What are the reasons for high anion gap?
This is referred to as a high anion gap. Acidosis with a large anion gap is usually caused by an excess of organic acids or a proportionate reduction in anion excretion. Lactic acidosis, ketoacidosis, toluene intoxication, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory alkalosis, and severe hyperphosphatemia cause a spike in the anion gap.
What does it mean if anion gap is high?
What does a high anion gap blood test result mean? If your blood test results show a high anion gap, you may have acidosis. This means you may have a higher-than-normal level of acid in your blood (a lower-than-normal blood pH). Acidosis may be a sign of the following: Dehydration. Diarrhea. Too much exercise.
What are the symptoms of high anion gap?
- nausea.
- vomiting.
- malaise.
- hyperpnea (long, deep breaths at a normal rate)
- fatigue.
- cardiac dysfunction with hypotension, shock, ventricular arrhythmias.
What is the treatment for high anion gap?
- Glycols (ethylene glycol, propylene glycol)
- Oxoproline (pyroglutamic acid, the toxic metabolite of excessive acetaminophen or paracetamol)
- L-Lactate (standard lactic acid seen in lactic acidosis)
- D-Lactate (exogenous lactic acid produced by gut bacteria)
- Methanol (this is inclusive of alcohols in general)
- Aspirin (salicylic acid)
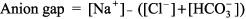
What is the most common cause of an elevated anion gap?
High anion gap acidoses are most often due to ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, chronic kidney disease, or certain toxic ingestions. Normal anion gap acidoses are most often due to gastrointestinal or renal HCO3− loss.
What are the symptoms of high anion gap?
Your doctor might order the anion gap test if you have symptoms of high blood acid levels, like:Shortness of breath.Nausea or vomiting.Abnormal heartbeat.Confusion or fatigue.
How high is too high for anion gap?
Although there are differences between laboratories and assays, the normal anion gap has traditionally been set between 8 mEq/L to 12 mEq/L. If the anion gap is greater than 12, this suggests an increased presence of unmeasured anions.
Should I be worried if my anion gap is high?
A high anion gap test result may mean that you may have acidosis (blood that is more acidic than normal). Acidosis may be caused by: Dehydration. Diarrhea.
What medications cause high anion gap?
Increased concentrations of lactic acid may also be present in the toxic forms of metabolic acidosis. The most common drugs and chemicals that induce the anion gap type of acidosis are biguanides, alcohols, polyhydric sugars, salicylates, cyanide and carbon monoxide.
How do I lower my anion gap?
Lithium is positively charged and is sometimes prescribed for treatment of bipolar disorder. In high concentrations, it can lower the anion gap. Increase in other positively charged ions. A large increase in other positively charged ions, such as calcium and magnesium, can also lower the anion gap.
Is anion gap of 18 high?
and a normal anion gap is approximately 10—16 mEq/L. An anion gap of 17 or higher represents an increased anion gap, and an anion gap of 9 or lower represents a decreased anion gap.
How do you fix acidosis?
Metabolic acidosis treatments may include :oral or intravenous sodium bicarbonate to raise blood pH.sodium citrate to treat metabolic acidosis due to distal renal tubular acidosis.insulin and intravenous fluids to treat ketoacidosis.renal replacement therapy (dialysis)
How do you fix albumin anion gap?
Conclusions: The observed anion gap can be adjusted for the effect of abnormal serum albumin concentrations as follows: adjusted anion gap = observed anion gap + 0.25 x ([normal albumin] [observed albumin]), where albumin concentrations are in g/L; if given in g/dL, the factor is 2.5.
What tests diagnose multiple myeloma?
Tests to Find Multiple MyelomaBlood counts. The complete blood count (CBC) is a test that measures the levels of red cells, white cells, and platelets in the blood. ... Blood chemistry tests. ... Urine tests. ... Quantitative immunoglobulins. ... Electrophoresis. ... Serum free light chains. ... Beta-2 microglobulin. ... Bone marrow biopsy.More items...•
What causes acidosis?
Acidosis is caused by an overproduction of acid that builds up in the blood or an excessive loss of bicarbonate from the blood (metabolic acidosis) or by a buildup of carbon dioxide in the blood that results from poor lung function or depressed breathing (respiratory acidosis).
What is the normal range for anion gap blood test?
Normal results are 3 to 10 mEq/L, although the normal level may vary from lab to lab. If your results are higher, it may mean that you have metabolic acidosis.
Is 17 a high anion gap?
and a normal anion gap is approximately 10—16 mEq/L. An anion gap of 17 or higher represents an increased anion gap, and an anion gap of 9 or lower represents a decreased anion gap.
What happens when your blood is acidic?
Blood acidity increases when people ingest substances that contain or produce acid or when the lungs do not expel enough carbon dioxide. People with metabolic acidosis often have nausea, vomiting, and fatigue and may breathe faster and deeper than normal.
Is lactic acidosis serious?
Untreated lactic acidosis can result in severe and life-threatening complications. In some instances, these can escalate rapidly.
What causes acidosis?
Acidosis occurs when acid builds up or when bicarbonate (a base) is lost. Acidosis is classified as either respiratory or metabolic acidosis. Respiratory acidosis develops when there is too much carbon dioxide (an acid) in the body.
What Does the Anion Gap Tell You?
The anion gap tells you if your electrolytes are unbalanced, which can cause changes in the acid levels in the blood. An anion gap result can be low, normal, or high.
How Do Doctors Measure the Anion Gap?
The anion gap is measured by a blood test. This blood test checks electrolytes in the blood, specifically sodium, potassium, and chloride. Electrolytes are positively or negatively charged, and the anion gap test measures these charges and determines if they are balanced.
What are the symptoms of acidosis?
This test is most commonly performed in patients with symptoms consistent with a condition caused by high levels of acid in the blood, such as: 1 Altered mental status 2 Abnormal heartbeat 3 Unknown exposures 4 Acute renal failure 5 Acute illnesses 6 Metabolic acidosis 7 Shortness of breath 8 Nausea / vomiting 9 Confusion
What is the anion gap?
The anion gap is a value that represents the difference between positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions) in the blood. The anion gap cannot be directly measured, instead, it is calculated from the results of an electrolyte panel, another type of blood test. The anion gap is calculated using the concentrations ...
What is the purpose of anion gap?
The anion gap is primarily used to determine the cause of metabolic acidosis, a condition where the body is producing too much acid or not enough acid is being removed from the body.
What is the term for the concentration of cations and anions in the blood?
Although the term anion gap usually refers to the concentrations of cations and anions in the blood, it can also refer to their concentrations in the urine, which is also clinically useful [ 3 ].
How many patients have low anion gap?
In a study of over 67,000 calculations of the anion gap, the prevalence of a low anion gap value was found in only 304 (0.8%) out of the 39,360 patients whose electrolyte blood levels were studied, and only 19 of them had a repeatedly low anion gap [ 37 ].
Why repeat electrolyte blood test?
It is worthwhile to repeat the electrolyte blood test and recalculate the anion gap value to ensure that the low anion gap value is not an outcome of a laboratory error in measurement .
What should the total positive charge from cations equal?
In the body, the total positive charge from cations should equal the total negative charge from anions in the blood to maintain overall neutrality.
How to treat metabolic acidosis?
Some possible treatments for metabolic acidosis include detoxification if caused by drugs or toxins and insulin if the condition is caused by diabetes [ 9 ].
What does it mean when you have a high anion gap?
If your doctor says you have a high anion gap, you may have a higher than normal amount of acid in your blood. The doctor may call this "acidosis."
What does an anion gap test tell you?
The anion gap test tells you how much acid is in your blood. Acid levels that are higher or lower than normal can tip your doctor off to a health problem and help them find the right treatment for you.
What is the normal anion gap?
An anion gap number between 3 and 10 is considered normal. But the "normal" range can vary from person to person, and it may also depend on the methods your lab used to do the test. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: "Serum Anion Gap: Its Uses and Limitations in Clinical Medicine.".
What does it mean when you have too much acid in your blood?
Too much acid in your blood can be a sign of short-term problems like dehydration and diarrhea, or long-term conditions like diabetes. It's not common, but too little acid may point to a serious problem like heart disease.
What are the symptoms of acidosis?
Acidosis can be a symptom of conditions like: 1 Dehydration 2 Diarrhea 3 Kidney disease 4 Ketoacidosis (diabetes complication)
Can too much exercise cause acidosis?
Acidosis can also be brought on by too much exercise.
What is high anion gap?
High anion gap metabolic acidosis is one of the most common metabolic derangements seen in critical care patients. Exact numbers are not readily available.
How to calculate anion gap?
Starting with a basic metabolic panel (BMP) or serum electrolyte panel, the anion gap (AG) should be calculated by subtracting the major anions (chloride & bicarbonate) from the major cation (sodium). Some sources argue for the use of potassium, but it has traditionally been omitted. Consider integrating it in patients with grossly abnormal potassium values. The single largest source of unmeasured anions in the healthy population is albumin, which is why evaluation of, and correction for, hypo/hyperalbuminemia will improve the accuracy of the high anion gap Metabolic Acidosis evaluation. The correction factor of +2.5 mEq per 1 g/dL of albumin below the baseline of four is standard. Therefore, failure to correct for a low albumin would falsely depress the AG, potentially masking the presence of high anion gap Metabolic Acidosis.
What is the best treatment for high anion gap?
In mild to moderate acidosis, treatment could be limited to supportive measures including intravenous fluids and respiratory support. Alkalization therapy should be reserved for those individuals with severe acidosis (pH less than 7.1). In the case of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), this value is even lower (pH less than 6.9). The most common alkalizing agent is sodium bicarbonate, but sodium and potassium citrate are alternative options. In the event of severe, recalcitrant acidosis, it may be appropriate to treat empirically with alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitors (fomepizole or ethanol) and prepare the patient for emergent hemodialysis. Fomepizole prevents the conversion of alcohols into toxic metabolites through competitive inhibition of alcohol dehydrogenase. Ethanol is not preferred, but it has a similar mechanism of action because alcohol dehydrogenase has a greater affinity for ethanol than for methanol or ethylene glycol. Importantly, fomepizole has the greatest impact on outcomes when given within six hours of presentation; however, given it is frequently in short supply and prohibitively expensive, universal treatment of all high anion gap metabolic acidosis with fomepizole is not advised.
Does acetone elevate osmolarity?
Do not underestimate the utility of the osmolar gap. Since the presence of toxic alcohols is not easily evaluated, and there are effective treatments to prevent the formation of their toxic metabolites, this test is key to evaluating for such ingestion. It must be noted, however, that the presence of an elevated osmolar gap is expected in ketoacidosis, as acetone can also elevate serum osmolarity. In such a situation, trending the osmolar gap can demonstrate improvement with appropriate treatment. Failure of the osmolar gap to decrease following treatment for ketoacidosis should prompt consideration of toxic alcohol ingestion and administration of an alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor.
Does microscopy show anion gap?
Microscopy has limited value in the evaluation of high anion gap metabolic acidosis. One exception is the ingestion of ethylene glycol. Given that the breakdown products of ethylene glycol include oxalate, sufficient doses can produce calcium oxalate monophosphate crystal that deposits into tissues (e.g., kidneys, brain) and precipitates in the urine. Calcium oxalate monophosphate can be seen on urine microscopy and are shaped like dumbbells, spindles, ovals or picket fences. These are differentiated from calcium oxalate diphosphate crystals, which are octahedral and traditionally described as "envelope shaped."
Is metformin a cause of lactic acidosis?
In fact, a Cochrane review found substantial evidence that metformin was not a cause of lactic acidosis. The same could not be said of the older biguanide, phenformin, which does increase the incidence of lactic acidosis by approximately tenfold.
Is high anion gap metabolic acidosis a sign of dyspnea?
Symptoms of high anion gap metabolic acidosis are generally non-specific, with dyspnea being common secondary to stimulation of the central respiratory center. A review of signs and symptoms associated with the various causes of acidosis can be helpful. Therefore, screening for toxic ingestions, including over-ingestion of aspirin and acetaminophen, is of utmost importance. Additionally, screening for features suggestive of diabetes (e.g., polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia) or renal failure (e.g., nocturia, pruritus, anorexia) is essential. Physical examination is similarly non-specific for metabolic acidosis in general, with Kussmaul respirations (i.e., deep, slow breaths instead of shallow rapid breathing) being a common finding. Evaluation for features of specific causes aids in narrowing the differential diagnosis. For example, a patient might have dry mucous membranes and ketotic scent in diabetic ketoacidosis. Alternatively, a patient may demonstrate excoriations, asterixis, and confusion in uremia.
What are the symptoms of high anion gap?
A high anion gap itself does not produce symptoms, but it may indicate an imbalance in blood acid levels, such as metabolic acidosis.Symptoms Nausea. Vomiting. Rapid and shallow breathing. Fatigue. Rapid/abnormal heartbeat. Low blood pressure. Confusion. Headaches.
What is too high for anion gap?
Although there are differences between laboratories and assays, the normal anion gap has traditionally been set between 8 mEq/L to 12 mEq/L. If the anion gap is greater than 12, this suggests an increased presence of unmeasured anions.
How is high anion gap metabolic acidosis treated?
The most common alkalizing agent is sodium bicarbonate, but sodium and potassium citrate are alternative options. In the event of severe, recalcitrant acidosis, it may be appropriate to treat empirically with alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitors (fomepizole or ethanol) and prepare the patient for emergent hemodialysis.
Is 17 a high anion gap?
and a normal anion gap is approximately 10—16 mEq/L. An anion gap of 17 or higher represents an increased anion gap, and an anion gap of 9 or lower represents a decreased anion gap.
Is 20 a high anion gap?
Healthy subjects typically have a gap of 0 to slightly normal (< 10 mEq/L). A urine anion gap of more than 20 mEq/L is seen in metabolic acidosis when the kidneys are unable to excrete ammonia (such as in renal tubular acidosis).
Which condition is most likely to cause acidosis?
The most common causes of lactic acidosis are: cardiogenic shock. hypovolemic shock. severe heart failure.Other causes of lactic acidosis include: kidney conditions. liver disease. diabetes mellitus. HIV treatments. extreme physical exercise. alcoholism.
How do you fix anion gap?
Lithium is positively charged and is sometimes prescribed for treatment of bipolar disorder. In high concentrations, it can lower the anion gap. Increase in other positively charged ions. A large increase in other positively charged ions, such as calcium and magnesium, can also lower the anion gap.
What Is An Anion Gap?
The human body is composed of various components present in the body which help in the proper functioning of the body. Electrolytes are one component that is used to perform essential functions in the body. Electrolytes are electrically charged minerals which help in the control of acid and bases present in the body. Some of the charged minerals are positively charged while the others are negatively charged. The anion gap determines the gap or difference between the negatively and positively charged electrolytes.
What does it mean when your anion gap is low?
It may also be a sign of something more serious, particularly kidney failure or diabetes. If you have a low anion difference, it could suggest that you have a low level of albumin, a protein in your blood. Low albumin levels may be a sign of kidney failure, heart disease, or some form of cancer. Due to the rarity of low anion gap outcomes, retesting is often performed to ensure that the results are correct.
What is the relationship between the serum anion gap level and the concentration and net positive charge of IgG paraprotein?
The serum anion gap level and the concentration and net positive charge of IgG paraproteins have a clear inverse relationship. As a consequence, the highest concentrations of paraproteins are correlated with negative values or values below the normal range.
What causes low albumin levels?
The following conditions will result in lower-than-normal albumin levels- liver diseases , such as cirrhosis, kidney disease, infection, burns, cancer, and hypothyroidism. Hypoalbuminemia is the second most common cause of the low anion gap.
What is the accumulating acid in ketoacidosis?
If the accumulating acid is lactate in lactic acidosis or -hydroxybutyrate in ketoacidosis, the decrease in serum bicarbonate will be followed by an increase in the unmeasured anion concentration. This is referred to as a high anion gap. Acidosis with a large anion gap is usually caused by an excess of organic acids or a proportionate reduction in anion excretion. Lactic acidosis, ketoacidosis, toluene intoxication, metabolic alkalosis, respiratory alkalosis, and severe hyperphosphatemia cause a spike in the anion gap.
How much is the anion difference in CO2?
The total CO2 content contains serum bicarbonate as well as other sources of carbon dioxide, with serum HCO3- accounting for approximately 95% of the total CO2 content. As a consequence, this measurement is commonly used to estimate serum HCO3- levels.
Why is my blood acidic?
Your blood is more acidic than average if your anion gap value is high. It may mean you’re suffering from acidosis. Metabolic acidosis, which is caused by the overproduction or reduced excretion of acid, is the most common condition associated with an elevated serum anion difference.
What are the reasons for high anion gap?
The most common causes of high anion gap metabolic acidosis are: ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, renal failure, and toxic ingestions.
How to lower anion gap?
Lithium is positively charged and is sometimes prescribed for treatment of bipolar disorder. In high concentrations, it can lower the anion gap . Increase in other positively charged ions. A large increase in other positively charged ions, such as calcium and magnesium, can also lower the anion gap .
What are the symptoms of a low anion gap?
Low Anion Gap Symptoms. The symptoms may include: Irregular or abnormal heartbeat. Muscle weakness. Fatigue/cramps. Hypotension (low blood pressure) Edema/swelling/buildup of fluid in legs or face. Lack of appetite.
What causes elevated anion gap?
Elevated Anion Gap. An increase in an anion gap is most often due to some for of a metabolic acidosis, such as, ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, acute/chronic kidney disease, toxic alcohol ingestion, and long term acetaminophen use.
What could cause low anion gap?
Having low levels of albumin, a negatively charged protein, can cause a decreased anion gap. High concentrations of positively charged proteins can also cause this change. Lab error, lithium intoxication, and bromide ingestion can all also cause a low anion gap.
What is the treatment for low anion gap?
Treatment of abnormality in anion gap is mainly based on addressing the underlying cause. In case of low anion gap, the first thing your doctor will suggest is to repeat serum electrolyte test. If the patient is taking certain medicines such as lithium or bromide containing medicine, he must talk with the doctor.
What causes high anion gap?
The most common causes of high anion gap metabolic acidosis are: ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, kidney failure, and toxic ingestions. Ketoacidosis can occur as a complication of diabetes mellitus (diabetic ketoacidosis), but can occur due to other disorders, such as chronic alcoholism and malnutrition.
What causes normal anion gap acidosis?
Normal anion gap acidosis (low serum HCO3 but normal anion gap) is caused by excess bicarbonate loss from either the gut (diarrhea) or kidney (renal tubular acidosis). An elevated or so-called positive anion gap suggests the presence of another unmeasured anion.
What does high chloride and low anion gap mean?
A high anion gap means you have more acid in your blood than normal. A low anion gap means you have a lower amount of acid in your blood than normal, but this result is uncommon and usually due to a lab error.
Why is the anion gap high?
In some instances, a high anion gap may occur because of high lactic acid levels or through alcohol abuse. If the anion gap blood test comes back with a low test result, then this is an indication that albumin levels are lower ...
What is an anion gap?
The anion gap blood test is typically ordered when someone is suffering from specific physical conditions. This may include confusion, edema, or a cardiac arrhythmia. It is also ordered when an illness occurs at regular intervals for an unknown cause. Sodium, potassium, and chloride are typically the most common results that are analyzed.
What is the normal result of anion gap?
Most people who have their anion gap calculated will have a normal result. A normal result may even occur if there is an electrolyte imbalance in place. Normal results are typically less than 11 mEq/L. Anything above 11 is considered a high test result, while anything below 3 will typically be considered a low test result, ...
Why is knowing the anion gap important?
Knowing the anion gap can help medical providers begin to find a correct diagnosis for what may be bothersome physical symptoms. Having balanced electrolytes is important to good health. These test results can help to find deficiencies or indicate when too much of one electrolyte is being consumed so that the proper balance can be achieved.
What is an anion gap blood test?
The anion gap blood test is a calculated value that comes from the results of an individual’s electrolyte panel. It is used to determine what a person’s anion and non-anion gap happens to be in regards to excess acid levels that may exist in the body. Called acidosis, too much acid can interfere with cell functioning and this may cause delays in ...
Why does my anion gap blood test come back low?
If the anion gap blood test comes back with a low test result, then this is an indication that albumin levels are lower than they should be. Immunoglobulins may also be increased. Low test results are extremely rare, however, and retesting usually occurs if this is the result because it is more likely that a lab error caused this result than a physical problem.
How to find anion gap?
The anion gap is discovered through the measurement of positive ions compared to negative ions. It is usually taken from the serum, but some medical providers may prefer a urine test instead of a blood test to get this information.