
What is the normal value of arterial blood gas?
Apr 09, 2022 · An arterial blood gases (ABG) test is a blood test that measures the acidity, or pH, and the levels of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from an artery. The test is used to check the function of the patient’s lungs and how well they are able to move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide.
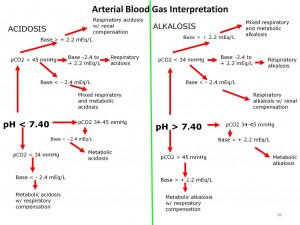
How to interpret arterial blood gas results?
Sep 20, 2021 · An arterial blood gas (ABG) tests explicitly blood taken from an artery. ABG analysis assesses a patient's partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) and carbon dioxide (PaCO2). PaO2 provides information on the oxygenation status, and PaCO2 offers information on the ventilation status (chronic or acute respiratory failure).
What are normal ABG values?
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in your blood. It also measures your body’s acid-base (pH) level, which is usually in …
What is the normal range for blood gases?
A blood gas test is also called an arterial blood gas test or a blood gas analysis. It measures oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood. The test can also show blood pH levels and lung function. Doctors often use blood gas tests in emergency situations to help diagnose the cause of breathing difficulty. Furthermore, what does a venous blood gas tell you?
What conditions do arterial blood gas monitor?
Many diseases are evaluated using an ABG, including acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), severe sepsis, septic shock, hypovolemic shock, diabetic ketoacidosis, renal tubular acidosis, acute respiratory failure, heart failure, cardiac arrest, asthma, and inborn errors of metabolism.Sep 20, 2021
What are normal arterial blood gases?
Normal Results Partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2): 75 to 100 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg), or 10.5 to 13.5 kilopascal (kPa) Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2): 38 to 42 mm Hg (5.1 to 5.6 kPa) Arterial blood pH: 7.38 to 7.42. Oxygen saturation (SaO2): 94% to 100%
What is a normal ABG For a COPD patient?
Normal values are between 7.38 and 7.42. The acidity or alkalinity of the blood is linked with the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. Acidic blood (pH less than 7.38) has high carbon dioxide levels in the blood.
What blood pH is fatal?
Normal cellular metabolism and function require that blood pH be maintained within narrow limits, 7.35-7.45. Even mild excursion outside this range has deleterious effect, and pH of less than 6.8 or greater than 7.8 is considered – according to medical and physiology texts – incompatible with life.
What is arterial blood gas interpretation?
Arterial blood gas interpretation is best approached systematically. Interpretation leads to an understanding of the degree or severity of abnormalities, whether the abnormalities are acute or chronic, and if the primary disorder is metabolic or respiratory in origin.
What is blood gas analysis?
A "blood gas analysis" can be performed on blood obtained from anywhere in the circulatory system (artery, vein, or capillary). An arterial blood gas (ABG) tests explicitly blood taken from an artery. ABG analysis assesses a patient's partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) and carbon dioxide (PaCO2).
What causes acid-base balance?
For instance, acute respiratory acidosis and alkalemia result in acidemia and alkalemia, respectively. Additionally, hypoxemic hypoxia leads to anaerobic metabolism, which causes a metabolic acidosis that results in acidemia.
What causes metabolic alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis is caused by conditions such as kidney disease, electrolyte imbalances, prolonged vomiting, hypovolemia, diuretic use, and hypokalemia. Quality control and Lab Safety. An arterial blood gas can be analyzed as a point-of-care test, along with electrolytes (often called a Shock panel).
What is the purpose of OI?
The OI is commonly used to guide management, such as initiating inhaled nitric oxide, administering surfactant, and defining the potential need for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. [12] The presence of a normal PaO2 value does not rule out respiratory failure, particularly in the presence of supplemental oxygen.
What is an ABG test?
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in your blood. It also measures your body’s acid-base (pH) level, which is usually in balance when you’re healthy. You may get this test if you’re in the hospital or if you have a serious injury or illness. The test gives your doctor clues about how well your lungs, heart, ...
What happens when you breathe in and out?
Every cell in your body needs oxygen to live. When you breathein (inhale) and breathe out (exhale), your lungsmove oxygen into your bloodand push carbon dioxide out. That process, called gas exchange, provides the oxygen we (and all of our cells) need to survive.
Why are my kidneys not working?
There could many reasons why your numbers might be not be in this range, including diseases or injuries that affect your breathing. Your doctor will interpret your ABG results as they related to your medical history and your current condition.
Does blood draw hurt?
Collecting blood from an artery typically hurts more than drawing it from a vein. Arteries are deeper than veins, and there are sensitive nerves nearby. You also may feel lightheaded, faint, dizzy, or nauseated while your blood is drawn.
Why is blood gas analysis important?
Because the body may naturally overcompensate for deficiencies in certain areas, the provider reading your ABG test results should be well trained in interpreting blood gases.
What does ABG mean in blood work?
ABGs also measure blood pH and the integrity of the body's acid-base balance. In total, an ABG test measures five different markers: 1 . Partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2): The pressure of oxygen dissolved in the blood ...
What is ABG test?
Arterial blood gas (ABG) testing is a diagnostic test performed on blood taken from an artery that provides a glimpse of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood, along with your blood's pH level. ABG tests are used to evaluate respiratory and kidney functions and give an overall look into the body's metabolic state. 1 .
What is the process of releasing carbon dioxide into the body?
Every cell in your body requires oxygen to live. Inhaling and exhaling brings oxygen into your body and pushes carbon dioxide out—a process called gas exchange. However, certain conditions may affect this, leading to imbalances throughout the body's systems.
What is the pH of the blood?
Arterial blood pH, the amount of hydrogen ions in the blood: A pH of 7.35-7.45 is considered normal. Blood oxygen saturation (SaO2): The amount of oxygen carried by the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. Bicarbonate (HCO3): A chemical buffer that helps stabilize blood pH.
What is the needle used for ABG?
After cleaning the area with an antiseptic, a needle is used to collect a small amount of blood from either the radial artery in your wrist or the femoral artery in your groin. You may feel a slight prick when the needle breaks the skin.
What causes metabolic acidosis?
Low. Metabolic acidosis may be caused by kidney failure or severe diarrhea, while metabolic alkalosis may be caused by chronic vomiting or the use of steroids. 3 . In contrast, respiratory acidosis means you're holding onto too much carbon dioxide, likely due to a lung condition such as COPD.
What is a blood gas test?
A blood gas test provides a precise measurement of the oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in your body. This can help your doctor determine how well your lungs and kidneys are working. This is a test that is most commonly used in the hospital setting to determine the management of acutely ill patients.
What is the normal oxygen saturation?
In general, normal values include: arterial blood pH: 7.38 to 7.42. bicarbonate: 22 to 28 milliequivalents per liter. partial pressure of oxygen: 75 to 100 mm Hg.
How does oxygen flow through the lungs?
As blood passes through your lungs, oxygen flows into the blood while carbon dioxide flows out of the blood into the lungs. The blood gas test can determine how well your lungs are able to move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. Imbalances in the oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH levels of your blood can indicate ...
What are the symptoms of COPD?
shortness of breath. difficulty breathing. confusion. nausea. These symptoms may be signs of certain medical conditions, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Your doctor may also order a blood gas test if they suspect you’re experiencing any of the following conditions: lung disease.
What is partial pressure?
Partial pressure of oxygen, which is a measure of the pressure of oxygen dissolved in the blood. It determines how well oxygen is able to flow from the lungs into the blood. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide , which is a measure of the pressure of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood. It determines how well carbon dioxide is able to flow out ...
What does a lower pH mean?
A lower blood pH may indicate that your blood is more acidic and has higher carbon dioxide levels.
What is the purpose of ABG?
Arterial blood gases (ABG), a clinical test that involves measurement of the pH of arterial blood and the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide dissolved in arterial blood, is routinely used in the diagnosis and monitoring of predominantly critically/acutely ill patients being cared for in hospital emergency rooms and intensive care units.
What is the clinical value of p O 2?
The principal clinical value of measuring p O 2 (a) and s O 2 (a) is to detect hypoxemia, which can be defined as a reduced amount of oxygen in blood. Hypoxemia is diagnosed if p O 2 (a) and/or s O 2 (a) are below the lower limit of their respective reference range. However, as will hopefully be made clear, normal p O 2 (a) and/or s O 2 (a) do not necessarily exclude a diagnosis of hypoxemia.
Why is hypoxemia important?
Blood is merely the means for transporting oxygen to tissue cells and hypoxemia is only really significant because it threatens adequate oxygenation of tissue cells.
What are the causes of hypoxemia?
There are five mechanisms that give rise to hypoxemia: 1 Partial pressure of oxygen of inspired air reduced (altitude effect) 2 Global alveolar hypoventilation (common) 3 Mismatch of alveolar ventilation/perfusion (the most common) 4 Cardiovascular shunting (rare) 5 Diffusion limitation (usually only a contributory mechanism)
What is an ABG test?
24336-0. An arterial blood gas ( ABG) test measures the amounts of arterial gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. An ABG test requires that a small volume of blood be drawn from the radial artery with a syringe and a thin needle, but sometimes the femoral artery in the groin or another site is used. The blood can also be drawn ...
Is carbon dioxide a weak acid?
In the context of arterial blood gases, the most common occurrence will be that of respiratory acidosis. Carbon dioxide is dissolved in the blood as carbonic acid, a weak acid; however, in large concentrations, it can affect the pH drastically.
What is PCO2 in blood?
The collection of samples and the use of PCO2 is a topic of further discussion below. The partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) is the measure of carbon dioxide within arterial or venous blood. It often serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar ventilation within the lungs. Generally, under normal physiologic conditions, ...
How is PCO2 measured?
Typically the measurement of PCO2 is performed via an arterial blood gas ; however, there are other methods such as peripheral venous, central venous, or mixed venous sampling. The collection of samples and the use of PCO2 is a topic of further discussion below. Issues of Concern.
What is the value of PCO2?
It often serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar ventilation within the lungs. Generally, under normal physiologic conditions, the value of PCO2 ranges between 35 to 45 mmHg, or 4.7 to 6.0 kPa.
How long does PCO2 last?
In chronic respiratory alkalosis, or alkalosis lasting 3 to 5 days, for every 10mmHg drop in PCO2, it is expected that serum bicarbonate will decrease by 4 to 5 mEq/L.[5][6] . The regulation of PCO2 is also involved in metabolic acidosis and alkalosis, as well.
What is the minute ventilation?
Under normal physiologic conditions, the minute ventilation, or the liters per minute of air exchanged in the lungs, is primarily controlled by the partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2). The minute ventilation is used routinely as a surrogate for alveolar ventilation. It is with alveolar ventilation that the gases, including PaCO2, ...
Which system regulates pH?
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation demonstrates that the governing of pH is not only by bicarbonate but also by PCO2. As discussed above, while PCO2 is mainly under the regulation of minute ventilation and respiratory mechanics, it is the kidney and the bicarbonate buffer system that regulate bicarbonate.
What is a blood gas analyzer?
Analysers that measure hydrogen ion concentration and P CO 2 are generically termed ‘blood gas analysers’; they also measure P O 2 and may provide other information of value in determining arterial oxygen content. They also frequently generate various derived terms, including ‘standard bicarbonate’, ‘base excess’ and ‘standard base excess’. These are calculated terms and add nothing to the characterization of disorders of hydrogen ion homoeostasis beyond what can be determined from consideration of [H +] and P CO 2.
What is a BGA?
The BGA is used as the reference standard for evaluation of intraarterial blood gas monitors in clinical trials. Among the limitations of intermittent blood gas analysis listed in Box 42.2, 57–61 interanalyzer variability as a cause of potential discrepancy between BGA and CIABGM merits further discussion. Interanalyzer measurement variability (6% to 8%) on the same blood sample has been reported as a result of differences in calibration techniques, sample chamber design, sample introduction technique, sample size, warming, and electronics. 62–66 BGAs are recalibrated at frequent, predetermined intervals, in contrast to CIABGMs. Although quality control limits exist for bench-top BGAs, 67 no such regulatory measures have been developed for CIABGMs.
How is free calcium measured?
Free calcium is measured using ISE, which is available on some of the blood gas analyzers. Calcium ISEs use calcium selective membrane that contains organic molecules such as ETH 1001 dissolved in a plasticizer and trapped in a polyvinyl chloride membrane. These molecules have a favorable stearic and electrostatic pocket or site for selectively binding calcium, resulting in different electric potential. The membrane potential sensed by the electrode is a function of the calcium activity in the sample obeying Nernst Equation. Modern electrodes have a high selectivity of calcium over Na+, K +, Mg 2 +, H +, and Li + [77–79]. At normal concentrations, these cations have little effect on the accuracy of free calcium measurement. The pH of a blood sample can affect the concentration of free calcium because the binding of calcium by proteins is pH dependent. When a sample is exposed to air for a long period of time, CO 2 may be lost to the air thereby increasing the pH, rendering more binding sites to calcium thus decreasing free calcium concentrations. When pH is decreased, as in the case of lactic acid production by glycolysis of erythrocytes, the opposite occurs and free calcium is increased. Caution must be taken to minimize all the factors that may influence the pH of a blood sample. It is recommended that all syringes and evacuated tubes be filled completely, kept tightly sealed, and handled anaerobically to prevent the loss of CO 2 and erythrocytes glycolysis. If samples cannot be analyzed within minutes, they should be placed in ice water slurry to minimize the metabolisms of blood cells. If samples can be analyzed within minutes of blood draw, heparinized whole blood is preferred. If analysis cannot be performed within 30–60 min at room temperature, serum may be the optimal specimen. Tubes should be filled completely and centrifuged to form an effective barrier between the serum and cells [77].
What is a PCL Plus?
The GEM PCL Plus Portable Coagulation Laboratory is a small whole blood analyzer that is available as a free-standing unit or as a component of the International Laboratories GEM Premier 3000/3500 comprehensive, compact portable laboratory systems for POC testing (Instrumentation Laboratory, Bedford, Massachusetts). ITC and International Laboratories have formed a partnership to codevelop the coagulation component. The GEM PCL Plus was introduced in 2003 and offers PT (citrated or fresh blood), PTT, ACT (heparin concentration 1.0 to 6.0 U/mL), and low-range ACT (LR-ACT) (heparin concentration <2.5 U/mL) tests. The ACT and LR-ACT tests report results in “Celite-equivalent” clotting times. The PT and PTT tests take about 2 minutes to generate a result; the ACT tests take 1 to 5 minutes depending on heparin dose.
Is carbonic acid a buffer?
The carbonic acid/bicarbonate system in the blood would not be a powerful buffer in a test-tube. But because it can enrol the aid of the lungs and kidneys it is arguably the most powerful buffer in the body. •. Acid/base imbalance can result in acidosis or alkalosis.

Purpose of Test
A test which measures the oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH levels in the blood.
Type: Blood sample
Duration: Usually 2-5 mins
Results available: Usually 15-20 mins
Conditions it may diagnose: Chronic kidney disease · Heart failure · Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease · Asthma · Cystic fibrosis and more
Is Invasive: Invasive
Type: Blood sample
Duration: Usually 2-5 mins
Results available: Usually 15-20 mins
Conditions it may diagnose: Chronic kidney disease · Heart failure · Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease · Asthma · Cystic fibrosis and more
Is Invasive: Invasive
Ability to confirm condition: High
Ability to rule out condition: High
Risks and Contraindications
During The Test
Interpreting Results
- Every cell in your body requires oxygen to live. Inhaling and exhaling brings oxygen into your body and pushes carbon dioxide out—a process called gas exchange. However, certain conditions may affect this, leading to imbalances throughout the body's systems. Analysis of blood gases helps evaluate a person's respiratory and metabolic status. Your healthcare provider may order an AB…