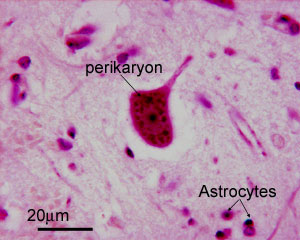
What are ependymal tumors also called?
Ependymomas are a type of glioma, which refers to any tumor that arises from glial cells (also called glia). Glial cells provide support to neurons and perform a variety of functions across the nervous system. Ependymal cells are just one type of glial cells. What are the symptoms of ependymoma?
Does the ependymal cells form the cerebrospinal fluid?
ependymal cells are simple cuboidal cells that line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal in the spinal cord. Ependymal cells form the lining of the ventricular system, including the aqueducts. They are in direct contact with the cerebrospinal fluid and play a role in fluid homeostasis.
Do all cells develop from existing cells?
The generally accepted parts of modern cell theory include: All known living things are made up of one or more cells. All living cells arise from pre-existing cells by division. The cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms.
What do normal cells do?
They function on their own, creating their own energy and self-replicating — the cell is the smallest unit of life that can replicate. However, cells also communicate with each other and connect to create a solid, well stuck-together animal.
Are ependymal cells part of the nervous system?
The ependyma constitute a ciliated epithelium that derives from the neuroepithelium during development and is located at the interface between the brain parenchyma and ventricles in the central nervous system (CNS).
What do ependymal cells secrete?
They secrete glycosaminoglycans and other molecules that repel axonal growth cones. The dorsal and ventral median septa of the spinal cord and brainstem are mainly ependymal basal processes of the roof and floor plate, respectively, joined later in gestation by glial processes.
What do ependymal cells circulate?
Ependymal Cells are a type of Glial Cell lining the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord. Their primary function is to secrete and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
What is the function of the ependymal cells quizlet?
protects brain and spinal cord from trauma, supplies nutrients to nervous system tissue, and removes waste products from cerebral metabolism.
Do ependymal cells form the blood brain barrier?
The Blood–Brain Barrier In the brain and spinal cord, the BBB is formed by cerebral endothelial cells that have highly specialized structural and functional properties [185,186].
What does ependymal mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (eh-PEN-dih-muh) A thin membrane that lines the fluid-filled spaces in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of a type of glial cell called an ependymal cell.
Are ependymal cells in the CNS or PNS?
Ependymal cells are another glial subtype that line the ventricles of the CNS, forming a permeable barrier between the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and underlying cells, and also aid in the circulation of CSF through cilial beat.
What type of cells work to help create cerebrospinal fluid?
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations.
How do ependymal cells produce CSF?
The layer of ependymal-derived cells surrounding the blood vessels of the choroid plexus functions mainly to produce CSF. This is accomplished through the selective uptake of water and certain other molecules from the blood into the cells.
Where are ependymal cells found quizlet?
What are ependymal cells? Ependymal cells (ependymocytes) are low columnar to cuboidal epithelial cells lining the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord.
What is the function of the ependymal cells of the choroid plexus quizlet?
*Ependymal cells of the surface of of the choroid plexus secrete cerebrospinal fluid.
Which of the following statements does not apply to ependymal cells quizlet?
A, B and C are correct. Which of the following statements does not apply to ependymal cells? They have cilia to move fluid in the brain.
What cell produces CSF?
ependymal cellsCSF is produced mainly by the choroid plexus epithelium and ependymal cells of the ventricles and flows into interconnecting chambers; namely, the cisterns and the subarachnoid spaces.
Where is CSF produced?
ventriclesCSF is secreted by the CPs located within the ventricles of the brain, with the two lateral ventricles being the primary producers. CSF flows throughout the ventricular system unidirectionally in a rostral to caudal manner.
Which type of cell is responsible for producing cerebrospinal fluid?
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. There is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day.
What cells line the ventricles and produce CSF?
Ependymal cells line the ventricular spaces of the adult brain. They have a simple ciliated cuboidal morphology. The cilia project into the ventricular space and spinal canal, oscillate approximately 200 times per minute, and are thought to assist the rostrocaudal flow of cerebrospinal fluid.
What are the functions of ependymal cells?
The cilia beat in a coordinated pattern to influence the direction of flow of cerebrospinal fluid(CSF), bringing nutrients and other substances to neuronsand filtering out molecules that may be harmful to the cells. The beating of ependymal cilia also is suspected to facilitatethe distribution of neurotransmittersand other chemical messengers to neurons. The layer of ependymal-derived cells surrounding the bloodvessels of the choroid plexus functions mainly to produce CSF. This is accomplished through the selective uptake of water and certain other molecules from the blood into the cells. The substances are then transported across the cells and are secreted into the lateral ventricles in the form of CSF.
What are ependymal cells?
Ependymal cells, similar to all other neuroglia, are derived from a layer of embryonic tissue known as neuroectoderm. Ependymal cells and their epithelial derivatives of the choroid plexus have several important functions. In the ventricles ependymal cells possess tiny hairlike structures called cilia on their surfaces facing the open space ...
Why is the ependymal cell connected to the choroid plexus?
Because the junctions between the ependymal cells are loose , CSF is able to diffuse from the ventricles into the central nervous system. The cells surrounding the choroid plexus are connected by tight junctions, which prevent the leakage of substances and fluids from the blood vessels into the CSF.
What are the cells that extend from the third ventricle to the brain?
Ependymal cells called tanycytes have long processes that extend from the third ventricle to neurons and capillaries in nearby parts of the brain, including the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
What is the epithelial lining of the ventricles?
See Article History. Ependymal cell, type of neuronal support cell ( neuroglia) that forms the epithelial lining of the ventricles ( cavities) in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. Ependymal cells also give rise to the epithelial layer that surrounds the choroid plexus, a network of blood vessels located in the walls ...
What is the purpose of the beating of the ependymal cilia?
The beating of ependymal cilia also is suspected to facilitate the distribution of neurotransmitters and other chemical messengers to neurons. The layer of ependymal-derived cells surrounding the blood vessels of the choroid plexus functions mainly to produce CSF.
Where are ependymal cells found?
Another type of ependymal cell, known as a tanycyte, is found only in the lining on the floor of the third ventricle in the brain.
Where do ependymal cells come from?
Ependymal cells line the brain ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord (Figs. 15, E, and 19 ). They arise from the pseudostratified neuroepithelium from which neurons and neuroglial cells originate. That surface is ciliated here and there, and some cilia are seen in the ependyma. They form an apparent simple cuboidal or columnar epithelium with microvilli and occasional cilia, but in fact the bases of certain cells taper into long, slender, outward processes.
How do ependymal cells protect and encourage axon extension?
One possibility is that they may be able to buffer the effect of glutamate excitotoxicity by the uptake and sequestration of calcium, which in turn might trigger epithelial to mesenchymal transformation through second messenger pathways ( Chernoff et al., 2003 ). Retinoic acid promotes axolotl neurite outgrowth in vitro. The ependymal cells can take up retinol, convert it to retinaldehyde and then to RA. The secreted RA is then taken up by neurons ( Hunter et al., 1991 ). Endogenous retinol and RA have been detected in the urodele spinal cord, implying that RA might be a crucial molecule for axon extension in vivo. Most or all of the other survival and guidance factors that have been shown to be important for peripheral nerve regeneration would presumably also be involved in urodele spinal cord regeneration, but this question has not yet been addressed.
Why are fetal ependymal cells important?
Another important function of the fetal ependymal cells is to arrest all further mitoses in the germinal matrix. For this reason it is important to delay differentiation of the ependymal cells at the ventricular surface as long as necessary to enable the requisite number of mitotic cycles to be completed. The ventricles are therefore largely lined by neuroepithelium until the ependyma differentiates. The last region of the ventricular system to be completely covered by ependymal cells is in the lateral ventricles, mainly the temporal and frontal lobes, at 22 weeks gestation.
What are specialized forms of ependymal cells called?
The specialized forms of ependymal cells are called tanycytes, which show elongated periventricular processes in the periventricular white matter. In H&E staining ependymal cells resemble cuboidal and columnar epithelia. They have a small oval nucleus with dense chromatin.
What are the cells that line the brain ventricles?
Ependymal cells are mostly known as the cell type lining the brain ventricles. As non-neuronal cells in the brain and derived from neuroectoderm, they are clearly defined as a subtype of glial cells. They include the ependymocytes, choroid plexus epithelial cells, tanycytes, and within the retina, Müller cells and retinal pigment epithelial cells.
What are ciliated ependymal cells?
Ciliated ependymal cells line the ventricular system of the mature brain. The floor plate of the neural tube is ependymal cells of the ventral midline of the central canal and are the first cells to mature in the early neural tube. They are induced by the floor plate that secretes a product of the gene sonic hedgehog ( SHH ). Floor plate cells, in addition to having receptors for SHH, also can express this gene, a function lacking in other ependymal cells, and they in turn induce the maturation of other cells of the spinal cord.
What cells are in the spinal canal?
The spinal canal is lined by ependymal epithelial cells. These cells transform into mesenchymal cells (red) that proliferate to bridge the gap. The mesenchymal cells then transform back to epithelial cells to re-establish the ependyma and provide paths for axon regeneration.
What are the functions of ependymal cells?
Ependymal cells provide insulation, nutrition, and support that aids in repairing neurons. They also eliminates waste products and serves the first line of viral defense for the brain to protect against viral infections.
What is Ependyma?
Ependyma is the sheath that lines the central canal of the spinal cord and also lines the ventricles inside the brain. It is made of by joining many of ependymal cells. There are five types of neuroglial in the brain and ependyma is one of them. There are many functions of it, as mentioned above.
What are the cells that line the ventricles of the brain?
Most importantly, ependymal cells line the ventricles in the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. These cells are simple columnar epithelial-like cells with their edges covered with the cilia, these cilia help to circulate the CSF around the central nervous system.
What is the ependyma called?
The ependyma can also be called tanycyte which plays a very vital role in the transportation of the hormones in the brain, also, it lines the floor of the ventricles in the brain.
What is the glue of the brain?
Ependymal cells are a type of brain cells. With in the central nervous system, there are glial cells that are commonly known as the glue of the brain. There are five types of glial cells in the brain and ependymal is one of the types of five.
What are the other types of glial cells?
The other four types of glial cells are astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, and schwanna cells.
Does the ependyma have cilia?
The ependyma possesses cilia on its surface as You can see in the picture above, that cilia influence the CSF flow and help in neuro signal transmission distribution to neuro channel.