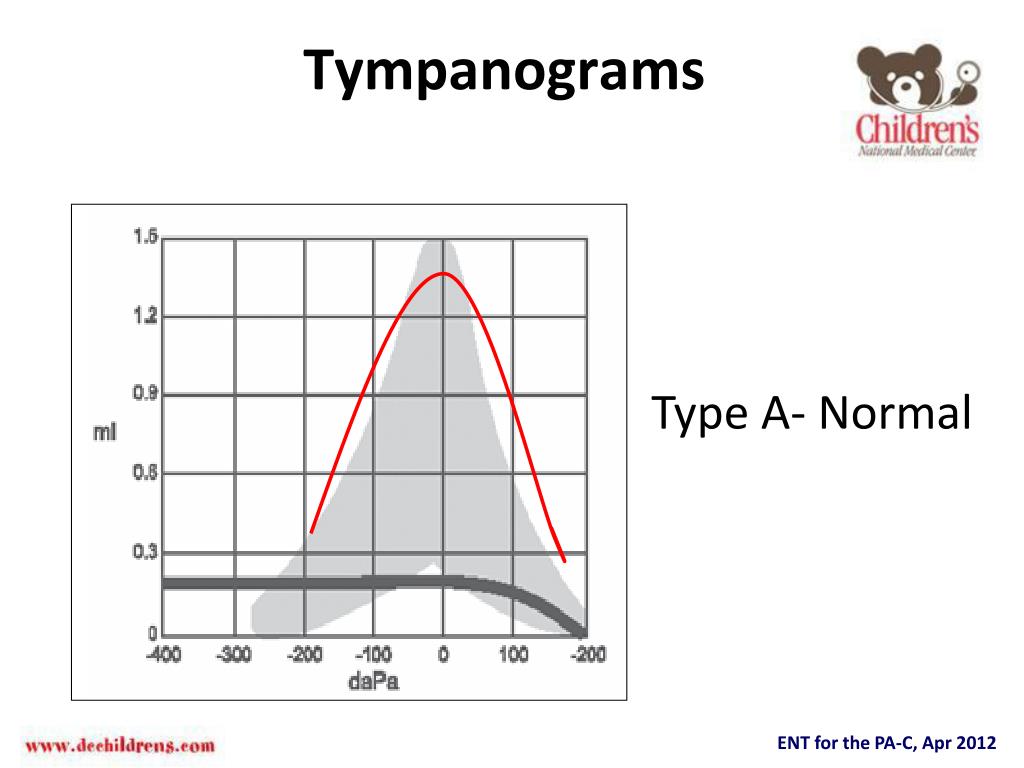
The tympanogram curve has a normal maximum height that occurs at a pressure close to zero and the width of the curve is normal. This is referred to as a type A tracing. In this figure, the ear canal volume is normal. Likewise, people ask, what does a Tympanogram show?
How to interpret a tympanogram?
How to Read a Tympanogram: Tympanometry is a method of assessing the status of the middle ear. The compliance (inverse of stiffness) of the tympano-ossicular system is charted against various pressure changes. X axis shows the pressure gradient. Y axis shows the compliance. There are three types of tympanograms.
What does a flat tympanogram mean?
A flat tympanogram (type B) means a stiff tympanic membrane and predicts fluid in the middle ear (a positive predictive value of approximately 90%). A normal tympanogram (type A) means a middle ear without fluid and an intact tympanic membrane (a negative predictive value up to more than 95%).
What does it mean to have a flat eardrum?
Retracted eardrums are caused by a problem with your Eustachian tubes. These tubes drain fluid to help maintain even pressure inside and outside of your ears. When your Eustachian tubes aren't working correctly, decreased pressure inside your ear can cause your eardrum to collapse inward.
What does shallow tympanogram mean?
Type AD (deep) tympanograms demonstrate increased compliance, as seen with ossicular chain discontinuity. Type AS (shallow) tympanograms show decreased compliance, suggesting a stiff middle ear system, which can be caused by myringosclerosis or otosclerosis.
What does an abnormal tympanogram mean?
Abnormal tympanometry test results may suggest: fluid in the middle ear. perforation of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) scarring of the eardrum, which usually results from frequent ear infections. middle ear pressure beyond the normal range.
What type of Tympanogram is considered normal?
Tympanogram tracings are classified as type A (normal), type B (flat, clearly abnormal), and type C (indicating a significantly negative pressure in the middle ear, possibly indicative of pathology).
What type of hearing loss is a type C Tympanogram?
Finally, a Type C tympanogram indicates a significantly negative peak pressure, which is possibly caused by Eustachian tube dysfunction or a developing or resolving middle ear infection.
What can tympanometry diagnose?
Tympanometry is typically used to detect or rule out several things: the presence of fluid in the middle ear, a middle ear infection, a hole in the eardrum (perforation), or Eustachian tube dysfunction.
What does a normal tympanogram look like?
Type A tympanograms look like a teepee, and indicate a normal middle ear system, free of fluid or physiological anomalies which would prevent the admittance of sound from the middle ear into the cochlea. Figure 1 shows an example of a Type A tympanogram.
What assessment findings are usually present with sensorineural hearing loss?
If you are diagnosed with sensorineural hearing loss, your results may show that the hearing loss is: Mild: you can't hear certain sounds, such as tones that are too high or too low. Moderate: you can't hear many sounds, such as speech in a noisy environment. Severe: you can't hear most sounds.
How is fluid in middle ear diagnosis?
An instrument called a pneumatic otoscope is often the only specialized tool a doctor needs to diagnose an ear infection. This instrument enables the doctor to look in the ear and judge whether there is fluid behind the eardrum. With the pneumatic otoscope, the doctor gently puffs air against the eardrum.
What does it mean to have negative pressure in your ear?
Obstruction or blockage of the eustachian tube results in a negative middle ear pressure, which will cause the ear drum to retract (suck in). In adults this is usually accompanied by some ear discomfort, a fullness or pressure feeling and may result in a mild hearing impairment and ringing in the ear (tinnitus).
Will a retracted eardrum fix itself?
A retracted eardrum can sometimes resolve on its own. If treatment is needed, it may include nasal steroids, oral antibiotics, the placement of a temporary ventilation tube in the eardrum, or the surgical removal of enlarged tonsils or adenoids.
Can an eardrum grow back?
If your ear does not heal on its own, your doctor may patch the eardrum. Patching involves placing a medicated paper patch over the tear in the membrane. The patch encourages the membrane to grow back together.
Does the eardrum repair itself?
Most ruptured (perforated) eardrums heal without treatment within a few weeks. Your provider may prescribe antibiotic drops if there's evidence of infection. If the tear or hole in the eardrum doesn't heal by itself, treatment will likely involve procedures to close the tear or hole.
Do ear perforations heal?
A perforated or burst eardrum is a hole in the eardrum. It'll usually heal within a few weeks and might not need any treatment. But it's a good idea to see a GP if you think your eardrum has burst, as it can cause problems such as ear infections.
What is the purpose of a tympanogram?
A tympanogram provides information regarding the compliance of the middle ear system (how well sound passes through the eardrum to the middle ear system), ear canal volume, and middle ear pressure. Compliance is plotted vertically on the tympanogram, and is measured in ml or mmho.
What does a larger ear canal volume mean?
In some cases, these tympanograms are seen when there is a hole in the ear drum; the difference lies in the ear canal volume: a larger ear canal volume indicates a perforation in the ear drum. Figure 2. Type B tympanogram.
What happens if a tympanogram is not normal?
If the tympanogram is not normal then there will a fluid behind the eardrum. If the tympanogram is normal then there will be no fluid present in the middle ear. It shows the normal movement of the middle ear, eardrum, and the conduction bones. The tympanogram gives relief for both the children and adults.
What is a tympanometer?
Tympanometry checks whether someone can get the treatment for the hearing loss by a hearing aid or not and whether the treatment will give relief or not. Tympanometer consist of the following; air pump, a probe with a loudspeaker, a microphone, and a manometer. There is no risk related to the tymp test.
What is the tymp test?
The graphics representation of tymp test data is the tympanogram. Tympanogram represents the relationship between the air pressure in the ear canal and the movement of the eardrum, or tympanic membrane, and the tiny bones in the air-filled middle ear space.
What is the role of tympanometry in the eardrum?
Tympanometry provides some extra information Eustachian Tube Functioning.
Why do you need a tymp test for otoscopy?
Otoscopy test with tympanometry enhances the reliability of the diagnosis as there are several ear canal and eardrum abnormalities that in some cases cause might cause different types of abnormalities which can easily be traced through tympanogram. The graphics representation of tymp test data is the tympanogram.
How often should a child have a tymp test?
For your child tympanometry may be performed every week for several months to figure out the change in the fluid over time. The Tymp test also helps to examine the conduction bones by generating air pressure changes in the ear canal. It becomes easier for doctors to diagnose the problems in the middle of the ear.
What is the middle ear test?
There are many tests that makeup through evaluation and act like pieces of a puzzle which when put together helps to determine the type and cause of hearing loss. One such middle ear test is tympanometry. Tympanometry is a type of test which is helpful in determining if the hearing loss can be helped by hearing aid or any medical treatment is ...
What is flat tympanogram?
Flat tympanograms occur with perforation of the tympanic membrane, occlusion of the tympanometry probe against the wall of the canal, obstruction of the canal by a foreign body or impaction by cerumen, or large middle ear effusion.
What is the function of a tympanometer?
The tympanometer measures the flow of sound energy into the middle ear under conditions of changing air pressure. When the air pressure is equal on both sides of an intact eardrum, with the drum in neutral position, the transmission of sound energy through the tympanic membrane is at its maximum.
What does it mean when the volume of the ear canal is abnormally small?
If the ear canal volume is abnormally small and a Type B tympanogram is observed, this is suggestive of blockage of the ear canal because of cerumen impaction. If the ear canal volume is abnormally large and the tympanogram is peakless, this is a sign of a perforation in the tympanic membrane.
What are the parameters of acoustic immittance?
Acoustic immittance measurements by tympanometry yield a series of objective parameters: tympanic admittance or compliance, related to tympanic membrane mobility, Eustachian tube function, and external auditory ear canal volume, which is increased in case of perforated eardrum or permeable transtympanic ventilating tubes.
What is the difference between immittance and acoustic reflexes?
Tympanometry assesses the volume of the ear canal, integrity of the tympanic membrane, and the middle ear pressure, while the acoustic reflexes examines the presence of retrocochlear and facial nerve pathology by using the reflexive contraction of the stapedius muscle in the middle ear in response to loud sound. Compared with the acoustic reflexes, tympanometry, in most cases, is ordered more often when clinically indicated a condition that cannot be explained solely by age-related changes (e.g., presence of a conductive or mixed hearing loss and any signs of ear infection mostly detected by the otoscopic examination, or higher risks indicated by the case history). It is important for clinicians to keep in mind that the elderly population is susceptible to ear infection owing to less efficient immune system.
What is tympanometry in the middle ear?
Tympanometry is a measure of middle ear function and is used to assess health and function of the outer and middle ear, including the external auditory canal. Measures of external ear canal volume, a part of tympanometric assessment, are used clinically to validate overall tympanometric results and can provide evidence of cerumen impaction, middle ear fluid, or tympanic membrane perforation when thorough visual inspection cannot be performed, a common problem with children who have Down syndrome because of stenotic ear canals. Because of the smaller ear canals of children with Down syndrome, measures of ear canal volume are notably smaller than those of typically developing children. Middle ear pathology, including fluid, can reduce the mobility of the tympanic membrane, another common tympanometric finding for individuals with Down syndrome and cause of reduced hearing.
How is tympanometry administered?
Tympanometry is administered by inserting a probe in the ear canal and forming a hermetic seal. Through the probe a tone is presented, air pressure is systematically varied in the ear canal from positive to negative, and the amount of acoustic energy admitted through the middle ear is determined.
