
Arachidonic acid is essential for your brain, liver, and organs, according to the National institutes of Health. A study published in 2013 in the American Journal of Cell Physiology reports that arachidonic acid appears to help increase muscle mass, and a study published in 2012 in the Journal...
What is arachidonic acid and how does it work?
Arachidonic acid is actually the chemical messenger first released by your muscles during intense weight training, controlling the core physiological response to exercise and regulating the intensity of all growth signals to follow. Also, anytime you have tissue injury, inflammation is involved in healing the wound.
Where is arachidonic acid found in food?
Arachidonic Acid. Arachidonic acid is found in animal products, like poultry and eggs. The amount of arachidonic acid found in just one egg a day elevated arachidonic acid levels in the bloodstream, Japanese researchers learned.
Is arachidonic acid good for anxiety?
Arachidonic Acid. High blood levels have been associated with a greater risk of suicide and depressive episodes. On the other hand, diets high in carbohydrate and low in fat and protein (with little or no arachidonic acid) may be associated with lower levels of anxiety and depression, according to epidemiological studies.
Should athletes take arachidonic acid supplements?
Now that arachidonic acid supplements are on the market, athletes need to be aware that there needs to be a balance of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in their diet. Supplementation is acceptable only if you are consuming enough omega-3 fatty acids to balance with the added omega-6 fatty acid (arachidonic acid) from the supplement.
What is the role of arachidonic acid in inflammation?
Following irritation or injury, arachidonic acid is released and oxygenated by enzyme systems leading to the formation of an important group of inflammatory mediators, the eicosanoids. It is now recognised that eicosanoid release is fundamental to the inflammatory process.
What is arachidonic acid used for in the body?
In the body Arachidonic acid promotes the repair and growth of skeletal muscle tissue via conversion to prostaglandin PGF2alpha during and following physical exercise.
What does it mean if arachidonic acid is low?
A low AA level can result from impaired enzyme activity in the AA synthesis (Figure 1) or inadequate omega-6 linoleic acid (LA) consumption from a fat-free or severely fat-restricted diet. Low levels of AA may lead to more frequent infections or delayed wound healing [37, 38].
Is arachidonic acid anti-inflammatory?
Arachidonic Acid Has Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Diabetic Actions In Vitro and In Vivo | Current Developments in Nutrition | Oxford Academic.
What foods are rich in arachidonic acid?
Claiming that arachidonic acid is only inflammatory may be too simple and not explain the whole picture of this fatty acid's role.Sardines. Sardines have one of the highest amounts of arachidonic acid, per an April 2019 study in Lipids in Health and Disease. ... Salmon. ... Eggs. ... Chicken. ... Pork. ... Beef. ... Milk. ... Seaweed.
What produces arachidonic acid?
Arachidonic acid is obtained from food or by desaturation and chain elongation of the plant-rich essential fatty acid, linoleic acid. Free ARA modulates the function of ion channels, several receptors and enzymes, via activation as well as inhibition.
How much arachidonic acid should I take a day?
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid, common in our diets. It is found in animal products, most notably beef, chicken, eggs, and fish. On average we consume about 100–200mg of it per day.
Is arachidonic acid omega-3?
Arachidonic acid (AA) is a fatty acid of the omega-6 class, and is the main fatty acid of interest when referring to an omega-3:6 ratio (relative to fish oil fatty acids).
How do I know if I need more omega-3?
Symptoms of omega-3 fatty acid deficiency include fatigue, poor memory, dry skin, heart problems, mood swings or depression, and poor circulation. It is important to have the proper ratio of omega-3 and omega-6 (another essential fatty acid) in the diet.
Do we need to consume arachidonic acid?
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid, which is consumed in small amounts in our regular diets. It is considered an "essential" fatty acid because it is an absolute requirement for the proper functioning for the human body.
What are the 5 classic signs of inflammation?
Based on visual observation, the ancients characterised inflammation by five cardinal signs, namely redness (rubor), swelling (tumour), heat (calor; only applicable to the body' extremities), pain (dolor) and loss of function (functio laesa).
What does high arachidonic acid mean?
- A high Arachidonic acid level promotes gallstone formation by stimulating mucin production in the gallbladder mucosa. - Arachidonic acid may trigger brain inflammation. High blood levels have been associated with a greater risk of suicide and depressive episodes.
Do humans need arachidonic acid?
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid, which is consumed in small amounts in our regular diets. It is considered an "essential" fatty acid because it is an absolute requirement for the proper functioning for the human body.
How much arachidonic acid should I take a day?
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid, common in our diets. It is found in animal products, most notably beef, chicken, eggs, and fish. On average we consume about 100–200mg of it per day.
Where is arachidonic acid found?
Arachidonic acid is naturally found incorporated in the structural phospholipids in the cell membrane in the body or stored within lipid bodies in immune cells [13]. It is particularly abundant in skeletal muscle, brain, liver, spleen and retina phospholipids [14].
What does high arachidonic acid mean?
- A high Arachidonic acid level promotes gallstone formation by stimulating mucin production in the gallbladder mucosa. - Arachidonic acid may trigger brain inflammation. High blood levels have been associated with a greater risk of suicide and depressive episodes.
Why is arachidonic acid important?
Arachidonic acid (AA) is important for growth and development , especially in infants. It plays a central role in the inflammatory response. AA supplements have gained popularity for their supposed benefits in strength training and bodybuilding. This post reveals the roles of arachidonic acid in health and disease and discusses the uses & safety of AA supplements.
Where is arachidonic acid produced?
The first is internal production from shorter fatty acids like linoleic acid, which mainly occurs in the liver. The second pathway is through food, especially fish and poultry [ 11 ].
Why are omega 6s bad for you?
Excess omega 6s are often seen as bad because they get converted to arachidonic acid, which can increase inflammation in some situations.
What is the role of AA in inflammation?
Even during extreme fat-free diets low in AA, it is difficult to reduce levels past a certain point.
What are the products of AA metabolism?
In white blood cells, the main products of AA metabolism are leukotrienes, which are involved in inflammation [ 11, 12, 15 ].
What is the function of AA?
Most of the functions of AA is attributed to its conversion into other molecules – leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and more – through the action of enzymes (oxygenases) [ 5, 3 ]. AA is naturally produced in the body from another molecule (linoleic acid), and can also be ingested through different foods.
Does AA increase inflammation?
Although there is no consensus on whether high AA in take increases inflammation , certain populations may want to be cautious in their consumption [ 19, 4 ].
Why is arachidonic acid important?
Arachidonic acid is vital to the operation of the prostaglandin system. Prostaglandins are part of a class of substances called eicosanoids.
How do eicosanoids help with blood pressure?
These eicosanoids help support normal blood pressure by relaxing the arteries and blood vessels and decreasing blood lipids. They also decrease blood-clotting factors. Omega-6 fatty acids can produce both anti-inflammatory and/or inflammatory and vasoconstricting eicosanoids.
How many carbons are in eicosanoids?
The eicosanoids contain twenty carbons and include the prostaglandins (PG), prostacyclins (PGI2), thromboxanes (TX), leukotrienes (LT), and hydroxy acids. There are bad (pro-inflammatory) and good eicosanoids (anti-inflammatory) and they compete with each other. Two prostaglandins arachidonic acid is the substrate to are PGE2 and PGF2a.
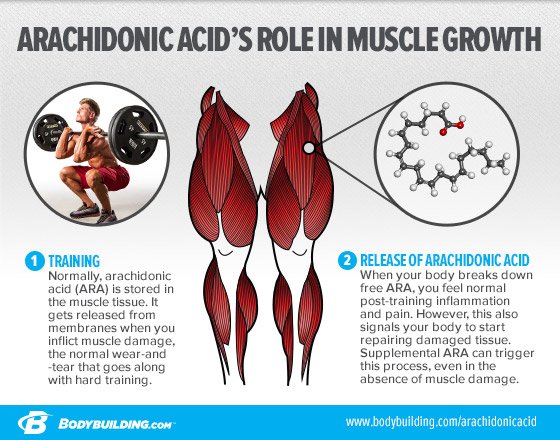
What is the chemical messenger released by the body during intense weight training?
Arachidonic acid is actually the chemical messenger first released by your muscles during intense weight training, controlling the core physiological response to exercise and regulating the intensity of all growth signals to follow. Also, anytime you have tissue injury, inflammation is involved in healing the wound.
What enzymes do eicosanoid cells compete for?
Also, they compete for cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase, the enzymes necessary for eicosanoid synthesis.
Does exercise lower arachidonic acid?
Furthermore, in both animal and human studies it has been shown that exercise lowers the content of arachidnoic acid in skeletal muscle tissue. Therefore, there has been talk of arachidonic acid supplementation. The omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acid families form different eicosanoids with different activities.
Can linoleic acid be converted to arachidonic acid?
Linoleic acid can be converted into arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid can be found mainly in the fatty parts of meats and fish (largely red meat), so vegetarians usually have lower levels of arachidonic acid in the body than those with omnivorous diets. There is a great deal of controversy about arachidonic acid.
What is arachidonic acid?
AA is an essential fatty acid. It’s found in the membranes of your cells, which means that every cell in your body makes use of AA at some point in your life. That alone tells you that you should make sure to get enough of it if you want to be helpful.
How can arachidonic Acid be used in bodybuilding?
One of the primary uses of AA is as a bodybuilding supplement. It’s currently marketed as an anabolic bodybuilding supplement, and it can be found in a lot of different products.
What is the name of the supplement that helps with health?
Sometimes we just need regular, everyday nutrients. Despite having a pretty insane name, arachidonic acid (AA) is one of these everyday nutrients that can help improve your overall health and well-being - especially if you’re a bodybuilder.
How much muscle mass does arachidonic acid gain?
A study showed that after 8 weeks of taking arachidonic acid, the subjects gained on average 1.6kg of lean muscle mass.
Why do organs and muscles function better?
This means that your organs, muscles, and tissues are all going to function better because they’re going to have more oxygen and nutrients available.
What foods contain linoleic acid?
That means that you’re going to want to make sure to eat foods that contain a lot of linoleic acids. Think healthy vegetable-based foods, like olive oil and avocados.
Why is aerobic exercise so intense?
When this happens, you place a lot of demand on your body in a short period. Your need for oxygen overwhelms the amount of oxygen that you actually have available , causing you to ‘max out.’
What is the role of arachidonic acid in the body?
While our body needs arachidonic acid, it also plays a key role in the development of diseases like heart disease, cancer and inflammatory condition like arthritis and asthma, according to a February 2021 review in Nature .
What are the sources of arachidonic acid?
Most animal products are rich sources of arachidonic acid.
What percentage of arachidonic acid is found in eggs?
One study found that 30 percent of people's arachidonic acid intake came from eggs — not because they ate an omelet every morning, but because eggs are an ingredient in so many different foods, according to December 2009 research in The Journal o f Nutrition .
Which meat has the highest arachidonic acid content?
In the 2005-2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, or NHANES, chicken and chicken-mixed dishes contributed the most to arachidonic acid intake in America. A 1-cup serving of a roasted chicken broiler contains 0.154 gram of arachidonic acid. Duck contains the highest level of arachidonic acid among lean meats, according to a study conducted on dietary arachidonic acid among meat fat.
Which meats contain arachidonic acid?
While beef and beef products are the third top contributor of arachidonic acid to the American diet, according to NHANES, they contain lower levels of arachidonic acid when compared to white meats. Dark meats including beef and lamb are higher in omega-3 fatty acids but still contain arachidonic acid.
Do eggs have arachidonic acid?
Eggs have arachidonic acid, regardless of if you eat them on their own or in desserts.
Is salmon high in arachidonic acid?
Salmon may be best known as a food high in omega-3s, but it also contains arachidonic acid. The amount is based on what the fish eats and whether it's farmed or wild. The omega-6 to omega-3 ratio was found to be higher in farmed salmon than wild-caught salmon in a small December 2020 study in the journal Foods .
What is arachidonic acid?
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated fatty acid covalently bound in esterified form in the cell membranes of most body cells. Following irritation or injury, arachidonic acid is released and oxygenated by enzyme systems leading to ...
Which enzyme metabolizes arachidonic acid?
Lipoxygenase enzymes metabolise arachidonic acid to a group of noncyclised eicosanoids, the leukotrienes, some of which are also important inflammatory mediators. They are probably of particular importance in leucocyte-mediated aspects of chronic inflammation.
Is arachidonic acid an inflammatory agent?
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated fatty acid covalently bound in esterified form in the cell membranes of most body cells. Following irritation or injury, arachidonic acid is released and oxygenated by enzyme systems leading to the formation of an important group of inflammatory mediators, the eicosanoids. It is now recognised that eicosanoid release is fundamental to the inflammatory process. For example, the prostaglandins and other prostanoids, products of the cyclooxygenase enzyme pathway, have potent inflammatory properties and prostaglandin E2 is readily detectable in equine acute inflammatory exudates. The administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs results in inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis and this explains the mode of action of agents such as phenylbutazone and flunixin. Lipoxygenase enzymes metabolise arachidonic acid to a group of noncyclised eicosanoids, the leukotrienes, some of which are also important inflammatory mediators. They are probably of particular importance in leucocyte-mediated aspects of chronic inflammation. Currently available non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, however, do not inhibit lipoxygenase activity. In the light of recent evidence, the inflammatory process is re-examined and the important emerging roles of both cyclo-oxygenase and lipoxygenase derived eicosanoids are explored. The mode of action of current and future anti-inflammatory drugs offered to the equine clinician can be explained by their interference with arachidonic acid metabolism.
