What do soil wetters do? Soil wetters, both liquid and granular; work by improving the absorption of water, reducing the surface tension of water and helping it to spread more evenly through the soil profile.... Most soil wetters, as well as kitchen or laundry detergents; will strip soils of goodies, kill earthworms and upset the soil biota
Life
Life is a characteristic that distinguishes physical entities that have biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from those that do not, either because such functions have ceased, or because they never had such functions and are classified as inanimate. Variou…
What is a soil wetter?
A soil wetter combines the soil and moisture in a deeper way, which makes it more difficult for the moisture to be evaporated away. Soil wetting agents usually come in a granular form, and can be spread by either hand or a seed spreader.
What is a Soil wetting agent?
A soil wetting agent is a detergent or disinfectant that attracts water to the soil surface, helping it to soak in and improve infiltration. This reduces water run-off and encourages deeper roots which help to make your lawn dry tolerant. Wetting agents come in liquid or granule form, and it is mixed in the lawn food or top dressing mixes.
What happens when soil is wet or dry?
Wet soil causes microbes to compete with plant roots for oxygen. It reduces oxygen flow to the plant and disrupts its growth. Damp soil also leads to wilting and yellowing of the plant’s leaves and produces a rotten or sour odor, a sign of root rot.
How does a wet area affect plant growth?
Wetter areas may have reducing conditions that will inhibit proper root growth for plants that require a balance of soil oxygen, water, and nutrients. Steepness, shape, and length of slope are important because they influence the rate at which water flows into or off the soil.

When should you use soil wetter?
To get the best results, apply soil wetting agents in early spring, early summer, or autumn, and in the cool of the morning to avoid the hottest part of the day. They can be applied to new or established lawns or to the soil before rolling out turf or seeding a new area of lawn.
Can you apply too much wetting agent?
Unlike fertilisers that can cause toxicity if applied too frequently or in too large an amount, wetting agents present no such risk. While they won't cause in problems, applying them too frequently is a waste of money – once they have done their job there is nothing more that can be achieved.
What does wetting agent do for plants?
A wetting agent is added into a spray mixture to reduce the surface tension of spray droplets which prevents droplets from beading up on the leaf surface. Therefore, the wetting agent lowers spray droplet surface tension which enables the spray to increase the leaf area covered by each droplet.
How do wetting agents work in soil?
"We believe that what happens in some soils when organic matter breaks down is that it leaves a waxy coating on the soil particles. Wetting agents are like detergents. They overcome that waxing coating and allow water to penetrate into the pore spaces between," Peter said.
Can you use dishwashing liquid as a soil wetting agent?
To wet hydrophobic soils, add several drops of liquid dish-washing soap to a watering can filled with water and slowly apply to the soil. The soap breaks the dried soil's surface tension and allows the water to be absorbed.
Are wetting agents worth it?
Wetting agents do wonders for your soil Sandy soils are known to be water repellent (hydrophobic), making it a challenge to maintain a healthy garden in WA. The simplest way to improve the absorption of water in your soil and help it spread more evenly throughout, is to add a wetting agent.
Can you make your own soil wetter?
You can make your own soil wetting agent using the food grade thickener, agar agar (algin), derived from seaweed. Buy powdered kelp from a health food store. Slowly add boiling water to agar agar and stir to make a paste about the same consistency as wallpaper paste.
What is a good wetting agent?
Dish soap is a great example of a wetting agent. With all the food oils and such on the plate cohesive forces make it difficult for the water to spread and clean the plate. The soap dissolves all theses unwanted particles, exposing a clean surface.
What is the difference between a surfactant and a wetting agent?
All wetting agents are surfactants, but not all surfactants are wetting agents. Wetting agents are a class of surfactants that lower the interfacial tension of a liquid. An example is water. Water has a high interfacial tension, so a drop of water tends to “bead” on a hydrophobic surface, such as plastic.
Why is my soil still dry after watering?
Plant soil can dry out quickly because of low humidity, internal water channels, excessive sunlight, loose soil, and unwanted fungi. As a result, water can run out of holes at the bottom of the pot, while atmospheric conditions around the plant can escalate the rate of evaporation, causing the soil to dry out fast.
Why is my soil not absorbing water?
Hard-packed clay soils and even garden soils can become crusted and resist wetting, letting water run off instead of absorbing it. To re-wet, repeatedly sprinkle the surface lightly, making sure there is no run off. Covering the surface with a mulch such as straw, leaves, wood chips, or compost will also help.
How do you fix soil that won't absorb water?
Add a layer of mulch, such as straw, leaves, wood chips and/or compost to the soil surface to hold moisture in the soil. Hard-packed clay and silty garden soils can also become crusted and resist wetting, allowing water to run off instead of absorbing it.
Does wetting agent need watering in?
The common misconception is that these products replace the need for watering! They don't. Water is still required but because it is now able to penetrate the soil and be held in the soil more easily you use less water. The water that you do use is also now more easily and readily available to the grass roots.
Can wetting agents burn?
Why do some wetting agents discolor and burn grass? High rates of nonylphenols, alkylphenols, and alcohols contained in many surfactants can cause cell damage. Some surfactants dissolve cuticle/wax layers on the leaf blades causing discoloration and burning if allowed to stay on the leaf surface too long.
What is the difference between a surfactant and a wetting agent?
All wetting agents are surfactants, but not all surfactants are wetting agents. Wetting agents are a class of surfactants that lower the interfacial tension of a liquid. An example is water. Water has a high interfacial tension, so a drop of water tends to “bead” on a hydrophobic surface, such as plastic.
How do you apply a wetting agent?
How to apply a wetting agent to your lawn? Shake & mix well before use. ... Add the recommended product mix to a small amount of water. ... Apply evenly to the lawn. For best results apply in damp conditions or when rain is expected. Do not apply in hot, dry conditions or during periods of frost.
What is a soil scientist?
A soil scientist studies the upper few meters of the earth's crust in terms of its physical and chemical properties; distribution, genesis and morphology; and biological components. A soil scientist needs a strong background in the physical and biological sciences and mathematics.
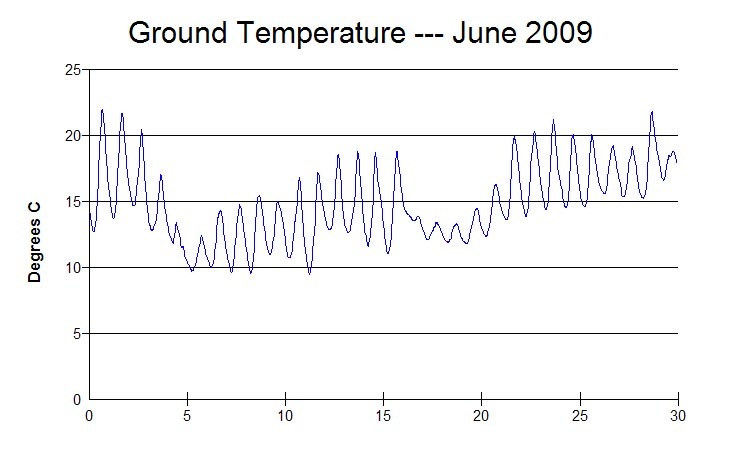
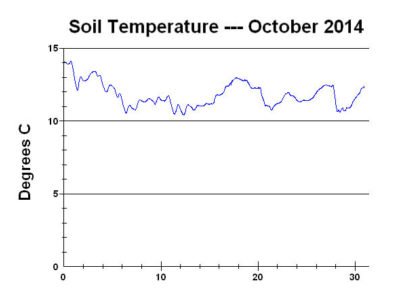
How does climate affect the soil?
Climate through its influence on soil temperature, determines the rate of chemical weathering.
How does soil form?
Soils develop as a result of the interactions of climate, living organisms, and landscape position as they influence parent material decomposition over time. Differences in climate, parent material, landscape position, and living organisms from one location to another as well as the amount of time the material has been in place all influence the soil-forming process.
What are soil horizons?
These layers, called horizons, can be seen where roads have been cut through hills, where streams have scoured through valleys, or in other areas where the soil is exposed.
What is a soil survey?
One of the main tools available to help land users determine the potentials and limitations of soils is a soil survey. Soil surveys are available through the USDA, Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). The surveys are made by NRCS in cooperation with other Federal, State, and local agencies. Our offices can provide this information, but more and more soil surveys are also available on the Internet. Web Soil Survey allows you to produce a customized soil survey for your own area of interest.
What are the ingredients in soil?
Soil is a naturally occurring mixture of mineral and organic ingredients with a definite form, structure, and composition. The exact composition of soil changes from one location to another. The following is the average composition by volume of the major soil ingredients: 1 45% Minerals (clay, silt, sand, gravel, stones). 2 25% Water (the amount varies depending upon precipitation and the water-holding capacity of the soil). 3 25% Air (an essential ingredient for living organisms). 4 5% Organic matter or humus (both living and dead organisms).
What is the upper limit of soil?
The upper limit of soil is the boundary between soil and air, shallow water, live plants, or plant materials that have not begun to decompose. Areas are not considered to have soil if the surface is permanently covered by water too deep (typically more than 2.5 meters) for the growth of rooted plants.
How to Prevent Wet Soil?
Many homeowners find it daunting to deal with wet soils. Determining an indoor plant’s exact water requirements is not easy, especially if you lack knowledge about it.
What are the signs of wet soil?
There are various signs and symptoms of wet soil, such as root rotting, yellowing or browning of leaves, mold and fungus growth, edema, and wilting. All these are signs of wet soil that can significantly damage your indoor plant. Let us talk about these symptoms in detail. Continue reading!
Why is my potted plant wet?
Potted plant soil will remain wet after watering if the soil does not have proper drainage or is being watered too often, as a result yellowing of the leaves, edema, root rot and wilting may occur. Overwatered soil can be prevented by providing the proper soil mix and employing methods to prevent overwatering.
Why does my indoor plant smell rotten?
It reduces oxygen flow to the plant and disrupts its growth. Damp soil also leads to wilting and yellowing of the plant’s leaves and produces a rotten or sour odor, a sign of root rot. In today’s article, we will talk about the causes and symptoms of wet soil for indoor plants and what you can do to prevent it.
Why do plants die in the garden?
Poorly drained soil is more prone to waterlogging, which leads to the death of roots because they don’t absorb enough oxygen to function normally.
What is a plant disease that occurs when there is more water in the roots and less transpiration by the leaves?
Edema is a plant disease that occurs when there is more water in the roots and less transpiration by the leaves.
Can you grow aquatic plants in wet soil?
Wet soil is favorable if you are growing aquatic plants at home. On the other hand, a regular indoor plant’s roots don’t like to sit in wet soil.
How to increase water retention in soil?
Spoon or stick. Tip. Improving the soil can increase water retention without the need for a soil-wetting agent. Incorporate up to a 4-inch layer of compost with the existing soil and break up large chunks in the soil before planting. Warning.
What is the best way to repel water from a garden bed?
Sandy soil, poorly tilled soil and soil that contains organic matter but has been allowed to dry out completely are most likely to repel water. A soil-wetting agent, also called a surfactant, coats the soil particles on the molecular level so the water can infiltrate the garden bed.
How to make a soap and water sprayer?
Water the soil with the soap and water mixture. Apply the mixture directly to the soil and avoid spraying any plants when possible. Thoroughly saturate the soil so it feels moist to at least a 4-inch depth. Monitor the soap level in the sprayer bottle and refill it as necessary. Advertisement.
Can soap be used on plants?
Warning. Homemade soil-wetting agents made from soap may contain small amounts of salt, boron or other elements that become harmful to plants as they build up. Avoid applying these agents more than once or twice a year, and test the agent on a small area before widespread use to ensure it doesn't damage the plants.
When to use soil wetter in Australia?
In Australia soil wetters are best used in the beginning of spring, as the last of the winter rains will help the granules penetrate the soil, preparing it for the coming heat and dryness. If you spread your soil wetter too late in the year it may not be as effective.
Why is soil wetting agent used in potting?
The fact that the majority of Australians live near the coast makes this hydrophobicity all the more prevalent, as sandy soils are the worst for retaining moisture. But even the most fertile soils can have issues with taking on moisture, as the breakdown of organic matter can leave a waxy coating on the particles of the soil which repels water. In this situation the soil wetting agent will act as somewhat of a detergent, washing away the waxiness and allowing the soils to take on moisture. Potting mix can have similar waxiness issues, so soil wetting agents can help to make these mixes far more effective.
What is the purpose of a wetting agent?
A wetting agent may be the answer to your soil moisture prayers. These agents are surfactants – they work to lower the surface tension between two compounds (liquid water and solid soil particles in this case) which allows the soil to better take in moisture. Certain soils in certain situations can act somewhat hydrophobic, leading to moisture being removed via evaporation. A soil wetter combines the soil and moisture in a deeper way, which makes it more difficult for the moisture to be evaporated away.
How much area does restore soil weather cover?
Restore Granular Soil Wetter is bought by the kilogram, with 3kg capable of covering an area of 100 square metres. If you have any further queries on whether Restore Soil Wetter is the right choice for you, don’t hesitate to contact the friendly team at McKays!
Can you mix soil wetting agents?
Soil wetting agents usually come in a granular form, and can be spread by either hand or a seed spreader. They generally needn’t be mixed into the soil, as they will penetrate it naturally when wet (this may mean that you need to water certain types of soil wetting agent in).
Is McKays Restore Granular Soil Wetter good for soil?
If your soil is sandy or generally hydrophobic, if you’ve found bare and dry patches in your lawn, or if your composting efforts needs a hurry-up, McKays Restore Granular Soil Wetter is about as complete a soil wetting agent as there is. Perfect for areas with minimal rain or water-restrictions, it is one of the best products on the market for the penetration and retention of moisture in soil.
Why Does Weather Affect Soil?
- “Weather is a huge factor in determining the condition of the soil. In gardening, it’s important that you know the present variables to understand how you can counter and create alternative methods to maintain a specific temperature. Weather contributes to a soil’s moisture and its organic matter content. During rainfall, the pH level of soil decre...
Top 5 Positive Effects of Climate and Weather on Soil
- Brings Enough Moisture
“The positive and negative effects of weather on soil are often the same. Too much or not enough rain is bad for the soil, while an ideal amount of rain is perfect. Moisture is necessary for the microorganisms that make up the living parts of soil to thrive, as is a moderate temperature, neit… - Helps Get Nutrients
“Typical climates are responsible for helping soil get the nutrients it then passes on to plants. Every aspect of climate is involved in this process.” Jeremy Yamaguchi, CEO of Lawn Love
Negative Effects of Climate and Weather on Soil
- Can Break Down Soil Structure
“Negative effects from too much rain include a breakdown in soil structure – turning to mud, in other words – and even the potential for microbes and roots to be drowned if the soil is oversaturated for too long.” Garth Brown, Cairncrest Farm - Can Lower the Productivity of the Land
“Extremely hot weather dries out soil and leads to the rearrangement of the normal soil profile. As the soil dries up, plants cannot grow. This leads to the loosening of the soil (instability). Loose soil is then distributed by different factors such as wind, animals, or human activities. Normally, the t…
3 Best Ways to Preserve Soil
- While it can take a lot of effort and time to stop climate change, there are still a few easy things gardeners and farmers can do to help preserve soiland ensure a good harvest season.