Why does Mc cut average cost curve?
When the MC is smaller the AC, the AC decreases. This is because when the extra unit of output is cheaper than the average cost then the AC is pulled down. Similarly, when the MC is greater than the AC, the AC is pulled up. The point of intersection between the MC and AC curves is also the minimum of the AC curve.
What is the long run average cost curve?
The long-run average cost curve shows the lowest total cost to produce a given level of output in the long run. Long-term unit costs are almost always less than short-term unit costs because, in a long-term time frame, companies have the flexibility to change big components of their operations, such as factories, to achieve optimal efficiency.
When marginal cost equals average total cost,?
Following the grade analogy, average cost will be decreasing in quantity produced when marginal cost is less than average cost and increasing in quantity when marginal cost is greater than average cost. Average cost will be neither decreasing nor increasing when marginal cost at a given quantity is equal to average cost at that quantity.
Does the total cost include opportunity costs?
Total costs include both the outlay cost and opportunity cost. Outlay costs reduce earnings immediately with cash accounting, while with accrual accounting they are split across all periods the expense applies and matched to related revenues.

How do you describe the total cost curve?
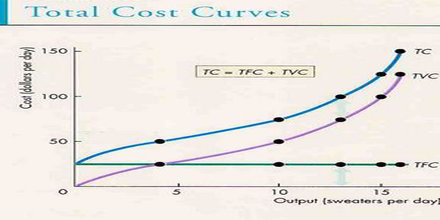
The total cost (TC) curve is found by adding total fixed and total variable costs. Its position reflects the amount of fixed costs, and its gradient reflects variable costs.
What shape is the typical total cost curve?
The average total cost curve is typically U-shaped. Average variable cost (AVC) is calculated by dividing variable cost by the quantity produced. The average variable cost curve lies below the average total cost curve and is typically U-shaped or upward-sloping.
Is total cost curve horizontal?
Total fixed cost curve depicts the relation between the total fixed cost of production and the level of output while other things being constant. Since total fixed costs are fixed, the curve representing it, is a horizontal line.
What are the three total cost curves?
There are three different cost curves --Total Cost (TC), Average Cost (AC), and Marginal Cost (MC).
Why is the total cost curve S shaped?
a Total Variable Cost is zero at zero level of output. It initially increases at decreasing rate and later it increases at increasing rate. TVC is an inversely S-shaped curve due to the Law of Variable Proportion.
Why is total cost curve horizontal?
The graph of total fixed cost is simply a horizontal line since total fixed cost is constant and not dependent on output quantity.
Why is total cost curve upward sloping?
The total cost of producing a given quantity of output is the sum of the fixed cost and the variable cost of producing that quantity of output. The total cost curve becomes steeper as more output is produced due to diminishing returns.
Why TC curve is inverse S shaped?
The TC curve is inverted-S shaped. This is because of the TVC curve. Since the TFC curve is horizontal, the difference between the TC and TVC curve is the same at each level of output and equals TFC. This is explained as follows: TC – TVC = TFC.
What is the slope of the total cost curve?
marginal costThe slope of the total cost curves equals marginal cost.
How do you draw a cost curve?
3:508:07Drawing Cost Curves, A shorter video - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAround here I'll call it q1. You come up and we find that the average fixed cost is about here andMoreAround here I'll call it q1. You come up and we find that the average fixed cost is about here and our average variable. Cost is about here.
What are the 4 basic cost curves?
Answer. The output is represented along OX and cost along OY; AFC curve represents average fixed cost. AVC curve represents average variable cost, ATC curve represents average total cost (i.e., total of AFC and AVC and is called AC, i.e., average cost). MC curve represents marginal cost.
How do you create a cost curve?
2:1119:11Micro: Unit 3.4 -- Graphing Cost Curves - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThese curves will visualize the trends and patterns of the fixed variable and total costs ofMoreThese curves will visualize the trends and patterns of the fixed variable and total costs of production. And how they correlate to the output level of the firm. Let's begin with the fixed cost curve.
Why is MC curve is U shaped?
The marginal cost curve is U-shaped in the short-run due to the operation of the "law of variable proportions". According to the law, MC curve initially slopes downward till it reaches its minimum point and thereafter, it starts rising. Therefore, it leads to U-shape of the curve when presented graphically.
Why is total cost curve upward sloping?
The total cost of producing a given quantity of output is the sum of the fixed cost and the variable cost of producing that quantity of output. The total cost curve becomes steeper as more output is produced due to diminishing returns.
What is the shape of total cost curve of a monopolist?
The total cost curve is upward-sloping. Profits will be highest at the quantity of output where total revenue is most above total cost. The profit-maximizing level of output is not the same as the revenue-maximizing level of output, which should make sense, because profits take costs into account and revenues do not.
What is average total cost?
In economics, average total cost (ATC) equals total fixed and variable costs divided by total units produced. Average total cost curve is typically U-shaped i.e. it decreases, bottoms out and then rises.
What is total cost?
A firm’s total cost is the sum of its variable costs and fixed costs. Variable costs are costs which vary with change in output level. Fixed costs, on the other hand, do not change with change in output. Whether amount spent on an input is a variable cost or fixed cost depends on whether we are talking about short-run or long-run. In the short-run, labor is variable cost and capital is fixed but in the long-run, all costs are variables.
Why are average costs high at low levels of output?
To begin with, the Average Costs are high at low levels of output because both the Average Fixed Costs and Average Variable Costs are more. ADVERTISEMENTS: But, as the level of output increases, the Average Costs fall more sharply due to the combined effect of the declining average fixed and Average Variable Costs.
What would happen if the firm tries to raise output after that point?
This would lead to diseconomies of production and diminishing returns. The Average Costs will start rising rapidly. Hence, due to the operation of Law of Variable proportions the short-run as well as long-run Average Cost Curve is TJ shaped’.
Why does the average variable cost rise?
This is due to the change of economies into dis-economies. This gives the short-run as well as long-run Average Cost Curve of the firm IP shaped.
Why does average cost continue to fall?
The Average Cost will continue to fall till they reach the minimum point which is the optimum point level of output. Once the optimum level of output is reached, Average Costs starts rising as more are produced beyond this level.
What is the U-shaped average cost curve?
The nature ‘U’ shaped short-run Average Cost curve can be attributed to the law of variable proportions. This law tells that when the quantity of one variable factor is changed while keeping the quantities of other factors fixed, the total output increases with an increasing rate and then declines with more than proportionate.
What does the addition of fixed and variable cost give us?
The addition of fixed and Variable Cost gives us total costs, which when divided by the output give us Average Costs in the short period.
Why does average cost fall as output increases?
Thus, the Average Costs of the firms continue to fall as output increases because it operates under the increasing returns due to various internal economies. Due to the operation of the law of increasing returns the firm is able to work with the machines to their optimum capacity and as a consequence the Average Cost is minimum.