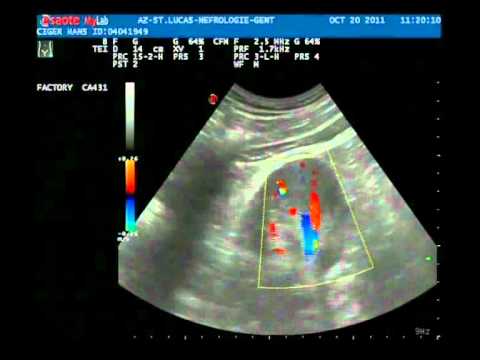
Can you see appendicitis on ultrasound?
Acute appendicitis on ultrasound can be done for young patients in an attempt to diagnose appendicitis without using radiation. If the appendix is abnormal, acute appendicitis can be diagnosed on ultrasound. In cases that are not clear, or the appendix is not found, than CT can be done.
What are the symptoms of acute appendicitis?
Acute appendicitis causes pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. It is most common in young patients below 30, but can occur in anyone. CT is the best test to diagnose appendicitis, however, ultrasound can be very useful as well. What Causes Acute Appendicitis? Acute appendicitis is causes by obstruction of the lumen of the appendix.
Which imaging modality is used to diagnose acute appendicitis (AA)?
• Ultrasound (US) should be the first imaging modality for diagnosing acute appendicitis (AA). • Primary US for AA diagnosis will decrease ionizing radiation and cost. • Sensitivity of US to diagnose AA is lower than of CT/MRI.
What is a vermiform appendix ultrasound?
Appendix Ultrasound The small organ that can cause big trouble. The vermiform (worm like) appendix is a finger-like projection off of the base of the cecum, it can become inflamed and require surgical removal.
How big is the appendix?
What is the condition of the vermiform appendix?
Is ultrasound good for appendicitis?
Can you pinpoint appendicitis?
Can you see appendicitis on an ultrasound?
Imaging tests Doctors use an ultrasound as the first imaging test when checking for possible appendicitis in infants, children, young adults, and pregnant women.
What scan confirms appendicitis?
Your doctor may also recommend an abdominal X-ray, an abdominal ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help confirm appendicitis or find other causes for your pain.
What does appendicitis look like on imaging?
The criteria for appendicitis include the visualization of the enlarged appendix (over 7 mm diameter), wall thickening over 2 mm, peri-appendiceal fat stranding, fluid-filled appendix, or free fluid. These are consistent imaging criteria throughout the different modalities.
What are the 5 signs of appendicitis?
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis may include:Sudden pain that begins on the right side of the lower abdomen.Sudden pain that begins around your navel and often shifts to your lower right abdomen.Pain that worsens if you cough, walk or make other jarring movements.Nausea and vomiting.Loss of appetite.More items...•
What can mimic appendicitis?
2. Conditions that mimic appendicitis1 Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) ... 2 Infectious enterocolitis. ... 3 Radiation enteritis. ... 4 Neutropenic colitis. ... 5 Diverticular disease and diverticulitis. ... 6 Meckel's diverticulitis.
Do appendicitis pains come and go?
Appendicitis typically starts with a pain in the middle of your tummy (abdomen) that may come and go. Within hours, the pain travels to your lower right-hand side, where the appendix is usually located, and becomes constant and severe. Pressing on this area, coughing or walking may make the pain worse.
Can you have appendix pain for months?
Chronic appendicitis can also occur, although it is rare. In chronic cases, symptoms are less severe and can last for days, weeks, or even months. Treatment for appendicitis will depend on how severe the case is.
Can you have appendicitis with normal blood work?
A blood test with a high white blood cell count means you have an infection. But about a third of people with appendicitis have a normal white blood cell count.
Is ultrasound or CT better for appendicitis?
CT is more precise than ultrasonography and more reproducible from hospital to hospital (Figures 3 through 5). It has a diagnostic accuracy rate for acute appendicitis of 93 to 98 percent. In a recent meta-analysis, findings on CT increased the certainty of diagnosis more than findings on ultrasonography.
Can you see appendicitis on CT scan?
Appendiceal CT scans are considered to be 98 percent accurate in diagnosing acute appendicitis when read by an experienced radiologist [9]. Other methods of imaging, such as nuclear scans, use a radiolabeled mononuclear antibody directed against neutrophils.
Can appendicitis be missed on a CT scan?
Among patients who received a CT scan at the index ED visit, 5.5% of adults and 4.7% of children were in the potentially missed appendicitis group.
How accurate is ultrasound for appendicitis?
Studies have shown that the sensitivity of ultrasound to detect acute appendicitis was 55-96% and the specificity is 85-98%. The sensitivity of ultrasound to detect acute appendicitis was also reported to be 95% and reported to be 97% in another study.
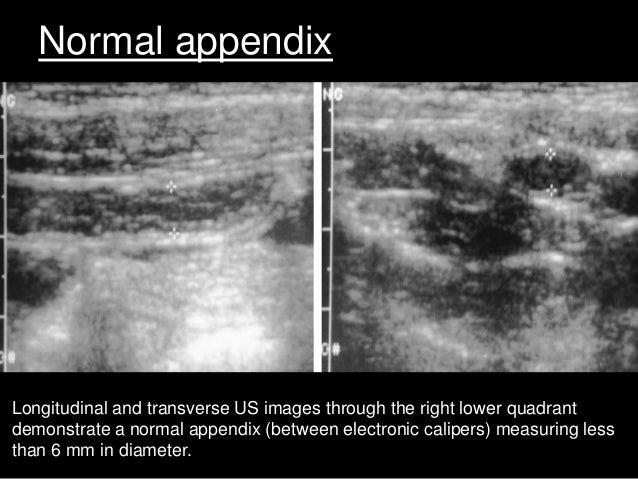
How big is the appendix?
In normal appendix, there's a subtle wall and a small diameter under six millimeters. It's also a mobile structure and can shift under pressure from a probe. When the appendix is inflamed, it becomes stylated and attaches itself to the other abdominal structures.
What is the condition of the vermiform appendix?
[00:00:00] Appendicitis is inflammation of the vermiform appendix. It's a very common condition and it's one of the main reasons for abdominal surgery in young patients. Acute appendicitis is typically a disease of children and young adults with a peak incidence in the second and third decades of life. The classical presentation consists of periumbilical pain, which within a day or more can move to the right hypogastrium. It is associated with fever, nausea, and vomiting.
Is ultrasound good for appendicitis?
We want to avoid using ionizing radiation whenever possible. With a competent user, ultrasound is reliable at identifying abnormal appendices, especially infant patients.
Can you pinpoint appendicitis?
Appendicitis can sometimes be quite tricky to pinpoint. What do you do when a patient presents with acute abdominal pain? Whip out your ultrasound probe and go digging! By the end of this video, you'll be able to look at an ultrasound image and distinguish between a normal appendix and an inflamed one so you can quickly identify and treat a case of appendicitis.
How long is the appendix?
The location of the tip of the appendix is much more variable, especially as the length of the appendix has an extensive range (2-20 cm) 9. The distribution of positions is described as 8,9:
When does acute appendicitis peak?
Acute appendicitis is typically a disease of children and young adults with a peak incidence in the 2 nd to 3 rd decades of life 1.
What causes appendicitis?
Appendicitis is typically caused by obstruction of the appendiceal lumen, with the resultant build-up of fluid, suppurative inflammation, secondary infection, venous congestion, ischemia and necrosis . Obstruction may be caused by 1,23: lymphoid hyperplasia (~60%)
How much mortality is there from appendicitis?
Treatment is appendectomy, which can be performed either open or laparoscopically 6. Mortality from simple appendicitis is approximately 0.1% but is as high as 5% in perforation with generalized peritonitis 6.
What are the challenges of imaging the appendix?
One of the biggest challenges of imaging the appendix is finding it. Once confidently identified, assessing its normality is relatively straightforward.
Where is the fecal loading of the cecum?
24. The location of the base of the appendix is relatively constant, located roughly between the ileocecal valve and the apex of the cecum.
Is MRI recommended for appendicitis?
MRI. MRI is recommended as the second-line modality for suspected acute appendicitis in pregnancy patients , where available 14,15. Protocols vary widely, but most include imaging in three planes with a rapidly acquired sequence with T2 weighting, and some include T2 fat-suppressed imaging.
Where is the appendix located in ultrasound?
The appendix is found either in between these structures and/or anterior to these structures. Graded compression moves gas and bowel out of the plane of the ultrasound bringing the appendix closer to the abdominal wall, making it more easily visualized. View fullsize. View fullsize. View fullsize.
What happens if the appendix is not visualized?
If the appendix is still not visualized, the patient is returned to the supine position for a repeat attempt with the supine technique.
How to use a probe for appendix?
1. Place the patient supine. 2. Place the probe over the point of maximal tenderness in the RLQ or ask the patient to place the probe at the most painful site. If its appendicitis and it is tender in the RLQ, they're likely pointing to the area that the inflamed appendix is irritating the peritoneum. 3.
What is the cut off for appendix growth?
Note that the literature usually uses a cut-off of 6 to 7 mm; however, infants may have a smaller diameter, with growth of the appendix reported at ages 3 to 6 years. This highlights the need to look for secondary findings of appendicitis, especially in pediatric patients who may have a normal appendiceal diameter. (3)
Where does the transducer go in the pelvis?
4,5. With the psoas muscle and iliac vessels kept in view, move the transducer down into the pelvis and toward the umbilicus at the border of the cecum
What if you still cannot visualize the appendix?
What if you still cannot visualize the appendix? Perhaps the appendix is retrocecal. In one study (6), visualization of the appendix was improved 21.5% by following a 3-step technique.
How big is an appendix?
5. Measure the appendix and compress. A normal appendix is < 6 mm in diameter ( <6 to 7 mm described in some literature for pediatrics) from outer wall to outer wall and compressible (2).
What tests do you need to know about appendicitis?
They may also give you blood and urine tests. You may need to get imaging tests, like an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, that make pictures of the inside of your abdomen. Exams like these help your doctor spot signs of appendicitis or rule out other conditions. Swipe to advance.
What Is Appendicitis?
Your appendix is a finger-shaped pouch attached to your colon. It's in the lower-right side of your belly. Experts aren't sure exactly what it does. But if it becomes infected and inflamed, you get a painful condition called appendicitis. Most people who get it need surgery to remove their appendix, and they recover completely. Appendicitis can be life-threatening, though, if you don't get it treated.
What is it called when you have an appendix removed?
Surgery to Remove Your Appendix. 9 / 15. It's called an appendectomy . You'll get medicine called anesthesia so that you're asleep and pain-free during the operation. There are two types of surgery. If you get an "open appendectomy ," your surgeon makes one long cut in your belly and removes your appendix through it.
Why does my appendix swell?
This lets bacteria that normally live inside your appendix grow out of control, making it infected and swollen. Other things that can bring on appendicitis include digestive tract infections and inflammatory bowel disease. A lot of the time, doctors can't pinpoint the cause. Swipe to advance.
How to get rid of an appendix?
Your doctor might drain it through a needle or tube that goes in your belly. After the abscess is drained and your infection is under control, which could take a few weeks, you'll get surgery to take out your appendix.
How long does it take to recover from appendix surgery?
You might get out of bed and move around after a few hours if you had laparoscopic surgery, or the next day if you had open surgery. You may go home in 1 to 2 days, or longer if your appendix burst.
How do you know if you have a stomach infection?
Symptoms. 3 / 15. You'll usually have serious stomach pain. It may start near your belly button and gradually move to the lower right. It might also get worse when you move around, breathe deeply, cough, or sneeze. You may also have signs like: No appetite. Nausea and vomiting. Fever.
What is the appendix ultrasound?
Appendix Ultrasound. The small organ that can cause big trouble. The vermiform (worm like) appendix is a finger-like projection off of the base of the cecum, it can become inflamed and require surgical removal. Use a linear probe 7-9 mHz. Try others if difficult to image patient.
Where is the appendix located?
The normal location of the appendix is usually McBurney’s point (halfway between anterior iliac spine and umbilicus) appendix can vary in location and be behind the cecum (retrocecal), deep in the pelvis, behind the bladder, draped over the iliac vessels, in the RUQ, midline near spine.
How big is the appendix?
In normal appendix, there's a subtle wall and a small diameter under six millimeters. It's also a mobile structure and can shift under pressure from a probe. When the appendix is inflamed, it becomes stylated and attaches itself to the other abdominal structures.
What is the condition of the vermiform appendix?
[00:00:00] Appendicitis is inflammation of the vermiform appendix. It's a very common condition and it's one of the main reasons for abdominal surgery in young patients. Acute appendicitis is typically a disease of children and young adults with a peak incidence in the second and third decades of life. The classical presentation consists of periumbilical pain, which within a day or more can move to the right hypogastrium. It is associated with fever, nausea, and vomiting.
Is ultrasound good for appendicitis?
We want to avoid using ionizing radiation whenever possible. With a competent user, ultrasound is reliable at identifying abnormal appendices, especially infant patients.
Can you pinpoint appendicitis?
Appendicitis can sometimes be quite tricky to pinpoint. What do you do when a patient presents with acute abdominal pain? Whip out your ultrasound probe and go digging! By the end of this video, you'll be able to look at an ultrasound image and distinguish between a normal appendix and an inflamed one so you can quickly identify and treat a case of appendicitis.
Terminology
Epidemiology
Clinical Presentation
Pathology
Radiographic Features
Treatment and Prognosis
Differential Diagnosis
Practical Points
- on CT, identify first the ileocecal valve, which usually has fatty lips, and then look for the appendix more inferiorly on the same side
- >6 mm outer diameter is a reliable measurement to characterize appendicitis in all imaging modalities
- inflammation may be initially limited to the distal end of the appendix (tip appendicitis). It is c…
- on CT, identify first the ileocecal valve, which usually has fatty lips, and then look for the appendix more inferiorly on the same side
- >6 mm outer diameter is a reliable measurement to characterize appendicitis in all imaging modalities
- inflammation may be initially limited to the distal end of the appendix (tip appendicitis). It is crucial (particularly with US) to completely evaluate the appendix, and consider further assessment...
- prior appendectomy does not completely rule out a recurrent stump appendicitis, the risk of which is significant if the appendiceal remnant is greater than 5 mm
See Also