What is the function of Your Nerve impulses?
Nerve impulses are signals carried along nerve fibers. These signals convey, to the spinal cord and brain, information about the body and about the outside world. They communicate among centers in the central nervous system and they command your muscles to move.
What is the function of a nerve impulse?
Nerve Impulse
- Membrane potential – It is the difference in the total charge between the inside of the cell and the outside of the cell.
- Resting membrane potential – It is the difference in voltage across the cell membrane in a resting state. ...
- Action potential – It is a short-term change in the electrical potential that travels across the neuron cell.
What happens during a nerve impulse?
What happens during nerve impulse? When the neuron is stimulated, electrical and chemical changes occur. At the stimulated point, the outside of the nerve cell becomes negative and the inside becomes positive. The ions change places. As soon as the impulse passes, the stimulated point returns to its original electrical and chemical state.
How are nerve impulses usually transmitted?
Transmission of Nerve Impulses. The transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of electrical changes across the membrane of the neuron. The membrane of an unstimulated neuron is polarized—that is, there is a difference in electrical charge between the outside and inside of the membrane.

Why do nerve impulses occur?
A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules.
Which cell receives the nerve impulse?
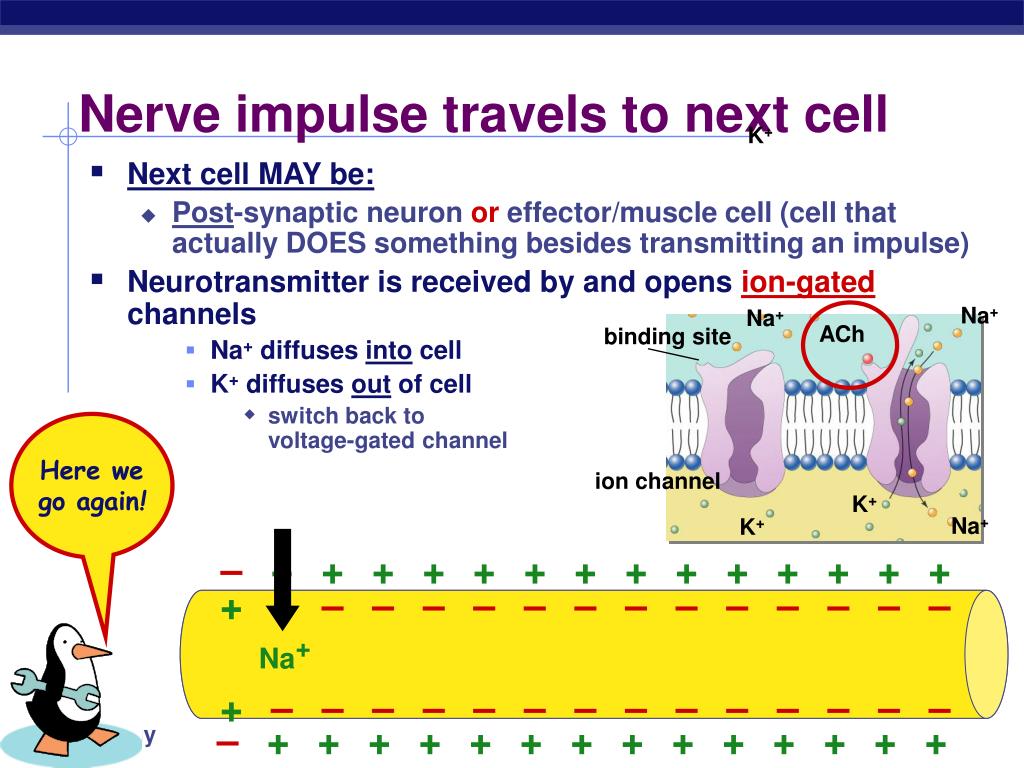
The cell that sends the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell, and the cell that receives the nerve impulse is called the postsynaptic cell. Some synapses are purely electrical and make direct electrical connections between neurons. However, most synapses are chemical synapses.
How does neurotransmitter affect post-synaptic cells?
The effect of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell depends mainly on the type of receptors that it activates, making it possible for a particular neurotransmitter to have different effects on various target cells. A neurotransmitter might excite one set of target cells, inhibit others, and have complex modulatory effects on still others, depending on the type of receptors. However, some neurotransmitters have relatively consistent effects on other cells.
What happens when a neuron reaches a certain threshold?
The change in membrane potential results in the cell becoming depolarized.
What is action potential?
Action Potential. An action potential, also called a nerve impulse, is an electrical charge that travels along the membrane of a neuron. It can be generated when a neuron’s membrane potential is changed by chemical signals from a nearby cell.
Where do ion flows occur in myelinated neurons?
In myelinated neurons, ion flows occur only at the nodes of Ranvier. As a result, the action potential signal "jumps" along the axon membrane from node to node rather than spreading smoothly along the membrane, as they do in axons that do not have a myelin sheath.
What is the purpose of the sodium-potassium pump?
The sodium-potassium pump is a mechanism of active transport that moves sodium ions out of cells and potassium ions into cells.
What is the result of nerve impulses?
Nerve impulses are electrical in nature. They result from a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions, which are electrically charged atoms or molecules.
How does a nerve impulse start?
A nerve impulse begins when a neuron receives a chemical stimulus. The nerve impulse travels down the axon membrane as an electrical action potential to the axon terminal. The axon terminal releases neurotransmitters that carry the nerve impulse to the next cell.
How does a nervous system signal move from one cell to the next?
It literally jumps by way of a chemical transmitter. Notice the two cells are not connected, but separated by a small gap. The synapse. The space between a neuron and the next cell.
How does action potential work in neurons?
As a result, the action potential jumps along the axon membrane from node to node, rather than spreading smoothly along the entire membrane. This increases the speed at which it travels.
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
Resting Potential. When a neuron is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse, it is in a resting state, ready to transmit a nerve impulse. During the resting state, the sodium-potassium pump maintains a difference in charge across the cell membrane (see Figure below ). It uses energy in ATP to pump positive sodium ions (Na +) ...
How does the neuron receive a chemical signal?
It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell. The signal causes gates in sodium ion channels to open, allowing positive sodium ions to flow back into the cell. As a result, the inside of the cell becomes positively charged compared to the outside of the cell.
Why is the inside of a neuron negatively charged?
This is due to many more positively charged ions outside the cell compared to inside the cell. This difference in electrical charge is called the resting potential.
Generating Nerve Impulses
A nerve impulse , like a lightning strike, is an electrical phenomenon. A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron. How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves , which are electrically-charged or .
Action Potential
A nerve impulse is a sudden reversal of the electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a resting neuron. The reversal of charge is called an action potential . It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell or some other type of .
Transmitting Nerve Impulses
The place where an axon terminal meets another cell is called a . This is where the transmission of a nerve impulse to another cell occurs. The cell that sends the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell , and the cell that receives the nerve impulse is called the postsynaptic cell .
What is nerve impulse?
Owning to the importance of this discovery, he was awarded Noble Prize in 1932. Nerve Impulse is a major mode of signal transmission for the Nervous system. Neurons sense the changes in the environment and as a result, generate nerve impulses to prepare the body against those changes.
Why is nerve impulse important?
A nerve impulse is thus an important signal transduction mode for triggering a response in major body parts due to a strong stimulus. Any distraction in this process can have drastic effects on the body.
What is action potential?
The action potential is a result of the movement of ions in and out of the cell. Particularly the ions included in this process are sodium and potassium ions. These ions are propagated inside and outside the cell through specific sodium and potassium pumps present in the neuron membrane. The transmission of a nerve impulse from one neuron ...
How do electrical synapses work?
Electrical synapses. In electrical synapses, two neurons are connected through channel proteins for transmitting a nerve impulse. The nerve impulse travels across the membrane of the axon in the form of an electrical signal.
Why does the axon diameter increase?
As the axon diameter increase, the speed of nerve impulses increases as well. This is because a larger axon diminishes the ion-leakage out of the axon. This helps in maintaining the membrane potential and thus favors faster nerve impulses.
How does a nerve impulse propagate?
Nerve impulse propagates by jumping from one node of Ranvier to the next. This makes the process of nerve impulse faster as the nerve impulse does not travel the entire length of the axon ( this happens in case of continuous conduction). The nerve impulse travels at a speed of 100 m/s in saltatory conduction.
What is the term for a wave of electrical chemical changes across the neuron that helps in the generation of the action?
Definition. Nerve Impulse is defined as a wave of electrical chemical changes across the neuron that helps in the generation of the action potential in response to the stimulus. This transmission of a nerve impulse across the neuron membrane as a result of a change in membrane potential is known as Nerve impulse conduction.
What is the purpose of nerve impulses?
Conduction of Nerve Impulse. A nerve impulse is the electric signals that pass along the dendrites to generate a nerve impulse or an action potential. An action potential is due to the movement of ions in and out of the cell. It specifically involves sodium and potassium ions.
How does nerve impulses occur?
Conduction of nerve impulse occurs due to the presence of active and electronic potentials along the conductors. Transmission of signals internally between the cells is achieved through a synapse. Nerve conductors comprise relatively higher membrane resistance and low axial resistance. The electrical synapse has its application in escape reflexes, heart and in the retina of vertebrates. They are mainly used whenever there is a requirement of fast response and timing being crucial. The ionic currents pass through the two cell membrane when the action potential reaches the stage of such synapse.
What is the action potential of a nerve?
The nerve fibres are either depolarized or they are said to be in the action potential. The action potential travelling along the membrane is called the nerve impulse. It is around + 30 mV. The sodium-potassium pump starts to operate once the action potential is completed.
How fast is the nerve impulse in white fibres?
That is impulse jumps from node to node and it increases with increase in the speed of nerve impulse. It is around twenty times faster compared to that of the non-medullated nerve fibres. The transmission of nerve impulse would rely upon the diameter of the fibre. For instance, the nerve impulse of a mammal is one twenty meters per second whereas nerve impulse of a Frog is 30 meters per second.
How many meters per second is a frog's nerve impulse?
For instance, the nerve impulse of a mammal is one twenty meters per second whereas nerve impulse of a Frog is 30 meters per second. 60,239. To learn more about nerve impulse, download BYJU’S-The Learning App. Learn Better through BYJU'S Quiz.
Where is the electrical synapse used?
The electrical synapse has its application in escape reflexes, heart and in the retina of vertebrates. They are mainly used whenever there is a requirement of fast response and timing being crucial. The ionic currents pass through the two cell membrane when the action potential reaches the stage of such synapse.
What was the original finding of the nerve impulse?
The original nerve impulse findings were that the rate of impulse firing governed the impact on neuronal targets, whether they be muscle or other neurons. Various labs, including my own, in the 1980s, discovered that the intervals between impulses also contained their own kind of information.
Why are field potentials more ambiguous to interpret than individual nerve impulses?
Field potentials are technologically easier to record than individual nerve impulses, but more ambiguous to interpret because of the spatial summation of voltages from hundreds of heterogeneous neurons.
How are computers and brains similar?
This provided evidence of the basic similarity and difference between brains and the later development of computers. Both computers and brains convert the real world into representations. In computers, information is coded, in the form of 1s and 0s, and as nerve impulses in brains. Both computers and brains distribute and process this represented information, and can store it as memories. However, because brains are biological and use impulses to represent information, they can change their circuitry and can self-program. Unlike computers, brains also have will, including a likely degree of free will .
What is the most conspicuous measure of neuronal electrical activity?
The most conspicuous of these activity measures exist in terms of nerve impulse firing and the extracellular ionic currents they create at synapses, known as field potentials.
What happens to CIPs when they are active?
As long as the CIPs remain active, the representation of sensation or neural processing is intact and may even be accessible to consciousness . However, if something disrupts ongoing CIPs to create a different set of CIPs, as for example would happen with a different stimulus, then the original representation disappears.
Who demonstrated temporal summation of impulse effects in neuromuscular junctions in 1951?
Bernard Katz demonstrated temporal summation of impulse effects in neuromuscular junctions in 1951 and later J.P. Segundo and colleagues confirmed it in neuronal synapses (Segundo et al., 1963). article continues after advertisement. It should not be surprising that there are serial dependencies in impulse intervals.
Do impulses have serial dependencies?
It should not be surprising that there are serial dependencies in impulse intervals. For example, intracellular recording of postsynaptic potentials revealed that the polarization change caused by a single impulse input decays in a few milliseconds. However, a succession of closely spaced impulse inputs allows the polarization changes to summate.
Resting Potential
- When a is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse, it is in a resting state, ready to transmit a nerve impulse. During the resting state, the maintains a difference in charge across the of the neuron. The sodium-potassium pump is a mechanism of that moves sodium ions (Na+) out of cells and potassium ions (K+) into cells. The sodium-potassium pump...
Chemical Synapses
- At a chemical synapse, both the presynaptic and postsynaptic areas of the cells are full of molecular machinery that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As shown in Figure 8.4.3, the presynaptic area contains many tiny spherical vessels called that are packed with chemicals called . When an reaches the axon terminal of the presynaptic cell, it opens channels …
Neurotransmitters and Receptors
- There are more than a hundred known neurotransmitters, and more than one type of neurotransmitter may be released at a given synapse by a presynaptic cell. For example, it is common for a faster-acting neurotransmitter to be released, along with a slower-acting neurotransmitter. Many neurotransmitters also have multiple types of to which they can bind. Re…
Attributions
- Figure 8.4.1 Lightening/ Purple Lightning, Dee Why by Jeremy Bishop on Unsplash is used under the Unsplash License(https://unsplash.com/license). Figure 8.4.2 Action Potential by CNX OpenStax, Biology on Wikimedia Commons is used under a CC BY 4.0(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/deed.en) license. Figure 8.4.3 Chemical_synap…
References
- Amoeba Sisters. (2020, January 29). Sodium potassium pump. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7NY6XdPBhxo&feature=youtu.be CNX OpenStax. (2016, May 27) Figure 4 The action potential is conducted down the axon as the axon membrane depolarizes, then repolarizes [digital image]. In Open Stax, Biology(Section 35.2). OpenStax CNX. https://cnx.…
Introduction
Definition
- Nerve Impulse is defined as a wave of electrical chemical changes across the neuron that helps in the generation of the action potential in response to the stimulus. This transmission of a nerve impulse across the neuron membrane as a result of a change in membrane potential is known as Nerve impulse conduction. It is a change in the resting state ...
Mechanism of Nerve Impulse Conduction
- Nerve impulse conduction is a major process occurring in the body responsible for organized functions of the body. So, for conduction of nerve impulse there are two mechanisms: 1. Continuous conduction 2. Saltatory conduction
Process of Transmission of Nerve Impulse
- For the transmission of a nerve impulse, the stages are below: 1. Polarization 2. Depolarization 3. Repolarization 4. Refractory Period 5. Synapse Before going into the details of the process of nerve impulse transmission, let’s first discuss action and resting potential states.
CNS and Nerve Impulse
- Neurons help in transmitting signals in the form of a nerve impulse from the Central nervous system to the peripheral body parts. Neurons are a complex network of fibers that transmit information from the axon ending of one neuron to the dendrite of another neuron. The signal finally reaches the target cell where it shows a response. In conducting nerve impulse, the follow…
Factors Affecting The Speed of Nerve Impulse
- Following are some major factors that affect the speed of nerve impulse: 1. Myelin Sheath 2. Axon Diameter 3. Temperature