How bad is an EMG?
Today is a different story. Although EMGs aren’t necessarily bad, you’ll find fewer people wanting to include the pickups with their playing style. What makes it even more confusing is that the loudest complainers about EMG pickup quality often send their sounds through multiple noise gates and compressors with passives instead.
What does EMG tell you?
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them (motor neurons). EMG results can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with nerve-to-muscle signal transmission. Motor neurons transmit electrical signals that cause muscles to contract.
Why would an EMG be abnormal?
What can affect EMG results?
- Are taking any drugs. Certain drugs that act on the nervous system (such as muscle relaxants) can interfere with electromyography results.
- Have had bleeding problems or are taking blood thinning drugs, such as warfarin (Coumadin®) or heparin.
- Have a pacemaker.
How do I interpret my EMG results?
Understanding Your Electromyography Results
- Purpose of Test. Your healthcare provider may opt for EMG when you have signs and symptoms such as weakness, tingling, numbness, pain in your muscles, cramping, or other abnormal sensations. ...
- Risks and Contraindications. Both EMG and NCS are low-risk. ...
- Before the Test. ...
- During the Test. ...
- After the Test. ...
- Interpreting Results. ...
What does a normal EMG rule out?
Overview. Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them (motor neurons). EMG results can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with nerve-to-muscle signal transmission.
Can you have a normal EMG and still have nerve damage?
Could it still be neuropathy? You can still have polyneuropathy with a normal EMG nerve conduction study. EMG nerve conduction studies can only assess large fiber polyneuropathy. Small fiber cannot be evaluated by EMG nerve conduction study, but it may be assessed by skin biopsy.
What does a normal nerve conduction test rule out?
NCV tests can measure the speed and strength of nerve signals. Nerve conduction velocity between 50 to 60 meters per second is considered normal. A damaged nerve may send a slower and weaker signal than a healthy one. It is possible to have normal results even if a person has nerve damage.
How are EMG results interpreted?
An abnormal EMG result means there is a problem in an area of muscle activity—turning on and off, when it is active, how much it is active, if it is more or less active, and fatigue. This can offer a clue in diagnosing various nerve and muscle conditions.
What can EMG not detect?
EMG will show damage in muscles innervated by damaged motor axons. EMG will not detect injuries to purely sensory nerves, and NCS may not detect subtle partial injuries, injuries to nerve branches that are not recorded from, or injuries distal to the site of study. 5. Disorders of neuromuscular transmission.
Will an EMG show a pinched nerve?
EMG and NCS are tests that measure the electrical activity of the muscles and nerves of the body, usually to an arm or a leg. The tests can help identify nerve injury or muscle disease such as carpal tunnel syndrome, a pinched spinal nerve, peripheral neuropathy, myositis, or ALS.
Can an EMG detect MS?
EMG stands for electromyogram. The purpose of the EMG is to assess the health of muscles by measuring their response to stimulation. This can help doctors in diagnosing multiple sclerosis and other conditions when a patient has unexplained muscle weakness.
What are the signs of nerve damage?
The signs of nerve damageNumbness or tingling in the hands and feet.Feeling like you're wearing a tight glove or sock.Muscle weakness, especially in your arms or legs.Regularly dropping objects that you're holding.Sharp pains in your hands, arms, legs, or feet.A buzzing sensation that feels like a mild electrical shock.
What diseases does a nerve conduction test show?
Nerve conduction studies and EMGs can diagnose a variety of conditions, including:Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) aka: Lou Gehrig's disease.Carpal tunnel syndrome.Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease.Chronic inflammatory polyneuropathy and neuropathy.Guillain-Barre syndrome.Herniated disc disease.Muscular dystrophy.More items...
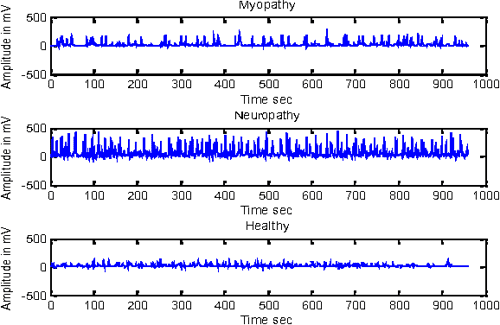
What does higher EMG value shows?
How does EMG work? As EMG activity (measured in microvolts) is linearly related to the amount of muscle contraction as well as the number of contracted muscles – or in other words, the stronger the muscle contraction and the higher the number of activated muscles, the higher the recorded voltage amplitude will be.
Are EMG results immediate?
Your doctor may review the results with you right after the procedure. However, if another healthcare provider ordered the EMG, then you may not know the results until you attend a follow-up appointment with your doctor.
What can affect EMG results?
ElectromyographyAre taking any drugs. Certain drugs that act on the nervous system (such as muscle relaxants) can interfere with electromyography results. ... Have had bleeding problems or are taking blood thinning drugs, such as warfarin (Coumadin®) or heparin.Have a pacemaker.
What test shows nerve damage?
A nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test — also called a nerve conduction study (NCS) — measures how fast an electrical impulse moves through your nerve. NCV can identify nerve damage. During the test, your nerve is stimulated, usually with electrode patches attached to your skin.
How does a neurologist check for nerve damage?
Electromyography, or EMG, is used to diagnose nerve and muscle disorders, spinal nerve root compression, and motor neuron disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EMG records the electrical activity in the muscles. Muscles develop abnormal electrical signals when there is nerve or muscle damage.
Can you still have carpal tunnel with normal EMG?
Patients are often sent for a test called an electromyelogram (EMG) and nerve conduction velocity test (NCV) which are often very helpful in establishing the diagnosis. In some cases, the EMG and NCV are negative for carpal tunnel syndrome, but that does not mean the patient does not have the disorder.
What scan shows nerve damage?
Nerve damage can usually be diagnosed based on a neurological examination and can be correlated by MRI scan findings. The MRI scan images are obtained with a magnetic field and radio waves. No harmful ionizing radiation is used.
What is EMG in medical terms?
Overview. Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them (motor neurons). EMG results can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with nerve-to-muscle signal transmission. Motor neurons transmit electrical signals that cause muscles to contract.
What is the purpose of EMG?
Motor neurons transmit electrical signals that cause muscles to contract. An EMG uses tiny devices called electrodes to translate these signals into graphs, sounds or numerical values that are then interpreted by a specialist. During a needle EMG, a needle electrode inserted directly into a muscle records the electrical activity in that muscle. ...
What does it feel like to have a needle electrode removed?
When the study is underway, the surface electrodes will at times transmit a tiny electrical current that you may feel as a twinge or spasm. The needle electrode may cause discomfort or pain that usually ends shortly after the needle is removed.
What is nerve conduction study?
A nerve conduction study, another part of an EMG, uses electrode stickers applied to the skin (surface electrodes) to measure the speed and strength of signals traveling between two or more points.
Why do we need EMG?
EMG results are often necessary to help diagnose or rule out a number of conditions such as: Diseases affecting the connection between the nerve and the muscle , such as myasthenia gravis . Disorders of nerves outside the spinal cord (peripheral nerves), such as carpal tunnel syndrome or peripheral neuropathies.
What to ask before EMG?
When you schedule your EMG, ask if you need to stop taking any prescription or over-the-counter medications before the exam. If you are taking a medication called Mestinon (pyridostigmine), you should specifically ask if this medication should be discontinued for the examination.
Who interprets EMG results?
The neurologist will interpret the results of your exam and prepare a report. Your primary care doctor, or the doctor who ordered the EMG, will discuss the report with you at a follow-up appointment.
What is an EMG test?
A Look at Nerve and Muscle Function. An EMG—electromyogram—is a test that checks the health of nerves and muscles. An EMG involves inserting tiny needles into your muscles to record electrical activity. Your doctor may recommend this nerve conduction study to help diagnose nerve and muscle diseases and seizures.
What are the conditions that can be diagnosed with EMG?
Read on to learn about conditions that doctors may diagnose with an EMG. 1. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis— ALS, or Lou Gehrig’s disease—is a progressive neuromuscular disease. ALS causes muscle weakness and disability, eventually leading to breathing failure.
What is needle EMG?
The needle EMG examination is performed “on the fly” requiring in-depth knowledge of nerve and muscle physiology and how they relate to both normal and abnormal electrical activity in the muscle. While the muscle fibers belonging to a single motor unit can be distributed over 5-10 mm or more, the needle records activated motor units up to only about 1-2 mm from the recording tip. This means that only a small portion of the muscle is actually evaluated during the needle EMG portion of the test. Needle EMG studies can be broken down into two basic components: 1) the muscle at rest and, 2) voluntary muscle contraction.
What are the components of needle EMG?
Needle EMG studies can be broken down into two basic components: 1) the muscle at rest and, 2) voluntary muscle contraction.
What is the first component of muscle evaluation?
Evaluation of the muscle at rest can be divided into two additional categories. The first component is insertional activity. Inser tional activity deals with what happens immediately following insertion of the needle into the muscle and minimally advancing it with short, quick bursts.
What is the normal amplitude of a fiber?
Amplitude is measured from the peak of the negative deflection to the peak of the positive deflection. Normal amplitude for Type I fibers is between 300 V to 1000 V and for Type II fibers between 1000 V and 5000 V. Duration is measured from the initial deflection from the baseline to the final return to baseline. Normal duration is less than 12 ms.
Which muscle has a positive wave conduction?
The left deltoid, biceps, infraspinatus, and cervical paraspinal muscles showed positive sharp waves and fibrillation potentials with decreased recruitment and interference pattern in the left biceps. What is the impression based on these findings?
Can EMG be related to specific diseases?
Now that you understand nerve conduction and EMG findings, you can relate them to specific diseases. Let’s look at a couple case studies to put it all together.

Overview
A test to evaluate the response of muscle against nerve stimulation.
Type: Imaging
Duration: Usually 40-60 mins
Results available: Usually 1-2 days
Conditions it may diagnose: Stroke · Myasthenia gravis · Lou Gehrig's disease · Carpal tunnel syndrome · Muscular dystrophy
Is Invasive: Invasive
Why It's Done
Risks
How You Prepare
- Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure to assess the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them (motor neurons). EMG results can reveal nerve dysfunction, muscle dysfunction or problems with nerve-to-muscle signal transmission. Motor neurons transmit electrical signals that cause muscles to contract. An EMG uses tiny devices ...
What You Can Expect
- Your doctor may order an EMG if you have signs or symptoms that may indicate a nerve or muscle disorder. Such symptoms may include: 1. Tingling 2. Numbness 3. Muscle weakness 4. Muscle pain or cramping 5. Certain types of limb pain EMG results are often necessary to help diagnose or rule out a number of conditions such as: 1. Muscle disorders, such as muscular dys…
Results
- EMG is a low-risk procedure, and complications are rare. There's a small risk of bleeding, infection and nerve injury where a needle electrode is inserted. When muscles along the chest wall are examined with a needle electrode, there's a very small risk that it could cause air to leak into the area between the lungs and chest wall, causing a lung to collapse (pneumothorax).
Clinical Trials
- Food and medications
When you schedule your EMG, ask if you need to stop taking any prescription or over-the-counter medications before the exam. If you are taking a medication called Mestinon (pyridostigmine), you should specifically ask if this medication should be discontinued for the examination. - Bathing
Take a shower or bath shortly before your exam in order to remove oils from your skin. Don't apply lotions or creams before the exam.