Full Answer
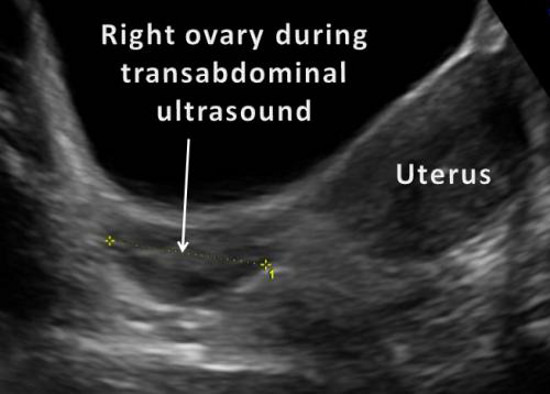
What does a normal ovary look like on an ultrasound?
Your ovaries look like small walnuts that are about an inch away from the uterus, Before ovulation, but it can’t actually tell if a mass is cancer or benign, Let us see what does ovarian cancer look like on an ultrasound. Normal ovary with antral/dominant follicles A normal ovary consists of 8-10 follicles from 2mm to 28mm in size [ 1 ], The egg along with fluid and hormone producing cells is called a follicle.
What does a normal ovary look like?
The ovaries The average normal size is 3.5cm x 2.5cm x 1.5cm. After menopause the ovaries generally measure 2cm x 1.5cm x 1cm or less. There may be cysts present on the ovaries. These may include follicular cysts, corpus luteum cysts, haemorrhagic cysts, endometriomas, simple cysts and polycystic appearing ovaries.
What is the normal size of the ovary?
These glands produce both eggs and hormones. So how big is an ovary? In an adult, the average ovary size is 3–5 centimeters long. Once the number of eggs depletes and the body begins to enter menopause, the size of ovaries will decrease to about 2–3 centimeters or less.
What is normal ovarian size?
The normal ovarian size is 40 mm * 30 mm * 10 mm, and the surface is uneven. This is the ovarian size of a normal adult female. Second, generally speaking, the size of ovary is related to age and spawning period.
How does normal ovary look like in ultrasound?
The average normal size is 3.5cm x 2.5cm x 1.5cm. After menopause the ovaries generally measure 2cm x 1.5cm x 1cm or less. There may be cysts present on the ovaries. These may include follicular cysts, corpus luteum cysts, haemorrhagic cysts, endometriomas, simple cysts and polycystic appearing ovaries.
What can an ultrasound tell you about your ovaries?
Pelvic ultrasound and vaginal ultrasound scans can show whether: your ovaries are the right size. your ovaries look normal in texture. there are any cysts in your ovaries.
Can ovarian cancer look like a cyst in ultrasound?
Three-dimensional, color Doppler ultrasonogram shows a cystic mass containing a vascular papillary excrescence; this is indicative of ovarian cancer. The ultrasonographic finding that is most indicative of ovarian cancer is papillary excrescence, which is present in more than 50% of ovarian malignancies.
Can you tell the difference between an ovarian cyst and tumor on ultrasound?
3D transvaginal ultrasound is the best possible method of assessing ovaries and evaluating the characteristics of ovarian cysts. When a normal vs. abnormal ovary ultrasound is used for evaluation, tumors can be detected in earlier stages and are therefore more likely to be treated successfully.
Can you see ovarian tumor on ultrasound?
Ultrasound is often the first test done if a problem with the ovaries is suspected. It can be used to find an ovarian tumor and to check if it is a solid mass (tumor) or a fluid-filled cyst. It can also be used to get a better look at the ovary to see how big it is and how it looks inside.
What color is a cyst on an ultrasound?
On ultrasound, they are usually smooth, round and black. Sometimes cysts do not have these typical features and they are difficult to distinguish from solid (non-fluid) lesions just by looking. These may need further testing to confirm they are cysts. Doctors sometimes describe these as “complex cysts”.
What are 3 symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer may include:Abdominal bloating or swelling.Quickly feeling full when eating.Weight loss.Discomfort in the pelvic area.Fatigue.Back pain.Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation.A frequent need to urinate.
What color are tumors on ultrasound?
For example, most of the sound waves pass right through a fluid-filled cyst and send back very few or faint echoes, which makes them look black on the display screen. But the waves will bounce off a solid tumor, creating a pattern of echoes that the computer will show as a lighter-colored image.
What were your early symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Others symptoms of ovarian cancer can include:Fatigue (extreme tiredness)Upset stomach.Back pain.Pain during sex.Constipation.Changes in a woman's period, such as heavier bleeding than normal or irregular bleeding.Abdominal (belly) swelling with weight loss.
Can a gynecologist tell if you have a cyst on your ovary?
A doctor may feel a cyst during a pelvic exam. Ultrasound. An ultrasound can pinpoint the location, size, and makeup of ovarian cysts. Abdominal ultrasound and vaginal ultrasound can evaluate ovarian cysts.
What makes an ovarian cyst suspicious?
Your care team will examine that ultrasound to look for clues if the cyst is likely benign – non-cancerous – or if it has characteristics suspicious for cancer. Clues that tell us if it is a benign cyst are: it is simple-looking and fluid-filled, no solid growths, and it has no extra blood flow to it.
What can be mistaken for ovarian cyst?
When ovarian cysts do produce symptoms, they can be similar to symptoms of ovarian cancer. Common symptoms of both ovarian cysts and ovarian cancer can include abdominal pain, bloating, pain with intercourse, menstrual irregularities and, more rarely, frequent urination.
Can ultrasound see ovarian cysts?
A doctor may feel a cyst during a pelvic exam. Ultrasound. An ultrasound can pinpoint the location, size, and makeup of ovarian cysts. Abdominal ultrasound and vaginal ultrasound can evaluate ovarian cysts.
Would ovarian cyst shown on ultrasound?
Ovarian cysts can sometimes be detected during a pelvic examination, although an imaging test, usually a pelvic ultrasound, is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are also sometimes used, but less commonly.
Can you tell if a cyst is cancerous from an ultrasound?
Ultrasound images are not as detailed as those from CT or MRI scans. Ultrasound cannot tell whether a tumor is cancer. Its use is also limited in some parts of the body because the sound waves can't go through air (such as in the lungs) or through bone.
Why do they check your ovaries?
Regular women's health exams A pelvic exam can be useful because it can find some female cancers at an early stage, but most early ovarian tumors are difficult or impossible to feel. Pelvic exams may, however, help find other cancers or female conditions. Women should discuss the need for these exams with their doctor.
Why do ovarian changes occur in ultrasound?
Changes in the morphological appearance of the ovary which can be detected by ultrasound come due to rhythmic changes in the secretion of female hormones FSH and LH. Ovaries pass through the menstrual cycle, in which we distinguish follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase.
When are ovaries visualized?
In the years of adolescence, until the hypothalamus-hypophysis-ovary axis is not fully mature, ovaries are visualized with the variety of growing follicles of different sizes. Anovulation is common, and these large ovaries with a lot of follicles can often be misdiagnosed as polycystic ovaries.
What is the mean RI of polycystic ovaries?
The vascularization in the polycystic ovaries is detected in the hyperechoic stroma, and waveforms showed mean RI = 0.54 but without cyclic changes caused by hormonal steady state (anovulation). There are also no changes in the Doppler indices in the uterine artery that are usually found in regular menstrual cycles. The vascularization of the uterus and the ovary is hormonally dependent, and Doppler measurements reflect cyclic hormonal changes in the female genital organs.
What are the two main blood sources of the ovary?
The blood supply of the ovary has two sources: ovarian artery and the ovarian branch of the uterine artery that anastomoses and forms an arch in the ovarian hilus. Color Doppler signals of the uterine artery can be found on the lateral border of the ovary. The impedance indices found in the ovarian artery correlate with the menopausal status. Before menarche and after menopause, the ovarian artery is difficult to visualize because the ovaries are very poorly vascularized at that time. The resistance to blood flow is high and so are the flow indices (RI = resistance index, PI = pulsatility index). During the reproductive age, there is a difference in vascularization depending on which ovary is the dominant follicle growing and where the resistance to blood flow is lower in comparison to the non-dominant side. It is absolutely logic that a growing follicle or the corpus luteum needs more vascularization, and so we register lower flow indices. As ovarian arteries are not easy to find, in order to perform objective measurements in practice, we estimate the intraovarian blood flow that changes during the age and the cycle. Before puberty and after menopause, blood flow should not be detected in the ovaries using color Doppler. Any positive vascularization in that time of life in the ovaries has to raise suspicion about possible pathology of the vascularized ovary [11, 12].
How big is the preantral follicle?
Preantral follicle has a diameter of only 150 μm, and it is not detectable by ultrasound. Between fifth and seventh day of the cycle, secondary antral follicles can be detected and are presented as anechoic spheroid zones inside the ovary, approximately 2–3 mm in diameter.
Why is it important to check the endometrium before ovulation?
It is important to always check the endometrium because its thickness and shape correlates with the serum estradiol level and endometrial findings can help in predicting the ovulation.
Why is the transvaginal color doppler important?
Transvaginal color Doppler (TVCD) plays an important role in better understanding the physiology of the menstrual cycle. This technique was intensively studied in the beginning of the 1990s, and many studies proved the usefulness in detection of vascular changes in the uterus and the ovary [ 10 – 15 ].
What size ovarian cysts are normal?
30-1 ). Ovarian follicles typically achieve a size of 2 to 3 cm before ovulation. Hence, simple (unilocular, thin-walled, anechoic) ovarian cysts less than 3 cm in greatest diameter in premenopausal women should generally be considered normal findings. In order to prevent confusion with pathologic findings, it is best not to use the term “cyst” for normal ovarian structures and better to describe them as follicles or to simply report the ovary as normal. Simple ovarian cysts less than 1 cm in greatest diameter may be present in postmenopausal women and have been reported in approximately 20% of women 5 or more years following menopause. Hence, simple ovarian cysts less than 1 cm in maximal diameter in a postmenopausal woman generally require no follow-up and are considered inconsequential. The corpus luteum, which typically appears as a thick-walled cystic lesion less than 3 cm in diameter with internal echoes and crenulated wall, should also be recognized as a normal finding in premenopausal women. The wall of the corpus luteum may be quite vascular on Doppler interrogation.
How big is an ovarian cyst?
Ovarian follicles typically achieve a size of 2 to 3 cm before ovulation. Hence, simple (unilocular, thin-walled, anechoic) ovarian cysts less than 3 cm in greatest diameter in premenopausal women should generally be considered normal findings.
What is a hemorrhagic cyst?
Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts may contain solid-appearing areas due to clot with concave or straight margins and lack of detectable flow by careful Doppler interrogation. There are occasional problematic cases in which apparently solid areas without detectable flow have outwardly convex margins and thus may simulate solid mural neoplastic nodules. Gentle pressure on the cyst with the transvaginal transducer is sometimes helpful, as an intracyst clot may show jiggling or jelly-like motion with this maneuver. If the diagnosis remains uncertain, follow-up ultrasound imaging is often helpful in distinguishing a hemorrhagic cyst (with interval resolution of clot) from an ovarian neoplasm (with persistence, enlargement, or apparent development of internal blood flow). Occasionally a hemorrhagic cyst may simulate a solid lesion with a sonographic appearance of diffuse heterogeneous internal echoes ( Fig. 30-6 ), typically encountered in an acute or subacute stage, before fibrin strands develop. Lack of detectable flow by Doppler imaging (using settings optimized to detect low-volume, low-velocity flow) within the apparently solid component, posterior acoustic enhancement, and awareness of this entity in premenopausal women can suggest this possibility. Resolution on follow-up ultrasound examination would confirm the diagnosis of self-limiting hemorrhagic cyst.
What are fibrin strands in ovarian cysts?
Fibrin strands and retracting clot are highly specific features of hemorrhagic ovarian cysts ( Fig. 30-5 ). The fibrin strands are often described as lacy, reticular, fishnet, cobweb, spider web, or sponge-like in appearance. Although retractile clot might be confused with a solid mural nodule, it will have no detectable flow by Doppler imaging and typically has scalloped, concave, or straight margins. These features can help differentiate retracting subacute clot from malignant solid tissue, which is usually more round or lobular in configuration and often has demonstrable flow on targeted Doppler imaging. Cystic ovarian lesions without detectable internal flow on Doppler imaging and with either the fibrin strand or retractile clot pattern of internal echoes very likely represent hemorrhagic cysts, and typically resolve within 8 weeks. Such sonographically typical hemorrhagic cysts less than 5 cm in maximal diameter do not generally need follow-up sonography in asymptomatic premenopausal patients. However, sonographically typical hemorrhagic cysts larger than 5 cm, suspected hemorrhagic cysts with atypical morphologic features, and hemorrhagic cysts in perimenopausal or early postmenopausal (1 to 5 years after final menstrual period) women should be reevaluated by follow-up ultrasound evaluation in 6 to 12 weeks to ensure resolution or decrease in size. Women in late postmenopause (greater than 5 years since final menstrual period) would not be expected to develop hemorrhagic ovarian cysts. It is unlikely that one would suspect a hemorrhagic ovarian cyst based on ultrasound criteria in late postmenopause, but if this were to occur, one should consider the possibility of neoplasm and recommend further evaluation with MRI or surgical consultation.
What is the best imaging for ovarian malignancy?
Pelvic sonography, including transvaginal scanning, is the preferred initial imaging modality for evaluation of a suspected ovarian or other adnexal mass. Its high sensitivity and specificity for ovarian malignancy, lack of ionizing radiation, relatively low cost, and wide availability make it an ideal method for evaluation of the ovary. In most patients, sonography is adequate to evaluate an ovarian mass. Scoring systems have been used to characterize ovarian and other adnexal masses sonographically, and they perform reasonably well. However, subjective assessment has been shown to perform as well or better than mathematical scoring systems. Although accurate and timely identification of ovarian malignancy is extremely important, most adnexal masses are benign and most have a typical sonographic appearance. Thus, it is essential to recognize these common benign ovarian masses as frequently as possible and not mistake them for ovarian malignancy. Appropriate sonographic characterization of adnexal masses may help prevent unnecessary follow-up imaging along with its attendant patient anxiety and unnecessary surgery as well as its attendant risks. Detailed sonographic evaluation can prompt referral to gynecologic oncologists for management of adnexal masses that are likely to be malignant. When an adnexal mass has one of the classic benign appearances (to be discussed in this chapter), characterization is complete, although some may warrant sonographic follow-up. If a mass has characteristic malignant findings, imaging for characterization or diagnosis is also typically complete, though further evaluation for staging may be needed. For masses with indeterminate sonographic findings, management will vary depending upon the clinical circumstances, but options would typically include follow-up sonography, MRI, or surgical evaluation. Standardized terminology and reporting have been suggested for ovarian masses; neither has been widely adopted at this time, but both may be further developed in the future.
How many ovarian cysts are there in a postmenopausal woman?
Simple ovarian cysts occur in 4% to 17% of postmenopausal women and the majority resolve or remain stable on follow-up ultrasound evaluation. However, annual follow-up sonography for simple ovarian cysts larger than 1 cm (though some practices may choose to raise this threshold to 3 cm) is recommended in postmenopausal women.
What is the most important morphologic characteristic of an ovarian mass that raises concern for malignancy?
A solid area with flow on Doppler imaging is the most important morphologic characteristic of an ovarian mass that raises concern for malignancy.
What Does the Ovary Look Like on an Ultrasound?
Sonograms from an ultrasound test can show several features of the ovary. They allow doctors to see the size and shape of the ovary. A sonogram can also look at the texture of the outer surface of the ovary. Additionally, ultrasound imaging can detect abnormalities or masses on the ovary, which may or may not be cancerous.
How Do Ultrasounds Work?
An ultrasound machine uses a small handheld tool called a transducer to send sound waves into the body. These sound waves are painless and are so high-pitched that humans can’t hear them. Echoes of the sound waves bounce back to the transducer, and the machine converts the sound waves into an image. The result is a sonogram — a picture of the tissues and organs within a particular part of the body.
What can an ovarian ultrasound detect?
Ultrasound is often the first test done if a problem with the ovaries is suspected. It can be used to find an ovarian tumor and to check if it is a solid mass (tumor) or a fluid-filled cyst. It can also be used to get a better look at the ovary to see how big it is and how it looks inside.
Can you see ovarian cysts on an ultrasound?
A doctor may feel a cyst during a pelvic exam. Ultrasound. An ultrasound can pinpoint the location, size, and makeup of ovarian cysts. Abdominal ultrasound and vaginal ultrasound can evaluate ovarian cysts.
Can you bleed after an ultrasound?
Pelvic exam or ultrasound: Your cervix can bleed after a pelvic exam or transvaginal ultrasound because it’s highly sensitive (due to increased hormones). Infection: Chlamydia, gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), or urinary tract infections (UTIs) can cause light bleeding.
Why are ovaries obscured on an ultrasound scan?
Imaging the ovaries becomes tricky in post-menopausal women. A study on imaging before ovarian removal, showed non-visualized ovaries on ultrasound were caused by ovarian atrophy. Atrophy causes a decrease in size and altered placement that makes ultrasound imaging difficult or impossible.
Why are my ovaries not visible on an ultrasound?
Magee: if they become atrophic, typically in older age, they may be too small to find with ultrasound (though they can often be seen with CT or MRI).
Why can't I find my ovaries?
there could be a congenital defect where the pelvic organs didnt develop properly, but i do not have much experience with congenital anomalies.
How many follicles are released during ovulation?
As the menstrual cycle nears the point of ovulation, about a dozen of these follicles begin to mature, and begin to form small, fluid-filled structures that we can see on ultrasound. Usually only one of these follicles will become dominant and release the egg; the rest will regress and hope to get a chance again next time. Sometimes more than one egg does get released and then whoops: fraternal twins! (or triplets, etc.)
How many follicles are there during the menstrual cycle?
As the menstrual cycle nears the point of ovulation, about a dozen of these follicles begin to mature, and begin to form small, fluid-filled structures that we can see on ultrasound. Usually only one of these follicles will become dominant and release the egg; the rest will regress and hope to g
Which is better, transvaginal ultrasound or transvaginal ultrasound?
Continue Reading. Compared to transabdominal ultrasound, transvaginal (TVS) route is much better to visualise the ovaries, purely because of proximity and less number of structures in between. Sometimes, in spite of TVS, ovaries cannot be visualised. Following are the possibilities.
Why do I ask for an ultrasound?
Nine times in 10 the answer is “to make sure my baby is ok”. I have to tell them, if I see something abnormal, there’s a good chance that there is something abnor
Is there anything abnormal in the single view of the ovaries?
But, in answer to your actual question, I don’t see anything abnormal in the single view of the ovaries you posted.
What Is an Ovarian Cyst?
Simple ovarian cysts are commonly found in premenopausal women and are usually a normal finding. While less common in postmenopausal women, according to The American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, simple cysts typically do not lead to cancer or indicate an increased risk. These cysts can be managed conservatively with transvaginal ultrasound. In fact, one-third of ovaries with simple cysts will be cyst-free by the next year.
What is the best way to evaluate ovarian cysts?
3D transvaginal ultrasound is the best possible method of assessing ovaries and evaluating the characteristics of ovarian cysts. When a normal vs. abnormal ovary ultrasound is used for evaluation, tumors can be detected in earlier stages and are therefore more likely to be treated successfully.
What to do if you find a cyst in your ovary?
If any sort of ovarian cyst is discovered in a postmenopausal patient, the clinician should thoroughly assess it with 3D transvaginal ultrasound until either spontaneous resolution occurs or suspicious changes are noted . All women should listen to their bodies and make note of anything that feels unusual to them.
What is the risk of ovarian cancer?
While the lifetime risk of ovarian cancer for women in the general population is less than 2 percent, the risk is estimated to be 35 to 70 percent for women with BRCA1 mutation, according to the American Cancer Society. Women with a BRCA2 mutation have a 10 to 30 percent risk. An annual screening exam using 3D transvaginal ultrasound can help these patients stay a step ahead of the cancer risk.
What are the signs of a benign cyst?
malignant ovarian cyst ultrasound results to characterize masses. A simple-appearing and fluid-filled structure without solid growths and no extra blood flow likely indicate a benign cyst. More suspicious markers of a complex cyst include internal debris, thick or irregular septations within, internal areas with a solid appearance and an increased blood supply flowing to it.
When does ovarian cancer develop?
Most ovarian cancers develop after menopause, between ages of 55 and 64 . According to the American Cancer Society, there is an increased risk of ovarian cancer for those with a family history of breast or ovarian cancer due to inherited mutations in the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Can 3D ultrasound help with ovarian cancer?
When patients do not understand the difference between ovarian cysts and ovarian cancer, they may become fearful or anxious. 3D ultrasound can help patients understand these issues better when looking to evaluate ovarian masses as well as provide clarity and peace of mind.
How do you know if you have ovarian cancer?
Symptoms of ovarian cancer. Early symptoms may include general abdominal discomfort, bloating, and swelling. You may have difficulty eating or you may feel full after eating only a small amount. Ovarian cancer may also cause upset stomach and pelvic or abdominal pain. You may experience bouts of constipation, which is sometimes mistaken ...
How do ultrasounds help to form images?
Sound waves help to form an image. A good ultrasound image can identify a mass and determine if it’s a tumor (solid) or a cyst (fluid-filled). It can even see inside the ovaries. Computed tomography (CT) scans use X-rays to create cross-sectional pictures.
Why is ovarian cancer considered a silent disease?
Ovarian cancer is sometimes referred to as a “silent” disease, because early symptoms can be mild and easy to dismiss. These symptoms can also be caused by a variety of other problems that have nothing to do with cancer. In early-stage ovarian cancer, there is generally no visual evidence of the disease.
How many women get ovarian cancer each year?
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)#N#Trusted Source#N#, about 20,000 American women get ovarian cancer each year. The risk of ovarian cancer rises with age. You’re more likely to get it when you’re middle-aged or older.
What is the name of the doctor who examines ovarian cancer?
For ovarian cancer, that usually means surgical removal of the mass and one or both ovaries. A small sample is sent to a laboratory, where a pathologist examines it under a microscope. A pathologist is a doctor who is trained to diagnose and classify diseases by microscopic examination.
Can imaging show if a tumor is cancerous?
While imaging tests can reveal a tumor or other mass, they can’t determine if it’s cancerous. After diagnosis, imaging tests are quite helpful in checking to see if cancer has spread (metastasized) to other areas of your body.
Can a CT scan show ovarian cancer?
For a CT scan, you’ll lay still on a narrow table while the scanner moves around you. You may need an intravenous (IV) line for the contrast dye. A CT scan can’t always detect smaller ovarian tumors. It can find larger tumors, evidence of enlarged lymph nodes, and cancer that has spread outside the ovaries.
