Summing amplifier is basically an op amp circuit that can combine numbers of input signal to a single output that is the weighted sum of the applied inputs. The summing Amplifier is one variation of inverting amplifier.
How do you use op amp as a summing amplifier?
Op-Amp can be used as a summing amplifier by applying multiple inputs either to the inverting or to the non-inverting op-amp terminals. As shown in Fig.1, the op-amp is used as a summing amplifier in the inverting configuration.
What is the output voltage of a summing amplifier?
Then the output voltage of the Summing Amplifier circuit above is given as -45 mV and is negative as its an inverting amplifier. But as well as constructing inverting summing amplifiers, we can also use the non-inverting input of the operational amplifier to produce a non-inverting summing amplifier.
What are summing amplifiers used for?
Summing amplifiers are used in audio mixers. Theoretically, a summing amplifier can take on unlimited numbers of input. However, an op-amp in the real world is far from ideal. The output voltage range of an ideal op-amp is unlimited, but for a real opamp, it is limited by the DC supply connected to it.
Why do we need a summing circuit for op-amps?
Sometimes we need a summing circuit to just add together two or more voltage signals without any amplification. By putting all of the resistances of the circuit above to the same value R, the op-amp will have a voltage gain of unity and an output voltage equal to the direct sum of all the input voltages as shown:
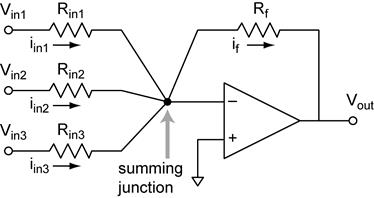
What are summing op amps used for?
Summing amplifiers are commonly used to process analog signals. You'll find summing amplifiers in audio mixers. It allows audio experts to combine signals from various channels and reproduce them into a single track. Every single audio input can be configured independently without affecting the output.
What is the gain of a summing op-amp?
The standard equation for the voltage gain of a non-inverting summing amplifier circuit is given as: The non-inverting amplifiers closed-loop voltage gain AV is given as: 1 + RA/RB.
What is the difference between adder and summing amplifier?
An op-amp based adder produces an output equal to the sum of the input voltages applied at its inverting terminal. It is also called as a summing amplifier, since the output is an amplified one.
Is summing amplifier a DAC?
Summing Amplifier based DAC The simplest DAC circuit includes a summing amplifier and also a weighted resistor n/w. The circuit diagram of the 4-bit digital to analog circuit using a summing amplifier is shown below.
What is inverting and non inverting summing amplifier?
The most commonly used Summing Amplifier is an extended version of the Inverting Amplifier configuration i.e., multiple inputs are applied to the inverting input terminal of the Op Amp, while the non-inverting input terminal is connected to ground.
Why ideal op-amp has infinite gain?
This is because of infinite input resistance. As the input resistance of ideal op amp is infinite, an open circuit exists at input, hence current at both input terminals is zero.
How do you calculate the output of a summing amplifier?
2:215:52Summing Amplifiers - Op Amp Circuits - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe output voltage is negative RF times V 1 over R 1 plus V 2 over R 2 plus V 3 over R 3. Now noticeMoreThe output voltage is negative RF times V 1 over R 1 plus V 2 over R 2 plus V 3 over R 3. Now notice that all of the resistors have the same value the feedback resistor RF is 5 kilo ohms r1 r2 and r3
How op-amp can be used as a differentiator?
Op-amp Differentiator Circuit The input signal to the differentiator is applied to the capacitor. The capacitor blocks any DC content so there is no current flow to the amplifier summing point, X resulting in zero output voltage.
What is the difference between integrator and differentiator?
A differentiator circuit produces a constant output voltage for a steadily changing input voltage. An integrator circuit produces a steadily changing output voltage for a constant input voltage.
How is op-amp used in DAC?
This circuit provides biasing of the DAC outputs, converts the DAC currents to voltages, and provides a single-ended output voltage through the op amp. The op amp is the active amplifier element for the circuit and uses R2, R3, RG, and RF to make a difference amplifier.
What is a comparator op-amp?
The Op-amp comparator compares one analogue voltage level with another analogue voltage level, or some preset reference voltage, VREF and produces an output signal based on this voltage comparison.
What is a 4 bit DAC?
-The encoder stage encodes the discrete values into a digital 4-bit binary word. The DAC is made up of decoder and operational amplifier. -The decoder is made up of 16 4-input NANDs. -The Op amp amplify the decoded signals and transfer them to the output.
What is adder circuit?
An adder is a circuit that sums the amplitudes of two input signals. A half-adder is a group of connected logic gates that create a logic circuit, incapable of handling addition for two numbers. A full-adder is a circuit that adds two binary numbers. CPU terms, Electronics terms, Transistor.
What is an inverting summing amplifier?
A summing amplifier is an example of an inverting amplifier with multiple inputs, enabling to effectively add several individual input signals, which proves to be useful in audio mixing applications.
What is the difference between common-mode and differential mode input signals?
What is the difference between common mode and differential mode? A. The common mode refers to signals or noise that flow in the same direction in a pair of lines. The differential (normal) mode refers to signals or noise that flow in opposite directions in a pair of lines.
What is slew rate?
Slew rate is defined as the maximum rate of change of an op amps output voltage, and is given in units of volts per microsecond. Slew rate is measured by applying a large signal step, such as one volt, to the input of the op amp, and measuring the rate of change from 10% to 90% of the output signal's amplitude.
What is a summing amplifier?from electronics-tutorials.ws
The Summing Amplifier is a very flexible circuit indeed , enabling us to effectively “Add” or “Sum” (hence its name) together several individual input signals. If the inputs resistors, R1, R2, R3 etc, are all equal a “unity gain inverting adder” will be made. However, if the input resistors are of different values a “scaling summing amplifier” is ...
What is a non-inverting summing amplifier?from electronics-tutorials.ws
As its name implies, the non-inverting summing amplifier is based around the configuration of a non-inverting operational amplifier circuit in that the input (either ac or dc) is applied to the non-inverting (+) terminal, while the required negative feedback and gain is achieved by feeding back some portion of the output signal (V OUT) to the inverting (-) terminal as shown.
What is non inverting in a op amp?from electronics-lab.com
In a non-inverting configuration, the output is always in phase with the inputs which save the trouble to use an inverting buffer to rectify the signal. Moreover, the non-inverting configuration presents the property of having a much higher input impedance which is an advantage to properly inject the desired voltages from a source (microphone for example) to the inputs of the op-amp.
What is the advantage of inverting summing?from electronics-lab.com
The advantage of the inverting configuration is that even in the general case, the output is simply expressed as a function of the different resistor and input values.
Why do we need a summing circuit?from electronics-tutorials.ws
Sometimes we need a summing circuit to just add together two or more voltage signals without any amplification. By putting all of the resistances of the circuit above to the same value R, the op-amp will have a voltage gain of unity and an output voltage equal to the direct sum of all the input voltages as shown:
What is a DAC?from electronics-lab.com
A DAC is a summing amplifier based circuit that converts binary data (0 and 1) into an analog signal (a real number). An example of this circuit with four binary inputs known as a four-bit DAC and is presented in Figure 5:
How to find the voltage gain of a non-inverting amplifier?from electronics-tutorials.ws
The non-inverting amplifiers closed-loop voltage gain A V is given as: 1 + RA/RB. If we make this closed-loop voltage gain equal to 2 by making R A = R B, then the output voltage V O becomes equal to the sum of all the input voltages as shown.
What is an opamp circuit called?
There is an opamp circuit called an integrator, but the summing circuit in this video is not it. An integrating opamp circuit includes a capacitor, typically in the feedback path. Here's an example of an integrator: http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/opamp/opamp_6.html. A differentior opamp circuit is less common.
How to differentiate op amp?
For the differentiating op-amp replace the input resistor with a capacitor. Now the output will be the derivative of the input. For example, no output for a DC input. steady output voltage for a ramp input.
How many resistors are in an inverting op amp?
Start with an inverting op-amp. Here there are two resistors the feedback resistor and the input resistor.
What does vout do?
Depends. Vout does whatever is necessary to keep the inverting terminal at zero. If Vin is pos then Vout must be neg. If Vin is neg ten Vout is pos.
Summing Amplifier Circuit
In this simple summing amplifier circuit, the output voltage, ( Vout ) now becomes proportional to the sum of the input voltages, V 1, V 2, V 3, etc. Then we can modify the original equation for the inverting amplifier to take account of these new inputs thus:
Summing Amplifier Equation
We now have an operational amplifier circuit that will amplify each individual input voltage and produce an output voltage signal that is proportional to the algebraic “SUM” of the three individual input voltages V1 , V2 and V3.
Non-inverting Summing Amplifier
So what’s the advantage of the non-inverting configuration compared to the inverting summing amplifier configuration.
Non-inverting Summing Amplifier Output Voltage
Thus for a 3-input non-inverting summing amplifier configuration, setting the closed-loop voltage gain to 3 will make V OUT equal to the sum of the three input voltages, V 1, V 2 and V 3. Likewise, for a four input summer, the closed-loop voltage gain would be 4, and 5 for a 5-input summer, and so on.
Summing Amplifier Audio Mixer
Another useful application of a Summing Amplifier is as a weighted sum digital-to-analogue converter, (DAC).
Digital to Analogue Converter
Of course this is a simple example. In this DAC summing amplifier circuit, the number of individual bits that make up the input data word, and in this example 4-bits, will ultimately determine the output step voltage as a percentage of the full-scale analogue output voltage.
What is a summing amplifier?
Summing amplifier is basically an op amp circuit that can combine numbers of input signal to a single output that is the weighted sum of the applied inputs. The summing Amplifier is one variation of inverting amplifier.
What is an OP amp?
An op amp is an amplifier. But an op amp can also perform summing operation. We can design an op amp circuit to combine number of input signals and to produce single output as a weighted sum of input signals.
What is a summing amplifier?
A summing amplifier is, in fact, an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured in a specific manner. An ideal op-amp has characteristics like infinite input impedance, infinite gain, and zero output impedance. Based on its unique properties, an op-amp can be configured for various functions, including a summing amplifier.
What is an OP amp?
Based on its unique properties, an op-amp can be configured for various functions, including a summing amplifier. Also known as the adder, the summing amplifier produces a voltage output that is equivalent to an amplified sum of two or more input voltages. Usually, a summing amplifier is in fact an inverting amplifier, ...
What determines the gain of a summing amplifier?
The value of the feedback resistor, Rf, and input resistors determine the gain of the summing amplifier. When the values of both types of resistors are equal, the gain is equal to 1 and the equation becomes.
Is a summing amplifier an inverter or an inverter?
While summing amplifiers are usually derived from inverting amplifiers, it can also be configured from a non-inverting amplifier. The principle is the same as the amplifier sums the total voltage inputs from the resistors connected to the non-inverting terminal of the circuit.
Can an op amp take unlimited inputs?
Theoretically, a summing amplifier can take on unlimited numbers of input. However, an op-amp in the real world is far from ideal. The output voltage range of an ideal op-amp is unlimited, but for a real opamp, it is limited by the DC supply connected to it.
Can you connect multiple input resistors to a summing amplifier?
Even if you’re using a resistor with a large power rating, it is still impossible to connect an infinite number of input resistors. Eventually, the feedback resistor will be overheated.
What is a summing amp?
A summing-amplifier is one of the op-amp applications, which performs summation or addition operations. Multiple input voltages are supplied into the amplifier, and the output provides an amplified summation of the voltages. Summing-amplifiers has various applications in electronics. It also has two types – inverting summing-amplifier and non-inverting summing-amplifier. In detail, we will discuss the analysis of the summing-amplifier in the following article.
How does a summing amplifier work?
Answer: The working of a summing-amplifier is straightforward. Inputs are given at one of the input terminals. The resistances add weight to the input voltages. The amplifier then sums up all the weighted input and produces output.
How to determine the output voltage of the summing-amplifier?
A few steps are to be followed to determine the O/P voltage of the summing-amplifier. At first, we have to use the concept of virtual ground. Using this, we make sure that voltages at both the input terminal are equal. Then apply Kirchhoff’s Current Law to get the voltage equations from the input terminals. After that, replace the necessary terms to get the final output in input voltages and resistances. Derivations for both the inverting and non-inverting types are given below.
What is the difference between a summing and a difference amplifier?
In the summing-amplifiers, input voltages are provided at one end , and the output , the sum of the voltages, is received with some amplification in the output.
What is a non-inverting summing amplifier?
Non-inverting summing-amplifier is one of the types of summing-amplifiers. In this type of operations, the input voltages are provided in the amplifier’s non-inverting terminal. The polarity of the output remains the same as the inputs and because of this, it is termed as non-inverting summing-amplifier.
How to measure input and output voltages of an op amp?
The input and output voltages of an op-amp can be observed and measured using a CRO. The CRO pins are connected with the input pins and the ground for observing the input voltages.
What is a DC summing amplifier?
The Dc summing-amplifier is referred to as the summing-amplifiers fed with the input dc voltages. In general, summing-amplifiers can be fed with either ac or dc voltages for their operation.
What does an OP-amp do?
Regardless of its particular purpose, an op-amp always aims to deliver an output voltage raising or lowering input voltages until the are equal. But how does it make that happen? Let’s take a look at a typical op-amp schematic symbol to explain how it works. Here’s what you need to know:
What are OP amps used for?
The great thing about op-amps is that they aren’t just used to amplify sound like a traditional amplifier. You’ll also see them being used for: 1 Audio and video frequency pre-amplifiers and buffers 2 Voltage and current regulators 3 Analog calculators 4 Precision peak detectors 5 Analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters 6 And a whole lot more!
Why is an OP-AMP a differential amplifier?
This is why an op-amp is commonly referred to as a differential amplifier because it provides an output result based on the difference between the two input signals.
What is the input impedance of an op amp?
High input impedance. Another key attribute is a high impedance, and the op-amps in production these days come with input impedances that are almost infinite, measuring in at 0.25M ohms or even hundreds of millions of ohms.
What is boost in amplifier?
The boost that an amplifier produces for a given signal is measured in gains, or gain factor. This is simply the difference in voltage between an input signal and an output signal. For example, if you start with 1 volt at your input, and get 5 volts at your output, then you have yourself a gain of 5.
Why do you need feedback on an OP amp?
This is why you’ll be adding feedback into your op-amp circuit with the addition of resistors, capacitors, or inductors to control the gain and get different results from your circuit. This addition of feedback loops also allow you to easily create variations on an op-amp circuit to get some widely different results. Here are the most common circuits you’ll be building when you first start out:
How high is the gain of an OP amp?
High gain. One of the most well-known features of op-amps is their very high gain, which can range from 10,000 to 100,000! Granted, this level of gain used in an open loop amplifier is a bit useless and overkill, which is why you’ll be adding sources of feedback to control gain levels and distortion.
what is the operational amplifier?
It is a simple electronic circuit, which works on the principle of electric amplification. It is used in all analog electronic circuits for the amplification of weak signals. An operational amplifier is an integrated circuit, which is used for the gain of electric current or voltage. It is also used to amplify small signals.
How operational amplifier is used as a summing amplifier?
An operational amplifier is a voltage amplifier that can be used in many different circuits. It is used in many different applications and the amplifier has a lot of functions. This amplifier has a very high gain and can be used in different applications which require a high gain.