Full Answer
What does airway resistance tell us about lung function?
What does airway resistance tell us about lung function? Spirometry is considered the primary method to detect the air flow limitation associated with obstructive lung disease. However, air flow limitation is the end-result of many factors that contribute to obstructive lung disease. One of these factors is increased airway resistance.
What does air resistance stand for?
The force of friction applied by the air against a moving/flying object is known as air resistance. It is the opposition provided by the air that resists the motion of an object or tends to slow down the speed with which it is moving. Air resistance force is also known as drag.
What does airway resistance mean?
Airway resistance is the opposition to flow caused by the forces of friction. It is defined as the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Resistance to flow in the airways depends on whether the flow is laminar or turbulent, on the dimensions of the airway, and on the viscosity of the gas. For laminar flow, resistance is quite low.
What is the meaning of the word air resistance?
Definition: By definition, air resistance describes the forces that are in opposition to the relative motion of an object as it passes through the air.
What is meant by airways resistance?
The definition of airway resistance is the change in transpulmonary pressure needed to produce a unit flow of gas through the airways of the lung. More simply put, it is the pressure difference between the mouth and alveoli of the lung, divided by airflow.
What does decreased airway resistance mean?
Airway resistance decreases as lung volume increases because the airways distend as the lungs inflate, and wider airways have lower resistance.
What causes increased airway resistance?
Airway resistance is usually increased with obesity. This is partially related to the narrowing of small airways that occurs at lower lung volumes. One case-controlled study with 190 subjects found the airway resistance of obese men (BMI of 47 kg/m2) to be almost twice that of normal controls.
What is airway resistance and how does it affect ventilation?
As the radius of the airways increases, resistance to airflow is lower during this inspiratory phase. Conversely, in expiration, the intrathoracic pressure increases due to the lower volume of the thoracic cavity. This pressure leads to narrowing of the smaller airways, so resistance is higher during expiration.
What does airway resistance tell us about lung function?
Airway resistance (Raw) is always related to the lung volume at which it is measured. It is useful to detect diseases such as asthma, which are associated with increased airway smooth muscle tone, as well as diseases such as COPD, in which there is a loss of airways or narrowing of airways due to secretions or edema.
How do you get airway resistance?
Resistance in an airway is equal to change in pressure divided by flow rate [Resistance = (Peak Pressure – Plateau Pressure) / Flow L/sec].
Does exercise increase airway resistance?
During exercise there is a dynamic increase in the dimensions of the conducting airways resulting in a decrease in the resistance to airflow and an increase in alveolar ventilation (de Bisschop et al., 2003).
Does asthma increased airway resistance?
Another characteristic of asthma is higher airway resistance at maximal inspiration compared to nonasthmatics.
Why is airway resistance increased in COPD?
Expiratory flow limitation is a key characteristic in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Increased airway resistance occurs due to bronchoconstriction, destruction of elastic tissue in the airways, and mucus hypersecretion from goblet cells caused by irritation of the epithelium.
What is normal airway resistance on ventilator?
In normal subjects, airway resistance values do not exceed 15–20 cmH2O/L/s under controlled mechanical ventilation (48). Several factors can modify Ppeak, such as endotracheal tube diameter (49,50), airflow intensity, plugging, or bronchospasm.
Where does the most airway resistance in our respiratory system occur?
In healthy lungs, the overall resistance in the conducting zone is high. The radius of an individual bronchiole is low, but the overall cross-sectional area of all the bronchioles is quite high. During quiet breathing, the difference between Palv and Patm is less than 2 mmHg.
What causes a decrease in airway resistance?
The increased sympathetic tone causes the relaxation of airway smooth muscle, which causes dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles, reducing airway resistance.
Which of the following will decrease airway resistance?
Stimulation by sympathetic fibers Sympathetic stimulation of the airways results in a relaxation of airways, decreasing resistance.
Does asthma decrease airway resistance?
Asthmatics exhibit reduced airway dilation at maximal inspiration, likely due to structural differences in airway walls and/or functional differences in airway smooth muscle, factors that may also increase airway responsiveness to bronchoconstricting stimuli.
What happened to breathing rate when airway resistance increased?
In the presence of increased airway resistance or decreased lung compliance, an increased transpulmonary pressure is required to produce a given tidal volume and, thus, the work of breathing is increased. Any change in the airway that increases the work of breathing may lead to respiratory failure.
What is airway resistance?
bookmarks Recommended reading. Airway resistance refers to degree of resistance to the flow of air through the respiratory tract during inspiration and expiration. The degree of resistance depends on many things, particularly the diameter of the airway and whether flow is laminar or turbulent. Alveolar expansion is also dependent on surfactant, so ...
Which airways have the highest resistance to air flow?
Therefore, smaller airways such as bronchioles and alveolar ducts all individually have much higher flow resistance than larger airways like the trachea. However, the branching of the airways means that there are many more of the smaller airways in parallel, reducing the total resistance to air flow. So due to the vast number of bronchioles that are present within the lungs running in parallel, the highest total resistance is actually in the trachea and larger bronchi.
Why is it harder to expand the alveoli?
Therefore, further expansion of the alveoli is resisted. This explains why once the lungs are mostly filled , it is harder to expand the lungs further to allow the entry of additional air.
How does sympathetic innervation affect airway diameter?
Sympathetic innervation causes relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle via beta-2 receptors, which increases diameter to allow more airflow. This is useful in situations such as exercise, as sympathetic nerve stimulation triggers airway muscle relaxation, increasing the diameter to allow more air into the lungs. This increases the rate of gas exchange at alveolar level compared to normal breathing.
How does resistance differ between inspiration and expiration?
On inspiration, the positive pressure within the alveoli and small airways causes their diameter to increase, and therefore resistance to decrease. The opposite is true for expiration, as airways narrow due to the reduced pressure, thus increasing resistance.
What is the degree of resistance to the flow of air through the respiratory tract during inspiration and expiration?
Airway Resistance. Airway resistance refers to degree of resistance to the flow of air through the respiratory tract during inspiration and expiration. The degree of resistance depends on many things, particularly the diameter of the airway and whether flow is laminar or turbulent.
Why are my airways narrowed?
In an asthma exacerbation , the already narrowed airways (due to mucosal inflammation and smooth muscle hypertrophy) are further constricted due to increased smooth muscle tone. This can decrease the diameter of the airways significantly, causing resistance to airflow to become very high.
What is the definition of airway resistance?
In respiratory physiology, airway resistance is the resistance of the respiratory tract to airflow during inhalation and exhalation. Airway resistance can be measured using plethysmography .
How does airway resistance change over time?
Therefore, diseases affecting the respiratory tract can increase airway resistance. Airway resistance can also change over time. During an asthma attack the airways constrict causing an increase in airway resistance. Airway resistance can also vary between inspiration and expiration: In emphysema there is destruction of the elastic tissue of the lungs which help hold the small airways open. Therefore during expiration, particularly forced expiration, these airways may collapse causing increased airway resistance.
What is specific airway conductance?
Also called volumic airway conductance. Similarly to specific airway resistance, specific airway conductance attempts to correct for differences in lung volume.
Which bifurcation is the greatest resistance?
Therefore, resistance is greatest at the bronchi of intermediate size, in between the fourth and eighth bifurcation .
Does air have less resistance when it is turbulent?
Where air is flowing in a laminar manner it has less resistance than when it is flowing in a turbulent manner. If flow becomes turbulent, and the pressure difference is increased to maintain flow, this response itself increases resistance. This means that a large increase in pressure difference is required to maintain flow if it becomes turbulent.
Is specific airway resistance measured at FRC?
Specific airway resistance is often measured at FRC, in which case:
Can you measure airway resistance at absolute volume?
It is not practically possible to measure airway resistance at a set absolute lung volume, therefore specific airway resistance attempts to correct for differences in lung volume at which different measurements of airway resistance were made. Specific airway resistance is often measured at FRC, in which case:
What is the primary method of detecting air flow limitation associated with obstructive lung disease?
Spirometry is considered the primary method to detect the air flow limitation associated with obstructive lung disease. However, air flow limitation is the end-result of many factors that contribute to obstructive lung disease. One of these factors is increased airway resistance. Airway resistance i ….
What is the primary method of detecting air flow limitation?
Spirometry is considered the primary method to detect the air flow limitation associated with obstructive lung disease. However, air flow limitation is the end-result of many factors that contribute to obstructive lung disease. One of these factors is increased airway resistance. Airway resistance is traditionally measured by relating air flow ...
What is the acronym for resistance in the airway?
Symbol R A or R AW.
What is the definition of resistance to the flow of gases during ventilation?
in physiology, the resistance to the flow of gases during ventilation resulting from obstruction or turbulent flow in the upper and lower airways; to be differentiated during inhalation from resistance to inflation resulting from decreases in pulmonary or thoracic compliance.
What is lung physiology?
Lung physiology A measure of the resistance–in cm H 2 O to the flow–in L/min of air in upper airways, the result of natural recoil–resiliency of anatomic structures–oro- and nasopharynx, larynx, and nonrespiratory portions of the lungs–trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles through which air passes on the way to the alveoli; assessment of AR evaluates airway responsiveness, provocation testing–eg bronchial challenge, evaluation of sites of airflow resistance or closures, and characterization of the type of lung disease; airway resistance is ↑, either focally or globally in asthma, COPD, and smokers. See Airway responsiveness, Asthma, COPD.
What is vascular resistance?
vascular resistance the opposition to blood flow in a vascular bed; the pressure drop across the bed divided by the blood flow, conventionally expressed in peripheral resistance units. Symbol R or R.
What is incomplete androgen resistance?
Incomplete androgen resistance is any of various forms less than the complete type, manifested by a male phenotype with various degrees of ambiguous genitalia such as hypospadias and a small vaginal pouch, a hooded phallus, or a bifid scrotum that may or may not contain gonads.
What is peripheral resistance?
peripheral resistance resistance to the passage of blood through the small blood vessels, especially the arterioles. pulmonary vascular resistance the vascular resistance of the pulmonary circulation; the difference between the mean pulmonary arterial pressure and the left atrial filling pressure divided by the cardiac output.
What is the term for the ability of a microorganism to withstand the effects of a drug that?
drug resistance the ability of a microorganism to withstand the effects of a drug that are lethal to most members of its species. insulin resistance see insulin resistance. multidrug resistance ( multiple drug resistance) a phenomenon seen in some malignant cell lines: cells that have developed natural resistance to a single cytotoxic compound are ...
What is the flow interval over which RAW is usually measured?
In addition the flow interval over which RAW is usually measured (i.e. ±0.5 L/sec) is relatively arbitrary. It was originally ±1.0 L/sec in the original 1956 DuBois article but by 1958 the same investigators had changed the measurement range to ±0.5 L/sec because “The oscilloscope tracing was sometimes alinear, showing a tendency to curve at the extremes, presumably due to turbulent flow at higher flow rates.”
Is FRC the same as expiratory resistance?
It is also usually assumed that inspiratory and expiratory resistance in the range it is measured (i.e. at FRC and ±0.5 L/sec) are the same. This is reasonably true for individuals without airways disease but is not the case when significant airway obstruction is present.
What is RAW in lung?
Airway resistance (RAW) and specific airway conductance (sGAW) are measures that reflect airway function. However, little is known of the variability of these measures between different lung diseases. In a recent study published in the journal Respiratory Research, a team of researchers from the Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, University of Leuven in Belgium found that RAW and sGAW are significant factors that contribute to the diagnosis and differentiation of obstructive airway diseases.
Is RAW a predictor of asthma?
To differentiate asthma from COPD, RAW was found to be more relevant and statistically significant. In patients with asthma with normal FEV1/FVC ratio, both RAW and sGAW were more specific than sensitive diagnostic tests in differentiating asthma from healthy subjects.
Overview
Applications
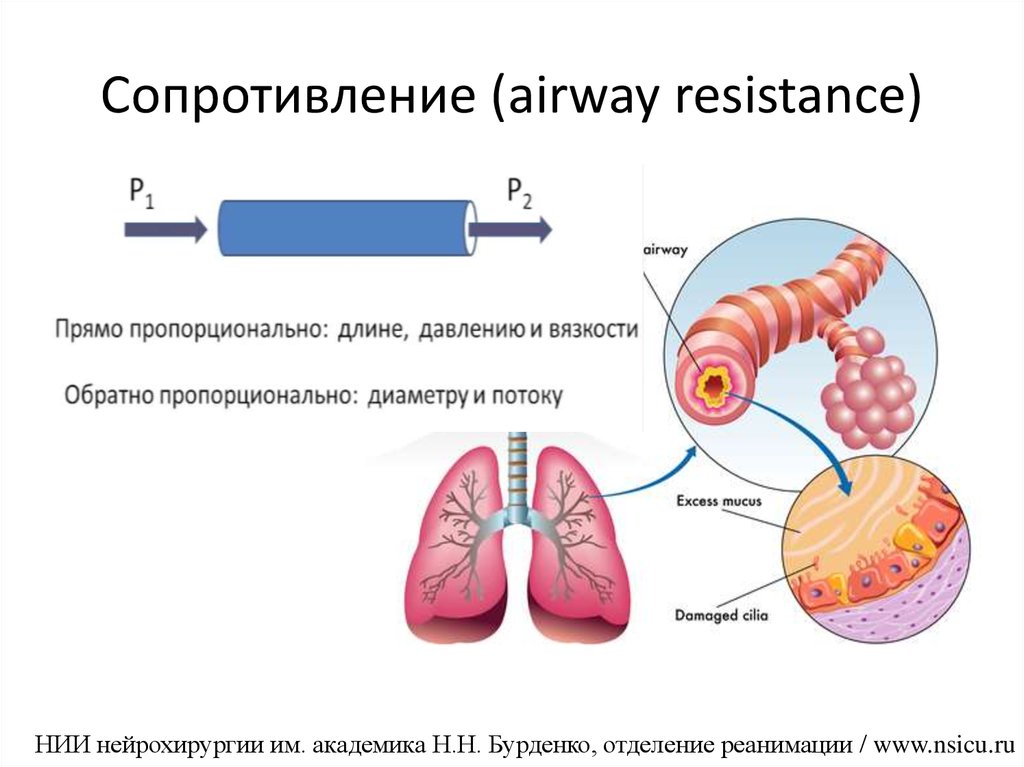
- Ohms law can be used to describe the relationship between airflow, pressure gradient and resistance.
Mechanism
- This demonstrates that as resistance increases, the pressure gradient must also increase to maintain the same airflow to the alveoli. Therefore, smaller airways such as bronchioles and alveolar ducts all individually have much higher flow resistance than larger airways like the trachea. However, the branching of the airways means that there are many more of the smaller a…
Other uses
- Poiseuilles Law, also known as the Hagen-Poiseuille equation, gives us the relationship between airway resistance and the diameter of the airway. The equation is
Variations
- Resistance is also slightly different on inspiration and expiration due to the diameter of the airways. On inspiration, the positive pressure within the alveoli and small airways causes the diameter to increase, and therefore resistance to decrease. The opposite is true for expiration, airways narrow due to low pressure and so resistance is increased.
Geology
- Laminar flow is where the air is flowing through the tube in parallel layers, with no disruption between the layers, and the central layers flowing with greater velocity.
Causes
- Turbulent flow is when the air is not flowing in parallel layers, but direction, velocity and pressure within the flow of air become chaotic. If airflow becomes turbulent, the pressure difference required to maintain airflow will need to be increased, which in turn would increase turbulence and therefore resistance.
Overview
In respiratory physiology, airway resistance is the resistance of the respiratory tract to airflow during inhalation and exhalation. Airway resistance can be measured using plethysmography.
Determinants of airway resistance
There are several important determinants of airway resistance including:
• The diameter of the airways
• Whether airflow is laminar or turbulent
In fluid dynamics, the Hagen–Poiseuille equation is a physical law that gives the pressure drop in a fluid flowing through a long cylindrical pipe. The assumptions of the equation are that the flow i…
Changes in airway resistance
Airway resistance is not constant. As shown above airway resistance is markedly affected by changes in the diameter of the airways. Therefore, diseases affecting the respiratory tract can increase airway resistance. Airway resistance can also change over time. During an asthma attack the airways constrict causing an increase in airway resistance. Airway resistance can also vary between inspiration and expiration: In emphysema there is destruction of the elastic tissue of th…
Derived parameters
This is simply the mathematical inverse of airway resistance.
Where V is the lung volume at which RAW was measured.
Also called volumic airway resistance. Due to the elastic nature of the tissue that supports the small airways airway resistance changes with lung volume. It is not practically possible to measure airway resistance at a set absolute lung volume, therefore specific airway resistance at…
See also
• Turbulent flow
• Laminar flow
• Reynolds number
• Upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS)
External links
• Calculator at medstudents.com.br