A blockade is an effort to cut off supplies, war material or communications from a particular area by force, either in part or totally. A blockade is not an embargo or sanctions, which are legal barriers to trade. It is also distinct from a siege in that a blockade is usually directed at an entire country or region, rather than a fortress or city. While most blockades historically took place at sea, blockade is still used on land to prevent someone entering a place.
What does the name blockade mean?
The physical blocking or surrounding of a place, especially a port, in order to prevent commerce and traffic in or out. The definition of a blockade is a shutting off or a blocking. An example of a blockade is not allowing ships to enter a harbor. The force that maintains a blockade. Any strategic barrier.
Why was blockade important?
This was a very important event in the cold war. There were two major reasons why this blockade was very important. The first reason being that it showed the determination of the USA to stop communism, it showed that they would spare no financial assets or important assets such as planes and pilots to buffer against
What is a sentence with the word blockade?
use "blockade" in a sentence. The road to the forest was blockaded by protesters trying to stop the logging company from cutting down the centuries-old trees. The police had set up a blockade to keep demonstrators from entering the Legislative Buildings. Student demonstrators had blockaded the street in attempt to prevent police from arresting the leaders of the protest.
What does military blockade mean?
blockade, an act of war whereby one party blocks entry to or departure from a defined part of an enemy’s territory, most often its coasts. Blockades are regulated by international law and custom and require advance warning to neutral states and impartial application.

What is a blockade?
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force. A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are legal barriers to trade rather than physical barriers.
What was the purpose of blockades?
During the Civil War, Union forces established a blockade of Confederate ports designed to prevent the export of cotton and the smuggling of war materiel into the Confederacy.
What was a blockade during the Civil War?
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading.
What is an example of blockade?
The definition of a blockade is a shutting off or a blocking. An example of a blockade is not allowing ships to enter a harbor.
Is a blockade an act of war?
A blockade is an act of war that is regulated by international law—namely, by the 1856 Paris Declaration Respecting Maritime Law and by Articles 1–22 of the 1909 London Declaration Concerning the Laws of Naval War. It is important to distinguish between the terms blockade and embargo .
What was the Union blockade quizlet?
What is the Union Blockade? Part of the Union's Anaconda Plan that was put into plan against the confederacy. Naval barrier set up to prevent the South from importing essential war supplies such as cotton, tobacco and other cash crops.
How did the blockade hurt the South?
The blockade forced the Confederacy to use less effective avenues for trade and transportation, including roads and the railroad system. This increased demand on the railroads increased in turn the cost of transporting goods, thus damaging the Southern economy.
What happened during the Union blockade?
After the April 1863 attack on the forts at the mouth of the harbor, the ironclads moved into the main ship channel and these warships effectively restricted the blockade running traffic. It was at this time that Wilmington, North Carolina, became the most important port in the Confederacy.
Why did the North wanted to blockade the South?
In less than a week, the Union began its blockade of the southern states in an effort to prevent the trade of goods, supplies, and weapons between the Confederacy and other nations. Prize law is that part of international law which concerns the capture of enemy property by a belligerent at sea during war.
What is the synonym of blockade?
In this page you can discover 40 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for blockade, like: barrier, barricade, beset, block, closure, dam, embargo, fence, stymy, encirclement and checkpoint.
What was economic blockade?
1. non-technical. an embargo on trade with a country, esp one which prohibits receipt of exports from that country, with the intention of disrupting the country's economy. 2. an embargo of all trade with a country or region, intended to damage or dislodge the government.
What kind of word is blockade?
Blockade can be a verb or a noun - Word Type.
Why had the British created a naval blockade?
During the First World War, Britain intended to use its powerful navy to starve Germany and Austria-Hungary into submission. By maintaining a blockade of enemy ports it hoped to cut off supplies from the outside world. The consequences of this strategy were complex.
What is meant by Pacific blockade?
Definition of pacific blockade : a blockade by one country of the ports of another without recourse to war.
What is the definition of a blockade runner?
Definition of blockade-runner : a ship or person that runs through a blockade.
What were the two main objectives of the Anaconda Plan?
The Anaconda Plan was the Union's strategic plan to defeat the Confederacy at the start of the American Civil War. The goal was to defeat the rebellion by blockading southern ports and controlling the Mississippi river. This would cut off and isolate the south from the outside world.
What is the meaning of blockade?
In a memorandum prepared for the London Naval Conference of 1908–09, the British government defined a blockade as “an act of war carried out by the warships of a belligerent, detailed to prevent access to or departure from a defined part of the enemy’s coast.”. This differs from a so-called pacific blockade ...
What is a military blockade?
A military blockade is undertaken to attain some specific military objective, such as the capture of a naval port. A commercial blockade has no immediate military objective but is designed to cause the enemy to surrender or come to terms by cutting off all commercial intercourse by sea.
Why is the law of blockade important?
The law of blockade, in common with other laws of war, has evolved historically to meet the needs of major powers. The development of submarines and aircraft, in particular, made it impossible to station blockading warships in constant positions off an enemy’s coasts to maintain close blockades, and it has subsequently been accepted that long-range blockades (maintained by naval forces out of sight of the enemy’s coast) are legal if they effectively prevent ingress and egress.
Why were neutral coasts not subject to blockade?
Since neutral coasts were not subject to blockade, neutrals facing the sea and also having land boundaries adjacent to belligerent territory could be made a source of supply for such belligerents in avoidance of a blockade. A system of rationing such neutrals was accordingly worked out by the British war cabinet in World War I whereby “rationing schedules showing the normal requirements of all the European neutrals in respect of all the more important commodities which they obtain from overseas” were implemented by agreements with neutral shipowners and traders containing rationing clauses under which the British government could automatically terminate many of the excessive shipments. The rationing system sought to limit neutral imports only to such stocks as would be needed for home consumption.
How does a blockade end?
A blockade terminates (1) if it is expressly raised by the blockading government or by the officer in command of the blockading force, (2) if it ceases to be effectively maintained, or (3) if the blockaded place is actually occupied by the blockading state.
How must a blockade be maintained?
A blockade, therefore, must be maintained by a force sufficient to truly prevent access to the coasts of the enemy. The blockade must be continuously maintained and impartially enforced against all vessels alike. If interrupted—except when temporarily interrupted by adverse weather—it must be duly reestablished.
Why did blockade running stop?
In spite of the Federal navy’s efforts, blockade-running only ceased to be a profitable activity when the ports were actually in Federal hands.
What was the importance of the blockade?
The strategic importance of the blockade was cemented during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, during which successful blockades on France were imposed by the Royal Navy, leading to major economic disruptions.
Why are blockades used?
While most blockades historically took place at sea, blockades are also used on land to prevent entrance of an area. For example, Armenia is a landlocked country that Turkey and Azerbaijan blockade. Accordingly, Armenia cannot use these countries' air or land space for international trade, and Armenia mainly uses its northern borders to trade. As a result, the country's economy cannot function on a full scale and distracts the country's economic development.
What is blockading power?
A blockading power can seek to cut off all maritime transport from and to the blockaded country; although stopping all land transport to and from an area may also be considered a blockade. Blockades restrict the trading rights of neutrals, who must submit for inspection for contraband, which the blockading power may define narrowly or broadly, sometimes including food and medicine. In the 20th century, air power has also been used to enhance the effectiveness of the blockade by halting air traffic within the blockaded airspace.
Why is it so difficult to blockade a ship?
Difficulties arise because the blockading ships must remain continuously at sea, exposed to storms and hardship, usually far from any support, and vulnerable to sudden attack from the blockaded side, whose ships may stay safe in harbor until they choose to come out.
How do blockaders work in a distant blockade?
In a distant blockade, the blockaders stay well away from the blockaded coast and try to intercept any ships going in or out. This may require more ships on station, but they can usually operate closer to their bases, and are at much less risk from enemy raids.
What was the name of the map that depicted the Union blockade of the Confederacy during the American?
Scott's great snake , a cartoon map illustrating the Union blockade of the Confederacy during the American Civil War, known as the Anaconda Plan, illustrated by J.B. Elliott. C47s unloading at Tempelhof Airport in Berlin, part of the airlift of supplies which broke the Soviet Union 's 1948 land blockade of West Berlin.
How did air power help the blockade?
In the 20th century, air power has also been used to enhance the effectiveness of the blockade by halting air traffic within the blockaded airspace. Close patrol of hostile ports, in order to prevent naval forces from putting to sea, is also referred to as a blockade.
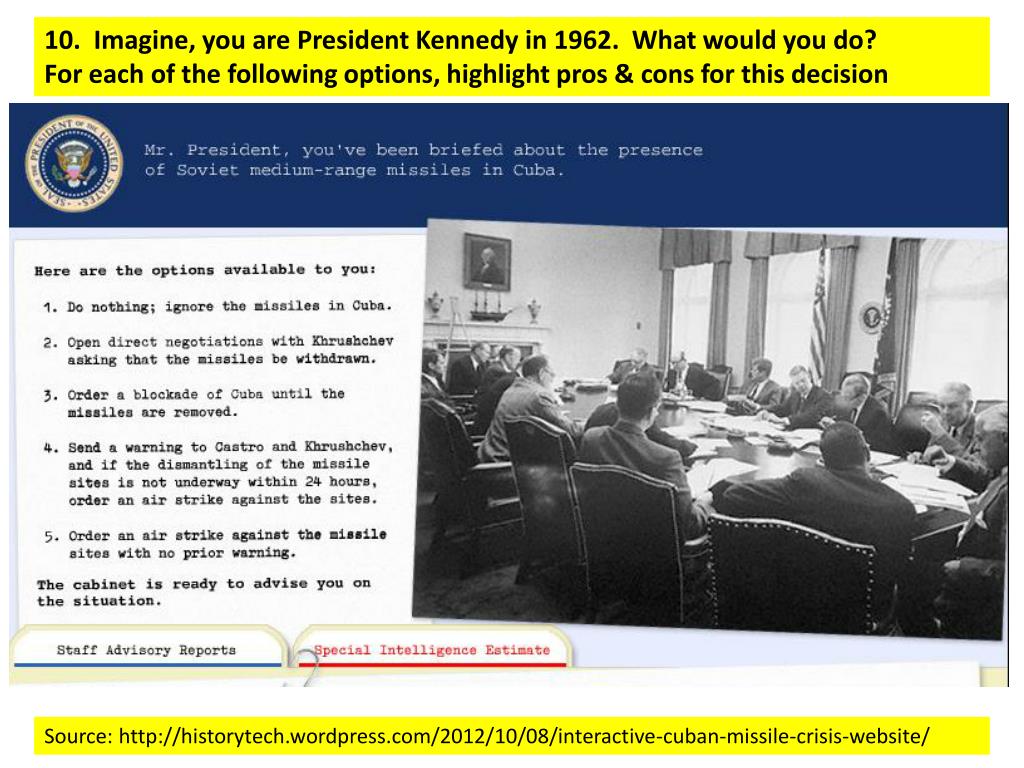
When was the blockade implemented?
The blockade was first implemented after the Bay of Pigs by President John F. Kennedy in 1962. Since then, the embargo has been lightened and toughened depending on the foreign policy view of the President sitting in the White House.
When did the Cuban blockade start?
In 1962 , President Kennedy formally introduced the Cuban blockade through Executive Order. The order banned ”importation into the United States of all goods of Cuban origin and all goods imported from or through Cuba the import of Cuban products.”. It also prohibited the export of all US products to Cuba.
What is an embargo in Cuba?
An economic embargo, or blockade [ known in Cuba as el bloqueo ], is a political tool aimed at distributing a countries economy by banning the export of products to the target country.
Which countries voted against lifting the embargo?
The only votes opposing the measure came from the United States and Israel. Three countries, Brazil, Colombia, and Ukraine obtained.
Did Biden support the protesters?
He did not, and in October, he enacted further sanctions targeting key revenue sources for the government and officials. President Biden has made his support for the protestors public but has not released any details on how his administration plans to address the failing diplomatic relationship.
Does the Cuban regime have an embargo?
There is no denying the brutality of the Cuban regime, which has negated the rights of its citizens to maintain power. However, for many activists, these actions do not make the embargo, which also deprives the Cuban people of their right to self-determination, ethical.
Who declared a blockade of the Southern ports as soon as the war had started?
President Lincoln had declared a blockade of the Southern ports as soon as the war had started. Hallowed Heritage: The Life of Virginia | Dorothy M. Torpey. The tumbled masses of slate-stratum fallen over one another was a proof that the blockade had been recently made. Black Diamonds | Mr Jkai.
What would have happened if Pakistan had a blockade?
A blockade would have rapidly cut off Pakistan from oil supplies .
What is colloidal dye?
n. Intravenous injection of large amounts of colloidal dyes in which the reaction of the reticuloendothelial cells to other influences is temporarily prevented. Arrest of nerve impulse transmission at autonomic synaptic junctions, autonomic receptor sites, or myoneural junctions through the action of a drug.
Where did Tuxedo get its name?
Tuxedo was given its name after gaining popularity among diners at Tuxedo Park, NY.
When was the word "lol" added to the dictionary?
The word "lol," short for laugh out loud, was added to Dictionary.com in 2015.
Who took out phones to demonstrate the blockade?
On a recent morning at Zhou’s third-floor walk-up apartment, he and his colleague, Ouyang Ruoyu, took out their phones to demonstrate the blockade.
What does "med" mean in medical terms?
something that prevents access or progress. med the inhibition of the effect of a hormone or a drug, a transport system, or the action of a nerve by a drug.
What is the history of blockades?
List of blockades. The list of historical blockades informs about block ades that were carried out either on land, or in the maritime and air spaces in the effort to defeat opponents through denial of supply, usually to cause military exhaustion and starvation as an economic blockade in addition to restricting movement of enemy troops.
When was the blockade in Lebanon?
The blockade was first imposed during the 1982 Israeli invasion of Lebanon. However, it was sporadically renewed after the Israel Defense Force was forced to withdraw to the South Lebanon security belt due to its continuing conflict with Hezbollah .
Why did NATO blockade Yugoslavia?
NATO imposed a blockade on the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia to enforce the UN sanctions on the country and enforced no-fly zones.
Why did the Spanish blockade the Strait of Gibraltar?
The Spanish Republican Navy blockaded the Strait of Gibraltar to hamper the transport of Francisco Franco 's Army of Africa to Peninsular Spain. The Allied Powers carried out a blockade to prevent the Axis Powers from acquiring materials. Although the blockade was initially ineffective due to the use of neutral ports in ...
What countries were involved in the blockade of Germany?
United Kingdom. Canada. France (until 1940) Soviet Union (after 1941) United States (after 1941) World War II. Main article: Blockade of Germany (1939–1945) The Allied Powers carried out a blockade to prevent the Axis Powers from acquiring materials. Although the blockade was initially ineffective due to the use of neutral ports in ...
What was the effect of the blockade on the slave trade?
The blockade suppressed the Atlantic slave trade .
Which country resumed its blockade of the Straits of Tiran shortly before the war?
Egypt resumed its blockade of the Straits of Tiran shortly before the war. Israel responded by invading and occupying the Sinai Peninsula .

Overview
History
Although primitive naval blockades had been in use for millennia, the first successful attempts at establishing a full naval blockade were made by Admiral of the Fleet Edward Hawke during the Seven Years' War (1754–1763). Following the British naval victory at Quiberon Bay, which ended any immediate threat of a major invasion of Britain, the British implemented a tight economic blockade on the French coast. This began to starve French ports of commerce, further weakenin…
Types of blockade
A close blockade entails placing warships within sight of the blockaded coast or port, to ensure the immediate interception of any ship entering or leaving. It is both the most effective and the most difficult form of blockade to implement. Difficulties arise because the blockading ships must remain continuously at sea, exposed to storms and hardship, usually far from any support, and vulnerable t…
Legal status
Since 1945, the United Nations Security Council determines the legal status of blockades and by article 42 of the UN Charter, the council can also apply blockades. The UN Charter allows for the right of self-defense but requires that this must be immediately reported to the Security Council to ensure the maintenance of international peace.
Blockade planning
Blockades depend on four general factors:
• The value of the item being blockaded must warrant the need to blockade. For example, during the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis, the items to be blockaded (or "quarantined" to use the more neutral term selected by President John F. Kennedy) were Medium-range ballistic missiles, capable of delivering nuclear …
See also
• Blockade of the Gaza Strip
• Command of the sea
• List of historical blockades
• No-fly zone
• Sea lines of communication