
What is the difference between Boyles and Charles law?
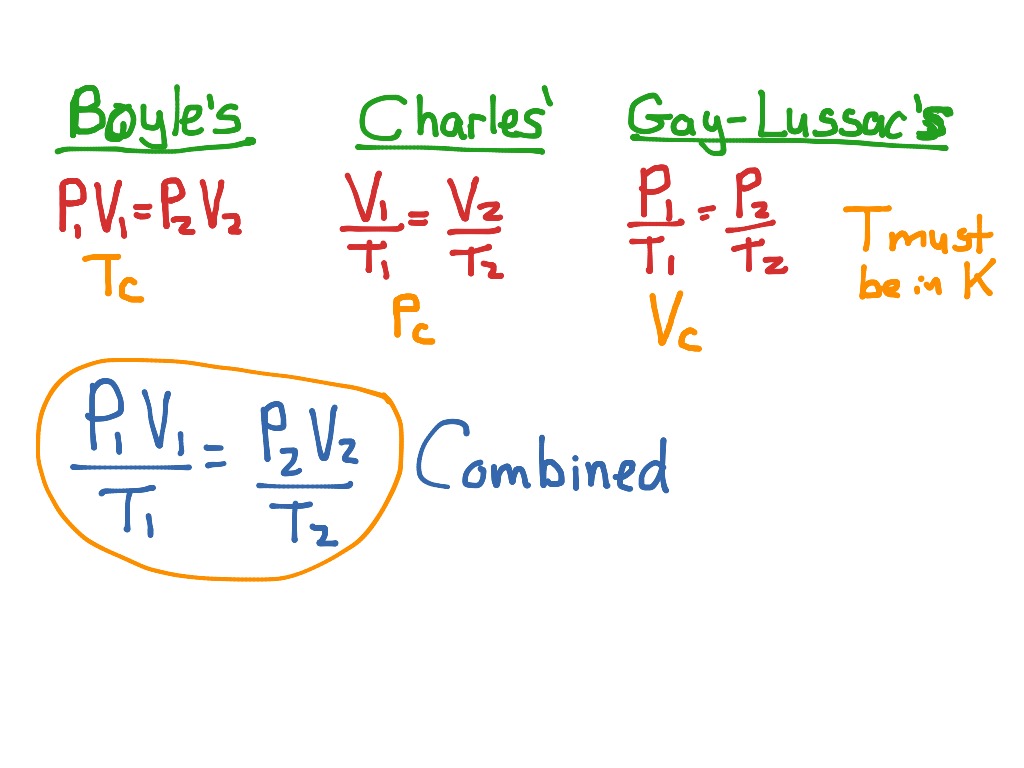
• Charles’ law is defined for a system with a constant pressure while Boyle’s law is defined for a system with constant temperature. • The two terms involved in Charles’ law are directly proportional to each other while the terms involved in Boyle’s law are inversely proportional.
What does Boyles law state about pressure and volume?
What does boyles law state? And what can it be summarized as? pressure and volume are inversely proportional An increase in pressure (more positive) will decrease in the volume of gas. A decrease in pressure (more negative) will increase the volume of gas.
What does Boyles law relate to?
Boyle’s law is a gas law that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of gas for a mass and temperature. This law is the mechanism by which the human respiratory system functions.
What are two variables relate to Boyles law?
gas laws: Gas Laws Relating Two Variables. The simplest gas laws relate pressure, volume, and temperature in pairs. Boyle's law (advanced by Robert Boyle in 1662) states that the pressure and volume of a gas are inversely proportional to one another, or PV = k, where P is pressure, V is volume, and k is a constant of proportionality.

What does the Boyles law state?
This empirical relation, formulated by the physicist Robert Boyle in 1662, states that the pressure (p) of a given quantity of gas varies inversely with its volume (v) at constant temperature; i.e., in equation form, pv = k, a constant. The relationship was also discovered by the French physicist Edme Mariotte (1676).
What is Boyle's law Kid definition?
Robert Boyle, a famous English chemist, discovered in 1662 that if you pushed on a gas, its volume would decrease proportionately. For example, if you doubled the pressure on a gas (increase the pressure two times), its volume would decrease by half (decrease the volume two times).
Which statement is correct with Boyle's law?
The correct option is A At a given temperature, pressure of a given mass of gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
What does Charles law state?
The physical principle known as Charles' law states that the volume of a gas equals a constant value multiplied by its temperature as measured on the Kelvin scale (zero Kelvin corresponds to -273.15 degrees Celsius).
Why is Boyle's law important?
Why is Boyle law important? Boyle's law is significant because it explains how gases behave. It proves beyond a shadow of a doubt that gas pressure and volume are inversely proportional. When you apply pressure on a gas, the volume shrinks and the pressure rises.
What is Boyle's law and Charles law?
Boyle's Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the pressure decreases. Charles' Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the temperature increases.
What are the assumptions of Boyle's law?
Answer and Explanation: The assumptions made in Boyle's law are the constant temperature and number of moles of gases or amount of gas, the gas is within a closed system and lastly, the gas behaves ideally.
What are the effects of Boyle's law?
Robert Boyle, a chemist and physicist from the 17th century, discovered that the volume of gas, meaning how much space it occupies, is related to its pressure—and vice versa. He found that if you pressurize a gas, its volume contracts. If you decrease its pressure, its volume increases.
Why is pressure inversely proportional to volume?
BRIAN M. Boyle's Law is a relationship between pressure and volume. In this relationship, pressure and volume have an inverse relationship when temperature is held constant. If there is a decrease in the volume there is less space for molecules to move and therefore they collide more often, increasing the pressure.
What is the difference between Boyle's law and Charles's law?
In Charles law, temperature and volume of the gas are kept at constant pressure. Whereas in Boyle's law, pressure and volume of the gas are kept at a constant temperature. In Boyle's law, pressure and volume vary inversely whereas, in Charles law, pressure and volume vary directly.
Is Boyle's law universally true?
Boyle's law is applicable only to ideal gases. The law holds good only at high temperatures and low pressures. The law fails at high pressures. the merchandise of the pressure and volume doesn't remain constant at high pressures but shows a small increase.
Who discovered Boyle's law?
Robert BoyleKnown for his law of gases, Boyle was a 17th-century pioneer of modern chemistry. Every general-chemistry student learns of Robert Boyle (1627–1691) as the person who discovered that the volume of a gas decreases with increasing pressure and vice versa—the famous Boyle's law.
What is Charles Law in simple terms?
Charles's law, a statement that the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, if the pressure remains constant.
What is Boyle's law quizlet?
what is Boyle's law? Boyle's law states that when the pressure of a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its volume at a constant temperature.
How do we use Boyle's Law in everyday life?
You can observe a real-life application of Boyle's Law when you fill your bike tires with air. When you pump air into a tire, the gas molecules inside the tire get compressed and packed closer together. This increases the pressure of the gas, and it starts to push against the walls of the tire.
What is the Voice law?
La Voz en el Derecho (“the Voice in the Law”) is a new initiative of the Hispanic National Bar Association to cultivate knowledge and understanding of the American legal system within the Hispanic community.
How does Boyle’s law work?
Boyle’s law is a gas law that states that a gas’s pressure and volume are inversely proportional. When the temperature is kept constant, as volume...
Why is Boyle law important?
Boyle’s law is significant because it explains how gases behave. It proves beyond a shadow of a doubt that gas pressure and volume are inversely pr...
What is the formula for Boyle’s gas law?
The empirical relation asserts that the pressure (p) of a given quantity of gas changes inversely with its volume (v) at constant temperature; i.e....
What is a good example of Boyle’s Law?
A balloon is a good example of Boyle’s law in action. The balloon is inflated by blowing air into it; the pressure of the air pulls on the rubber,...
Can Boyle’s law be experimentally proven?
Boyle’s law is a connection between pressure and volume. It asserts that under constant temperature, the pressure of a specific quantity of gas is...
What is Boyle’s law?
Boyle’s law is a gas law given by the Anglo-Irish chemist Robert Boyle in 1662. He stated that the pressure exerted by a gas is inversely proportio...
What is the relationship between pressure and volume?
The pressure and volume are inversely proportional to each other under Boyle’s law. P ∝ (1/V)
Why does volume decrease when pressure is increased?
Volume decreases with increasing pressure because the gas particles come close to each other with increasing pressure. Similarly, volume increases...
What happens to pressure if the volume is doubled?
For a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature, pressure is inversely proportional to volume. If the volume is doubled, the pressure will be hal...
Which law states that the pressure exerted by a given gas is proportional to its density?
Boyle’s law—that the pressure exerted by a given gas is proportional to its density if the temperature is kept constant as the gas is compressed or expanded—follows immediately from Bernoulli’s assumption that the mean speed of the molecules is determined by temperature alone. Departures from…
What is the name of the first gas law?
See Article History. Alternative Titles: Mariotte’s law, first gas law. Boyle ’s law, also called Mariotte’s law , a relation concerning the compression and expansion of a gas at constant temperature. This empirical relation, formulated by the physicist Robert Boyle in 1662, states that the pressure ...
Do real gases obey Boyle's law?
Real gases obey Boyle’s law at sufficiently low pressures, although the product pv generally decreases slightly at higher pressures, where the gas begins to depart from ideal behaviour. Demonstration of Boyle's law showing that for a given mass, at constant temperature, the pressure times the volume is a constant.
Who developed Boyle's law?
Daniel Bernoulli (in 1737–1738) derived Boyle's law by applying Newton's laws of motion at the molecular level. It remained ignored until around 1845, when John Waterston published a paper building the main precepts of kinetic theory; this was rejected by the Royal Society of England. Later works of James Prescott Joule, Rudolf Clausius and in particular Ludwig Boltzmann firmly established the kinetic theory of gases and brought attention to both the theories of Bernoulli and Waterston.
Who discovered the same law independently of Boyle?
The French physicist Edme Mariotte (1620–1684) discovered the same law independently of Boyle in 1679, but Boyle had already published it in 1662. Mariotte did, however, discover that air volume changes with temperature. Thus this law is sometimes referred to as Mariotte's law or the Boyle–Mariotte law.
What is the relationship between kinetic theory and ideal gases?
Boyle's law states that at constant temperature the volume of a given mass of a dry gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. Most gases behave like ideal gases at moderate pressures and temperatures.
How was the law of motion derived?
Boyle (and Mariotte) derived the law solely by experiment. The law can also be derived theoretically based on the presumed existence of atoms and molecules and assumptions about motion and perfectly elastic collisions (see kinetic theory of gases ). These assumptions were met with enormous resistance in the positivist scientific community at the time, however, as they were seen as purely theoretical constructs for which there was not the slightest observational evidence.
What is the law of inverse relationship?
Or Boyle's law is a gas law, stating that the pressure and volume of a gas have an inverse relationship.
What is the law of pressure and volume?
The equation states that the product of pressure and volume is a constant for a given mass of confined gas and this holds as long as the temperature is constant. For comparing the same substance under two different sets of conditions, the law can be usefully expressed as:
What is the name of the law that describes how the pressure of a gas tends to decrease as the volume of?
Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an experimental gas law that describes how the pressure of a gas tends to decrease as the volume of the container increases. A modern statement of Boyle's law is:
When would you use Boyle’s Law?
Since the volume of the gas is the only variable that has changed, we can use Boyle’s law in order to find the final pressure. Since pressure and volume are on the same side of the ideal gas law, they are inversely proportional to one another.
Why Boyle’s Law is important?
According to Boyle’s law, if a given amount of gas has a constant temperature, increasing its volume decreases its pressure, and vice-versa. When you inhale, muscles increase the size of your thoracic (chest) cavity and expand your lungs.
How do you calculate Boyle’s Law?
Then, the equation of Boyle’s law states that: p₂ = p₁ * V₁ / V₂ or p₂ / p₁ = V₁ / V₂ . As we can see, the ratio of the final and initial pressure is the inverse of the ratio for volumes.
How does Boyle’s law apply to ventilation?
Ventilation is an active example of Boyle’s Law, which states that the pressure of a container of gas decreases as the volume of that container increases. Inspiration occurs when intrapulmonary pressure falls below atmospheric pressure, and air moves into the lungs.
Does Boyle’s law have to be in ATM?
Example #10: A balloon contains 7.20 L of He. The pressure is reduced to 2.00 atm and the balloon expands to occupy a volume of 25.2 L.
Is Boyle’s Law valid at high temperature?
Boyle’s law states the inverse relationship between pressure and volume of a gas when the temperature is held constant. … At an extremely high temperature the gases in question will turn to plasma. Boyle’s law works, however, as long as the temperature range allows the gas to remain a gas.
What does Boyle’s Law state?
According to this law : If a fixed amount of ideal gas is kept at a fixed temperature, the pressure (P) and volume (V) are inversely proportional, that is, when one doubles, the other is reduced by half.
What is the name of the law that describes how the pressure of a gas tends to increase as the volume of?
Boyle’s Law is an experimental gas law that describes how the pressure of a gas tends to increase as the volume of the container decreases. It is named after the chemist and physicist Robert Boyle.
Overview
Definition
The law itself can be stated as follows:
For a fixed mass of an ideal gas kept at a fixed temperature, pressure and volume are inversely proportional.
Or Boyle's law is a gas law, stating that the pressure and volume of a gas have an inverse relationship. If volume increases, then pressure decreases and vice …
History
This relationship between pressure and volume was first noted by Richard Towneley and Henry Power in the 17th century. Robert Boyle confirmed their discovery through experiments and published the results. According to Robert Gunther and other authorities, it was Boyle's assistant, Robert Hooke, who built the experimental apparatus. Boyle's law is based on experiments with air, whic…
Human breathing system
Boyle's law is often used as part of an explanation on how the breathing system works in the human body. This commonly involves explaining how the lung volume may be increased or decreased and thereby cause a relatively lower or higher air pressure within them (in keeping with Boyle's law). This forms a pressure difference between the air inside the lungs and the environmental air pressure, which in turn precipitates either inhalation or exhalation as air move…
See also
Related phenomena:
• Water thief
• Industrial Revolution
• Steam engine
Other gas laws:
External links
• Media related to Boyle's Law at Wikimedia Commons