What are artifacts in EKG?
artifacts are extracerebral Artifact on EEG is anything that does not arise from the brain itself, and can generally be broken down into physiologic, electric, and environmental in etiology. Identifying artifacts on EEG can be challenging for several reasons.
What does an EKG tell you?
Your doctor uses the EKG to:
- assess your heart rhythm
- diagnose poor blood flow to the heart muscle (ischemia)
- diagnose a heart attack
- diagnose abnormalities of your heart, such as heart chamber enlargement and abnormal electrical conduction
What is a baseline artifact?
The term Baseline Artifact is a part of ‘configuration management’. Baselining means laying the foundation upon which software development activities depend. In simplest of terms, baselining an artifact means updating the version number of the artifact document during the process of development. Requirement Specifications. UML Diagrams.
What is cardiac artifact?
What is cardiac artifact? Electrocardiograph (EKG) artifacts are defined as EKG abnormalities, which are a measurement of cardiac potentials on the body surface and are not related to electrical activity of the heart. As a result of artifacts, normal components of the EKG can be distorted. Click to see full answer.
What causes artifact on ECG?
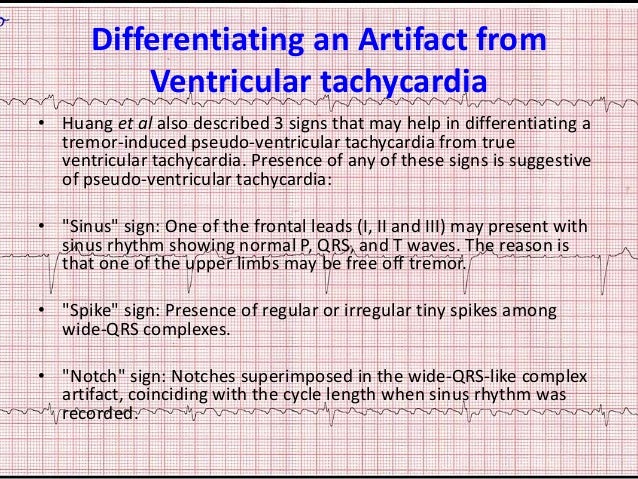
Causes of electrical artifacts on ECGs are manifold. External artifacts are usually caused by line current, which has a frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz. Internal electrical artifacts can be caused by tremors, muscle shivering, hiccups or, as in the present case, medical devices.
What does artifact mean in cardiology?
Artifacts are false measurement data, which do not come from the heart, but are caused by interference in the signal recording and/or signal transmission.
What are the 4 most common ECG artifacts?
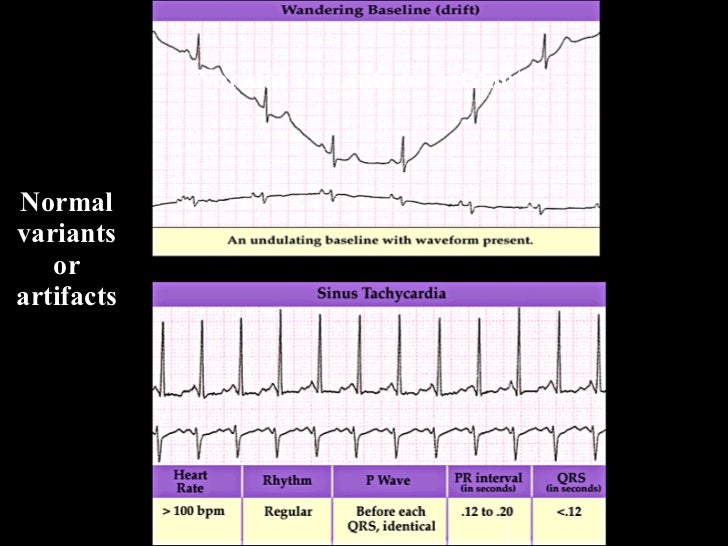
Here are some types of artifact you may encounter along with some tips to help you achieve excellent data quality on your ECG tracings.Loose lead artifact.Wandering baseline artifact.Muscle tremor artifact.Electromagnetic interference (EMI)CPR compression artifact.Neuromodulation artifact.Echo distortion artifact.More items...•
How do you fix artifacts on ECG?
Reducing ECG artifactShaving or clipping the patient's chest hair if present.Rubbing the skin vigorously with a gauze pad.Rubbing the skin with either isopropyl alcohol or soap and water to remove skin oils.
What does artifact mean medically?
artifact. In radiology, something artificial that appears on a medical image but is not a part of the living tissue being examined. The image distortion could be due to an obstruction, such as a surgical metal clip, or to a problem with the imaging equipment.
What are the most common types of artifacts you find while processing ECG signals?
The most common types of EEG artifacts are: Eye movement and blinks: The electrical potential difference between the cornea and the retina changes during the eye movement and produces Electrooculogram (EOG) signal.
What does artifact mean on a stress test?
Answer • An artifact, in this context, is anything that can keep the test from being interpreted correctly. People often think of medical tests as definitive — the stress test shows that either you have blockages in the arteries in your heart or you don't — but it usually is not so clear.
What are artifacts?
An artifact is an object made by a human being. Artifacts include art, tools, and clothing made by people of any time and place. The term can also be used to refer to the remains of an object, such as a shard of broken pottery or glassware. Artifacts are immensely useful to scholars who want to learn about a culture.
What are artifacts in EEG?
“Artifacts are signals recorded by EEG but not generated by brain. Some artifact may mimic true epileptiform abnormalities or seizures. Awareness of logical topographic field of distribution for true EEG abnormality is important in distinguishing artifact from brain waves.
What are the common errors of an ECG?
The most frequent errors in computer ECG interpretation are related to arrhythmias, conduction disorders, and electronic pacemakers. Computer ECG diagnosis of life threatening conditions e.g. acute myocardial infarction or high degree AV blocks are frequently not accurate (40.7% and 75.0% errors, respectively).
How can artifacts be prevented?
One of the simplest ways to help preserve your artifacts is to store them in a relatively dry environment. Typically, metal artifacts should be stored in living areas, which are much dryer then sheds garages or basements. Attics are generally too hot for most artifacts.
What can affect ECG results?
These include, but are not limited to:Obesity.Pregnancy.Fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites)Anatomical considerations, such as the size of the chest and the location of the heart within the chest.Movement during the test.Exercise or smoking before the test.Certain medicines.More items...
What causes artifact on a stress test?
“Attenuation artifact” observed in a nuclear stress test is due to the reduction in the intensity / strength of signal when it travels through various body tissues of different densities, such as breast tissues, chest wall, and organs under the diaphragm.
What are artifacts?
An artifact is an object made by a human being. Artifacts include art, tools, and clothing made by people of any time and place. The term can also be used to refer to the remains of an object, such as a shard of broken pottery or glassware. Artifacts are immensely useful to scholars who want to learn about a culture.
What does artifact mean on a nuclear stress test?
Artifacts in nuclear medicine are abnormalities observed that misrepresent a physiologic process or anatomical structure as pathological, and this does not include variants (either abnormal or normal).
What does likely artifactual mean?
adjective. (1) Referring to something produced by human hands. (2) Referring to an inaccurate finding, deviation or alteration of electronic readout or morphology due to some form of systemic error.
What is an EKG artifact?
Electrocardiograph (EKG) artifacts are defined as EKG abnormalities, which are a measurement of cardiac potentials on the body surface and are not related to electrical activity of the heart. As a result of artifacts, normal components of the EKG can be distorted.
What is required during EKG monitoring?
Attention to basic principles such as proper electrodes placement and lead connections (as mentioned above) is required during EKG monitoring.
What causes EKG disturbances?
Tremors and shivering cause motion artifacts. Simple movements such as brushing and combing the hair can produce EKG disturbances during ambulatory EKG monitoring.
What is a typical example of electrical interference?
Electrical interference from a nearby electrical appliance. A typical example is a 100 Hz background distortion from fluorescent lights. Not to be confused with atrial fibrillation .
What does the placement of electrodes on the torso do?
Electrodes on the torso: Placement of the electrodes on torso may lead to a change in vectors and produce pseudo-Q waves and pseudo-ST segment elevation, mimicking myocardial infarction.
What is electrode misplacement?
Electrode misplacements are a common artifact that can mimic life-threatening arrhythmias. Early identification and replacement of electrodes can help in avoiding unnecessary therapies. An algorithm has been described previously, which may help in recognizing these artifacts.
Why is it important to differentiate artifactual changes from genuine changes?
It is important to differentiate these artifactual changes from genuine changes to prevent misdiagnosis. If ST segments are affected by artifacts, either ST segment depression or elevation can occur on the EKG.
What is chewing artifact?
Chewing and tongue (hypoglossal) artifact are rather hard to miss on EEG. Chewing artifact is really just muscle artifact from the temporalis muscle , and is marked by sudden onset, intermittent bursts of generalized very fast activity (muscle artifact). It is quite easy to characterize with video studies, as you can just look at the video to correlate, but even without video studies chewing artifact does not usually share a close morphology with any other important physiologic activity. Just be careful not to mix it up with generalized periodic fast activity, which tends to be slightly slower (beta frequency) and lower in amplitude.
What is the positive side of EEG?
Recall that EEG helps you keep a positive attitude, so you always look to the positive side on EEG. As such, when considering F7 and F8--the electrodes maximally affected by lateral eye movements--when you see a positive phase reversal (the leads move away from one another) in the F8 leads, the patient is looking to the right, and should have a complementary, simultaneous negative phase reversal (the leads move toward one another) at F7. Other notable things on this tracing are a good PDR of around 11 Hz, a normal AP gradient, some myogenic frontal muscle artifact, and likely a drowsy state given the slow somewhat undulating frontal eye movement artifact in the temporal chains.
Why do we blink?
When you blink, the eye rolls slightly up and the negative retina moves away from the Fp1 and Fp2 electrodes, which thus become relatively positive.
What are the most common artifacts you'll see?
Eye Blinks. Eye blinks are one of the most common artifacts you'll see, and are marked by very high amplitude negative waveforms in the bifrontal regions.
What side of the heart is the ECG artifact?
They tend to be present more so or entirely on the left side, because the heart is in the left half of the chest, and tend to be relatively low amplitude.
Where is myogenic artifact most commonly found?
Myogenic artifact comes from muscle movements, and is most commonly found in the frontal or lateral temporal regions, due to the frontalis and temporalis muscles. It is marked by high frequency, often low amplitude activity overlying the normal cerebral rhythms, and is usually most prominent in the awake state. Of note, there's typically only minimal myogenic artifact near the vertex so if you see fast activity there, be slightly more suspicious (although, realistically, myogenic activity is much faster than the cerebral activity that can be picked up on scalp EEG).
Where is myogenic artifact from?
There is also a lot of myogenic artifact from the lateral temporal leads, likely from the temporal s muscle. Towards the end of the page (the last three seconds), there is some movement artifact seen as "sloppy" appearing and disorganized slow activity more prominent frontally the temporal chains.