
How to test for starch?
List the steps and reagents used to test for starch. In the first step, I added 2 ml of iodine to 2ml of water in the test tube and the color of the test tube turned to yellow. In the second test tube, I added 2 ml of iodine to a starch solution and recorded the color of the test tube. The color of the test tube changed to dark brown.
How do you know if a bacteria has hydrolyzed starch?
Examine for the clear zone around the line of bacterial growth. Positive test: A clear zone around the line of growth after addition of iodine solution indicates that the organism has hydrolyzed starch. Negative test: A blue, purple, or black coloration of the medium (depending on the concentration of iodine).
What does it mean if starch test is yellow?
A yellow or orange coloration indicates that starch amylose is not present. If the material that is tested contains only cellulose or disaccharides, a positive result does not appear. The iodine reagent used for the starch test is usually prepared by dissolving iodine in water, after potassium iodide has been added to improve iodine’s solubility.
How do you know if a reagent is positive or negative?
If the addition of the biuret reagent change the color of the test tube to violet or black, it is a positive test for protein. What does a negative reagent look like? If there is no change in the color of the test tube or it changes t blue color, it is negative test. List the steps and reagents used to test for lipids.
See more
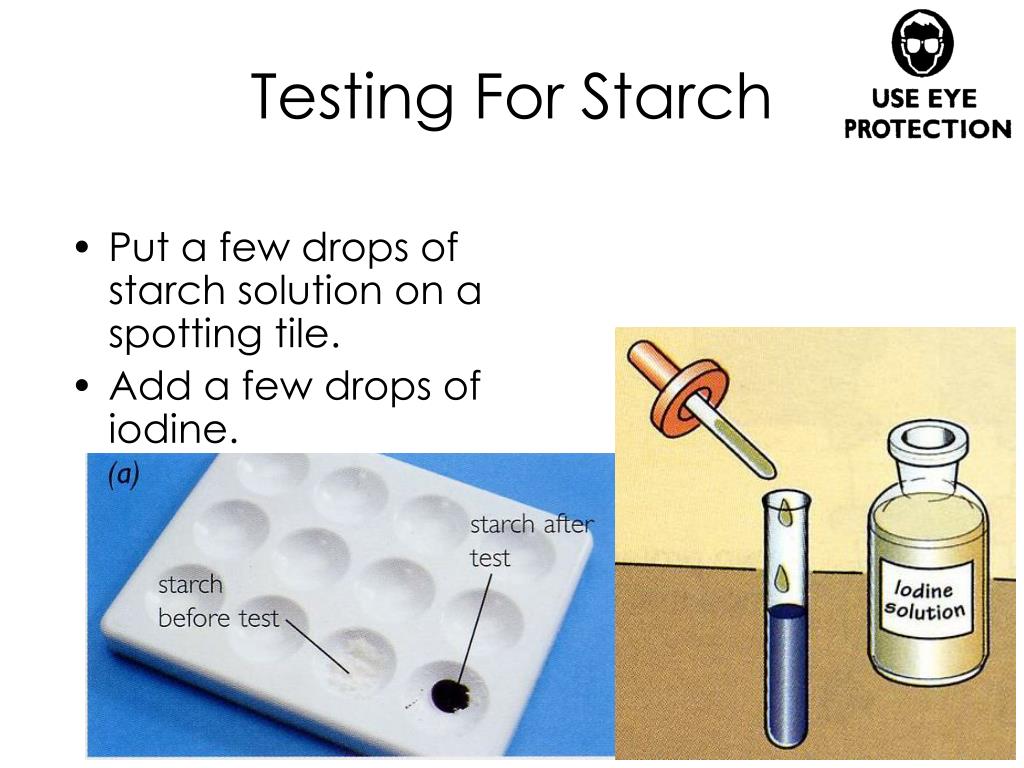
What color is a positive starch test?
blueUsing iodine to test for the presence of starch is a common experiment. A solution of iodine (I2) and potassium iodide (KI) in water has a light orange-brown color. If it is added to a sample that contains starch, such as the bread pictured above, the color changes to a deep blue.
What does a positive starch test mean?
Positive test:A clear zone around the line of growth after addition of iodine solution indicates that the organism has hydrolyzed starch. Negative test:A blue, purple, or black coloration of the medium (depending on the concentration of iodine).
How do starches test positive with the iodine test?
0:000:44Iodine Test for Starch - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSimple carbohydrates are the sugars found in anything sweet starchy carbohydrates are found in foodsMoreSimple carbohydrates are the sugars found in anything sweet starchy carbohydrates are found in foods like pasta potatoes cereals and rice a few drops of iodine. Solution produces a color change from
Which observation indicates a positive test for starch hydrolysis?
The iodine reacts with the starch to form a dark brown color. Thus, hydrolysis of the starch will create a clear zone around the bacterial growth. Bacillus subtilis is positive for starch hydrolysis (pictured below on the left).
What does a positive iodine test look like?
A positive result for the iodine test (starch is present) was a colour change ranging from violet to black; a negative result (no starch) was the yellow colour of the iodine solution.
What color does iodine turn in the presence of starch?
blue-blackMany different food groups contain a carbohydrate known as starch. Using an iodine solution, you can test for the presence of starch. When starch is present, the iodine changes from brown to blue-black or purple.
What colour does iodine turn when starch is not present?
Starch Test: Add Iodine-KI reagent to a solution or directly on a potato or other materials such as bread, crackers, or flour. A blue-black color results if starch is present. If starch amylose is not present, then the color will stay orange or yellow.
What is the difference between a positive and negative control for the starch test?
The negative control is the distilled water plus Benedict's solution. The positive control is the reducing solution. Which is a reducing sugar, sucrose or glucose?
Why do plants test positive for starch?
Starch is a white and powdery substance. It houses glucose, which plants use for food. The presence of starch in a leaf is reliable evidence of photosynthesis. That's because starch formation requires photosynthesis.
Which set up will give a positive starch test and why?
The presence of starch in leaves can be tested by the Iodine test. When we remove chlorophyll from the leaf by boiling it in alcohol and then putting two drops of iodine solution, it is a colour change to blue indicates the presence of starch.
What color is the plate that hydrolyzes starch?
Consequently, transparent clear zones are formed around the colonies that hydrolyze starch while the rest of the plate show a dark blue coloration as iodine forms the colored complex with starch.
What are the components of starch?
Starch consists of 2 components—amylose and amylopectin, which are present in various amounts. The amylose consists of D-glucose units linked in a linear fashion by α-1,4 linkages. It has 2 non-reducing ends and a reducing end. Amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide. In these molecules, shorter chains of glucose units linked by α-1,4 are also ...
What is starch agar?
Starch agar is a simple nutritive medium with starch added. Beef extract and pancreatic digest of gelatin provide nitrogen, vitamins, carbon and amino acids. Agar is the solidifying agent and starch is the carbohydrate.
What is the ability to degrade starch used for?
The ability to degrade starch is used as a criterion for the determination of amylase production by a microbe.
What does a clear zone around the line of growth after addition of iodine solution indicate?
Positive test: A clear zone around the line of growth after addition of iodine solution indicates that the organism has hydrolyzed starch.
What is the principle of starch hydrolysis?
Principle. Many bacteria produce extracellular enzymes used to catalyze chemical reactions outside of the cell. In this manner, nutrient sources, such as starch, that are too large to be absorbed through the cell membrane can be broken down into smaller molecules and transported into the cell via diffusion. In the starch hydrolysis test, the test ...
How long to incubate bacterial plates?
Incubate the bacterial inoculated plates for 48 hours at 37°C. Following incubation, flood the surface of the plates with iodine solution with a dropper for 30 seconds. Pour off the excess iodine. Examine for the clear zone around the line of bacterial growth.
What does the orange color on a glucose test tube mean?
The orange color in the test tube indicates a positive test for glucose
What is the color of the iodine test tube?
In iodine test for starch, first, the researcher added 2ml of iodine solution to 2 ml of water and the color of the test tube turned red, which indicated a negative test for the presence of starch. Then, the researcher added 2ml of iodine to the starch solution and the color of solution turned black, which is a positive test for starch.
What does it mean when a biuret reagent changes color?
If the addition of the biuret reagent change the color of the test tube to violet or black, it is a positive test for protein.
How to test for glucose in a solution?
Benedict’s reagent is used to identify the presence of simple sugars in a solution. For this test, the researcher took a test tube and added 2 ml of water to it. In the next step, the researcher added 2ml of the reagent to that test tube and heated the test tube for 5 minutes in boiling water and then recorded the color of the test tube. It turned to blue that indicated a negative test for the presence of glucose. In the next step, the researcher took a test tube and added 2ml of glucose and added 2ml of the reagent and heated this solution for 10 minutes. The color of the test tube changes to orange, which indicated the presence of glucose.
What color does biuret turn?
Proteins react with biuret reagent and turns the protein solution from light blue to violet, black. In the first step, the researcher took 2ml of water in a test tube and added 2ml of Biuret reagent and it did not change the color of the solution, which is an indication of negative test for protein. Then, the researcher added little amount of yellow colored protein in the test tube and added 2ml of biuret reagent to it, the color of the test tube changed to violet color, which indicated a positive test for protein.
What happens if there is no lipid in the test tube?
If there is no lipid in the test tube, Sudan reagent won’t be dissolved in the test tube and will show 2 layers.
What does it mean when the color of the solution turns black?
If the color of the solution turns to black, it is a positive test for starch.

Objective
- To determine the ability of an organism to hydrolyze starch
- To differentiate organism based on their α- amylase enzyme activity
Principle
- Many bacteria produce extracellular enzymes used to catalyze chemical reactions outside of the cell. In this manner, nutrient sources, such as starch, that are too large to be absorbed through the cell membrane can be broken down into smaller molecules and transported into the cell via diffusion. In the starch hydrolysis test, the test bacteria are grown on agar plates containing star…
Method
- Using a sterile technique, make a single streak inoculation of organism to be tested into the centre of labeled plate.
- Incubate the bacterial inoculated plates for 48 hours at 37°C.
- Following incubation, flood the surface of the plates with iodine solution with a dropper for 30 seconds.
- Using a sterile technique, make a single streak inoculation of organism to be tested into the centre of labeled plate.
- Incubate the bacterial inoculated plates for 48 hours at 37°C.
- Following incubation, flood the surface of the plates with iodine solution with a dropper for 30 seconds.
- Pour off the excess iodine.
Expected Results
- Positive test:A clear zone around the line of growth after addition of iodine solution indicates that the organism has hydrolyzed starch.
- Negative test:A blue, purple, or black coloration of the medium (depending on the concentration of iodine).
Uses
- It aids in the differentiation of species of genera Corynebacterium, Clostridium, Bacillus, Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, and members ofEnterococcus spp.
Limitations
- It is recommended that biochemical, immunological, molecular, or mass spectrometry testing be performed on colonies from pure culture for complete identification.
- Colonies cannot be subcultured from the medium after the addition of Gram’s iodine due to the oxidative nature of the reagent and the resulting cell death.
References
- Tille P.M. 2014. Bailey and Scott’s diagnostic microbiology. Thirteen edition. Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 3251 Riverport Lane. St. Louis. Missouri 63043
- https://www.austincc.edu/microbugz/starch_hydrolysis.php
- https://www.himedialabs.com/TD/M107.pdf
- https://www.uwyo.edu/molb2210_lab/info/biochemical_tests.htm
Similar Posts