
Like most antidepressants, atypical antidepressants work by ultimately effecting changes in brain chemistry and communication in brain nerve cell circuitry known to regulate mood, to help relieve depression. Atypical antidepressants change the levels of one or more neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin or norepinephrine.
Full Answer
What does having an atypical antibody mean for You?
What does it mean to have atypical antibodies? The presence or absence of antigens on the surface of red cells allows laboratories to identify the blood group of individuals. These atypical antibodies are formed upon exposure to foreign red cell antigens during transfusion or pregnancy.
What is the optimal dosing for atypical antipsychotics?
The antipsychotic should be immediately discontinued, and dantrolene 0.8 to 2.5 mg/kg every 6 hours up to 10 mg per day is the drug of choice. Adequate hydration, cooling, and there should be close monitoring of vital signs and serum electrolytes.
Why you should stop taking your antidepressants?
that antidepressants increase hunger and food cravings by adjusting neurotransmitters, it’s possible that stopping antidepressants could make you feel less hungry. If you decrease your daily calorie intake as a result, you could potentially lose weight by stopping your antidepressants.
Can antidepressants help with atypical depression?
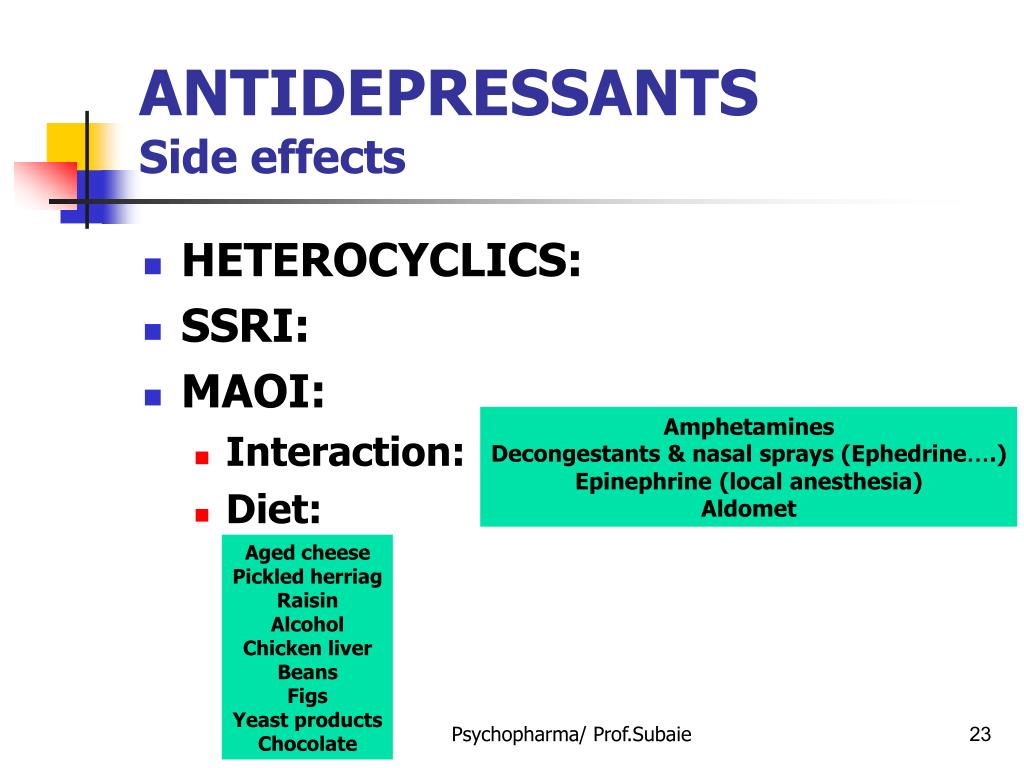
Still, MAOIs can be helpful if other types of antidepressants haven’t worked. They are sometimes used to treat bipolar disorder, or to treat neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease. They can also be helpful with atypical depression, or “depression with atypical features.”. Generic name.
What is the difference between typical and atypical antidepressants?
Typical antidepressants like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants work by increasing the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine, while atypical antidepressants often have multiple mechanisms of action.
What is meant by atypical antidepressants?
Atypical antidepressants are antidepressants that don't fall under any of the 4 main classes of antidepressants. They're most often prescribed if you've tried other types of antidepressants, and they didn't work for you.
Why are atypical antidepressants prescribed?
Atypical antidepressants ease depression by affecting chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) used to communicate between brain cells.
What do atypical antidepressants bind to?
Atypical antidepressants ease depression by affecting chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) used to communicate between brain cells.
What is the most tolerated antidepressant?
For most patients, sertraline and escitalopram are more effective and better tolerated than other antidepressants....Six medications accounted for 90% of the prescriptions, in the following order:fluoxetine (Prozac)duloxetine (Cymbalta)escitalopram (Lexapro)paroxetine (Paxil)venlafaxine (Effexor)sertraline (Zoloft).
What are the top 3 antidepressants?
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most prescribed type of antidepressant and include: Fluoxetine. Citalopram. Sertraline.
When are atypical antidepressants used?
Atypical antidepressants are frequently used in patients with major depression who have inadequate responses or intolerable side effects during first-line treatment with SSRIs [2].
Which of the following is an example atypical antidepressants?
An atypical antidepressant is any antidepressant medication that acts in a manner that is different from that of most other antidepressants. Atypical antidepressants include agomelatine, bupropion, mianserin, mirtazapine, nefazodone, opipramol, tianeptine, and trazodone.
What are atypical medications?
The term "atypical" refers to an antipsychotic medication that produces minimal extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) at clinically effective antipsychotic doses, has a low propensity to cause tardive dyskinesia (TD) with long-term treatment, and treats both positive and negative signs and symptoms of schizophrenia [1].
What are the three classes of antidepressants?
Types of antidepressantsSelective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Doctors often start by prescribing an SSRI . ... Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). ... Atypical antidepressants. ... Tricyclic antidepressants. ... Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). ... Other medications.
Is Prozac an atypical SSRI?
SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are the most commonly prescribed type of antidepressant. SSRIs improve how brain circuits use serotonin. They include Citalopram (Celexa); Escitalopram(Lexapro); Fluoxetine (Prozac); Fluvoxamine (Luvox); and Sertraline (Zoloft).
What are the 4 groups of antidepressants?
Antidepressants can be divided into four major classes which include:Tricyclic antidepressants.Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)Serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)Atypical antidepressants.
What are atypical medications?
The term "atypical" refers to an antipsychotic medication that produces minimal extrapyramidal side effects (EPS) at clinically effective antipsychotic doses, has a low propensity to cause tardive dyskinesia (TD) with long-term treatment, and treats both positive and negative signs and symptoms of schizophrenia [1].
When are atypical antidepressants used?
Atypical antidepressants are frequently used in patients with major depression who have inadequate responses or intolerable side effects during first-line treatment with SSRIs [2].
Which of the following is an example atypical antidepressants?
An atypical antidepressant is any antidepressant medication that acts in a manner that is different from that of most other antidepressants. Atypical antidepressants include agomelatine, bupropion, mianserin, mirtazapine, nefazodone, opipramol, tianeptine, and trazodone.
How do atypical antipsychotics work?
Atypical antipsychotics block serotonin 5-HT2 receptors. When the ratio of 5-HT2 to D2 receptor blocking is greater than 1, atypical antipsychotic action such as therapeutic effects on negative symptoms and few EPS are noted.
How Atypical Antidepressants Work
Atypical antidepressants ease depression by affecting chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) used to communicate between brain cells. Like most an...
Atypical Antidepressants Approved by The FDA
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved these atypical antidepressants to treat depression: 1. Bupropion (Wellbutrin, Forfivo XL, Aplenzin)...
Possible Side Effects of Atypical Antidepressants
Side effects may occur with antidepressants, including atypical antidepressants, though some people may not experience any. Some side effects may g...
Suicide Risk and Antidepressants
Most antidepressants are generally safe, but the FDA requires that all antidepressants carry black box warnings, the strictest warnings for prescri...
Stopping Treatment With Atypical Antidepressants
Atypical antidepressants aren't considered addictive. However, stopping antidepressant treatment abruptly or missing several doses may cause withdr...
Finding The Right Antidepressant
People may react differently to the same antidepressant. For example, a particular drug may work better — or not as well — for you than for another...
How Atypical Antidepressants Work
Atypical antidepressants ease depression by affecting chemical messengers (neurotransmitters) used to communicate between brain cells. Like most an...
Atypical Antidepressants Approved by The FDA
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved these atypical antidepressants to treat depression: 1. Bupropion (Wellbutrin, Forfivo XL, Aplenzin)...
Possible Side Effects of Atypical Antidepressants
Side effects may occur with antidepressants, including atypical antidepressants, though some people may not experience any. Some side effects may g...
Suicide Risk and Antidepressants
Most antidepressants are generally safe, but the FDA requires that all antidepressants carry black box warnings, the strictest warnings for prescri...
Stopping Treatment With Atypical Antidepressants
Atypical antidepressants aren't considered addictive. However, stopping antidepressant treatment abruptly or missing several doses may cause withdr...
Finding The Right Antidepressant
People may react differently to the same antidepressant. For example, a particular drug may work better — or not as well — for you than for another...
How do atypical antidepressants work?
Like most antidepressants, atypical antidepressants work by ultimately effecting changes in brain chemistry and communication in brain nerve cell circuitry known to regulate mood, to help relieve depression.
What is the FDA approved antidepressant?
A new antidepressant called esketamine (Spravato) is FDA approved for treatment-resistant depression. It's a nasal spray intended for use in combination with an oral antidepressant.
What are the neurotransmitters that are affected by antidepressants?
Atypical antidepressants change the levels of one or more neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin or norepinephrine.
What does a doctor take into account when choosing an antidepressant?
When choosing an antidepressant, your doctor takes into account your symptoms, any health problems, other medications you take and what has worked for you in the past.
Is antidepressant atypical?
Atypical antidepressants are not typical — they don't fit into other classes of antidepressants. They are each unique medications that work in different ways from one another.
Can antidepressants affect your genetics?
However, other variables besides genetics can affect your response to medication .
Can antidepressants cause sexual side effects?
Some antidepressants are more likely than others to cause sexual side effects.
How do atypical antidepressants work?
Atypical antidepressants differ from other antidepressants. They ease depression by interacting with the chemical messengers used to communicate between brain cells.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat depression?
Another name for Wellbutrin is Bupropion. This is one of the most common atypical antidepressant drugs.
What is the name of the drug that raises serotonin levels?
Another name for Viibryd is viazodone. It’s believed to improve your mood and depression by raising serotonin levels.
How does mirtazapine work?
It’s believed that Mirtazapine works by positively affecting the communication between nerve cells in the central nervous system. It might also restore the chemical balance in the brain. It’s used for major depressive disorder.
How does medication help with mental health?
Medication can help balance your brain’s chemistry to reduce your symptoms of mental health disorders. When your brain isn’t unbalanced, you can work with a mental health therapist to move toward a better quality of life.
Can antidepressants cause insomnia?
While some antidepressants might help with sleep, others can cause insomnia. Some can cause nausea while others increase your appetite leading to weight gain.
Is it safe to take antidepressants?
While most antidepressants are safe, there are some that have the potential of increasing the risk of suicide. They’ll have warnings for the prescription if that’s the case.
What is an atypical antidepressant?
Atypical Antidepressants. Atypical antidepressants are antidepressants that don’t fall under any of the 4 main classes of antidepressants. They’re most often prescribed if you’ve tried other types of antidepressants, and they didn’t work for you. But they can also be used as a first-line treatment, depending on your symptoms ...
What is the name of the drug that boosted serotonin levels in the brain?
Vortioxetine (brand names: Trintellix, Brintellix) Vortioxetine is a newer medication (approved by the FDA in 2013). Although it’s considered “atypical,” it has a similar effect to many other antidepressants [6]. It works by boosting serotonin levels in the brain.
Does bupropion affect serotonin?
Bupropion might be the most “atypical” antidepressant on this list. Unlike most antidepressants, bupropion has no effect on serotonin. Instead, it boosts dopamine and norepinephrine, two other neurotransmitters that affect energy level, motivation, and attention.
Does mirtazapine help with depression?
Mirtazapine works boosting both serotonin and norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that affects energy levels. It helps with depression but also improves sleep. It may work more quickly than most antidepressants. It’s being studied for potential use in anxiety disorders and other mental health conditions as well [5].
Does bupropion cause headaches?
Bupropion is unlikely to do any of these things—in fact, it is often prescribed alongside another antidepressant to counteract these side effects [1]. However, bupropion can have its own side effects. Common ones include: Dry mouth. Trouble sleeping. Headache and nausea.
What is an atypical antidepressant?
Atypical antidepressants are defined as any of the medications that don’t fit neatly into antidepressant categories (SSRI or SNRI). In this selection from our ongoing psychiatric video series, we examine the major atypical antidepressant medications available to New York City residents who have found difficulty maintaining success on a simple SSRI regimen.
Is trazodone a strong antidepressant?
Trazodone used to be prescribed regularly as an antidepressant; unfortunately, the dosage required for it to have strong antidepressant properties is very high and can run the risk of moderate to severe side effects.
What are some examples of atypical depression?
For example, atypical depression can be associated with: Weight gain due to an increased appetite. Personal and work relationship problems due to rejection sensitivity.
When does atypical depression start?
Atypical depression often starts in the teenage years, earlier than other types of depression, and can have a more long-term (chronic) course.
How to prevent atypical depression?
There's no sure way to prevent atypical depression, but these strategies may help. Take steps to control stress, to increase your resilience and to boost your self-esteem. Reach out to family and friends, especially in times of crisis, to help you weather rough spells.
What does it feel like to be depressed?
For some people, signs and symptoms of atypical depression can be severe, such as feeling suicidal or not being able to do basic day-to-day activities.
What are the causes of depression?
When these chemicals are abnormal or impaired, the function of nerve receptors and nerve systems change, leading to depression. Inherited traits.
Is depression more common in blood relatives?
Inherited traits. Depression is more common in people whose blood relatives also have the condition.
What is an atypical antidepressant?
Treatment Options. Risk and Considerations. An antidepressant, as the name implies, is a type of drug primarily used for the treatment of depression. Depression is a common disorder that affects the chemistry and function of your brain.
What is the most commonly prescribed antidepressant?
Of the five major classes of antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are the most commonly prescribed, particularly in first-line treatment. 2 Other antidepressants may be used if these drugs fail or in cases of intractable depression (also known as treatment-resistant depression ).
How do antidepressants help the brain?
Antidepressants can help correct the dysfunction by altering the circuits and chemicals that pass signals along nerve routes to the brain. 1 . Antidepressants are grouped into classes based on how they affect the chemistry of the brain. While the antidepressants in a class will tend to have similar side effects and mechanisms of action, ...
Why is it important to choose the right antidepressant?
Chief among them is tolerability. Because many antidepressants are equally effective in treating depression, a greater emphasis is placed on prescribing the drugs with the fewest short- and long-term side effects.
How many classes of antidepressants are there?
There are five major classes of antidepressant and several others that are less commonly used. Each has its own benefits, risks, and appropriate uses. While some may be considered preferred options, the drug selection can vary based on your symptoms, history of treatment, and co-existing psychological disorders .
When were antidepressants first developed?
One of the first classes of antidepressants developed were monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). This antidepressant class, first discovered in the 1950s, inhibits the action of an enzyme called monoamine oxidase, whose role it is to break down monoamines. 7 By blocking this effect, more neurotransmitters are available for use in mood regulation.
Is vivactil the same as tofranil?
Tofranil (imipramine) Vivactil (protriptyline) Ludiomil (maprotiline) belongs to the same class of the drug but is more appropriately described as a tetracyclic antidepressant (TeCA) due to its fourth atomic ring. Common symptoms include constipation, dry mouth, blurry vision, drowsiness, dizziness, and weight gain.
What is atypical depression?
Atypical depression (also called major depression with atypical features) is a specific type of depression in which the symptoms vary from the traditional criteria. One symptom specific to atypical depression is a temporary mood improvement in response to actual or potential positive events. This is known as mood reactivity.
What are the factors that contribute to atypical depression?
Genetics (having a family member with mood disorders including bipolar disorder and dysthymia [long-term depression] may also contribute to the development of atypical depression. Trauma. Stress. Additional risk factors for the development of atypical depression include: Negative childhood experiences.
How many people are affected by atypical depression?
Despite its name, atypical depression is actually quite common affecting 18 to 36% of people with a depressive disorder. Atypical depression is at least twice more likely to affect women than men.
How many people with major depressive disorder can improve their symptoms?
However, with appropriate treatment, 70 to 80% of individuals with a major depressive disorder can greatly improve their symptoms, although as many as 50% of patients may not respond to the initial treatment trial.
What is depression in psychology?
What is depression? Depression is a condition that causes people to feel ongoing sadness and lose interest in activities they once enjoyed.
Is atypical depression more common in women than men?
Atypical depression is at least twice more likely to affect women than men. In addition, atypical depression tends to begin at an earlier age (teen years and early 20s) and last longer (often becoming a chronic condition) than typical depression.
Does atypical depression respond to treatment?
Atypical depression often responds well to treatment. Your treatment may vary depending on the condition’s severity.
What does "atypical" mean?
Definition of atypical. 1 : not typical : irregular, unusual an atypical form of a disease atypical weather for this area. 2 medical : relating to or being an antipsychotic drug (such as risperidone) that tends to produce fewer adverse side effects on movement (such as dyskinesia) than previously used antipsychotic drugs (such as haloperidol) ...
What is atypical in medical terms?
(Entry 1 of 2) 1 : not typical : not like the usual or normal type The procedure, ductal lavage, washes cells from the milk ducts, where 95 percent of breast cancers start. Tests can then be performed to look for atypical or abnormal cells.
Why is Uche's offseason atypical?
Uche’s rookie offseason was atypical because of the coronavirus protocols in place. — BostonGlobe.com, 16 June 2021 The extreme temperatures are atypical in Los Angeles in June, which is usually still mired in a marine layer with clouds and fog, Woffard said.
Is Amazon's method atypical?
Recent Examples on the Web Design veterans with experience creating products for big tech brands like Apple and Samsung confirmed that Amazon’s method was atypical. — New York Times, 16 June 2021 Uche’s rookie offseason was atypical because of the coronavirus protocols in place. — BostonGlobe.com, 16 June 2021
