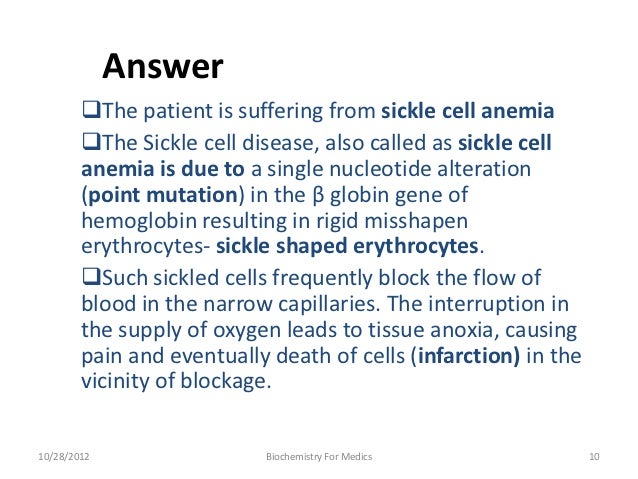
What is the mechanism of disease?
Mechanisms of Disease. Understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms of disease is one of the key goals of modern biomedical research, and MCB labs are working to understand cancer, neurodegeneration and aging. We investigate the mechanisms of genomic instability, signal transduction and the networks of cellular responses to...
What are the 3 types of cellular mechanisms?
Cellular Mechanism. Cellular mechanisms are defined as (I) cell cycle regulation, (II) induction of DNA damage and DNA repair, and (III) specific targeting of topo2.
What is the medical significance of the process of cell division?
The medical significance of these processes involves errors of cell division, which lead to the formation of an individual cell or of a cell lineage with an abnormal number of chromosomes and thus an inappropriate amount of genomic material.
What are the cellular mechanisms of aging?
The cellular mechanisms of aging described above may provide a convincing account of the cellular processes that determine the length of survival and fate of a cell as individuals grow older. Accumulated molecular and cellular damage by UV, ROS, Ca 2+, and changes in genomic function can be demonstrated in aging cells.

What is cellular mechanism?
Cellular mechanisms Definition The cellular mechanisms are those which take place in a cell involving the process of replication or repair of any damage that is done. The cellular mechanism comprises cell cycle regulation, induction of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage, DNA repair, and targeting of topo2.
What is the study of mechanism of disease?
Pathophysiology ( a.k.a. physiopathology) – a convergence of pathology with physiology – is the study of the disordered physiological processes that cause, result from, or are otherwise associated with a disease or injury.
Why is it important to study and understand mechanisms of disease?
Identifying the mechanism of the disease helps us to understand what has gone wrong. It is important to then understand exactly which molecules (often proteins) are involved – this forms the 'target' for the primary action of a medicine.
Why is it important to know the cellular basis of a disease?
By understanding how cells work in healthy and diseased states, cell biologists working in animal, plant and medical science will be able to develop new vaccines, more effective medicines, plants with improved qualities and through increased knowledge a better understanding of how all living things live.
What does mechanism of disease mean?
Definition. The defects in molecular and cellular processes that constitute the triggers of specific pathologies are referred to as mechanisms of disease. Research in this area is vital for designing appropriate and effective treatments.
What is biochemical mechanism of disease?
Biochemical diseases are genetic diseases that affect one of the biochemical processes in the human body. Biochemical processes determine the development and growth of organs and the maintenance of their function. Some of these functions are directly related to nutrition and others are not.
What does mechanism mean in medical terms?
Medspeak. The manner by which a process occurs; the arrangement or association of the elements or parts of a thing in relation to the effect generated. Psychology. The combination of mental processes by which an effect is generated.
What are health mechanisms?
The Mechanisms of Health and Disease Hub is a collaborative of scientists seeking to understand health and disease pathways in order improve health, development and quality of life across the lifespan.
What is the importance of mechanism?
Mechanisms allow us to understand complex systems (e.g., physiological or social systems) and can help us to explain, predict, and intervene.
What does cellular basis mean?
Organisms are made of one or more cells, which need a supply of energy and molecules to carry out life processes. "The cellular basis of life" is one of 15 big ideas of science in the Best Evidence Science Teaching collection.
How are cell modification important to the life of an organism?
Cell modifications are very important to carry out specialized functions because: 1. It will help it to survive the change in the surroundings and adapt to it. 2.
What is the function of cells in human body?
The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body's hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
What are the cellular mechanisms of sulfonamide?
Cellular Mechanisms. Cellular mechanisms are most often implicated in hypersensitivity reactions to sulfonamides. These have been shown to occur through multiple mechanisms. In the past, SMX had been thought to be too small to elicit an immune response on its own.
How does BCR/ABL predispose to further genetic changes?
How BCR/ABL predisposes to further genetic changes is also unclear. BCR/ABL may increase the risk of DNA damage by the formation of reactive oxygen species, by affecting cell cycle regulation, and/or by altering apoptosis signaling. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
What are the mechanisms of the basal forebrain?
Cellular mechanisms within the neurocircuitry of the basal forebrain include changes in the patterns of neuronal firing in freely moving animals, glutamate-dependent plasticity in the nucleus accumbens, and GABAergic plasticity in the central nucleus of the amygdala. In freely moving animals, extracellular recordings have revealed a neuronal population in the nucleus accumbens that exhibits phasic excitatory responses that are time-locked to drug-related events and decreases in background firing with repeated intravenous self-administration, suggesting a net enhancement of drug-related signals. This differential inhibition of drug reward-related firing and background firing may represent a form of filtering that could narrow the ensemble of neurons in the nucleus accumbens to those that mediate the strengthening of associations.
What is the function of AMPK?
Pathways that deplete ATP are inhibited by AMPK. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a master regulator of cellular energy homeostasis.
What is the process of purine catabolism?
During purine catabolism, the process of adenine bases degradation into hypoxanthine and eventually uric acid is inhibited by the presence of inorganic phosphate (P i) and ATP. Thus, loss of the inhibitory ATP molecule promotes urate generation.
Does ethanol inhibit glutamate receptors?
Inhalation of some solvents, such as toluene, benzene, xylene, and 1,1,1-trichloroethane, and ingested ethanol acutely inhibit the function of one of the glutamate receptors, the N -methyl- d -aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor ( Bowen et al., 2006; Chastain, 2006 ).
Bloom, George S
Pathogenic mechanisms in Alzheimer's Disease and other neurodegenerative disorders
Casanova, James E
Role of Arf family GTPases in vesicular transport and cytoskeleton assembly. Cell Biology of bacterial pathogenesis. The innate immune response to bacterial infection.
Dwyer, Noelle
Neural Development; Cell Division in Neural Stem Cells; Axon Outgrowth and Guidance
Keller, Susanna R
Insulin signaling, insulin-regulated membrane trafficking and associated changes in cellular function and whole body physiology
Lu, Xiaowei
Wnt/PCP signaling in inner ear development Mouse models for human deafness Wnt/PCP signaling in neural tube closure
Stukenberg, P. Todd
Mechanisms of chromosome segregation in Mitosis and generation of Chromosomal Instability in tumors
Winckler, Bettina
Endosomal function and dysfunction in neurons. Development of the nervous system: cytoskeleton and membrane traffic in axon and dendrite growth.
What is the process of cell death?
Cells that do not receive the proper supplies will die, through a step-wise process called apoptosis (or programmed cell death). This is a normal physiologic phenomenon and in fact apoptosis is crucial to the normal development of the nervous system. In contrast to apoptosis, necrosis is a type of cell death that results from a direct injury to the nervous system, or acute infection. Necrosis produces an explosion of cell contents accompanied by inflammation and immune activation. Unlike the messy death of infected or traumatized cells in necrosis, apoptosis is a process of carefully choreographed steps to self-destruction. But halting apoptosis when it is producing degenerative change in the nervous system is now a prime goal for researchers trying to design effective treatments for ALS as well as for other neurological disorders.
What is the name of the disease that attacks motor neurons?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) attacks motor neurons (a type of nerve cell) in the brain and spinal cord. There are two types of motor neurons: upper motor neurons (UMNs) that send nerve fibers down the from the motor cortex in the brain (part of the brain that controls movement) to the spinal cord; lower motor neurons (LMNs) ...
What is the role of motor neurons in transport?
Active transport along the extensive axons of motor neurons conveys newly made materials to even the farthest-reaching nerve endings and needed nutrients back to the cell body. Motor neurons may be particularly vulnerable to any genetic defect or cellular insult that impedes axon transport.
How do motor neurons help with ALS?
Transport of materials up and down the length of the motor neuron is an important cellular process that may play into the damage seen in ALS. Neurons normally move cellular materials along their axons, to keep nerve cell messages flowing and to maintain the health of the whole nerve cell itself.#N#Active transport along the extensive axons of motor neurons conveys newly made materials to even the farthest-reaching nerve endings and needed nutrients back to the cell body. Motor neurons may be particularly vulnerable to any genetic defect or cellular insult that impedes axon transport. Studies of the proteins within nerve fibers have highlighted their importance in maintaining motor neurons and point to the possible role of these axon proteins in ALS.
How do nerve cells communicate with each other?
Nerve cells pass signals to each other and to their target organs by releasing messenger molecules, called neurotransmitters. Many are simple amino acids such as the one called glutamate. The message is intended to tell the recipient neuron whether to fire off its own neurotransmitters.
What happens to the motor neurons in ALS?
The progressive degeneration of the motor neurons in ALS eventually leads to their death. When the motor neurons die, the ability of the brain to initiate and control muscle movement is lost. With voluntary muscle action progressively affected, patients in the later stages of the disease may become totally paralyzed.
What is the difference between apoptosis and necrosis?
In contrast to apoptosis, necrosis is a type of cell death that results from a direct injury to the nervous system, or acute infection. Necrosis produces an explosion of cell contents accompanied by inflammation and immune activation. Unlike the messy death of infected or traumatized cells in necrosis, apoptosis is a process ...