What is meant by aerobic metabolism?
Listen to pronunciation. (ayr-OH-bik meh-TA-buh-lih-zum) A chemical process in which oxygen is used to make energy from carbohydrates (sugars). Also called aerobic respiration, cell respiration, and oxidative metabolism.
What happens during aerobic metabolism?
During aerobic metabolism, your body creates energy through the combustion of carbohydrates, amino acids, and fats in the presence of oxygen. Combustion means burning, which is why this is called burning sugars, fats, and proteins for energy.
What is anaerobic metabolism?
Anaerobic metabolism, which can be defined as ATP production without oxygen (or in the absence of oxygen), occurs by direct phosphate transfer from phosphorylated intermediates, such as glycolytic intermediates or creatine phosphate (CrP), to ADP forming ATP.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism?
Conclusion: The Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic Metabolism. While aerobic metabolism generates more ATP and relies on oxygen, anaerobic metabolism does not need oxygen but only creates two ATP molecules per glucose molecule. However, anaerobic and aerobic metabolism are both required to produce cellular energy ...
How do you increase aerobic metabolism?
Cardiorespiratory training can enhance the body's ability to metabolize fats and carbohydrates into fuel, both with and without oxygen. While cardio training is most often associated with fat loss, it is also the best way to improve aerobic capacity, which is the ability to use oxygen to fuel exercise activity.
What are the benefits of aerobic metabolism?
Advantages of Aerobic Respiration With oxygen, organisms can break down glucose all the way to carbon dioxide. This releases enough energy to produce up to 38 ATP molecules. Thus, aerobic respiration releases much more energy than anaerobic respiration.
Where does aerobic metabolism take place?
Aerobic metabolism consists of two different pathways, the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain, both of which occur in the mitochondria, the energy factories of cells.
What causes an anaerobic metabolism?
Anaerobic metabolism at the cellular level occurs when oxygen transport and tissue oxygenation are compromised. This can be a result of hypoxemia, anemia, inadequate systemic blood flow, or a combination of these factors.
Which statement best describes aerobic metabolism?
Answer and Explanation: The conditions which correctly describes the condition of aerobic metabolism (c) The end products are 6 molecules each of carbon dioxide and water and 38 ATP. The end products of the aerobic metabolism of carbohydrates are formed only if the reaction occurs in the presence of oxygen.
How long does it take for the body to switch from anaerobic to aerobic metabolism?
All activities activate each energy system to some degree, depending on exercise intensity and duration. During maximal efforts, the anaerobic (lactic) system lasts from 45 seconds to 2 minutes, after which all further exercise would be aerobic.
Where is oxygen consumed during aerobic metabolism?
the mitochondriaThe electron transport chain is the major site of oxygen consumption and the generation of ATP in the mitochondria.
What are the waste products of aerobic metabolism?
Answer and Explanation: In aerobic respiration, ATP is released by burning the glucose molecule in the presence of oxygen. The waste products that excrete from the body are carbon dioxide through respiration and water through urine.
Where does aerobic metabolism happen?
Energy expenditure during the aerobic re-synthesis of ATP is not related to anaerobic substrate level phosphorylation. Instead, aerobic ATP re-synthesis takes place within a specific cellular organelle known as the mitochondria.
Which statement best describes aerobic metabolism?
Answer and Explanation: The conditions which correctly describes the condition of aerobic metabolism (c) The end products are 6 molecules each of carbon dioxide and water and 38 ATP. The end products of the aerobic metabolism of carbohydrates are formed only if the reaction occurs in the presence of oxygen.
Where is energy produced during aerobic metabolism?
Once inside the mitochondria, fat enters the β-oxidation pathway, which produces acetyl-CoA and reducing equivalents (NADH and FADH2), and the long-chain nature of fatty acids results in generation of large amounts of aerobic ATP (Box 1).
What is the process of aerobic glycolysis?
Aerobic glycolysis is a series of reactions wherein oxygen is required to reoxidize NADH to NAD+, hence the name. This ten-step process begins with a molecule of glucose and ends up with two molecules of pyruvate[1].
What do you understand by aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen.
What are the different stages of aerobic respiration?
The different stages of aerobic respiration are: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Citric acid cycle Electron Transport Chain
What are the end products of aerobic respiration?
The end products of aerobic respiration include 6 molecules of carbon dioxide, 6 molecules of water and 30 molecules of ATP.
Where does aerobic and anaerobic respiration take place?
Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondrial matrix of the cell. On the contrary, anaerobic respiration occurs in the fluid portion of the cytop...
What is the importance of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration provides energy to the living organisms to perform all the essential functions of life. That is why aerobic respiration is impo...
What are the different types of aerobes?
The different types of aerobes include: Obligate aerobes that strictly need oxygen to grow. Facultative aerobes can grow in the presence as well as...
Which is faster, glycolysis or aerobic metabolism?
But the strict definition of AT is that it is the point at which the rate of anaerobic metabolism, including glycolysis, begins to go significantly faster than aerobic metabolism including the trans carboxylic acid cycle (TCA) and its associated electron transport chain.
What bacteria are used to stimulate aerobic metabolism in shrimp?
Aerobic metabolism in shrimp responds considerably when shrimp are injected with the bacterium Vibrio campbellii .
Why do athletes need endurance training?
Even weight lifters, sprinters, and other power athletes can benefit from some endurance training as their recovery from anaerobic events requires aerobic metabolism to burn off the accumulated lactic acid.
What is the process of breaking down molecules to release energy for other cellular processes?
a catabolic process (see CATABOLISM) occurring in cells where complex organic molecules are broken down to release energy for other cellular processes. Cell respiration usually occurs in the presence of oxygen (see AEROBIC RESPIRATION) but some organisms can respire without oxygen (see ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION ).
How much energy does pyruvate generate?
Oxygen availability enables pyruvate to enter the mitochondria where it generates 18 times as much energy (net 36 ATP) as glycolysis alone does through aerobic metabolism. This fact exemplifies the critical importance of proper oxygenation of brain tissue (Zauner, Daugherty, Bullock, & Warner, 2002).
Does glycolysis produce carbon dioxide?
However, at exercise intensity high enough that glucose metabolism must be coupled with glycolysis to produce enough ATP for the needed exercise, the carbon dioxide produced from glycolysis must be added to the carbon dioxide produced from aerobic metabolism. Aerobically produced carbon dioxide plus anaerobically produced carbon dioxide yields greater carbon dioxide than the amount of oxygen brought in for aerobic metabolism (American College of Sports Medicine, 2006).
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a biological process in which food glucose is converted into energy in the presence of oxygen. The chemical equation of aerobic respiration is as given below-
Why is aerobic respiration important?
Aerobic respiration provides energy to the living organisms to perform all the essential functions of life. That is why aerobic respiration is important.
What is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP?
Aerobic respiration is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP. The pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. The Kreb’s cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule.
What is the third step of aerobic respiration?
The third step in aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle , which is also called the Krebs cycle. In this stage of Aerobic respiration, the oxaloacetate combines with the acetyl-coenzyme A and produces citric acid. The citric acid cycle undergoes a series of reactions and produces 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, 1 molecule of ATP, ...
How many ATP molecules are produced in the last step of aerobic respiration?
In this phase, the large amounts of ATP molecules are produced by transferring the electrons from NADH and FADH. A single molecule of glucose creates a total of 34 ATP molecules.
What is the energy released during the process of breaking the glucose molecule?
The 2900 kJ of energy is released during the process of breaking the glucose molecule and in turn, this energy is used to produce ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate molecules which are used by the system for various purposes. Aerobic respiration process takes place in all multicellular organisms including animals, plants and other living organisms.
What is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen?
Aerobic respiration is the process involved in the production of energy in the presence of oxygen.
Where does aerobic metabolism occur?
Aerobic metabolism occurs when the oxygen is present. It occurs in the cell’s mitochondria and responsible for the supply of 90% of the body’s energy requirement.
How much water does oxidative metabolism produce?
In general, oxidative metabolism produces nearly 150 to 300 mL of water in a 24 hour period of time. There are two pathways involved in aerobic metabolism; citric acid cycle; which occurs in the matrix of mitochondria, and electron transport chain; which occurs in the electron transport system located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is the process of converting carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy needed by cells?
Cell metabolism is the process of converting the carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into energy needed by cells. During the cell metabolism pathways, energy is stored in high-energy phosphate bonds of adenosine triphosphate molecules (ATP), which serves as the energy currency of cells. Depending on the oxygen demand during the production of ATP, there are two major types of metabolism present in the cell; namely, aerobic and anaerobic. Out of the three basic metabolic pathways, only glycolysis is considered as an anaerobic metabolism, whereas the rest including citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and electron transport chain are considered as aerobic metabolisms.
Which process produces a low number of ATP?
Anaerobic metabolism’s efficiency is low, and produced low number of ATP when compared to aerobic metabolism. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and does not require any organelle. Therefore, it is an important process of which the organisms lack mitochondria such as prokaryotes.
Can aerobic metabolism continue?
In contrast, aerobic metabolism can continue forever, only under theoretical conditions. • Carbohydrate, fat, and proteins are used as sources of aerobic metabolism while only carbohydrate is involved for anaerobic metabolism.
Is glycolysis anaerobic or aerobic?
Out of the three basic metabolic pathways, only glycolysis is considered as an anaerobic metabolism, whereas the rest including citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and electron transport chain are considered as aerobic metabolisms.
What waste molecule is produced during aerobic metabolism?
waste molecule produced during aerobic metabolism from the breakdown of glucose how many CO2 does glucose yield during aerobic metabolism process where atp is made in the presence of oxygen series of reactions occuring in the mitochondria in which the carbon based products of the transition reaction are broken down to yield atp, Carbon dioxide and reduced coenzymes process of removing the amino group from amino acids prior to metabolism series of reactions occurring in the inner folds of the mitochondria where reduced coenzymes give up their electrons which are transported through the reactions what does electron transport chain result in formation of most of the ATP of aerobic respiration the end product of fermentation reactions in yeast oxidized form of a coenzyme based on riboflavin (b vitamin) reduced form of a coenzyme based on riboflavin production of atp in the absence of oxygen glycosis, transition reaction, krebs cycle, electron transport phosphorylation the primary carbon based starting molecule for glycolysis what is the monomer unit of starch and clycogen the first state of metabolism common to both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism conversion of glucose to pyruvate/pyruvic acid type of anerobic metabolism in which the ned product of glycolysis is converted into lactate/lactic acid what is the purpose of lactic acid fermentation regenerating NAD+ to keep glycolysis going and at least yield 2 net atp water that is produced in the final step of the electron transport chain what does oxygen do in the electron transport chain picks up the electrons and joins with hydrogen ion to produce water chemical reactions involved in energy production category of diseases that affect the organelle responsible for most atp production in eukaryotic cells organelle in which Continue reading >>
How much energy is released in aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration may be represented by the general equation About 3000 kJ mol-1 of energy is released. Burning glucose in air would release this amount of energy in one go. However, it is not as simple as this in aerobic respiration.
What is the process of converting glucose into energy?
The breakdown of glucose into energy in the form of molecules of ATP is therefore one of the most important biochemical pathways found in living organisms. Glycolysis , which means sugar splitting, is the initial process in the cellular respiration pathway. Glycolysis can be either an aerobic or anaerobic process.
How does ATP work?
In oxidation, the electrons are stripped from a glucose molecule to reduce NAD+ and FAD . NAD+ and FAD possess a high energy potential to drive the production of ATP in the electron transport chain . ATP production occurs in the mitochondria of the cell. There are two methods of producing ATP: aerobic and anaerobic . In aerobic respiration, oxygen is required. Oxygen plays a key role as it increases ATP production from 4 ATP molecules to about 30 ATP molecules. In anaerobic respiration, oxygen is not required. When oxygen is absent, the generation of ATP continues through fermentation.There are two types of fermentation: alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation . There are several different types of carbohydrates : polysaccharides (e.g., starch , amylopectin , glycogen , cellulose ), monosaccharides (e.g., glucose , galactose , fructose , ribose ) and the disaccharides (e.g., sucrose , maltose , lactose ). Glucose reacts with oxygen in the following redox reaction, C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O, Carbon dioxide and water are waste products, and the overall reaction is exothermic . The breakdown of glucose into energy in the form of molecules of ATP is therefore one of the most important biochemical pathways found in living organisms. Glycolysis , which means sugar splitting, is the initial process in the cellular respiration pathway. Glycolysis can be either an aerobic or anaerobic process. When oxygen is present, glycolysis continues along the aerobic respiration pathway. If oxygen is not present, then ATP production is restricted to anaerobic respiration . The location where glycolysis, aerobic or Continue reading >>
What is the first step of aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
The first step in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration is called glycolysis . This is the process of taking one glucose (sugar) molecule and breaking it down into pyruvate and energy (2 ATP). We will discuss this in depth during aerobic respiration. The second step in anaerobic respiration is called fermentation.
How do cells get energy?
Just like we need energy to get through the day, individual cells need energy for survival too. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells get their energy in the form of ATP. There are two types of cellular respiration, aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic respiration is more efficient and can be utilized in the presence of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen. Many organisms (or cells) will use aerobic respiration primarily, however, if there is a limited oxygen supply they can utilize anaerobic respiration for survival. Although there are some organisms (or cells) that always require anaerobic respiration and others that will always require aerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration has fewer steps, so lets start there. The first step in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration is called glycolysis . This is the process of taking one glucose (sugar) molecule and breaking it down into pyruvate and energy (2 ATP). We will discuss this in depth during aerobic respiration. The second step in anaerobic respiration is called fermentation. Fermentation starts with pyruvate (the end product of glycolysis). Depending on the organism, pyruvate can either be fermented into ethanol (a fancy name for alcohol) or lactate (lactic acid). Fermentation releases CO2, but does not make any ATP all ATP during anaerobic respiration is produced during glycolysis. Since glycolysis produces 2 ATP, anaerobic respiration yields 2 ATP for every molecule of glucose. Both glycolysis and fermentation take place within the cytosol/cytoplasm of a cell. In fact, the entire process of anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytosol. Fermentation is the process by which we make wine and other types alcohol. Through an anaerobic process, yeast will break down the glucose in the Continue reading >>
How many ATP molecules are in a glucose molecule?
In this process, one molecule of glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate (or pyruvic acid), which generates energy in the form of two ATP molecules (two net molecules).
What is the process of cellular metabolism?
Cellular Metabolism. Cell metabolism is the series of processes that take place in living organisms to sustain those organisms. In cell biology and molecular biology, metabolism refers to the biochemical reactions that happen inside organisms to produce energy.
Why is metabolism important for cells?
Metabolism is important for cells because the processes keep organisms alive and allow them to grow, reproduce or divide.
What Is Cell Metabolism Like in Different Types of Prokaryotes?
You can categorize prokaryotes into different groups based on their metabolism. The main types are heterotrophic, autotrophic, phototrophic and chemotrophic. However, all prokaryotes still need some type of energy or fuel to live.
What are the different types of metabolic pathways?
The basic types of metabolic pathways include heterotrophic, autotrophic, phototrophic and chemotrophic reactions. The type of metabolism that a prokaryote has can influence where it lives and how it interacts with the environment. Their metabolic pathways also play a role in ecology, human health and diseases.
What is the process of breaking down glucose to make ATP?
There are actually multiple metabolism processes. Cellular respiration is a type of metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to make adenosine triphosphate, or ATP.
What is the term for the process of converting food into energy?
In cell biology and molecular biology, metabolism refers to the biochemical reactions that happen inside organisms to produce energy. The colloquial or nutritional use of metabolism refers to the chemical processes that happen in your body as you convert food into energy.
Which organisms depend on oxygen for metabolism?
Prokaryotes that depend on oxygen for metabolism are obligate aerobes. On the other hand, prokaryotes that cannot exist in oxygen and do not need it are obligate anaerobes. Prokaryotes that can switch between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism depending on the presence of oxygen are facultative anaerobes.
Where does aerobic respiration occur?
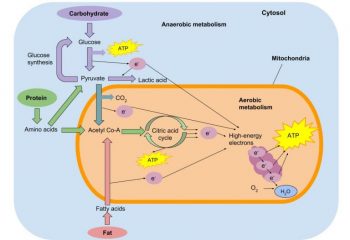
Aerobic respiration occurs within the mitochondria, the organelles located inside cells that produce energy. All three fuels however, undergo some primary preparation in order to prepare them for entry into the mitochondria. The pathways for all three macronutrients are illustrated in Figure 1-2, but before discussing each, let’s first define the fuels:
What is the attribute of fitness?
A fundamental attribute of fitness has always been our relentless pursuit of new ideas when it comes to programming. Whether evolutionary or incremental in nature; trend or fad, we appear to thrive on challenging the status quo in our quest for better, bigger, stronger or faster.
What do TGs represent in Krebs cycle?
Think of TGs representing single ladies coming to the Krebs cycle bar from the TG part of town. They arrive dressed to dance and socialize as acetyl-CoA (the compound that enters the Krebs cycle) – consider their preparation for the evening as beta-oxidation. This is illustrated by the number 3 in Figure 1-2. Unfortunately, the Krebs cycle bar has a couples-only policy, therefore all the single ladies need a partner to enter. Ordinarily, they count on meeting single men who are also converging on the Krebs cycle bar from a different part of town (i.e., carbohydrates). What this essentially means is that for fats to be completely metabolized, they need to have carbohydrates present.
How do proteins differ from fats and carbohydrates?
Proteins differ from fats and carbohydrates in that they contain the element nitrogen, which does not serve a function in respiration. Subsequently, it must be removed (deamination), producing ammonia which is potentially harmful to the body (4). Ammonia is quickly converted to urea in the liver and then excreted primarily through urine via the kidneys. This is illustrated by the number 6 in Figure 1-2.
Which pathway produces large amounts of energy?
As illustrated in Figure 1-1, the aerobic pathway produces large amounts of energy, albeit it more slowly, and can utilize all three macronutrients as a fuel source.
Does glycolysis produce pyruvate?
Now consider the fate of carbohydrates. As mentioned previously, glycolysis produces pyruvate which is unique in that it can produce either single ladies (acetyl-CoA) or single men (oxaloacetate). This is illustrated by the number 2 in Figure 1-2. Referring back to our bar analogy, considering how the TG part of town provides ample single ladies, the carbohydrate part of town generally provides the single men (i.e., oxaloacetate). Collectively, the single ladies from the TG part of town join with the single men from the carbohydrate part of town and enter the Kerbs cycle bar.