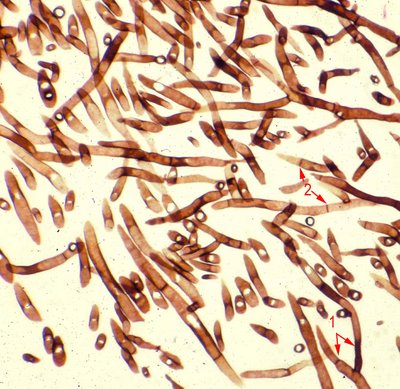
Grocott-Gomori’s Methenamine
Hexamethylenetetramine
Hexamethylenetetramine or methenamine, also known as hexamine or urotropin, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula₆N₄. This white crystalline compound is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like structure similar to adamantane. It is useful in the synthesi…
Who Uses GMS Stain?
This stain is used widely for both diagnostic and research purposes. For example, researchers studying fungal organisms may routinely examine GMS-stained sections to evaluate certain fungal elements in tissues of interest.
What is the initial step of GMS stain?
The initial step of the GMS stain is similar to that of the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain in that it uses chromic acid as an oxidizing agent. During this step, chromic acid oxidation forms aldehydes from fungal cell wall mucopolysaccharide components.
What is GMS staining?
GMS is probably best known for staining fungal organisms. Fungi are generally relatively large and morphologically diverse, and can occur in tissues in various forms: hyphae, endosporulating spores, budding yeasts, or a combination of these forms.
What is the most common fungi stain?
GMS and PAS are the two most common stains used to check for fungi in tissues. Both are considered ‘broad spectrum’ fungal stains, since most fungi can be readily seen with either stain.
Why do pathologists use GMS?
Therefore, pathologists will often use this stain to help answer questions after examining routine H&E-stained sections which contain changes suggestive of fungal infection.
Why do we use special stains on granulomatous?
So, when histological evidence of granulomatous inflammation or actual granulomas is found in tissues, special stains are generally performed to check for the presence of infectious organisms which can cause such changes- namely fungi and acid fast bacteria.
Can H&E be used to identify fungal infections?
However, although H&E is the stain of choice to identify naturally pigmented fungi (and the nuclei of yeast-like cells) it is not advisable to use this stain in isolation to diagnose fungal infections. This is because some fungi may be easily overlooked in H&E-stained sections, especially if not naturally pigmented, or if they are present in low numbers. It can also be difficult to differentiate poorly stained fungi from tissue components in H&E-stained sections. Additionally, fungal identification may be difficult if classic features are either absent or altered- the latter of which may occur in association with fungal therapy.
What is the chromic acid used in Grocott stain?
Gomori’s methenamine-silver nitrate and chromic acid comprise the major reagents used in conventional Grocott stain. It has also been used for the identification of fungi in tissue sections. Its application in Histology makes it ideal for the detection and demonstration of fungi in aspirates, tissues, and smears.
What is GMS stain?
Grocott-Gomori’s Methenamine Silver (GMS) stain is a histological stain that is used majorly for the identification of carbohydrates in fungal microorganisms. This staining method was named after György Gömöri, a physician from Hungary, who developed the staining methodology.
What is the reaction of fungi to silver?
Grocott’s alkaline hexamine-silver solution undergoes reduction to form precipitates of silver ions making the cell wall of the fungi appear black a reaction is known as argentaffin reaction (the ability of cells to reduce the silver solution to metallic silver forming a black tissue element). Argentaffin cells are found of the epithelial lining of the lungs, the intestines, and melanin. This reaction drives the outcome of the result of the stain.
How long to let slides stand in Coplin jar?
Dip slides up and down in the Coplin jar and allows to stand for another 1 minute. Rinse with distilled water and check under the microscope. Note: Dip back the slides in the silver solution if they are not stained sufficiently and check every 1 minute until the fungi stains dark brown.
Why do fungal cells stain black?
The fungal species will stain black due to the reduction process of the silver nitrate solution. Silver Nitrate solution after reduction forms silver ions which are black in color, thus producing a black stain for fungal cells.
What is Goromi used for?
In comparison to other stains like Periodic Acid-Schiffs stain and Gridley Stain, Goromi has a higher sensitivity to for detecting fungi and other polysaccharide-rich microorganisms in paraffin prepared sections. It has also been used for the identification of fungi in tissue sections.
How long to counterstain with light green?
Counterstain the section with the light green solution for 15 sec.
Why is GMS stain preferred?
Although some laboratories additionally perform a periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, the GMS stainis preferable, primarily because periodic acid-Schiff provides less contrast between fungi and background debris.
What is the stain for cellulose?
The movat pentachrome stain as a means of identifying microcrystalline cellulose among other particulates found in lung tissue
What stains are used to visualize hyphae?
PAS and GMS stainsmust be used to properly visualize the hyphae [5].
What is the purpose of the Gomori-Grocott silver stain?
Gomori-Grocott methenamine silver stain A chromic acid, sodium bisulfite stain used in histology and cytology to identify fungi and Pneumocystis carinii; the slide is placed in a hot bath for penetration and stains fungi black with sharp margins, and a cleared center. See Sealed envelope appearance.
What is chromic acid sodium bisulfite stain used for?
A chromic acid, sodium bisulfite stain used in histology and cytology to identify fungi and Pneumocystis jiroveci. The slide is placed in a hot bath for penetration and stains fungi black with sharp margins and a cleared centre.
What is the method used to make argentaffin cells?
techniques for argentaffin cells: a method using a methenamine-silver solution in combination with gold chloride, sodium thiosulfate, and safranin O ; argentaffin granules appear brown-black against a green background; urates: warm sections are treated directly with a hot methenamine-silver solution to produce a blackening of urates; fungi: see Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver stain; melanin, which reduces silver nitrate.
Does BAL show filamentous fungi?
BAL revealed filamentous fungi on direct GMS stain, and no microorganisms on acid fast stains.
What is GMS in a lab?
Grocott methenamine silver stain (GMS) is most widely used to highlight the wall of fungal organisms, with cultures advised for speciation.
What is the yeast in a lung biopsy?
A yeast of Cryptococcus is seen in the center of the field in this lung biopsy. The organism is stained with Gomori methenamine silver and shows a small narrow bud. Cryptococcal yeast are seen that stain bright red with the mucicarmine stain. The stain specifically highlights the lipid content of the capsule .
How do immunohistochemical stains work?
Immunohistochemical stains detect specific antigens on the surface of cells and thus help determine their lineage. The antigen binds to an antibody or a series of antibodies, which are detected using an enzymatic reaction that forms a colored product. The streptavidin–biotin–peroxidase technique is a commonly employed method. IHC is ideally performed on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded cell block material, but they can also be performed on cytospins and LBP. Some of the important applications of these stains include distinguishing reactive mesothelial cells and mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma and determining the primary site of malignancy in body fluid specimens (Figure 38 (a) – 38 (c) ).
What pathogens cross-react with Paracoccidioides brasiliensis?
Cross-reacts with Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, as well as rare human pathogens Gymnascella hyalinospora and Emmonsia parva
What is the appearance of cryptococcal organisms?
Histologic appearance of cryptococcal organisms shows round to oval yeasts with a double refractile capsule surrounding a central translucent core . The yeast are surrounded by abundant foamy histiocytes.
Is Gram positive for GMS?
Organisms are positive for Grocott methenamine silver (GMS) stain and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain. Negative for Gram stain and variably positive on Fontana-Masson stain (∼ 50%) Negative or weakly positive for mucicarmine stain.
Where is histoplasma capsulatum found?
Histoplasma capsulatum, the causative agent of histoplasmosis, is endemic in the Mississippi and Ohio River valleys and in South and Central America. It is usually contracted through inhalation of soil that is contaminated with bird or bat droppings containing the fungus. The kidneys are affected in 40% of patients with progressive disseminated histoplasmosis. Histologically, there is typically a significant degree of tubulointerstitial inflammation, which may be granulomatous and caseating. Macrophages show large numbers of nonencapsulated, intracellular, oval or round yeast forms measuring up to 5 µm in diameter, some of which may display budding ( Fig. 16.18 ). GMS stains, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence are useful for their recognition. 56,77,151,154,155